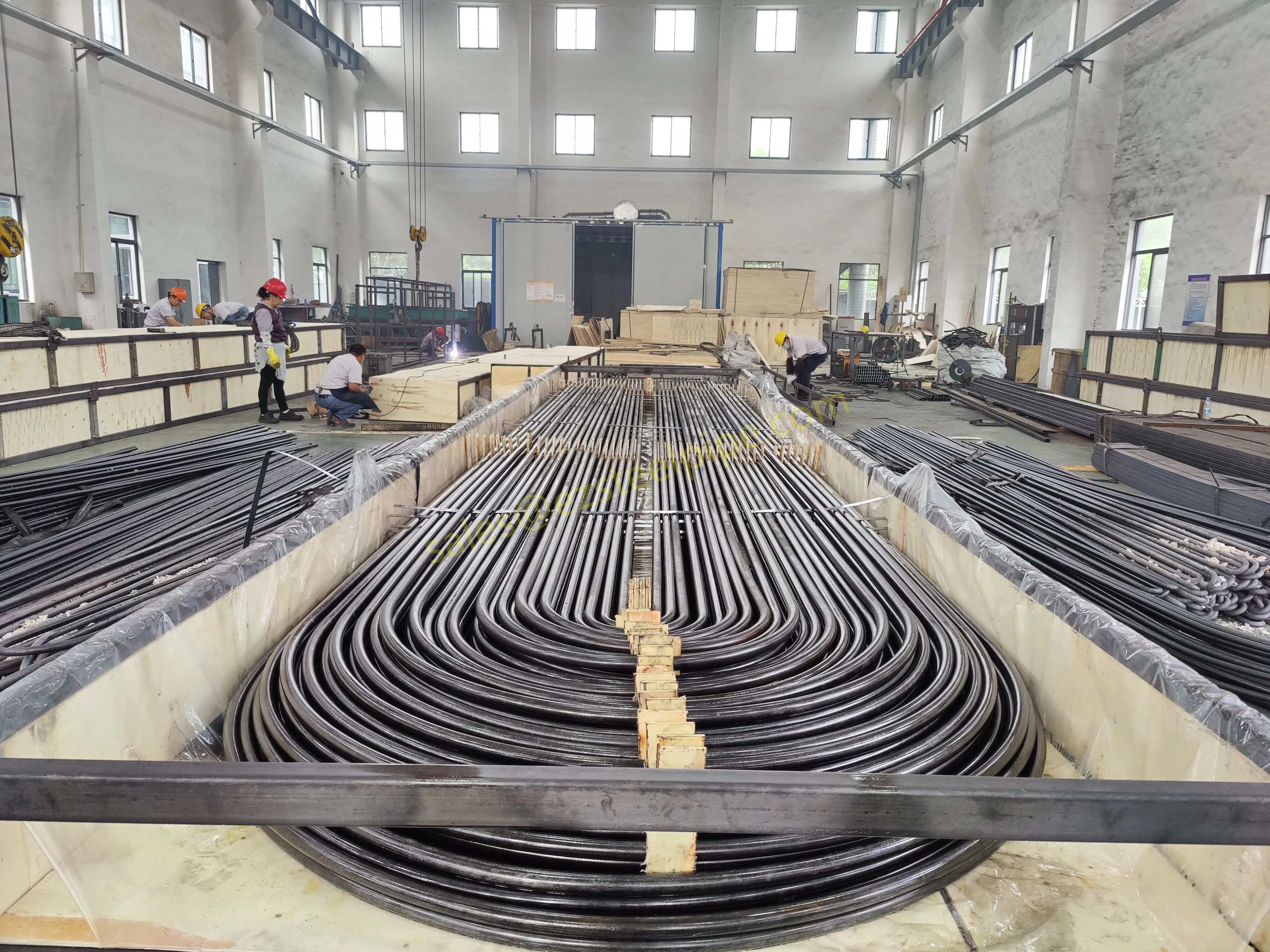
On a crisp autumn morning, as you sip a hot cup of coffee and flip on the heater, you might not pause to think about the complex machinery working behind the scenes to keep your home warm. But somewhere, in a sprawling power plant or a bustling industrial facility, a set of unassuming metal tubes is hard at work—U-shaped thermal efficiency tubes. These bent, unpretentious components are the quiet workhorses of heat transfer, ensuring that energy flows smoothly, machinery runs efficiently, and industries from power generation to shipbuilding stay operational. Let's take a closer look at these remarkable tubes: their design, their purpose, and the vital role they play in powering our modern world.
What Are U-Shaped Thermal Efficiency Tubes, Anyway?
At first glance, a U-shaped thermal efficiency tube might seem like little more than a metal pipe bent into a "U" shape. But that simple curve is a stroke of engineering brilliance. Unlike straight tubes, which require linear space and often limit heat transfer potential, the U-bend design packs a powerful punch in a compact form. Imagine trying to fit a 10-foot straight tube into a 5-foot space—it's impossible. But bend that tube into a U, and suddenly you've doubled the surface area for heat exchange without expanding the footprint. That's the magic of the U-shape: it maximizes efficiency by making the most of limited space, a critical advantage in industrial settings where every inch counts.
But these tubes aren't just about space-saving. They're engineered for thermal efficiency —the ability to transfer heat quickly and effectively between fluids or gases. Whether it's steam in a power plant, coolant in a ship's engine, or chemicals in a petrochemical refinery, U-shaped tubes ensure that heat moves where it needs to go, reducing energy waste and keeping systems running at peak performance. They're the reason power plants can generate electricity with minimal fuel, ships can cross oceans without overheating engines, and petrochemical facilities can process raw materials safely and efficiently.
The Design Behind the Efficiency: Why U-Shaped?
To understand why U-shaped tubes are so effective, let's break down their design. Straight tubes, while simple, have a major flaw: they create "dead zones" where fluid flow slows, reducing heat transfer. The U-bend, however, disrupts this pattern. As fluid flows through the curved section, it mixes more vigorously, breaking up stagnant layers and ensuring that the entire tube surface contributes to heat exchange. This turbulence boosts efficiency, meaning less energy is lost as waste heat and more is put to productive use.
Another key advantage is durability. Industrial environments are harsh—high pressures, extreme temperatures, corrosive chemicals, and constant vibration are par for the course. Straight tubes, with their rigid, fixed ends, can crack or leak under stress. U-shaped tubes, by contrast, have a built-in flexibility. The bend acts as a buffer, absorbing thermal expansion and contraction, reducing strain on tube sheets (the plates that hold tubes in place), and extending the lifespan of the system. It's like comparing a rigid metal rod to a flexible hose—one bends and adapts, the other snaps under pressure. In industries like marine & ship-building or power plants & aerospace, where reliability is non-negotiable, this flexibility is a lifesaver.
Materials Matter: Building Tubes for the Extremes
Not all U-shaped thermal efficiency tubes are created equal. The materials used depend on the job at hand, and manufacturers spare no detail in selecting the right alloy for the task. Let's take a look at some common materials and why they're chosen:
- Stainless Steel: A staple in many industries, stainless steel resists corrosion and stands up to high temperatures, making it ideal for power plants and petrochemical facilities where steam and chemicals are present.
- Nickel Alloys (e.g., Incoloy 800, Monel 400): For extreme environments—think nuclear power plants or aerospace applications—nickel alloys offer unmatched strength and heat resistance. These materials can withstand temperatures exceeding 1,000°F and resist attack from aggressive substances like acids and saltwater.
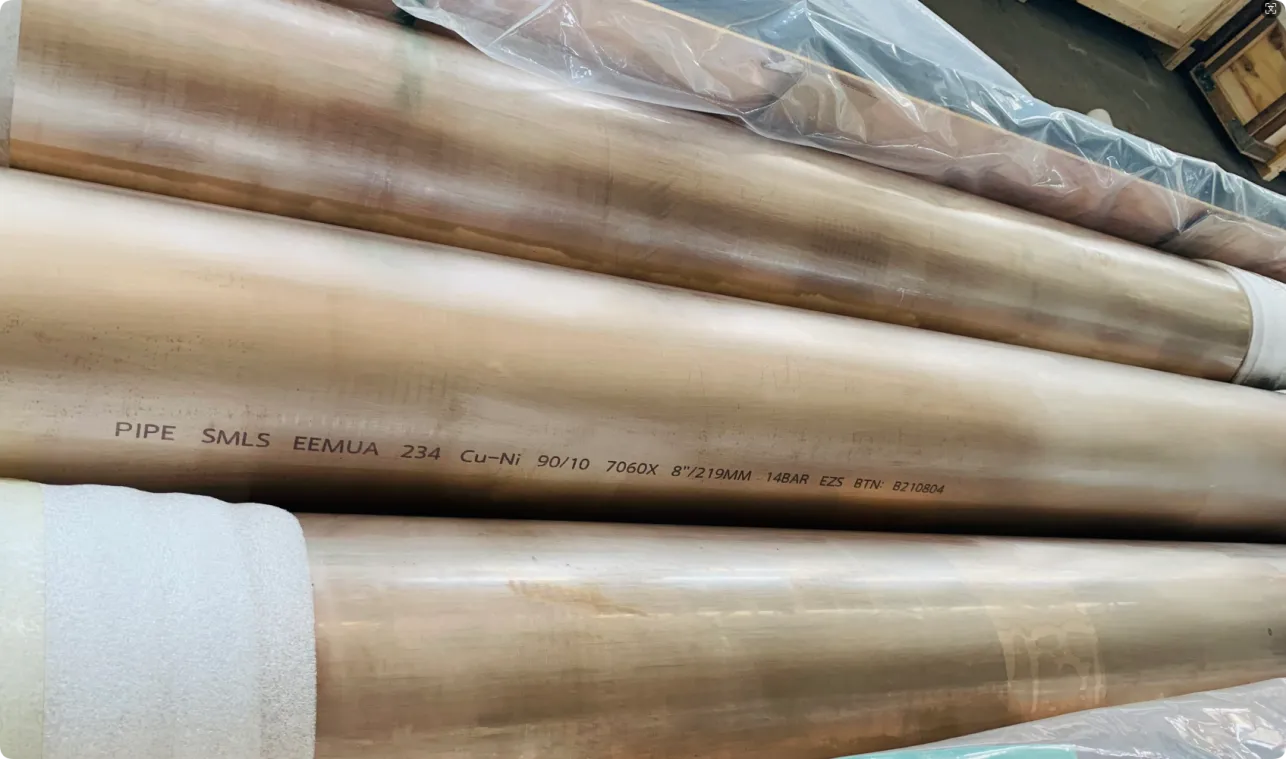
- Copper-Nickel Alloys: In marine settings, where saltwater corrosion is a constant threat, copper-nickel tubes (like those meeting BS2871 or B466 standards) are the go-to choice. They're tough, long-lasting, and ensure ships stay seaworthy for decades.
Each material is carefully selected to match the demands of the application. For example, a U-shaped tube in a nuclear reactor might use RCC-M Section II nuclear-grade tubing, designed to meet the strictest safety standards. Meanwhile, a tube in a commercial power plant might rely on ASTM A213 steel, a workhorse alloy known for its balance of strength and affordability. The goal? To create a tube that can handle the heat, resist wear, and keep systems running safely—no matter what.
Where Do U-Shaped Thermal Efficiency Tubes Work? Everywhere.
From the depths of the ocean to the heights of the aerospace industry, U-shaped thermal efficiency tubes are everywhere you look—even if you can't see them. Let's explore some of their most critical applications:
| Industry | Application | Why U-Shaped Tubes? |
|---|---|---|
| Power Plants & Aerospace | Boilers, heat exchangers, and turbine cooling systems | Compact design fits into tight engine compartments; high thermal efficiency reduces fuel consumption for rockets and jet engines. |
| Marine & Ship-Building | Engine cooling, desalination systems, and HVAC | Corrosion-resistant materials stand up to saltwater; U-bend flexibility absorbs ship vibrations, preventing leaks. |
| Petrochemical Facilities | Reactors, distillation columns, and heat recovery units | Handles high pressures and temperatures; maximizes heat transfer for processing crude oil and natural gas. |
| Nuclear Power | Steam generators and coolant loops | Nuclear-grade materials ensure safety; U-bend design simplifies maintenance and reduces radiation exposure risks. |
Take power plants, for example. In a coal-fired or natural gas power plant, U-shaped tubes are the heart of the boiler system. As hot gases rise from the combustion chamber, they pass over thousands of U-bend tubes filled with water. The tubes absorb the heat, turning water into steam, which then drives turbines to generate electricity. Without these tubes, the plant would need far more fuel to produce the same amount of power—wasting resources and increasing emissions. In fact, studies show that upgrading to high-efficiency U-shaped tubes can reduce a power plant's fuel consumption by up to 5%, a significant saving when scaled to industrial levels.
In marine & ship-building, U-shaped tubes are equally vital. A ship's engine generates enormous heat, and without proper cooling, it would seize up mid-voyage. U-bend tubes, often made of copper-nickel alloys, circulate seawater through the engine, absorbing heat and releasing it back into the ocean. The U-shape allows these tubes to fit into the tight spaces of a ship's engine room, while their corrosion resistance ensures they last for years in harsh saltwater environments. Next time you see a cargo ship carrying goods across the globe, remember: U-shaped tubes are helping it reach its destination safely.
Beyond the Bend: The Unsung Benefits of U-Shaped Tubes
While thermal efficiency and space-saving are the headline benefits, U-shaped tubes offer a host of other advantages that make them indispensable in industry:
Easy Maintenance
Unlike straight tubes, which often require removing entire systems for inspection or replacement, U-shaped tubes are accessible from one end. This simplifies cleaning, repairs, and upgrades, reducing downtime and cutting maintenance costs. In a petrochemical facility, where shutting down a reactor can cost millions in lost production, this ease of access is a game-changer.
Cost-Effectiveness
Yes, high-quality U-shaped tubes require precision manufacturing—bending thick-walled alloys without weakening the material takes skill. But over time, their efficiency pays off. Reduced energy use, longer lifespans, and lower maintenance costs mean that U-shaped tubes are often cheaper in the long run than their straight counterparts. It's an investment that keeps on giving.
Safety
In industries like nuclear power or aerospace, safety is non-negotiable. U-shaped tubes, with their robust design and flexible materials, minimize the risk of leaks or failures. The bend absorbs stress, preventing cracks from spreading, and the use of high-grade alloys ensures that even under extreme conditions, the tubes hold their integrity. When you're dealing with radioactive coolant or jet fuel, peace of mind is priceless.
The Future of U-Shaped Thermal Efficiency Tubes: Innovation on the Horizon
As industries push for greener, more sustainable practices, U-shaped thermal efficiency tubes are evolving too. Manufacturers are experimenting with new materials—like advanced ceramics or composite alloys—that offer even better heat transfer and corrosion resistance. There's also a focus on "smart" tubes, embedded with sensors that monitor temperature, pressure, and wear in real time, allowing for predictive maintenance and further reducing downtime.
Another trend is customization. Companies are increasingly demanding tubes tailored to their specific needs—whether it's a unique U-bend radius for a tight engine compartment or a specialized alloy for a niche chemical process. This shift toward custom solutions is making U-shaped tubes even more versatile, opening doors for use in emerging industries like renewable energy (think geothermal power plants or solar thermal systems) and electric vehicle manufacturing.
The Bottom Line: Small Tubes, Big Impact
U-shaped thermal efficiency tubes might not grab headlines or win design awards, but they're the backbone of modern industry. They're in the power plants that light our homes, the ships that carry our goods, the refineries that produce our fuels, and the aerospace systems that connect our world. They're a testament to the power of simple, thoughtful design—proving that sometimes, the most important innovations are the ones that work quietly behind the scenes.
So the next time you turn on the lights, start your car, or board a plane, take a moment to appreciate the unsung heroes: the U-shaped tubes that keep our world running smoothly. They may be small, but their impact is enormous. And as technology advances, one thing is clear: these little bends of metal will continue to shape the future of industry for years to come.
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































