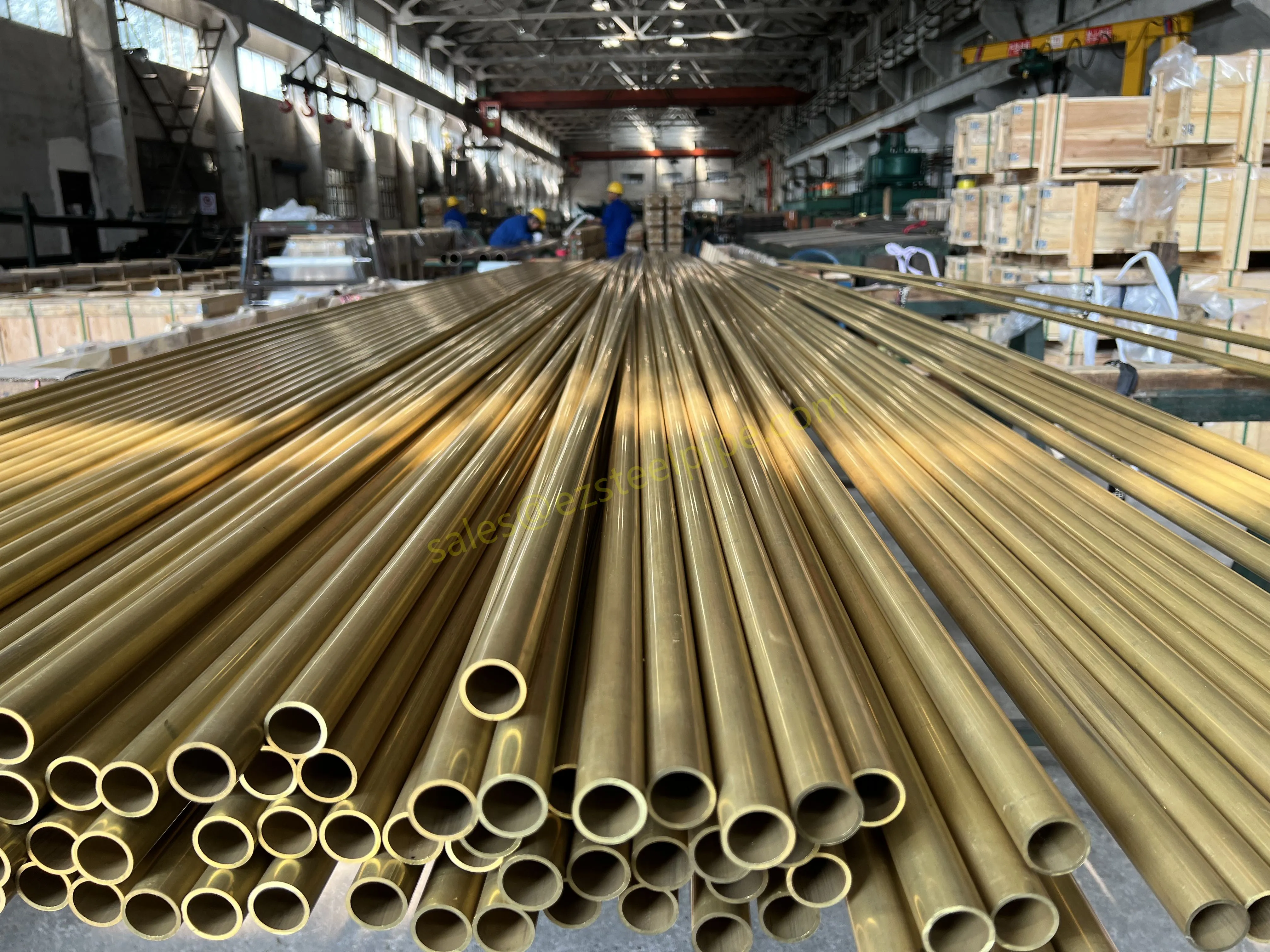
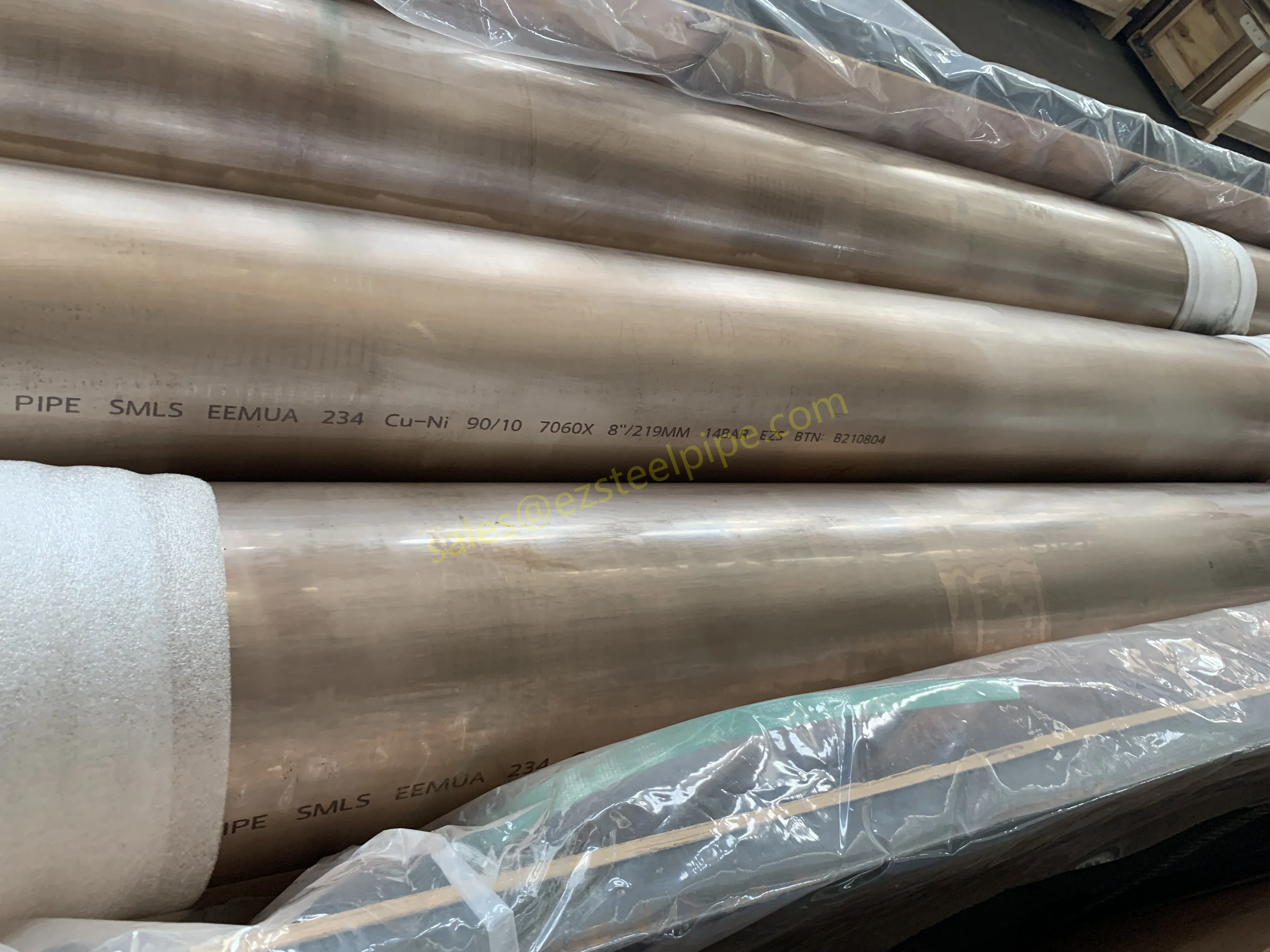
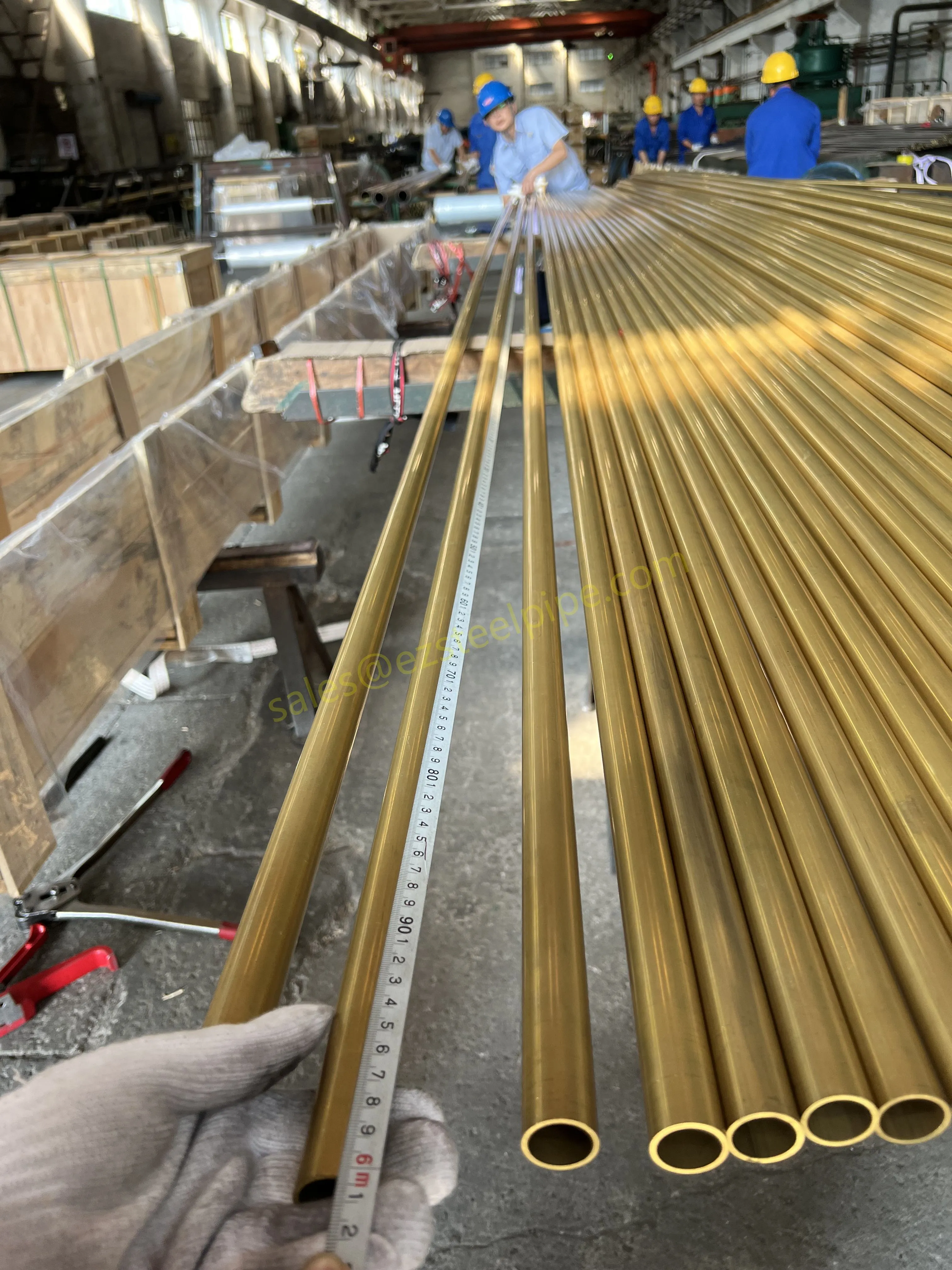
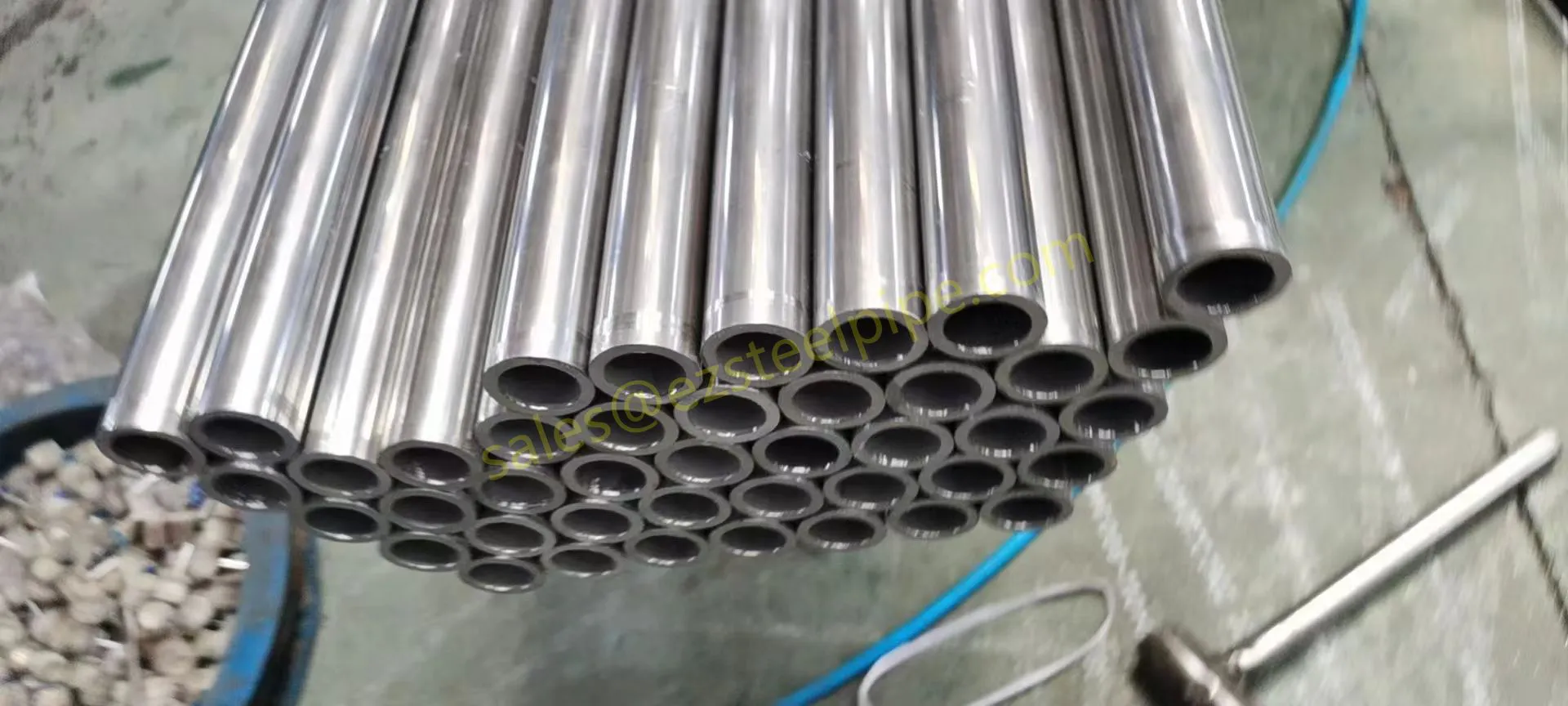
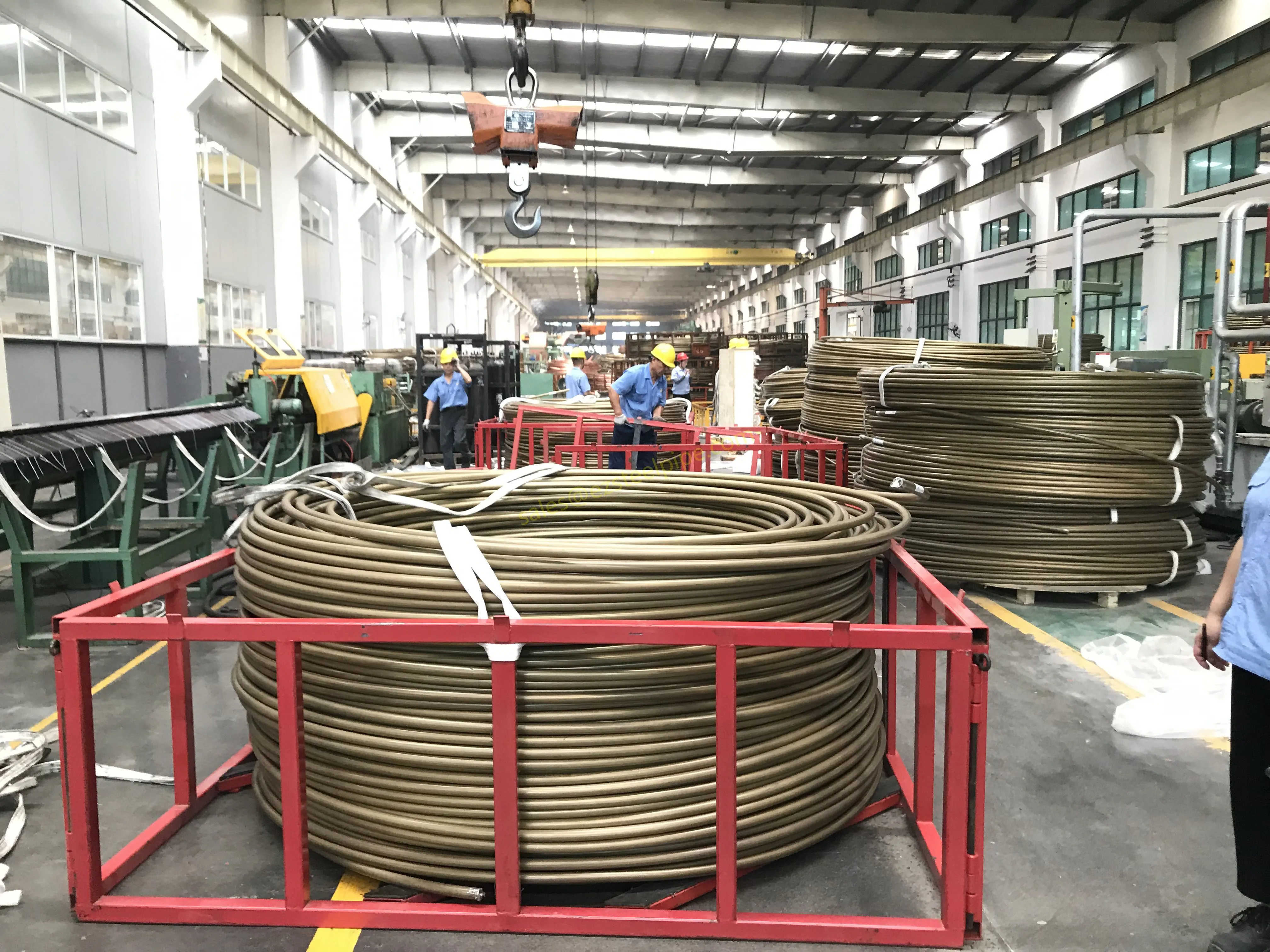
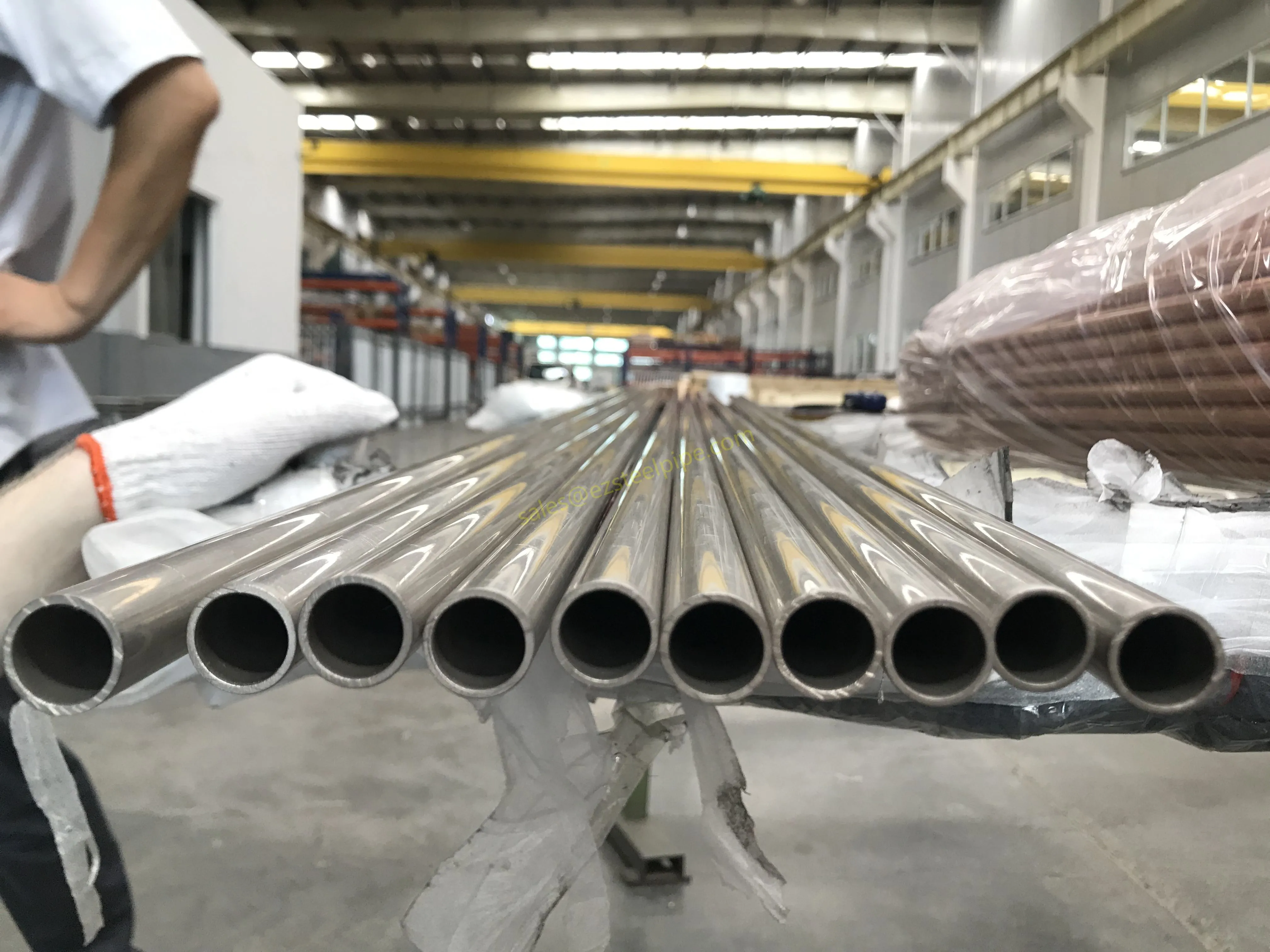
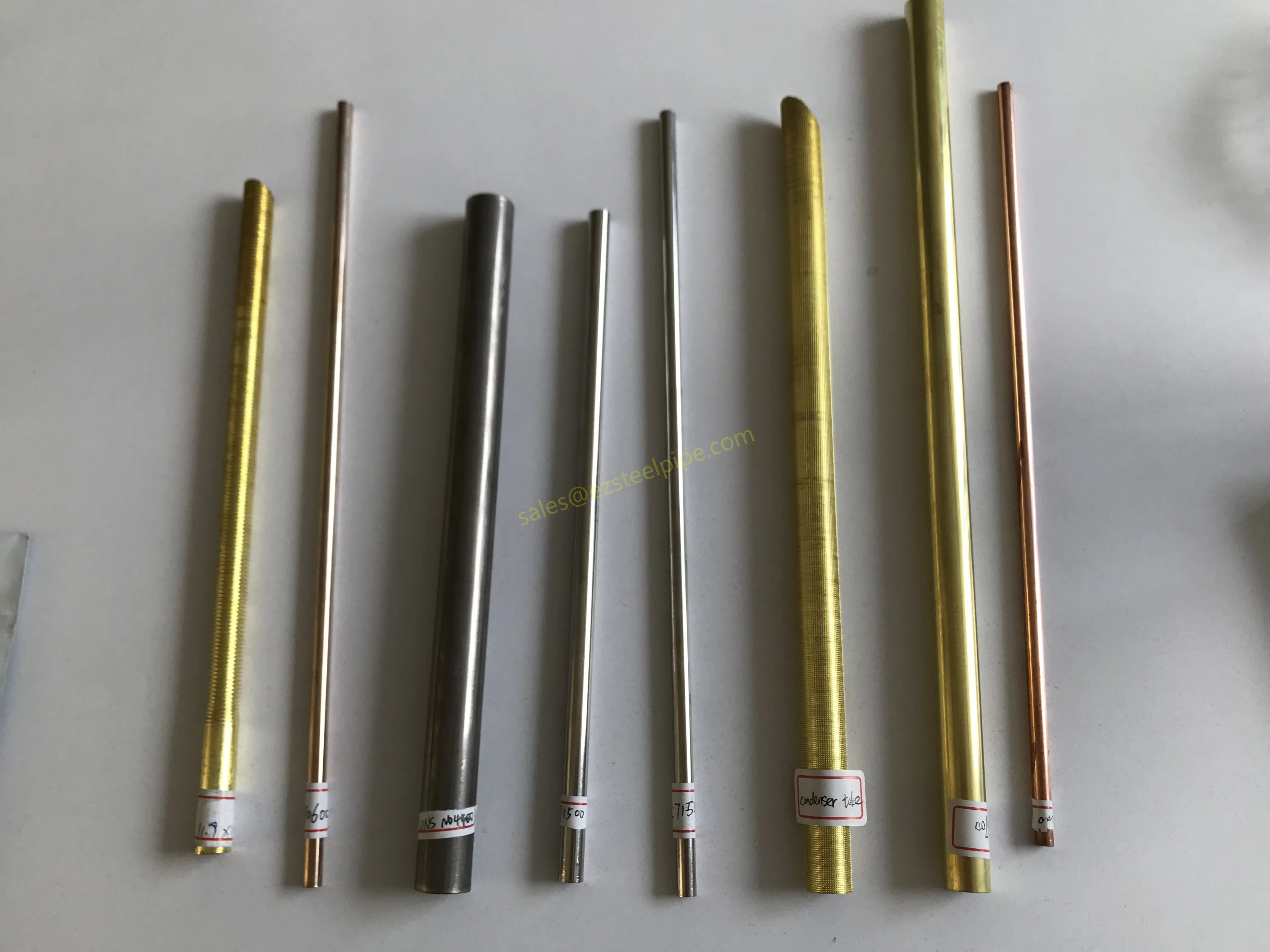
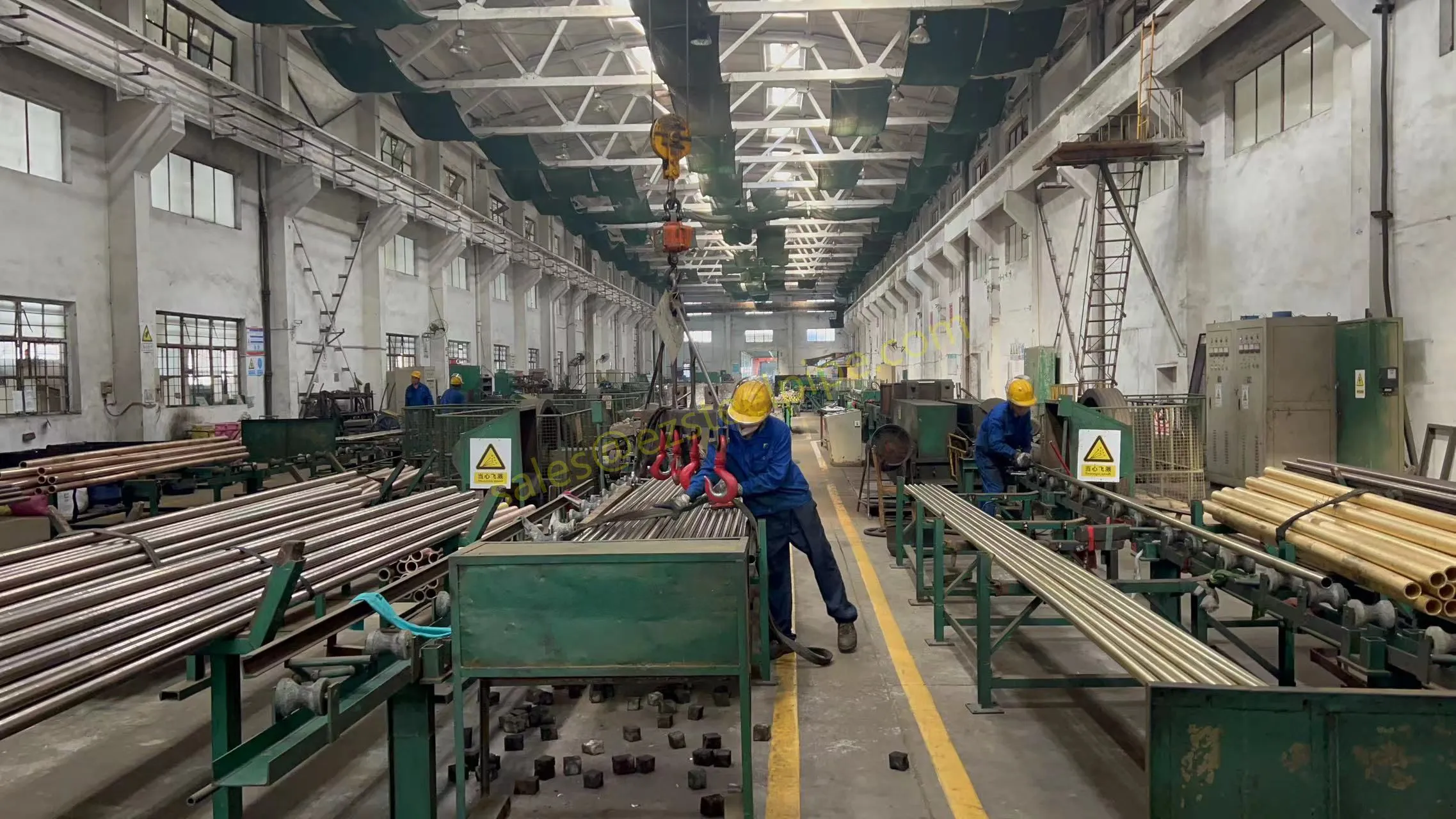
Walk into any modern factory, flip open the back of your smartphone, or peek under the hood of an electric car—chances are, you'll find thin, shiny strips of metal working quietly behind the scenes. These are copper alloy strips, and they're the unsung heroes of countless industries. What makes them so special? Two key traits: flexibility and electrical conductivity .
Think about it: when engineers design components that need to bend, twist, or fit into tight spaces without breaking, flexibility is non-negotiable. And when those same components also need to carry electricity efficiently—whether for powering a device, transmitting signals, or dissipating heat—conductivity becomes just as critical. Copper alloy strips strike a unique balance between these two properties, making them indispensable in electronics, automotive, aerospace, and even marine applications.
In this article, we'll dive into what makes copper alloy strips so flexible and conductive, how these properties are measured and optimized, and why standards like JIS H3300 , ASTM B111 , and GB/T 8890 matter in ensuring consistent quality. We'll also look at real-world examples where these strips shine, from tiny smartphone connectors to large marine heat exchangers. Let's get started!
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































