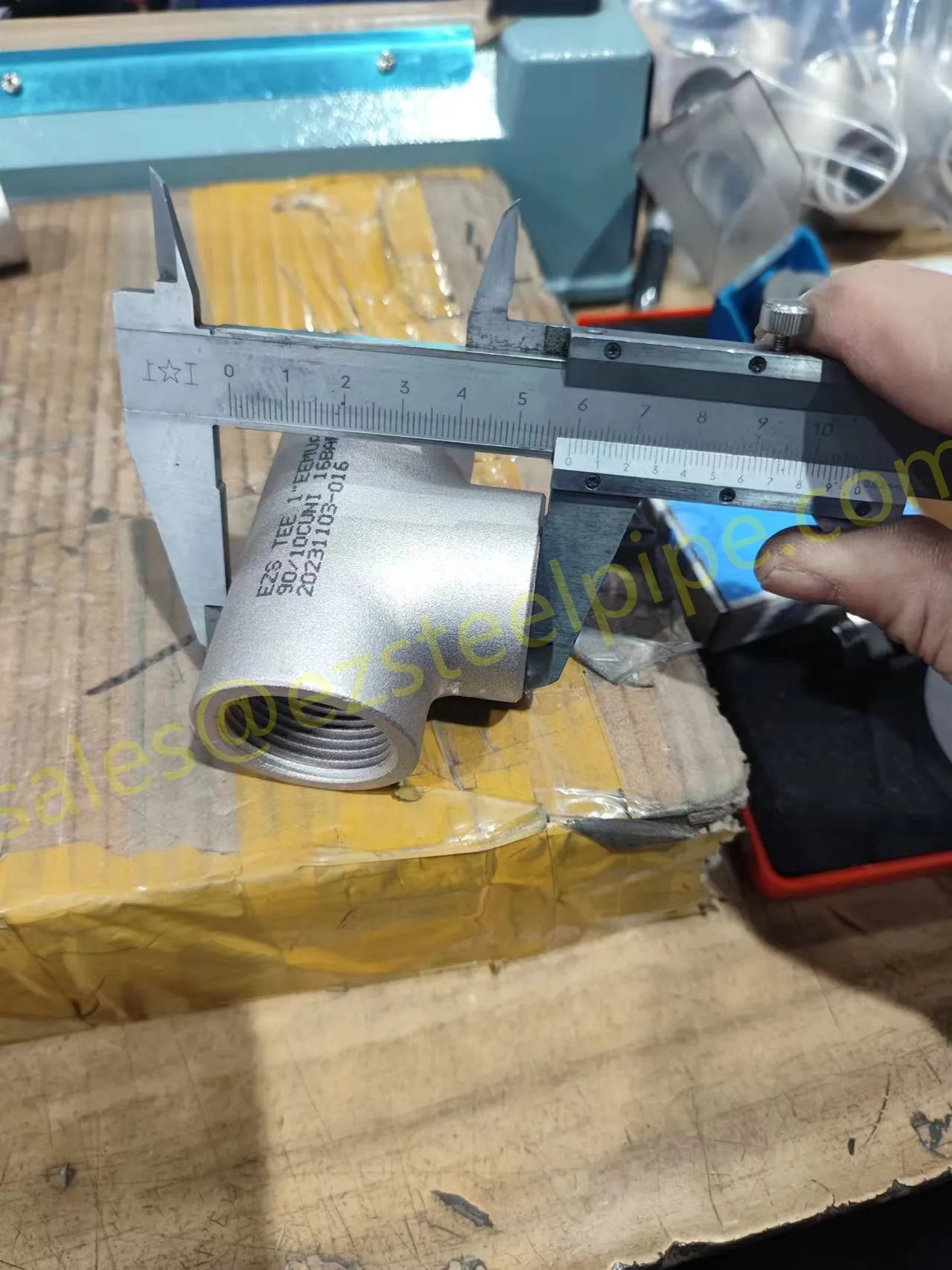
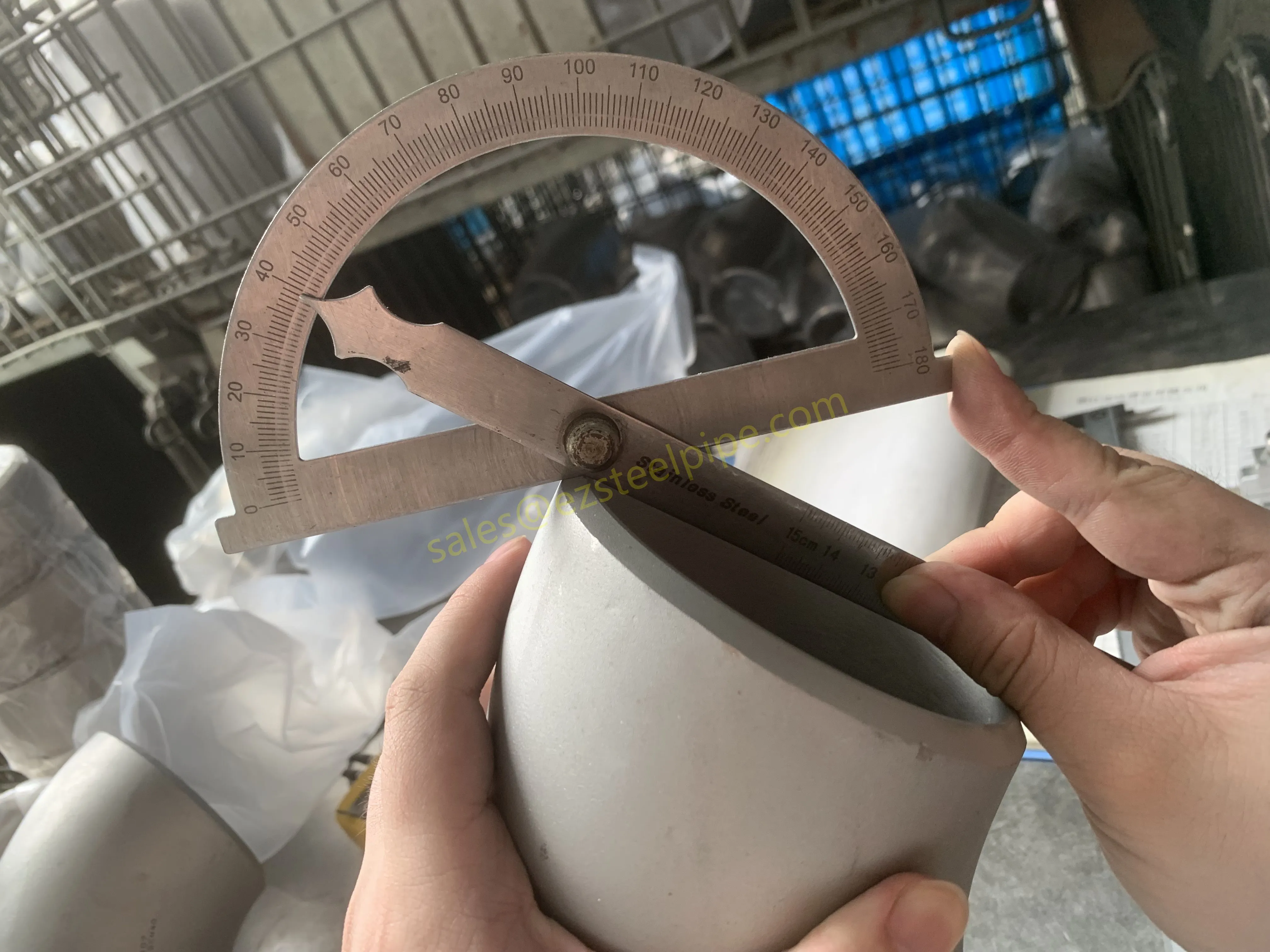
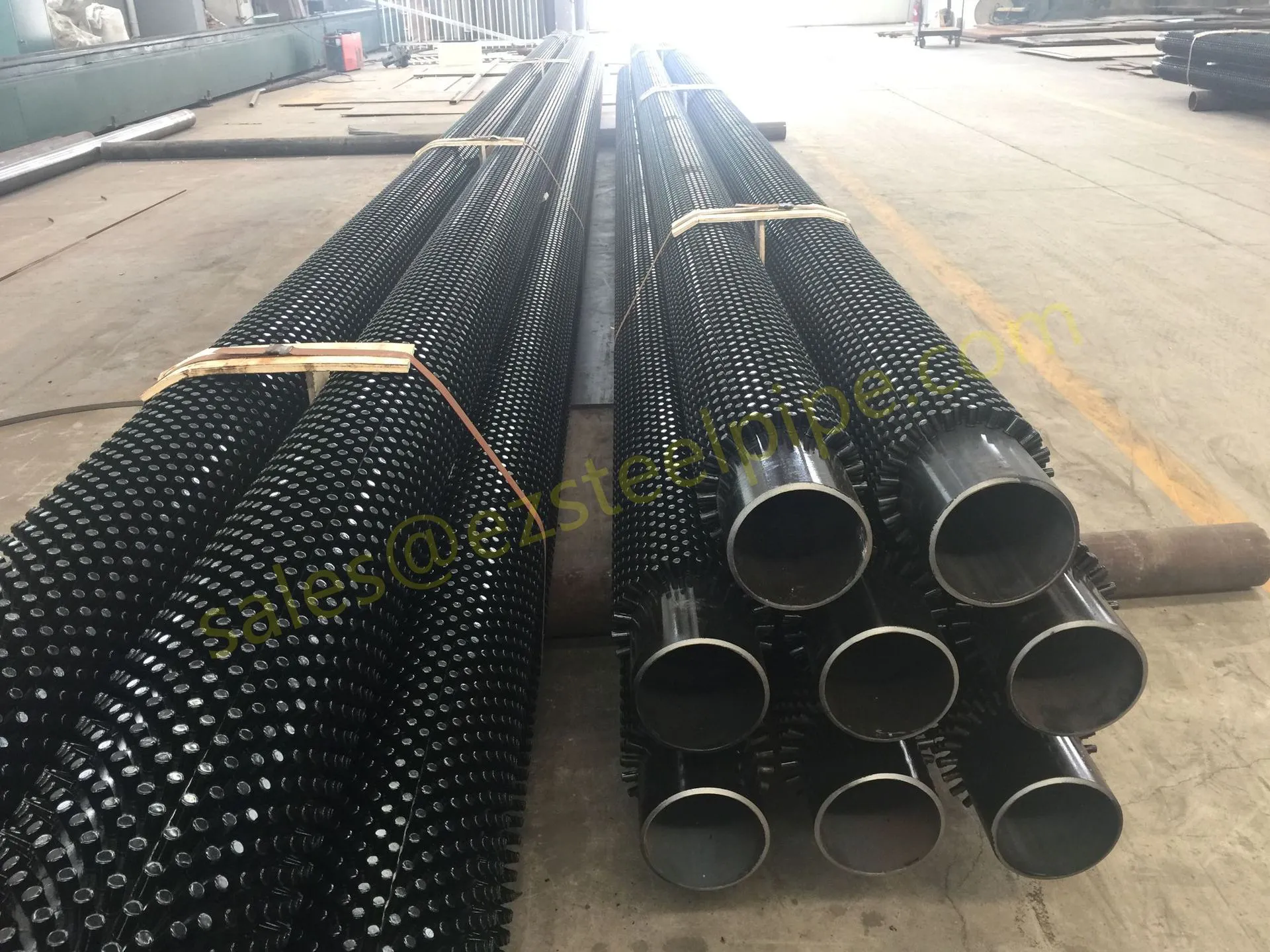
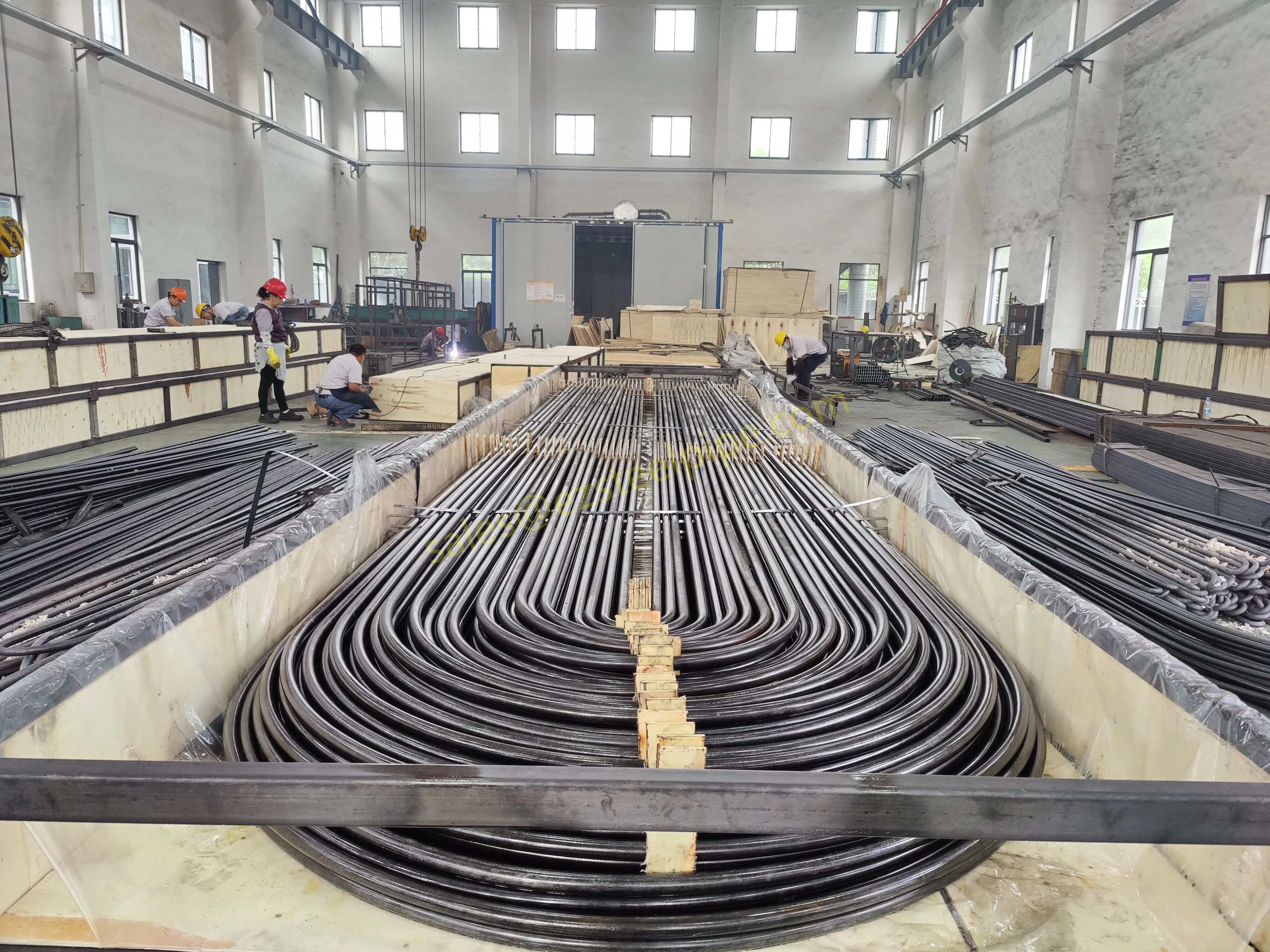
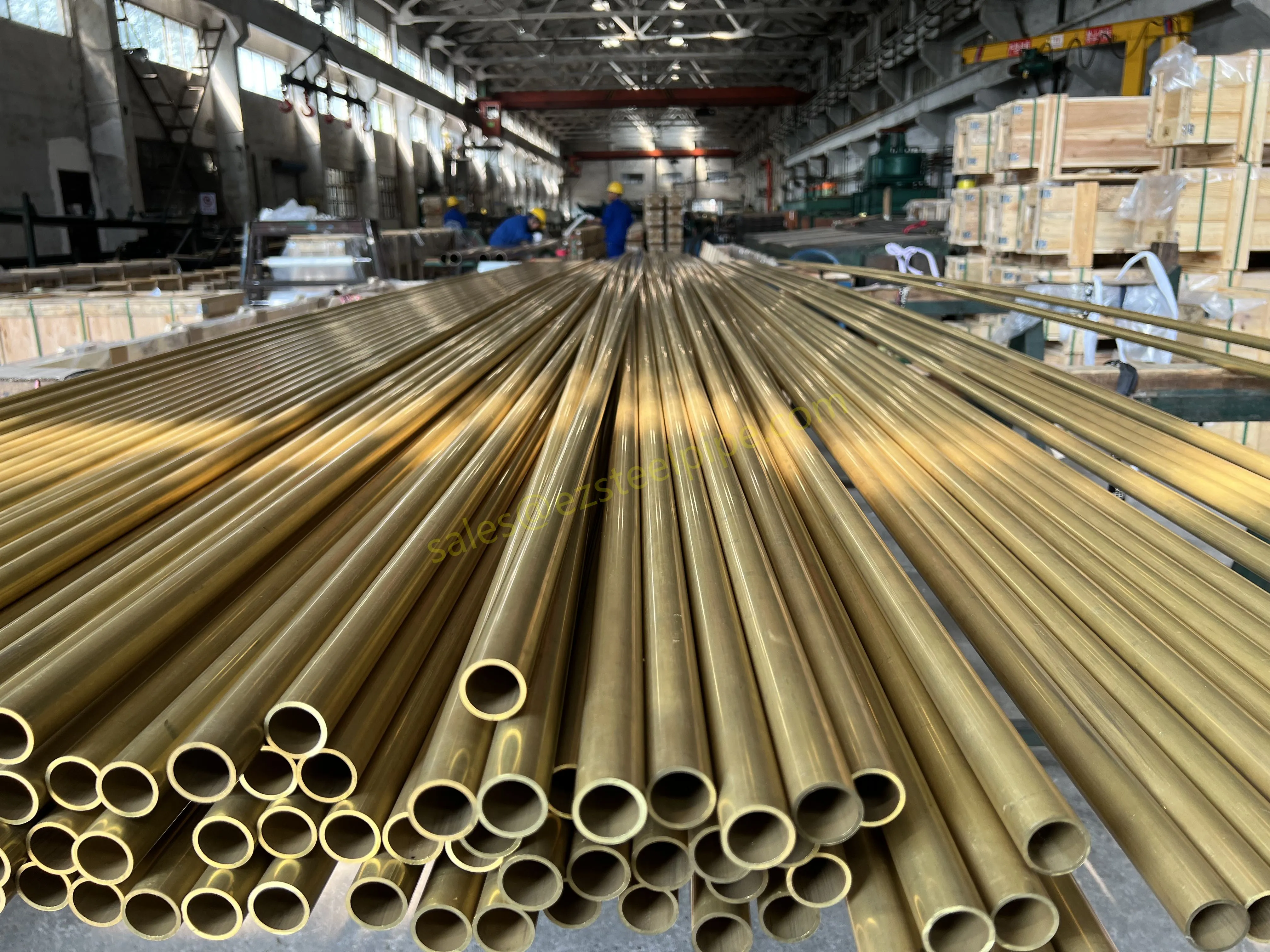
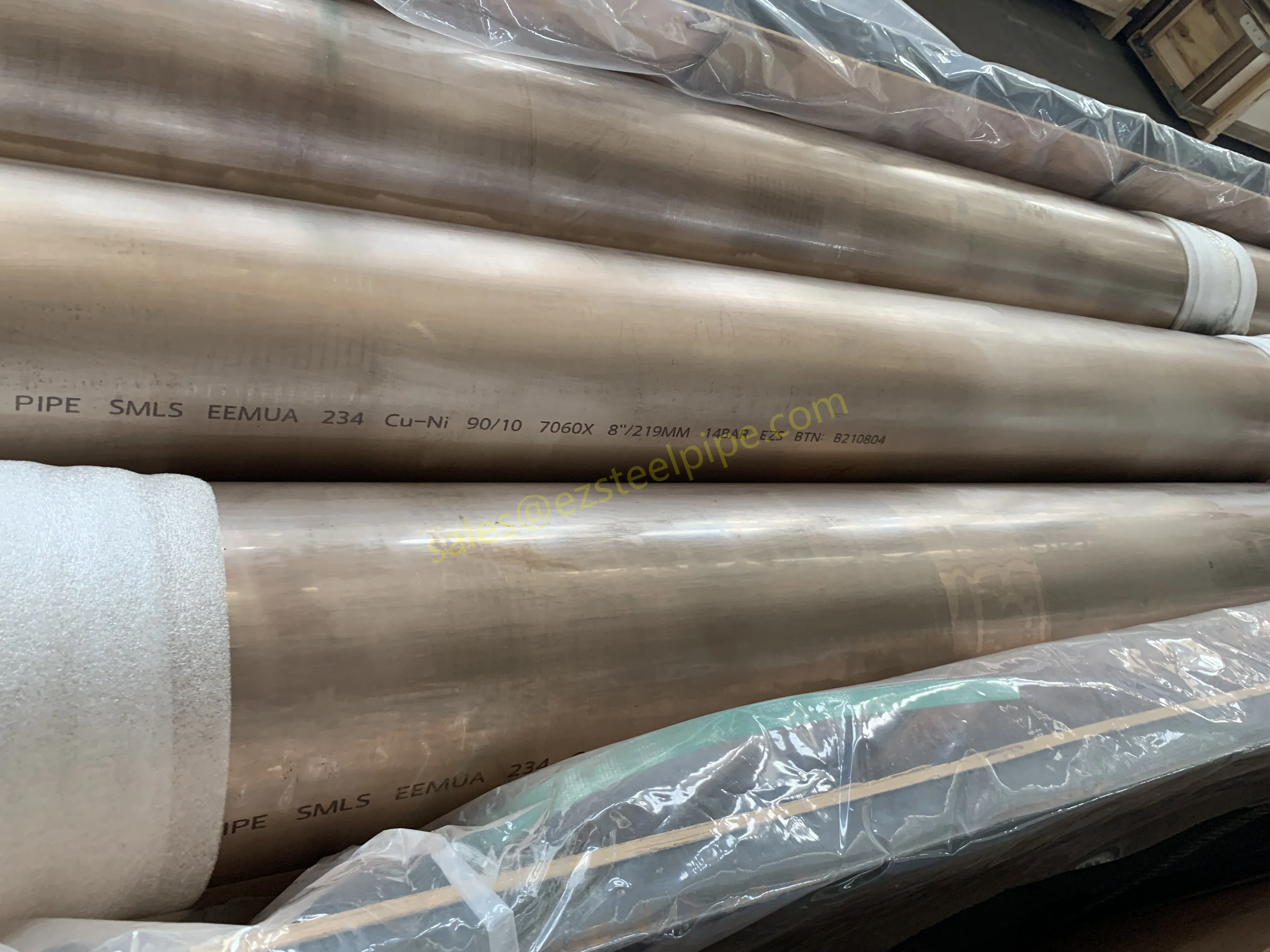
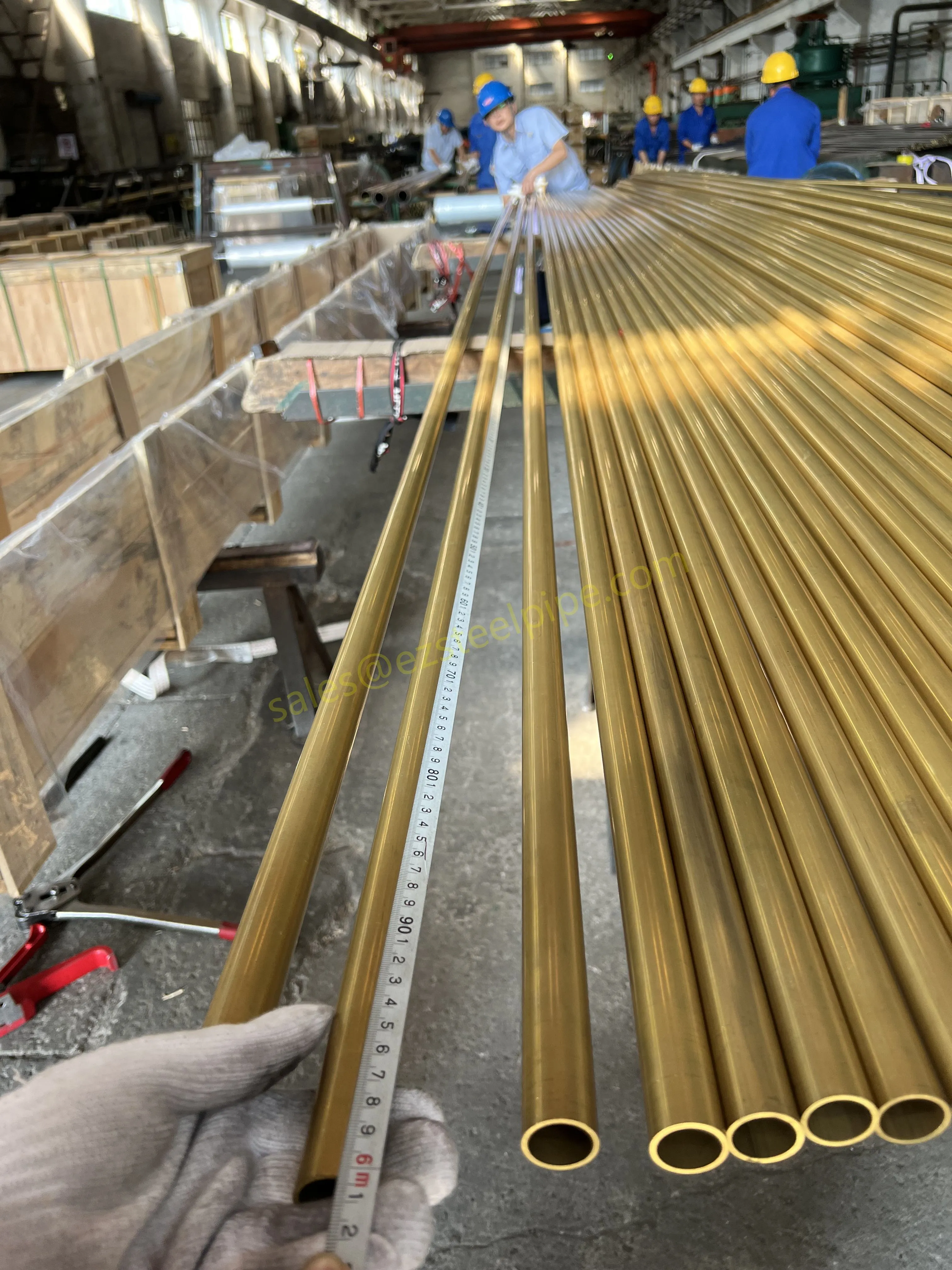
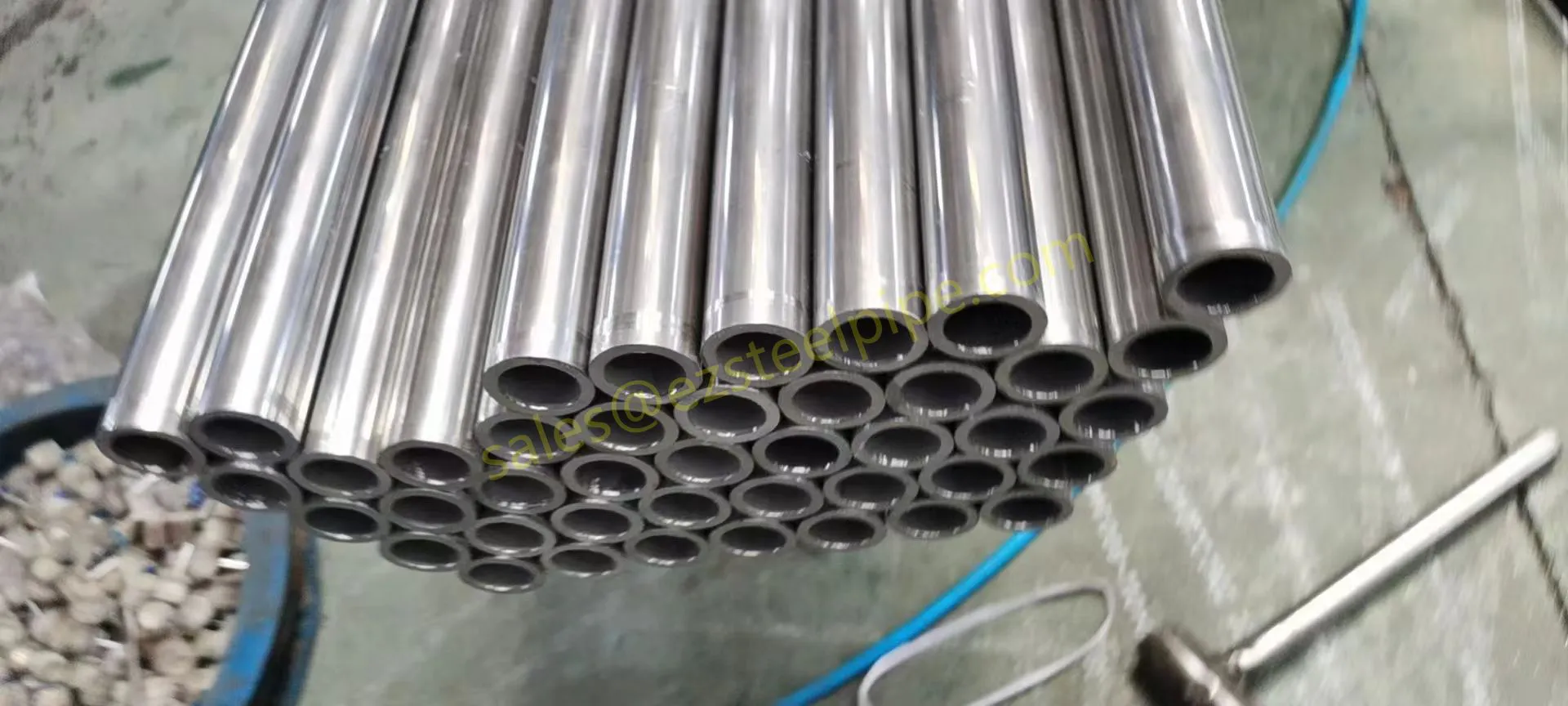
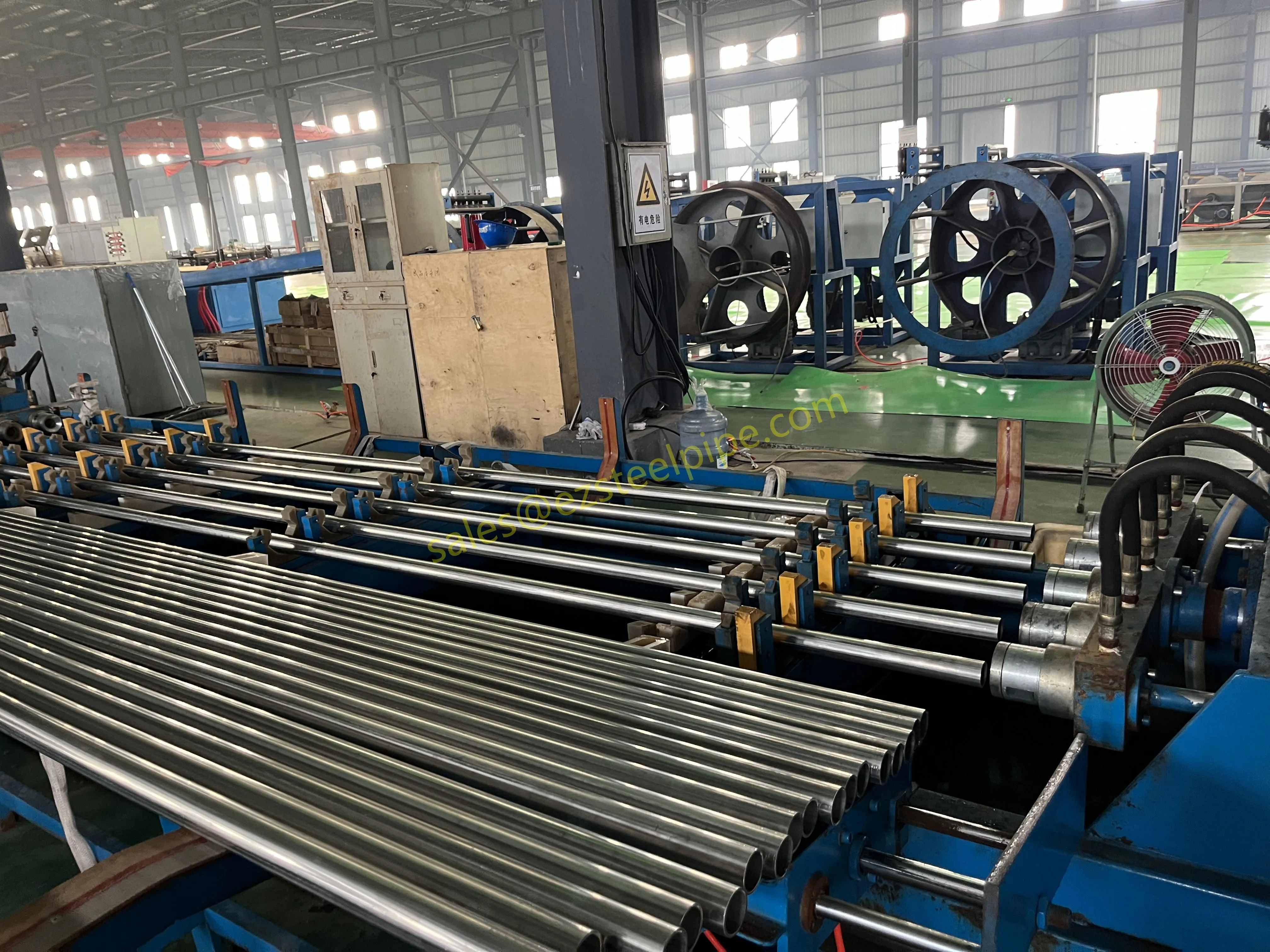
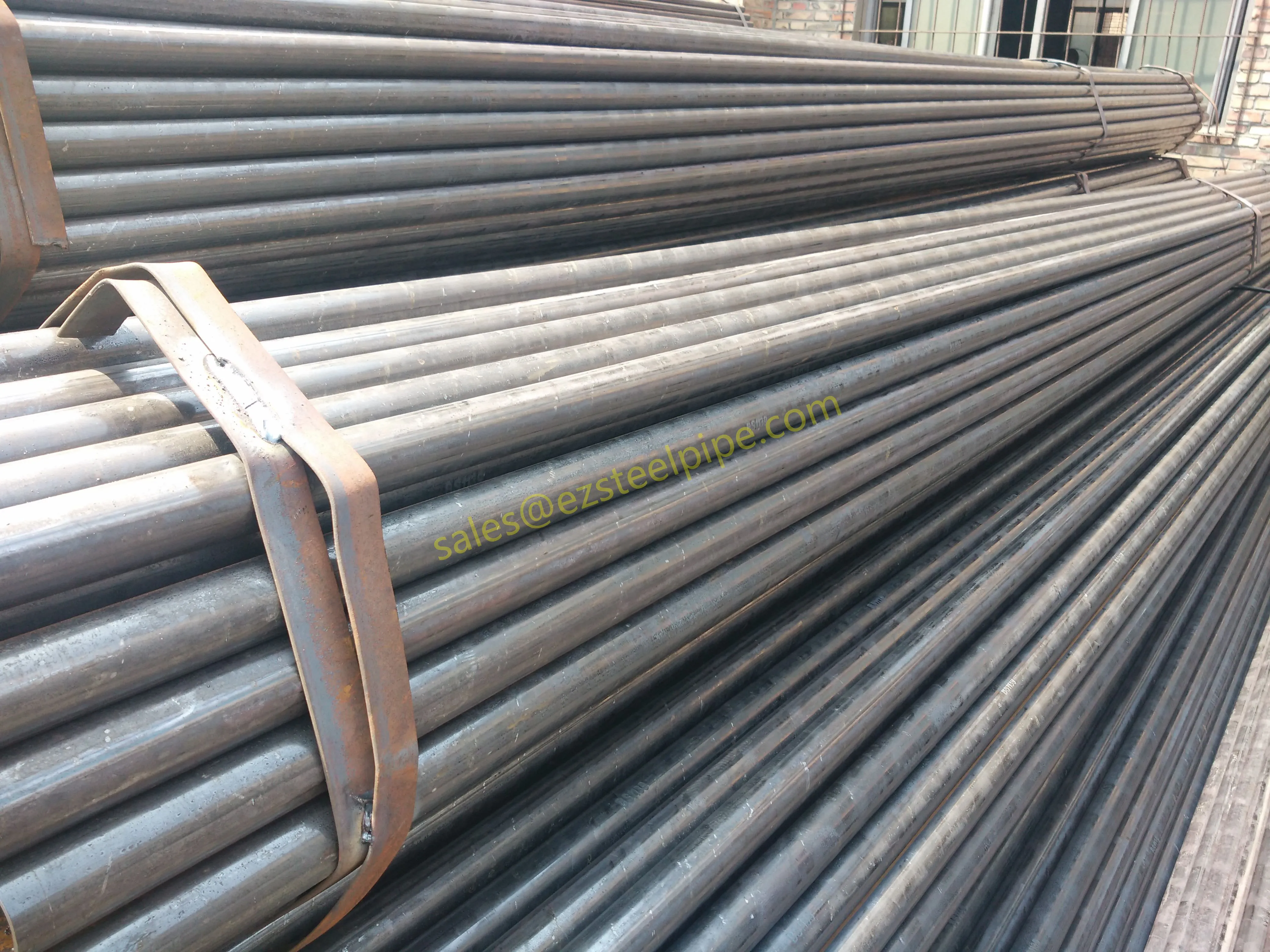
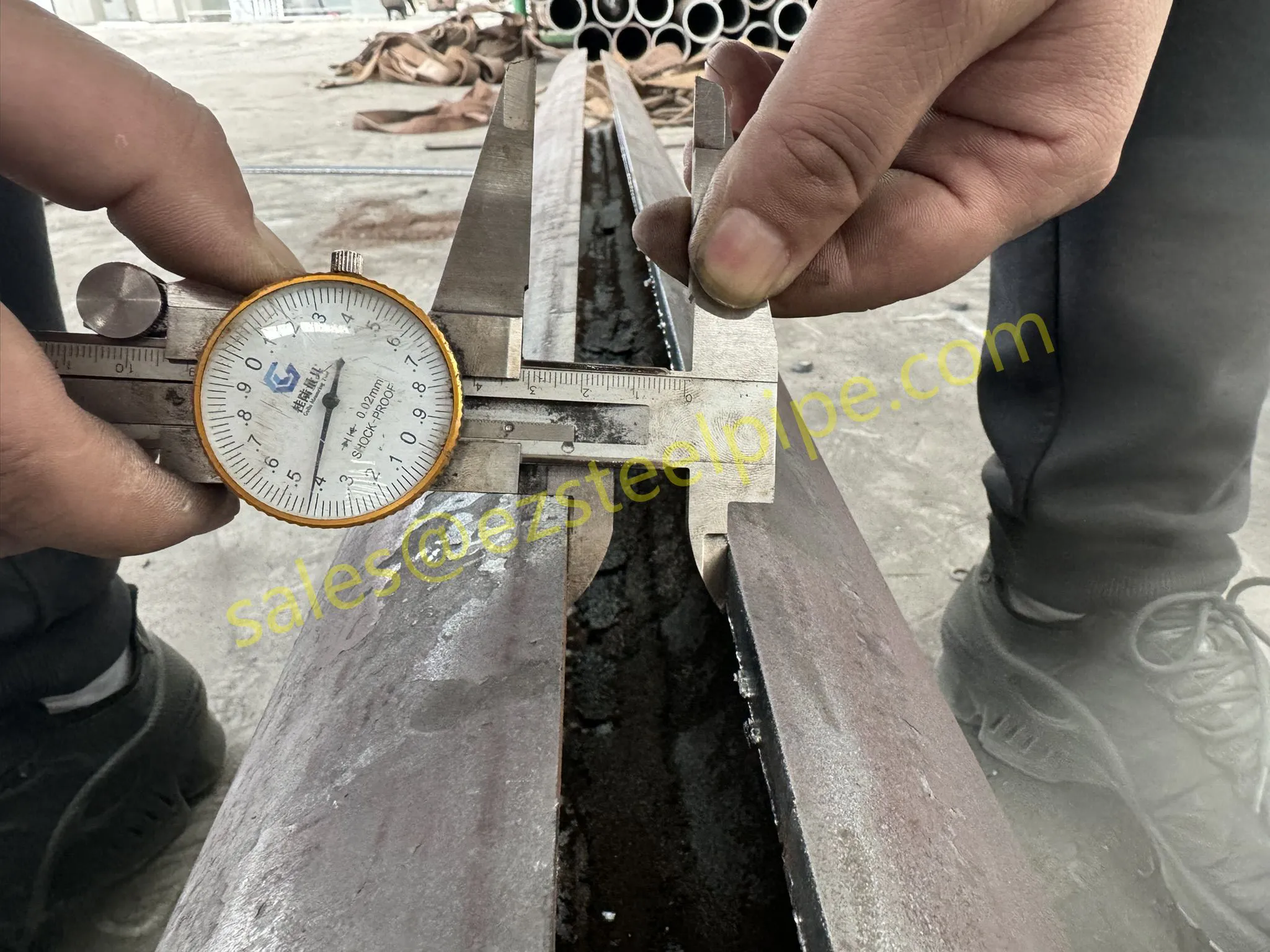
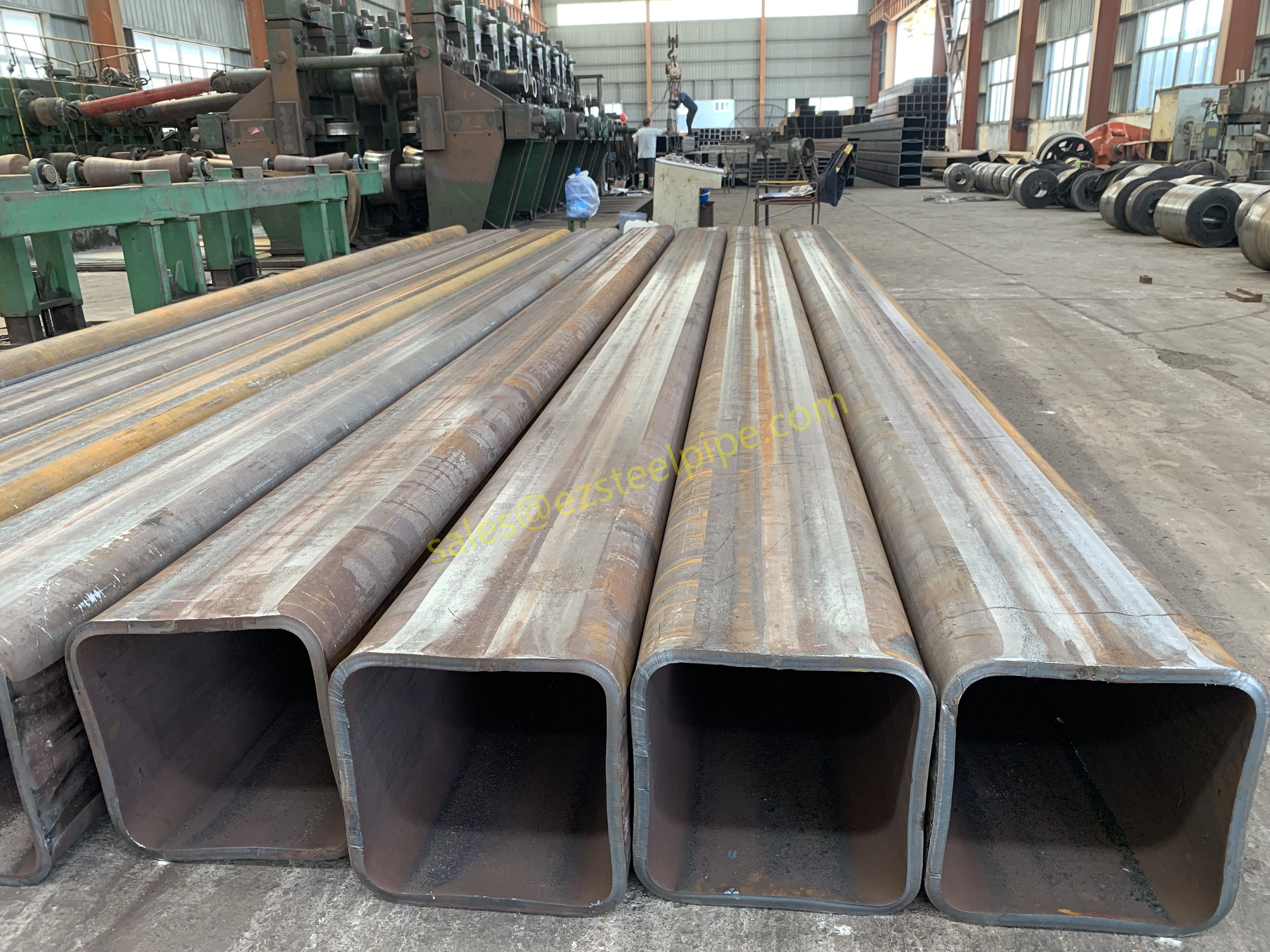
Let's start with the basics. Thermal expansion is what happens when matter heats up: molecules move faster, take up more space, and the material expands. Cool it down, and the opposite occurs—it contracts. We see this in everyday life: a balloon shrinking in the freezer, a sidewalk cracking on a hot day because the concrete expanded beyond its limits. In piping systems, though, the stakes are higher. Imagine a steel pipe carrying hot steam in a power plant or a copper nickel tube circulating coolant in a ship's engine room. When temperatures swing, that pipe isn't just getting a little bigger or smaller—it's exerting force. If that force isn't accounted for, you could end up with bent pipes, loose fittings, cracked flanges, or even catastrophic leaks.
For engineers, thermal expansion isn't an afterthought; it's a design driver. It dictates everything from the type of pipe fittings (think bw fittings or sw fittings) to the placement of expansion loops, and even the choice of materials in the first place. And when the material in question is copper nickel—used in critical applications like marine pipeline works or petrochemical heat exchanger tubes—understanding its thermal behavior becomes non-negotiable.
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































