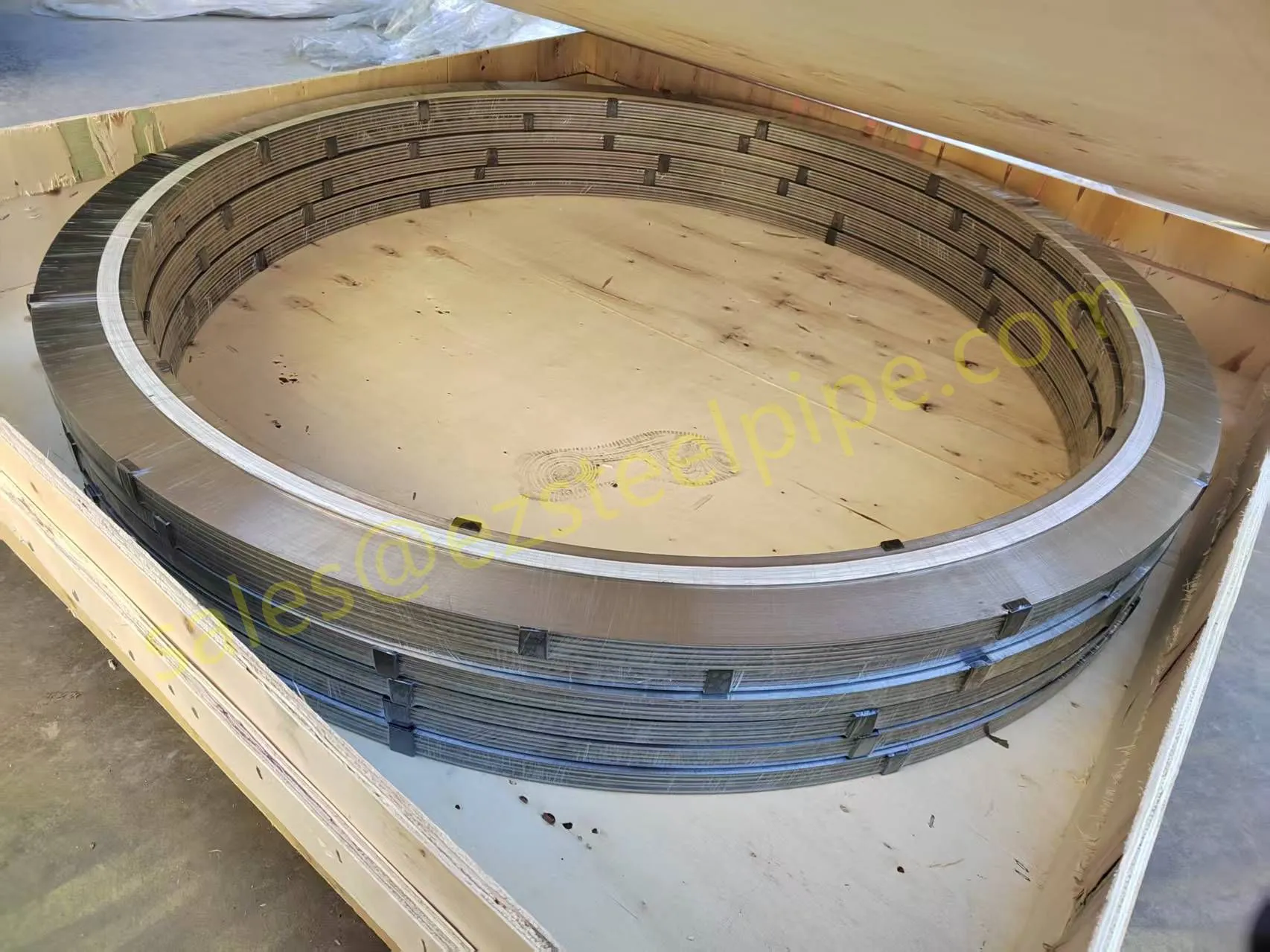
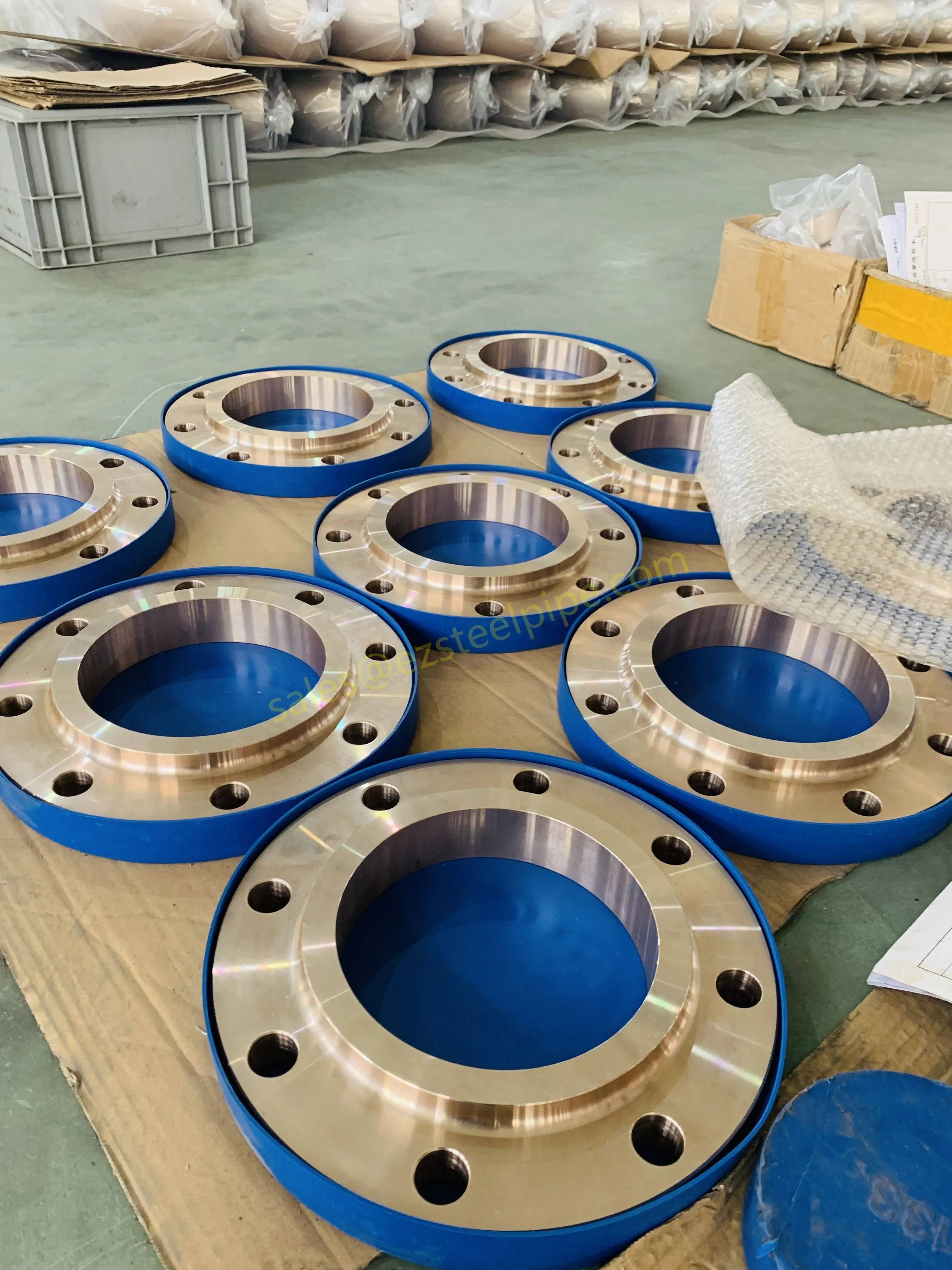
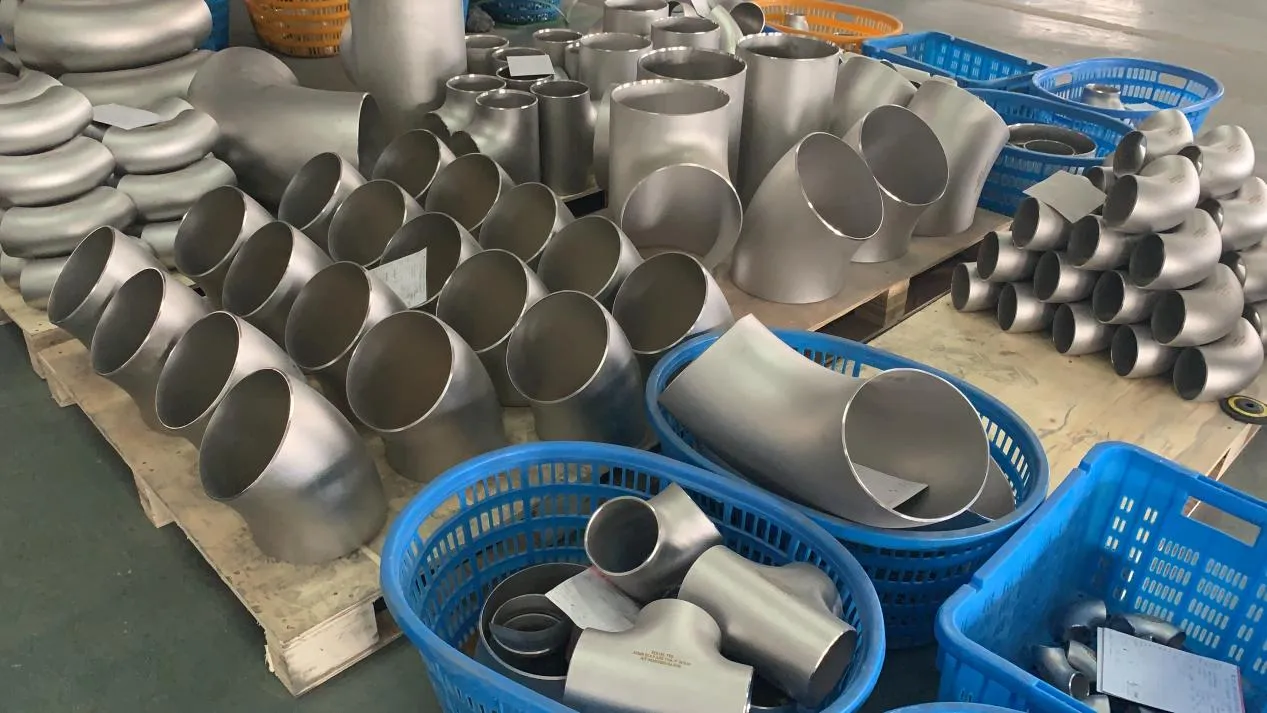
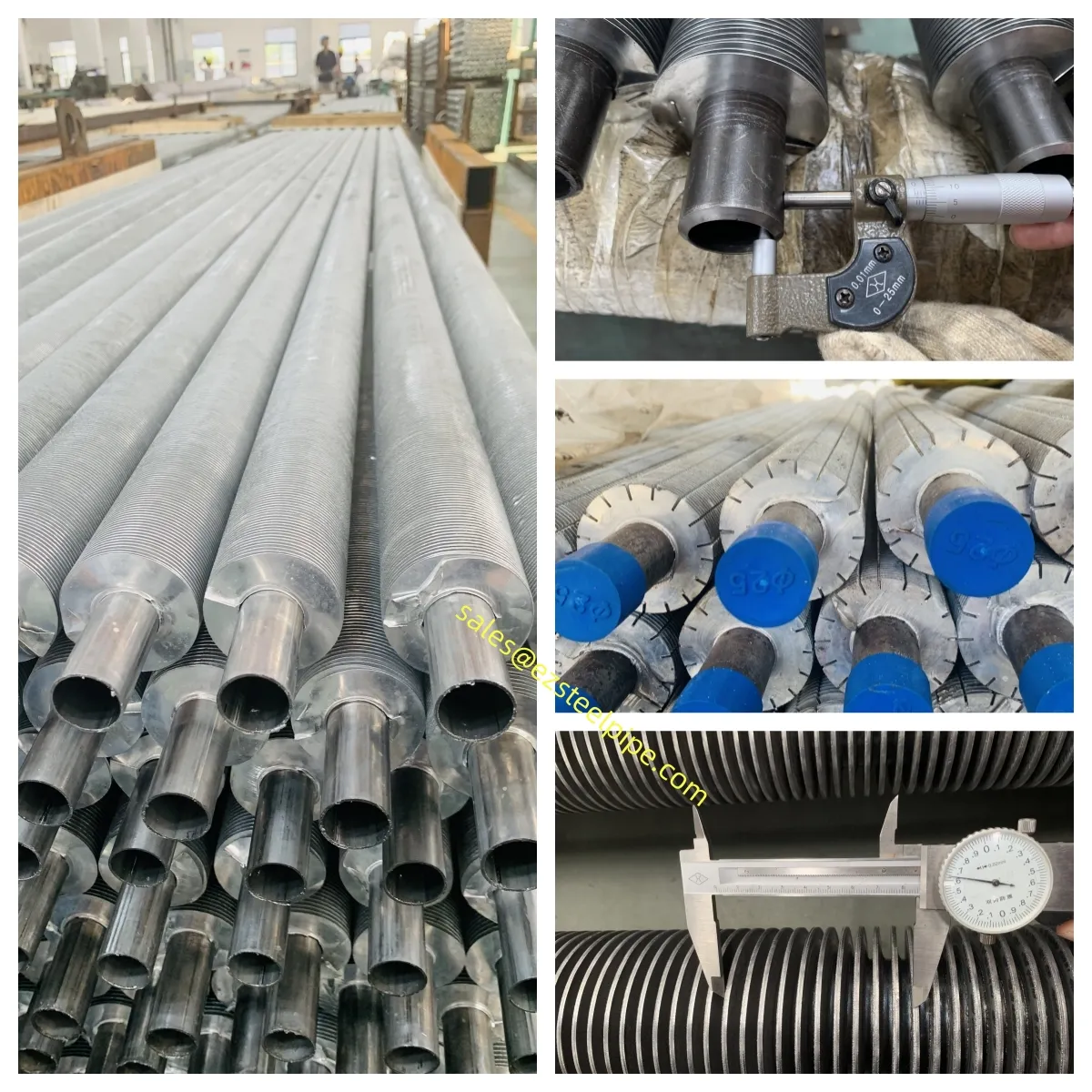
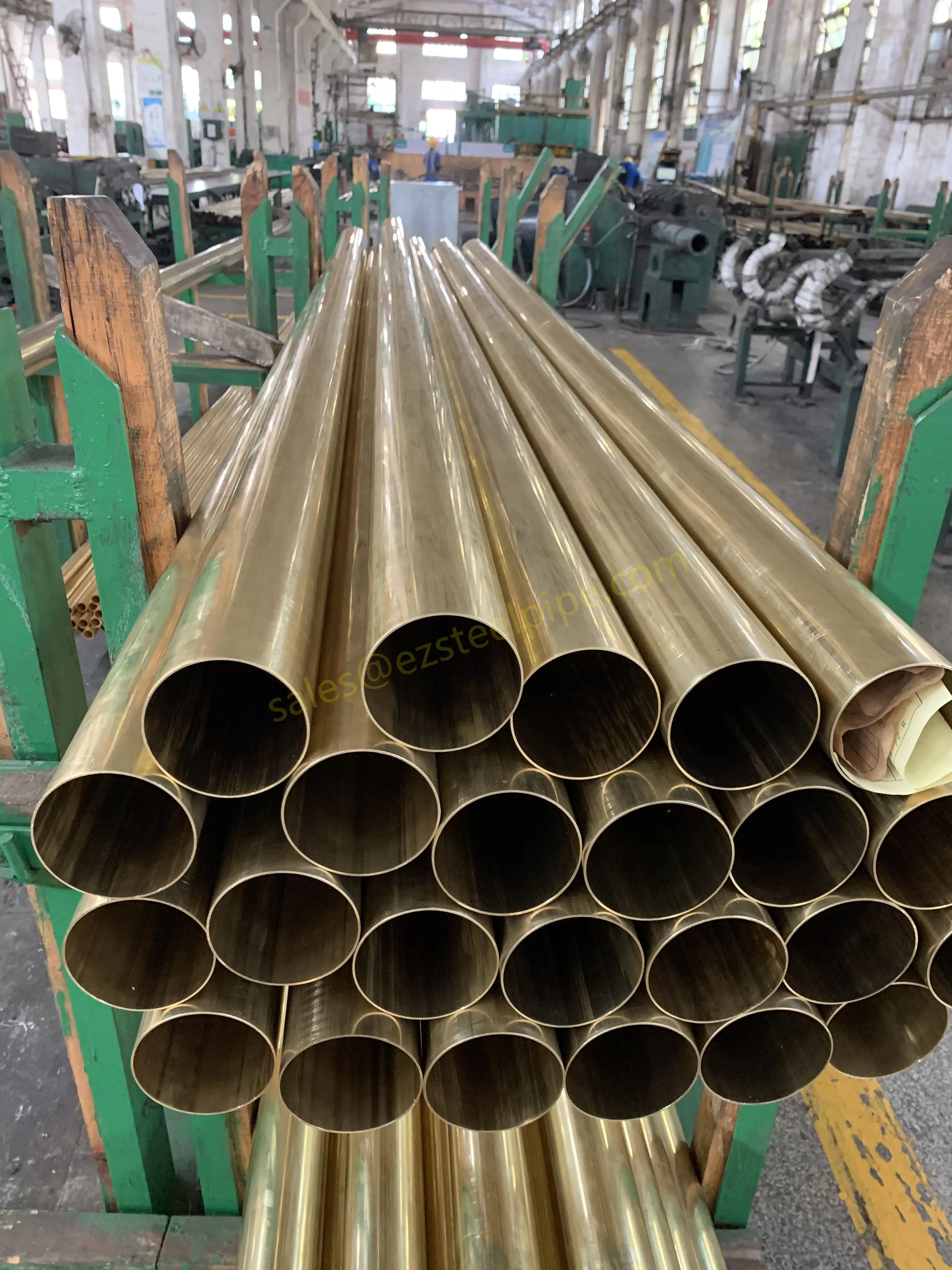
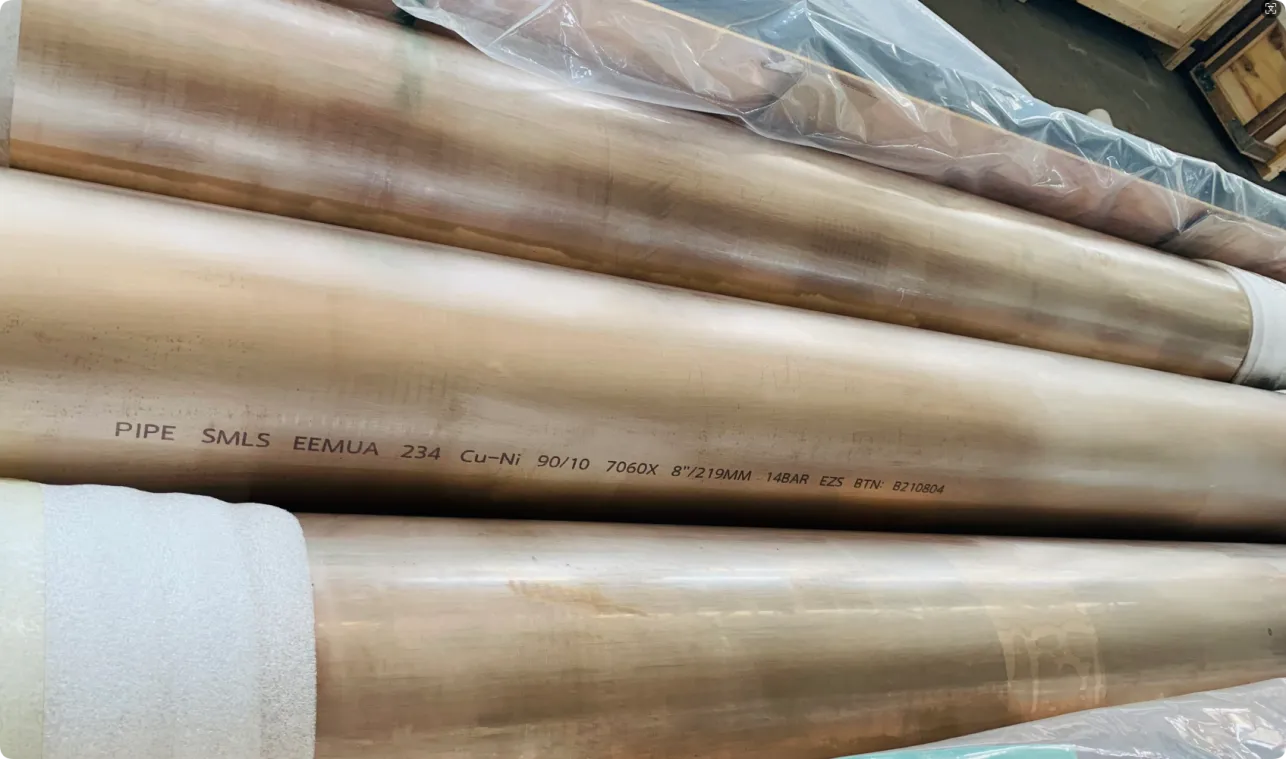
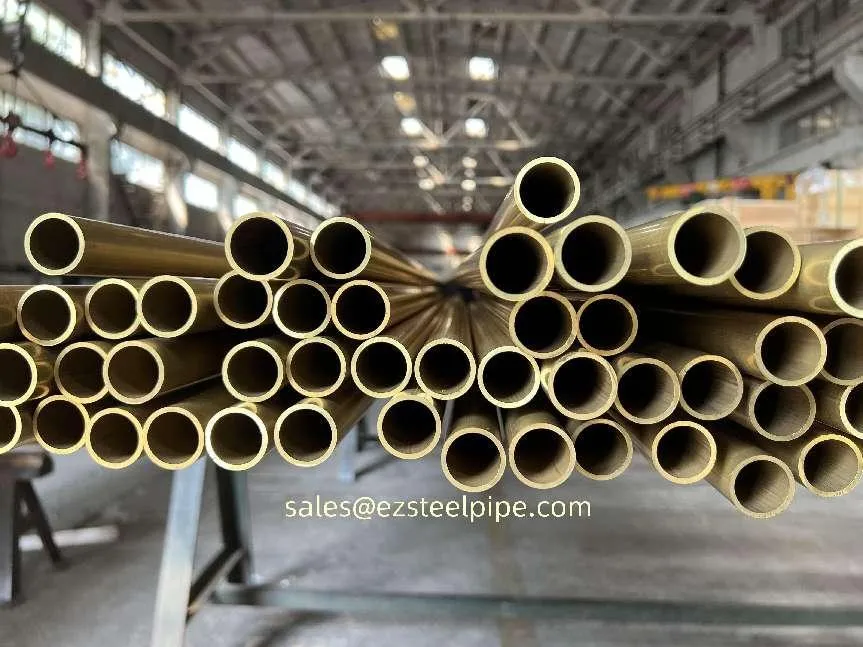
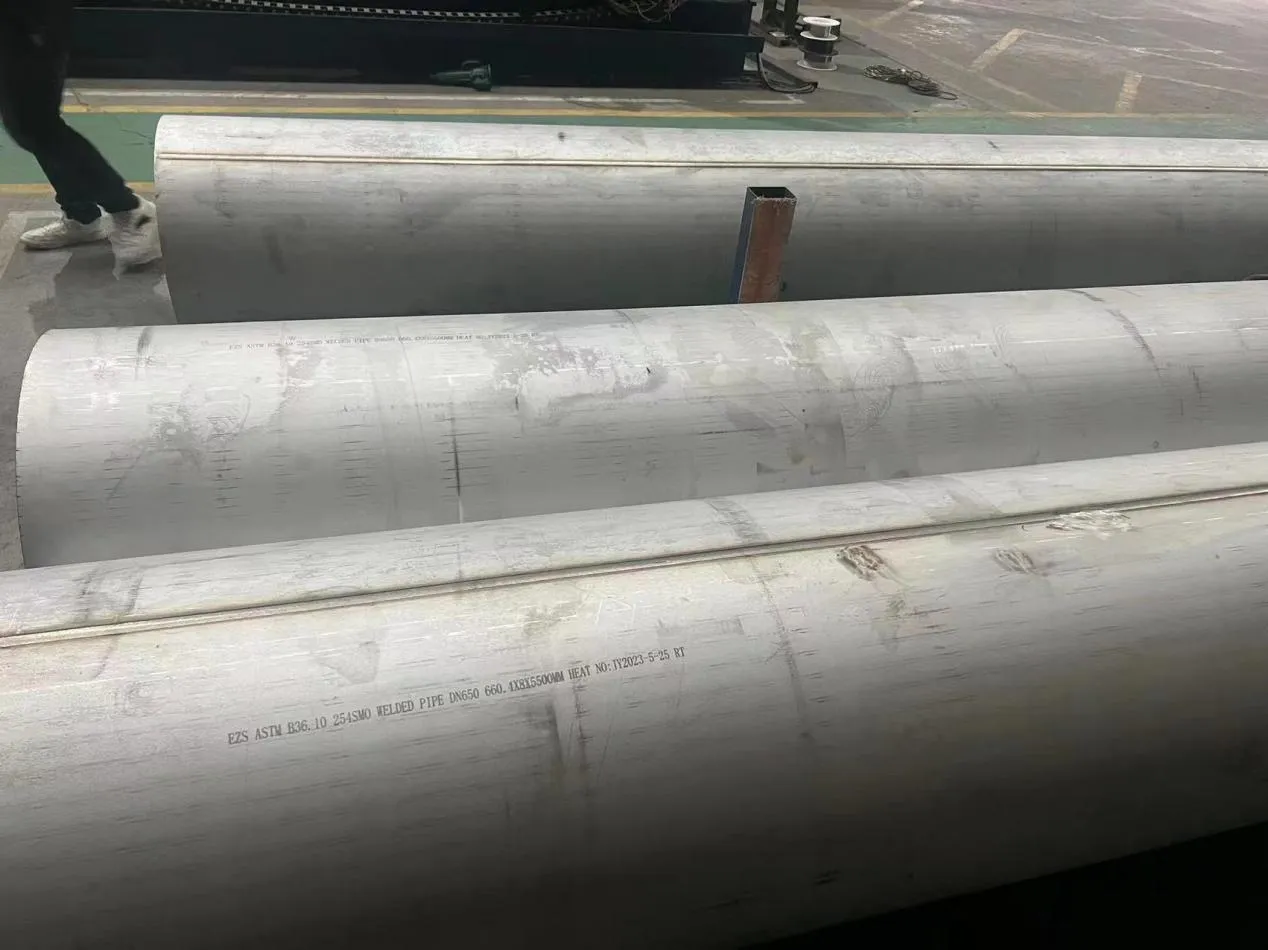
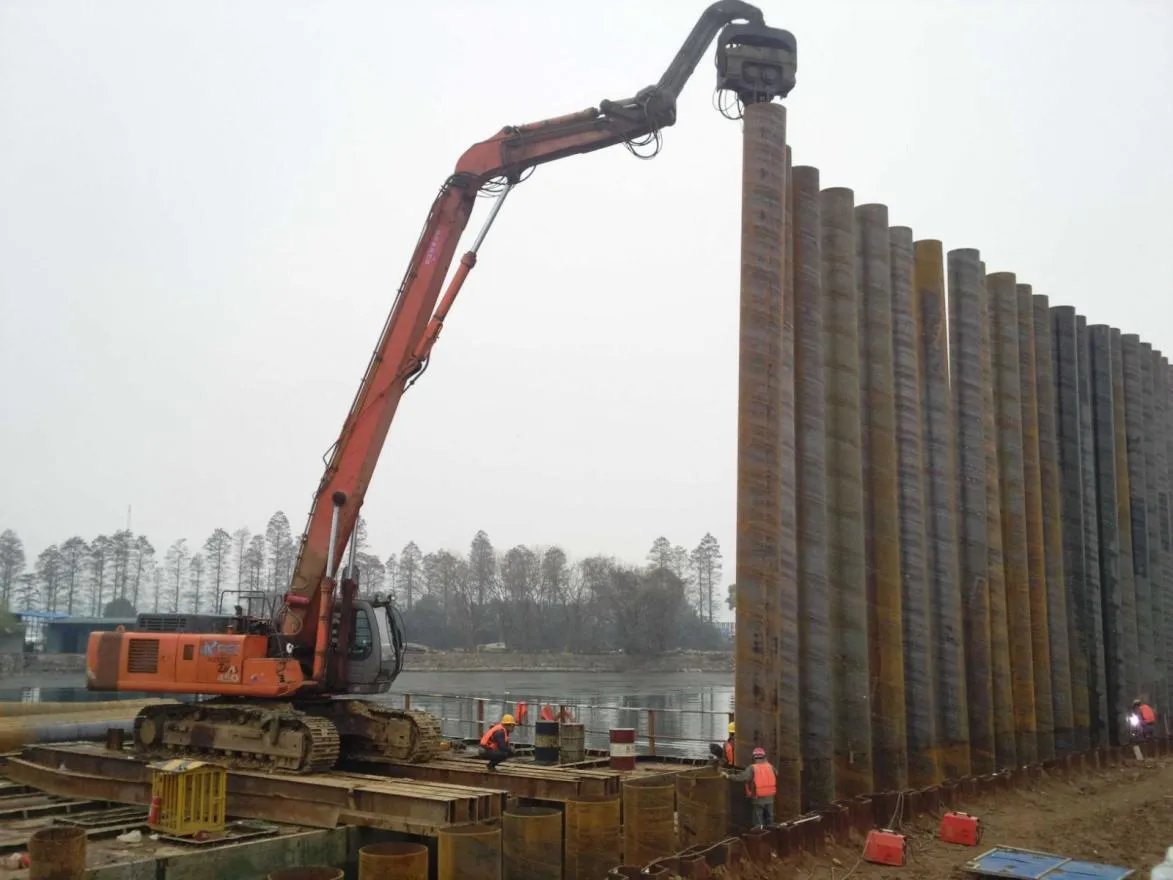
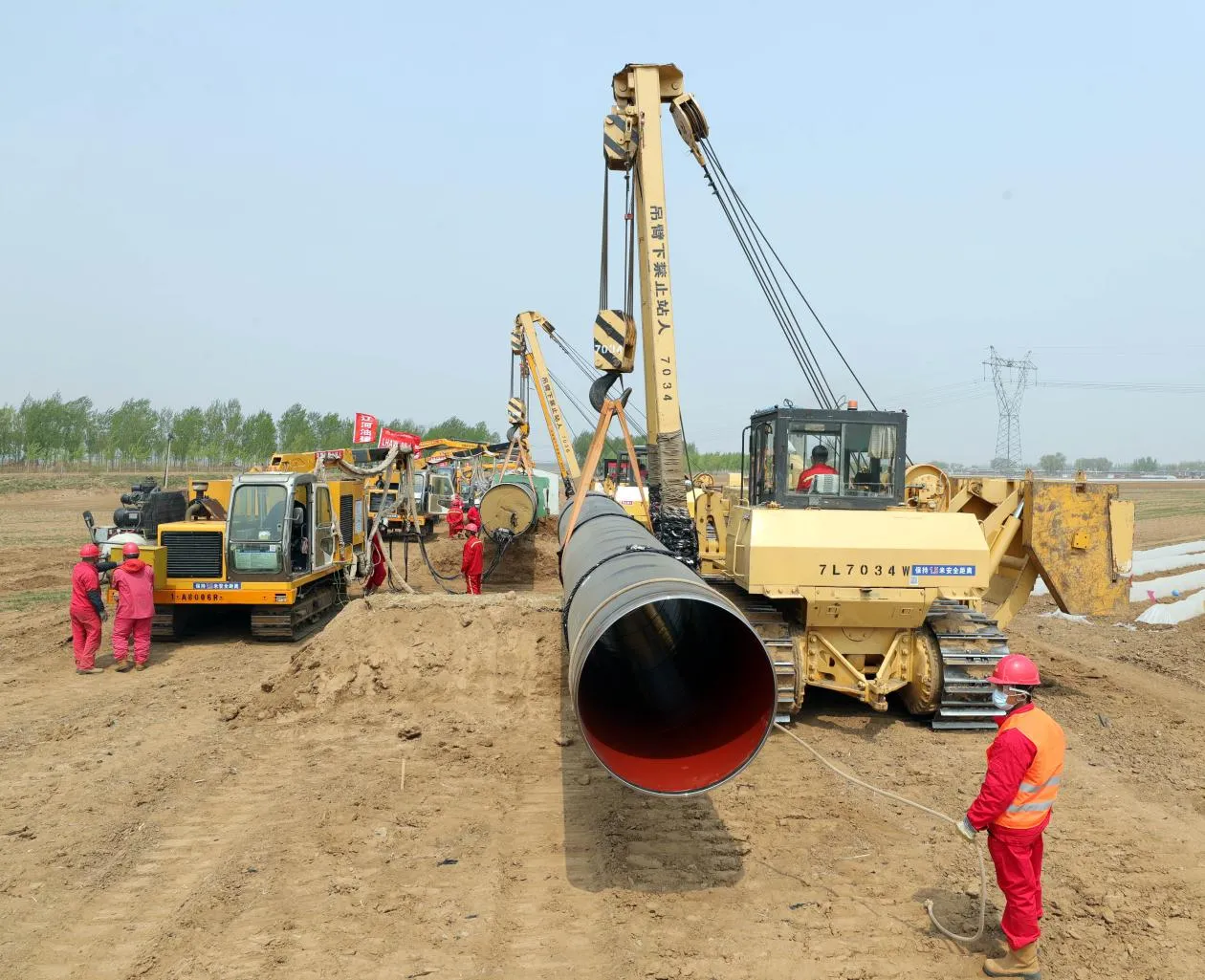
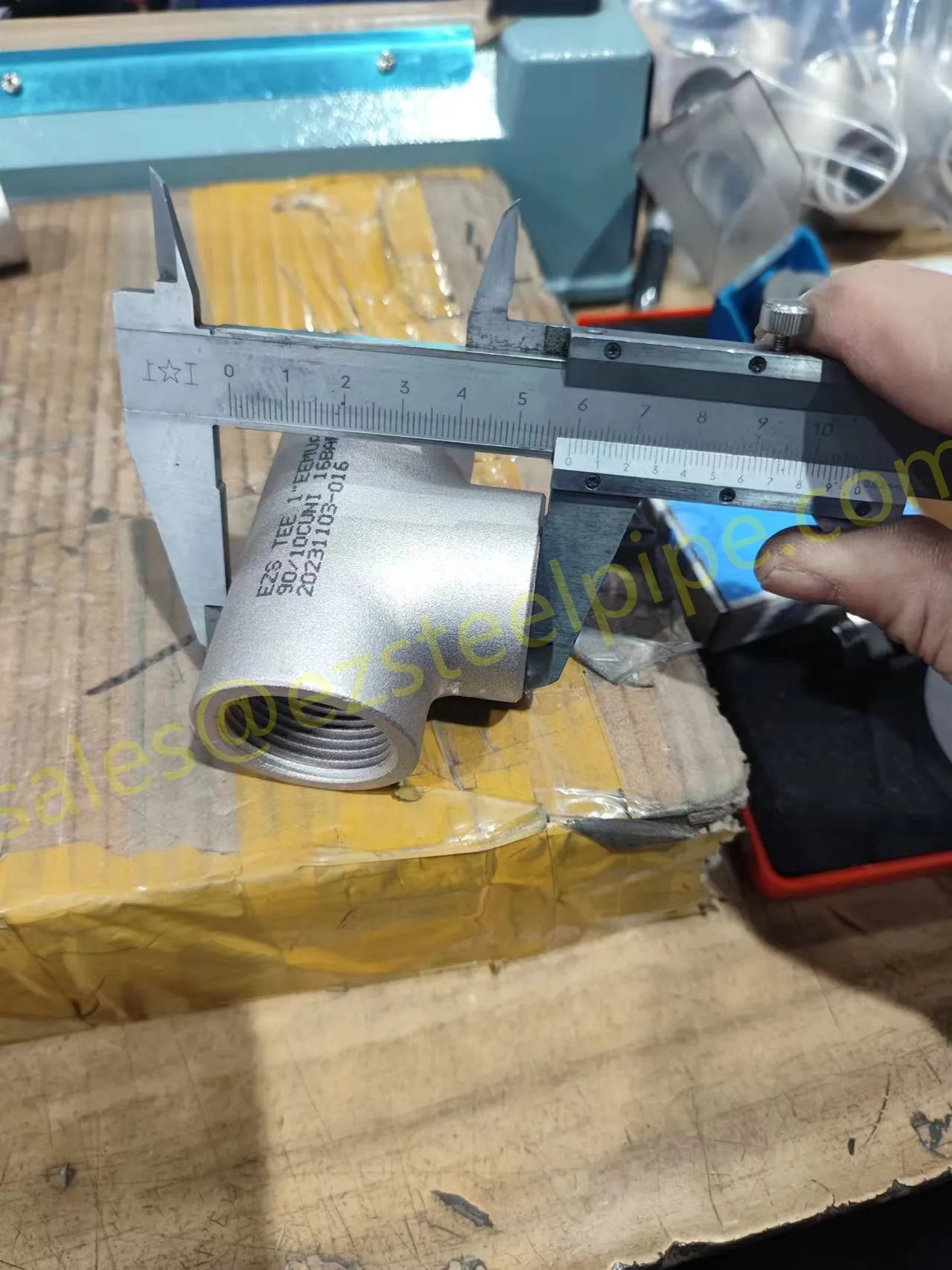
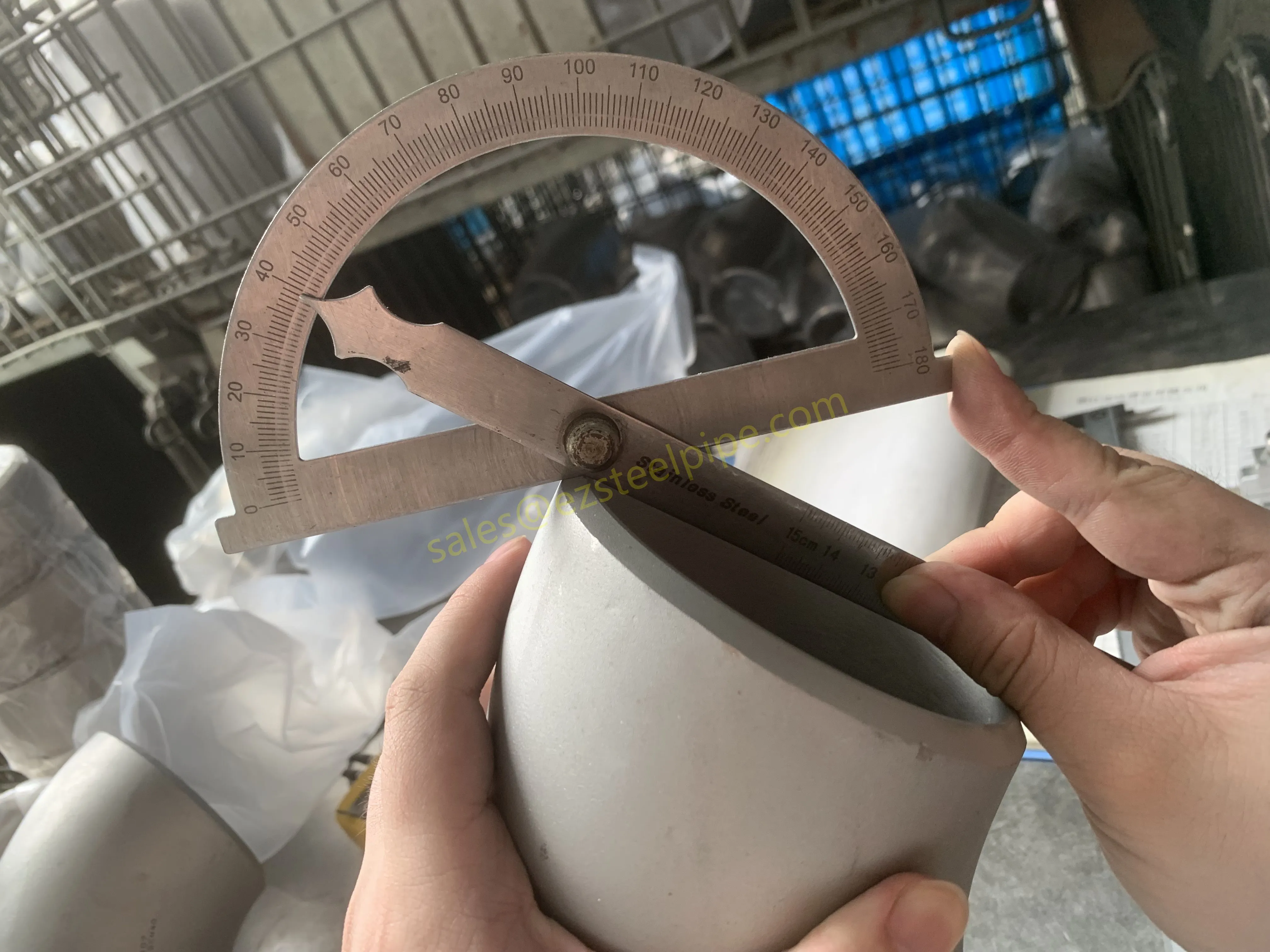
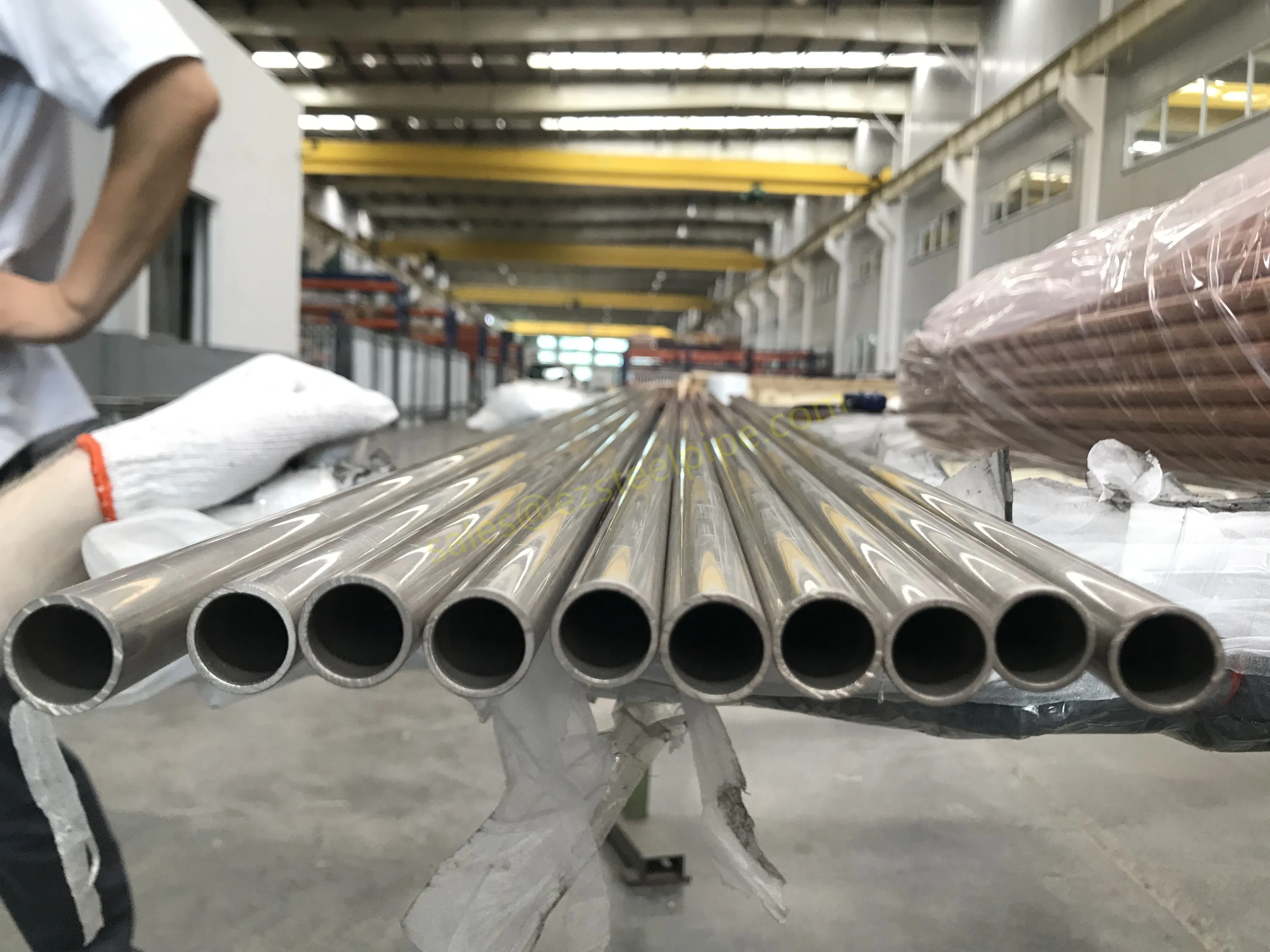
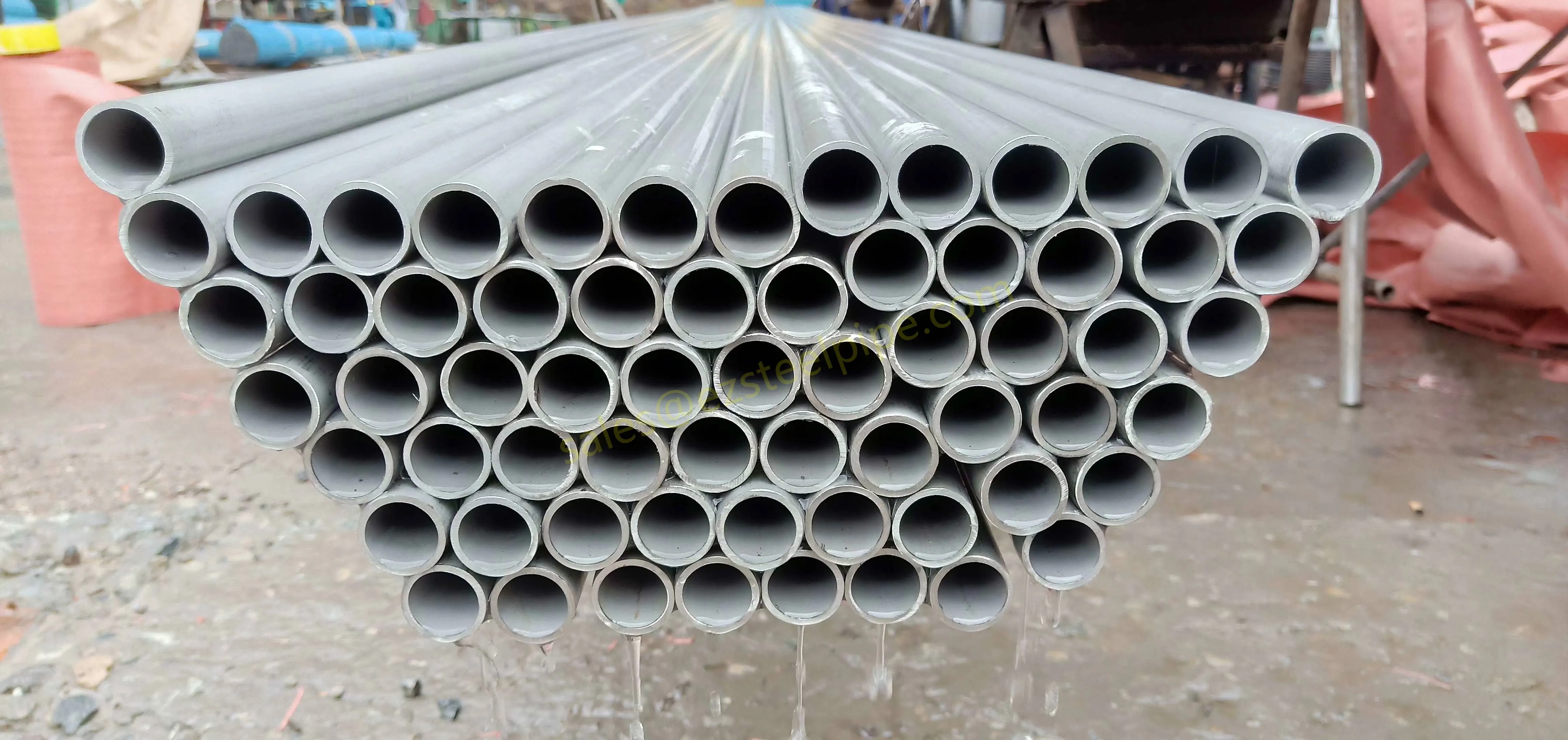
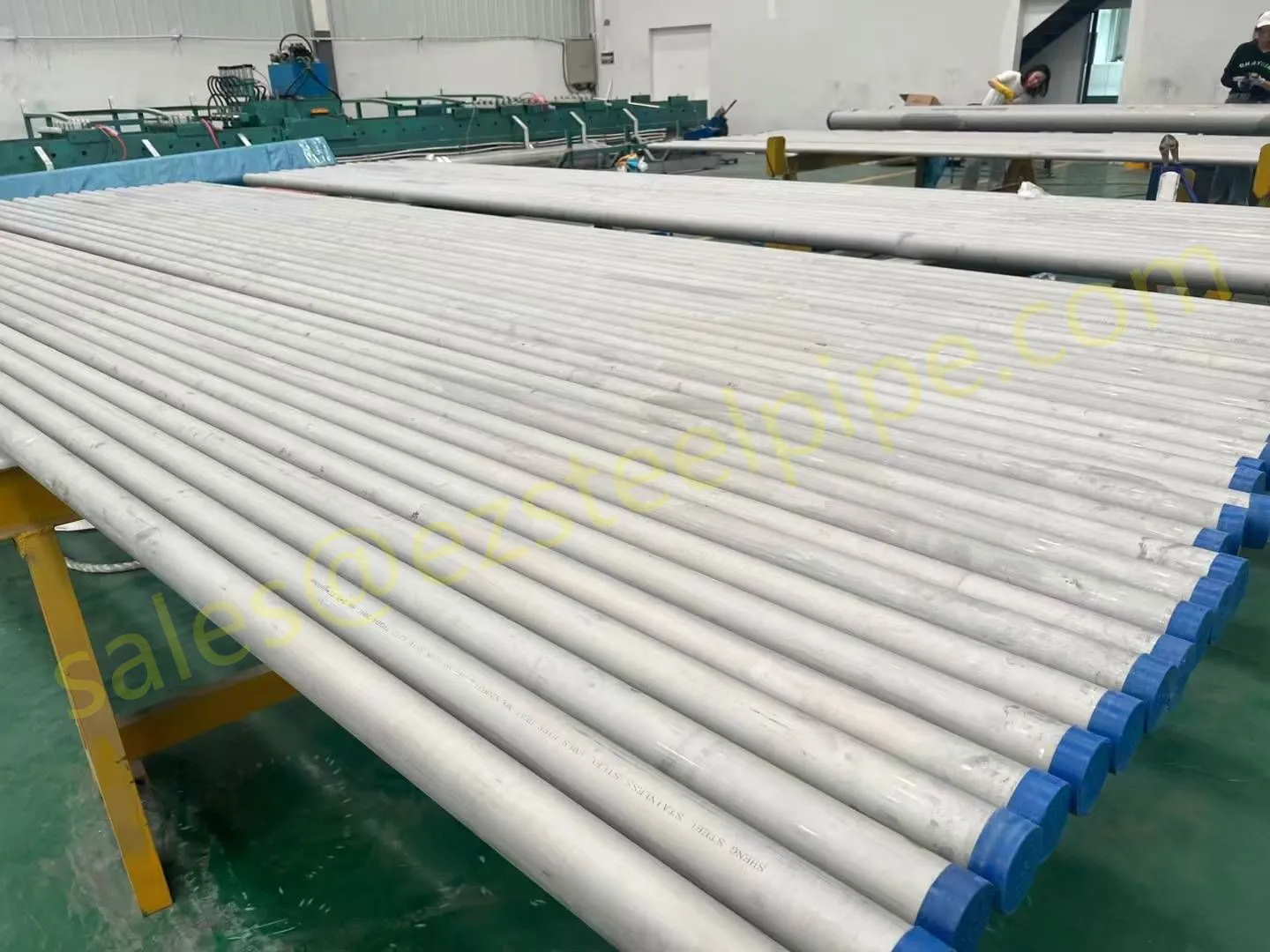
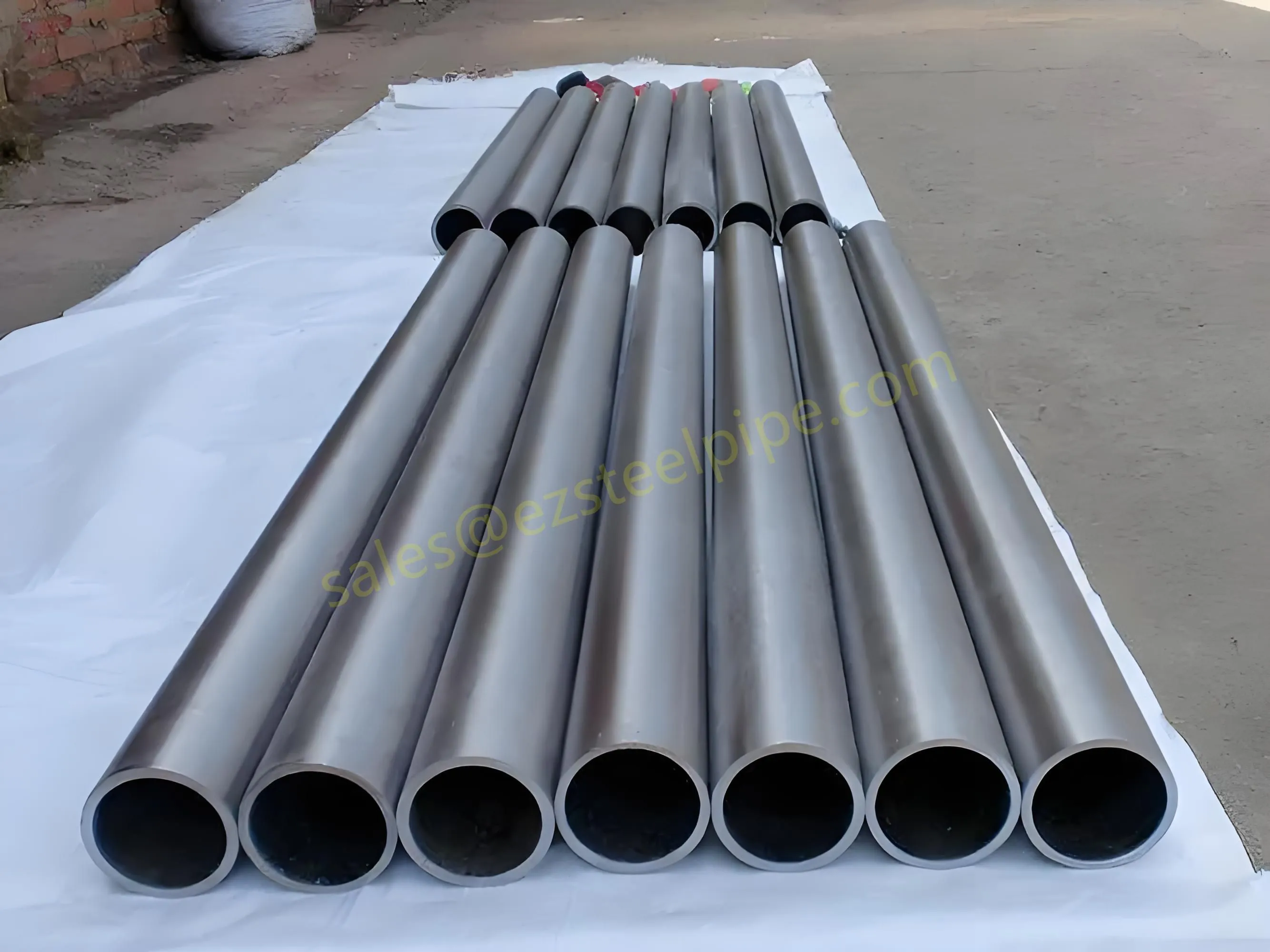
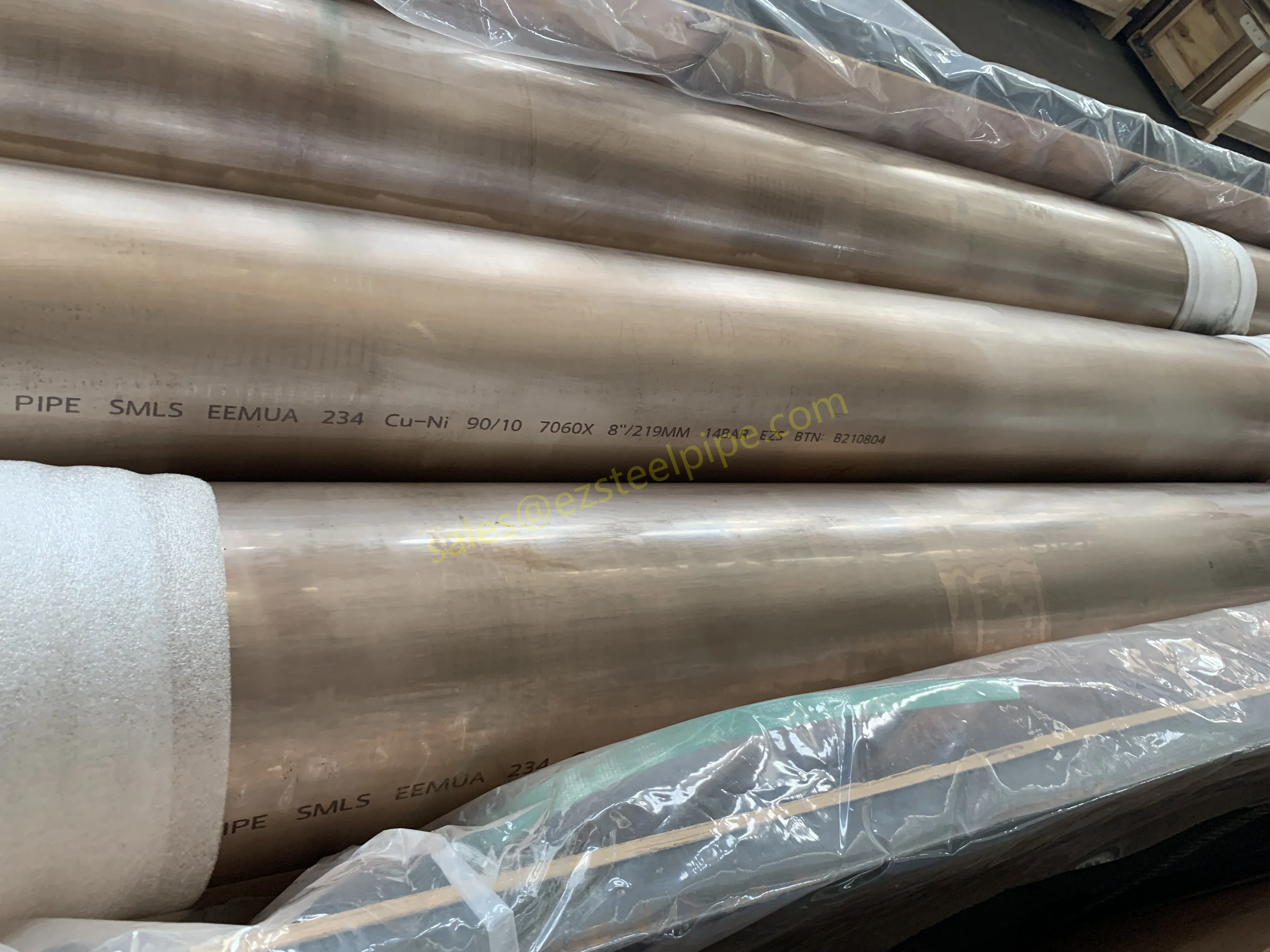
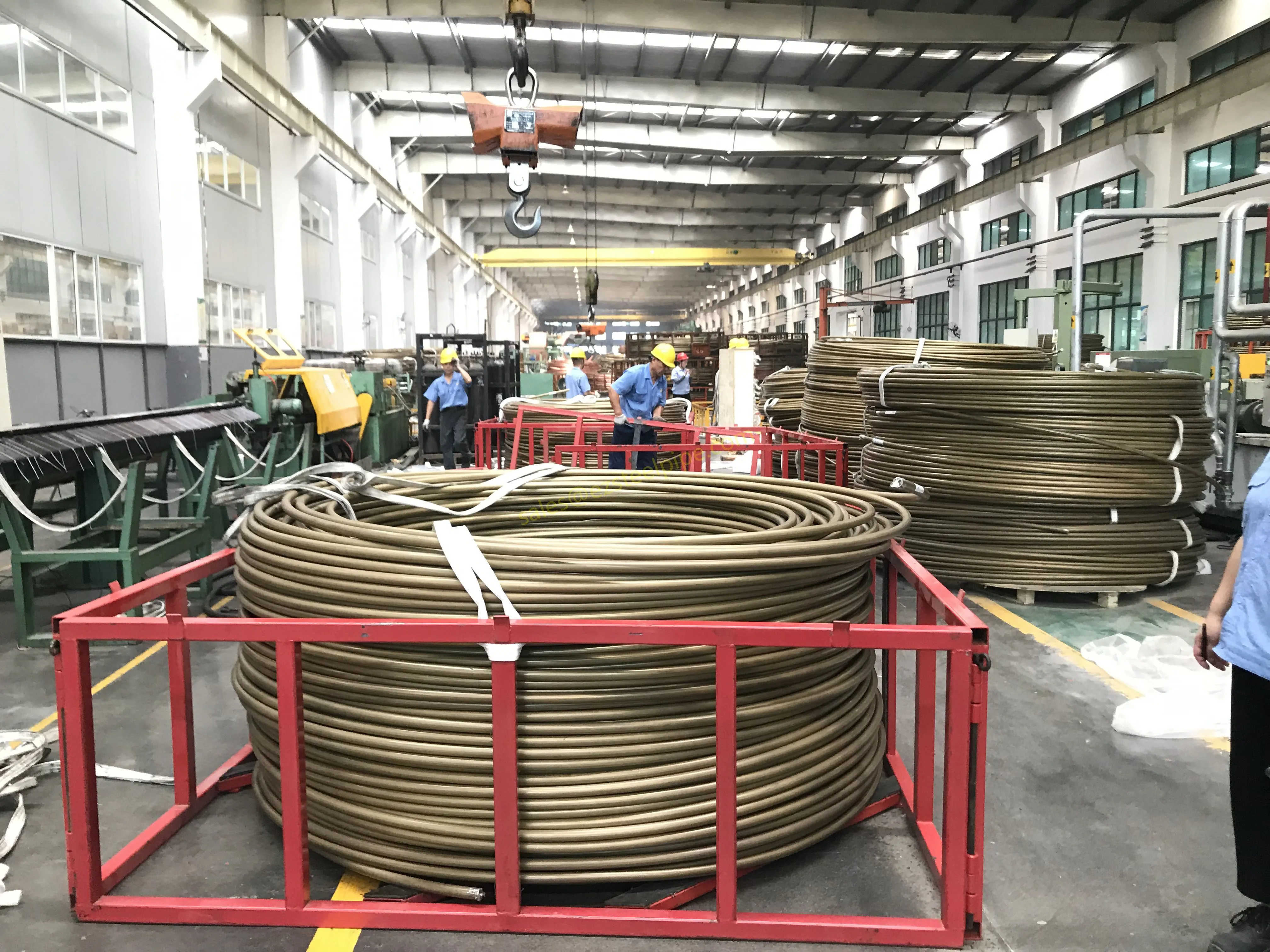
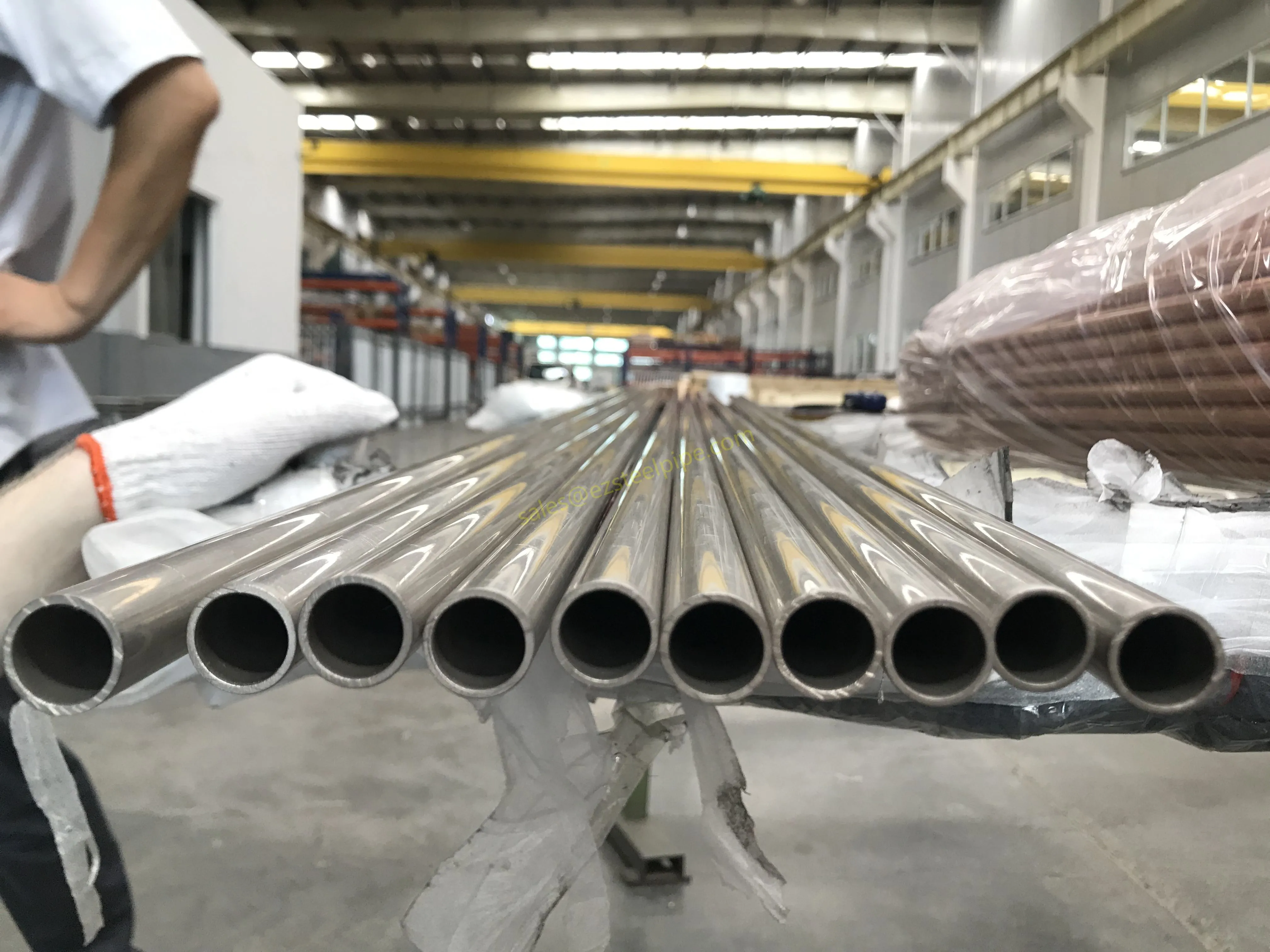
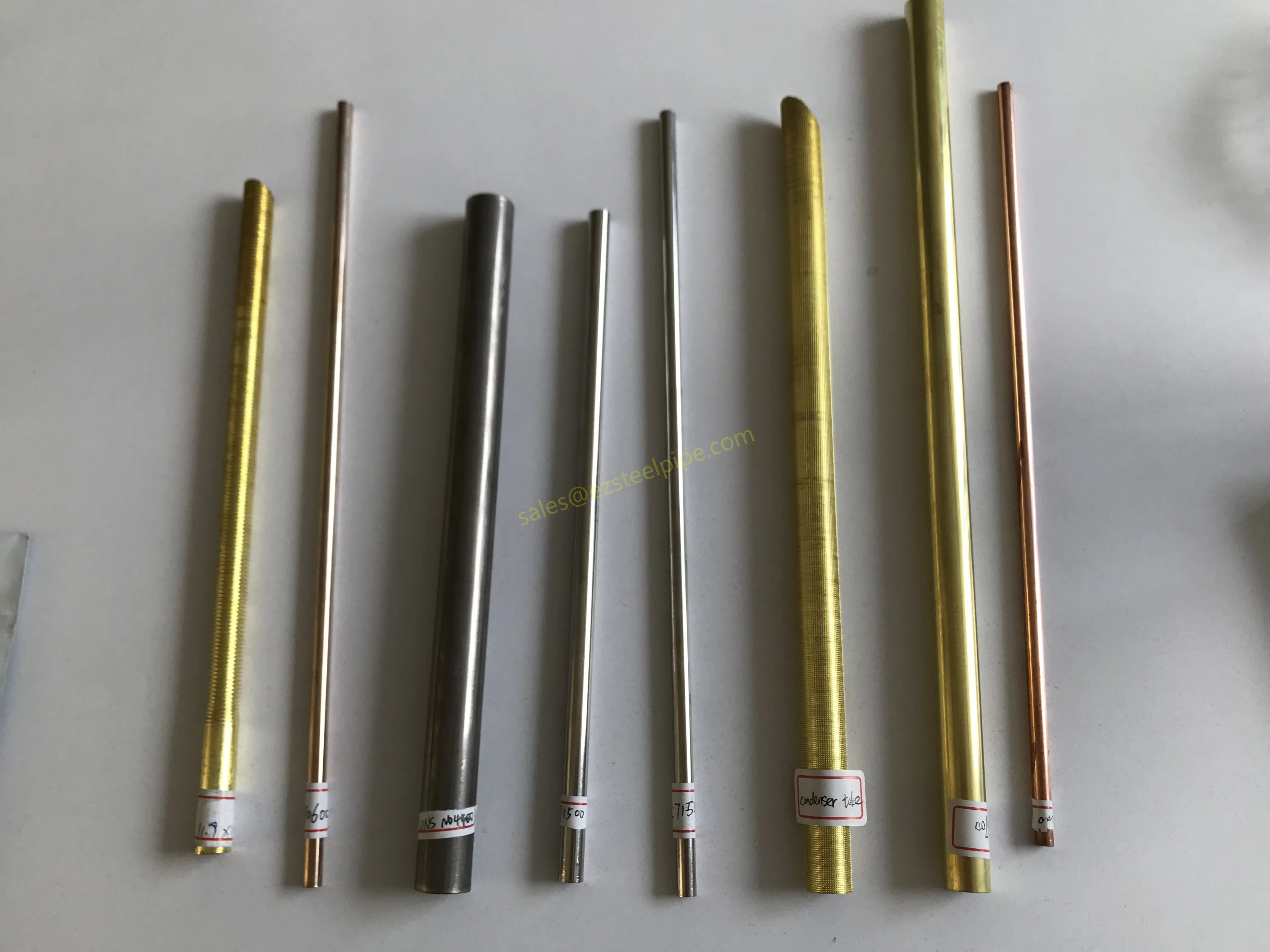
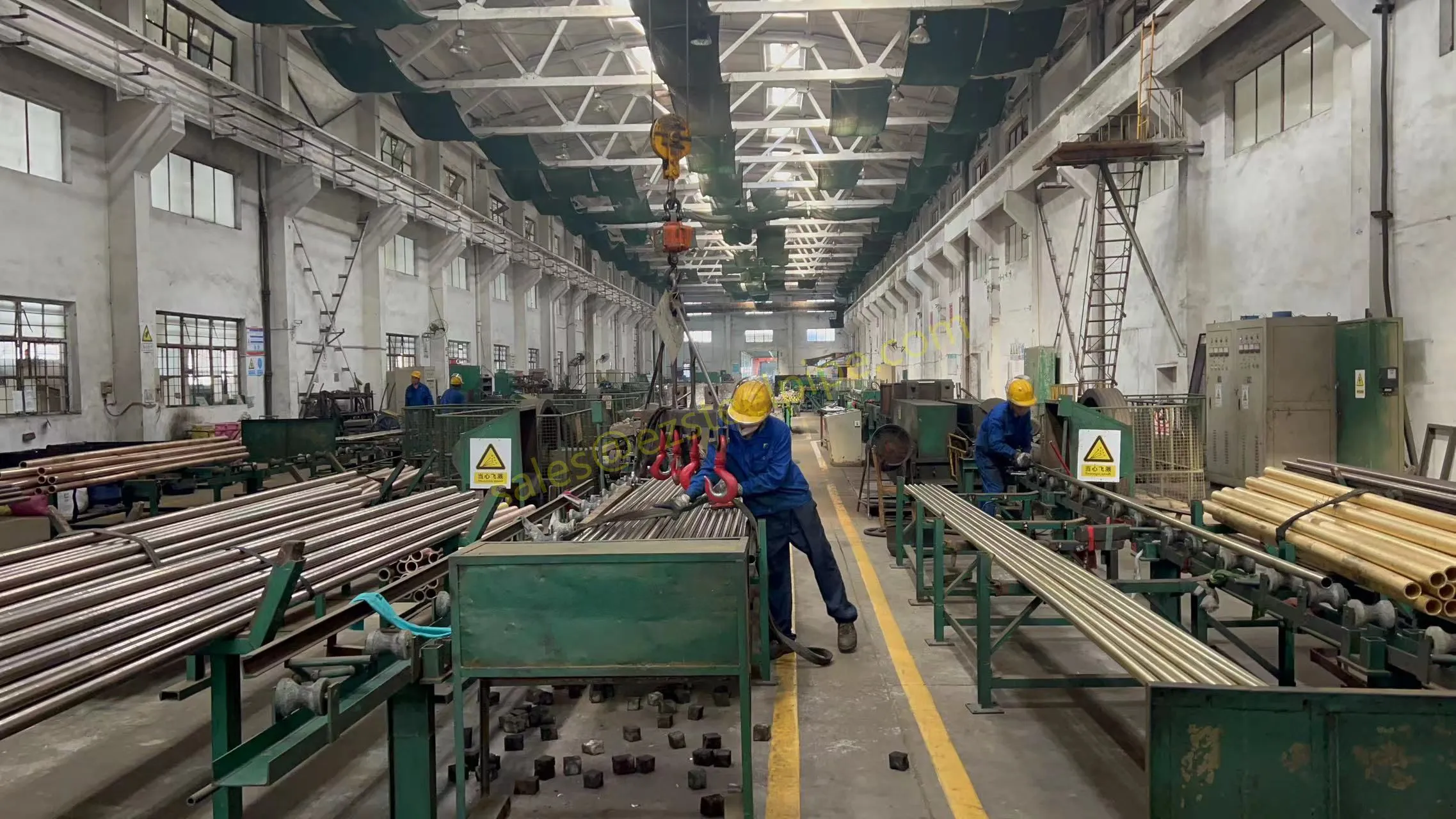
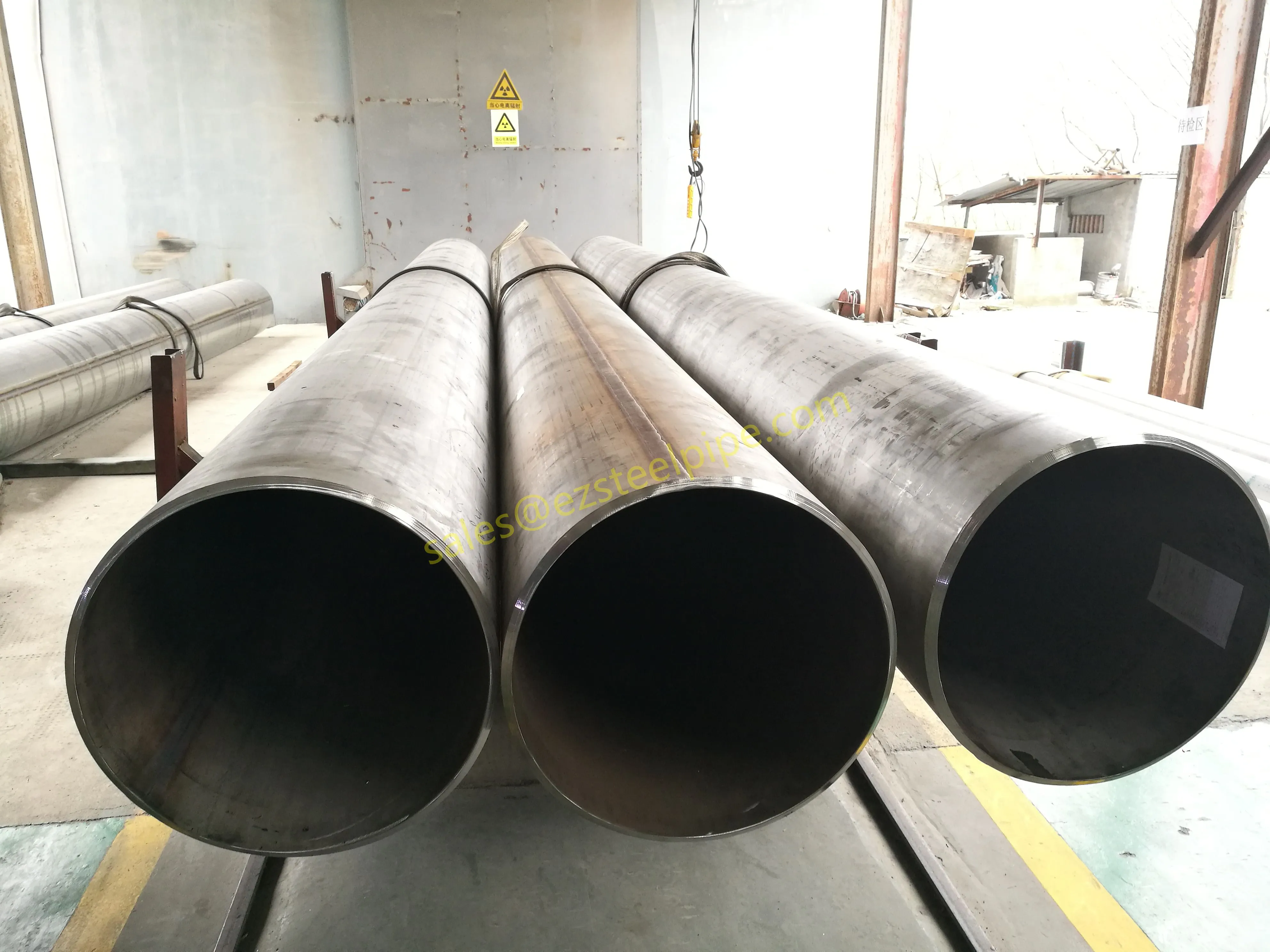
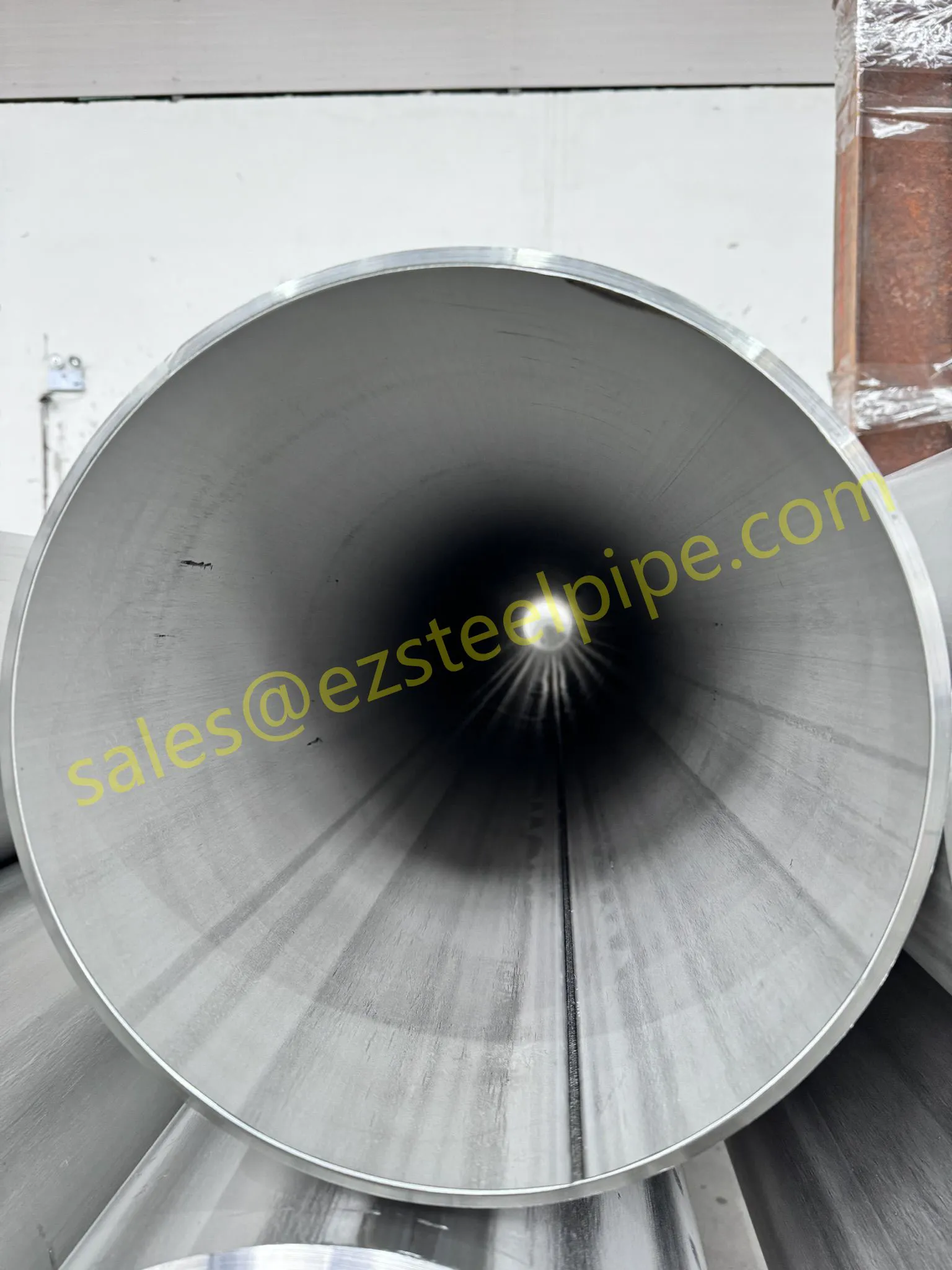
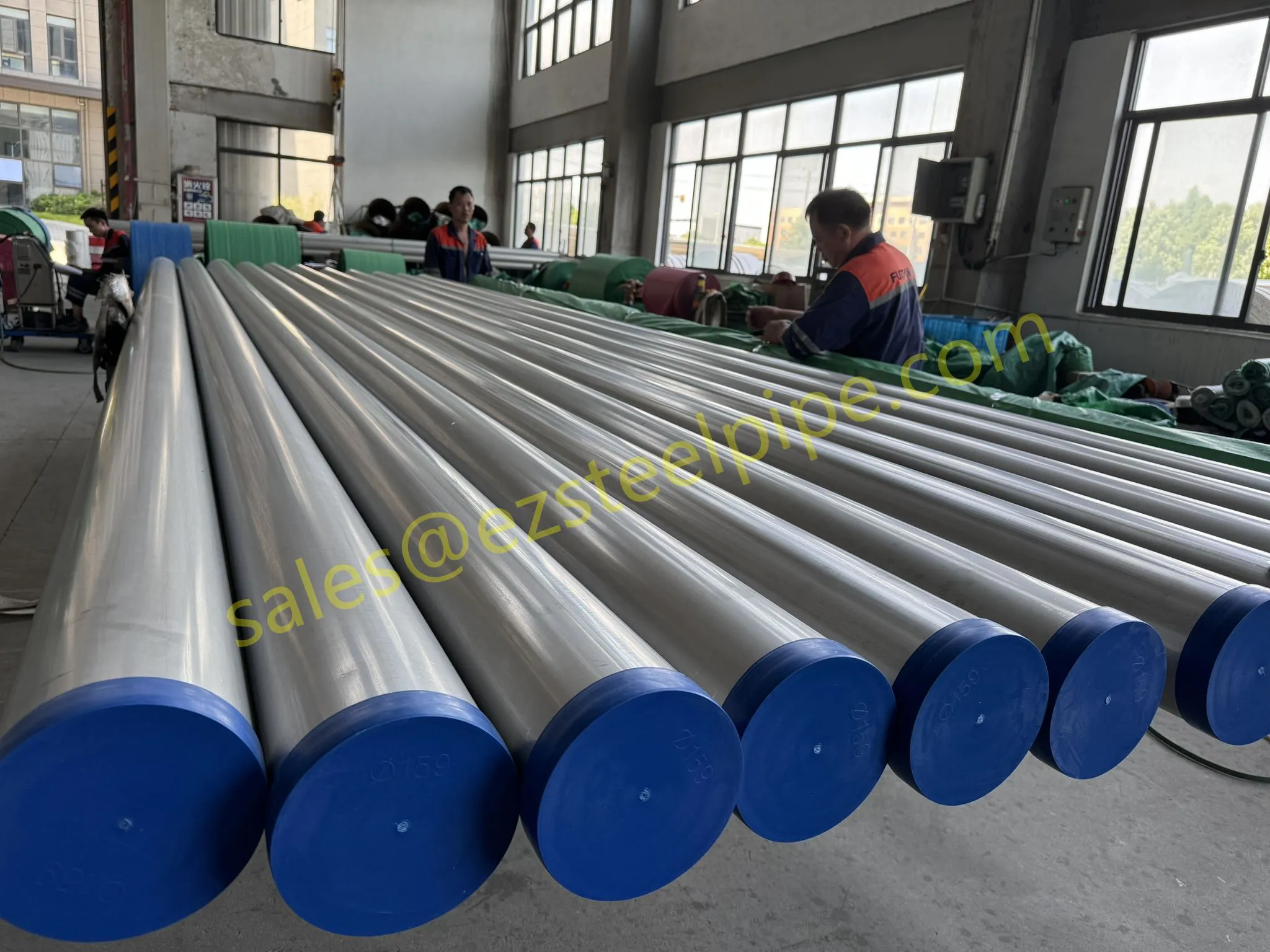
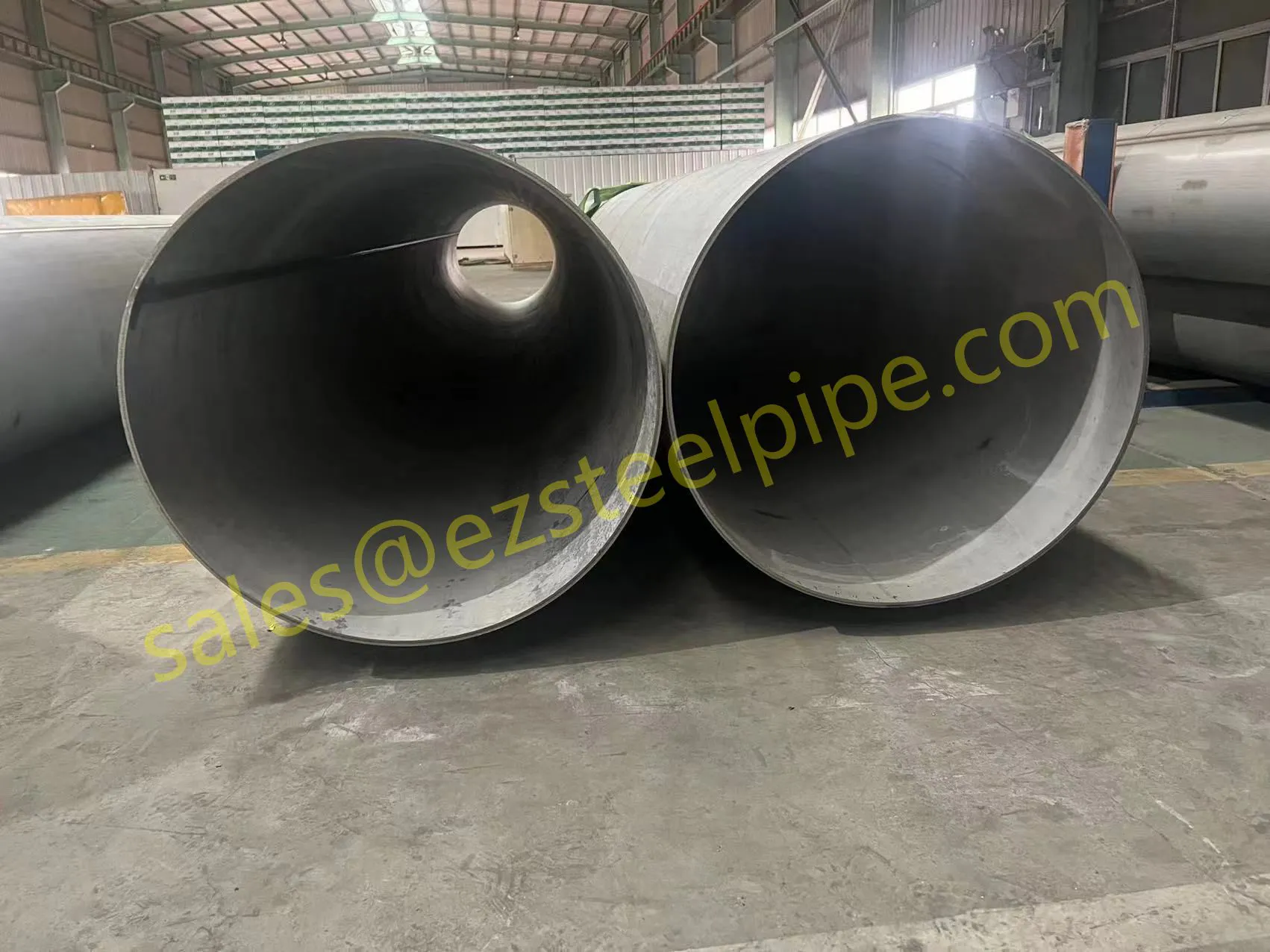
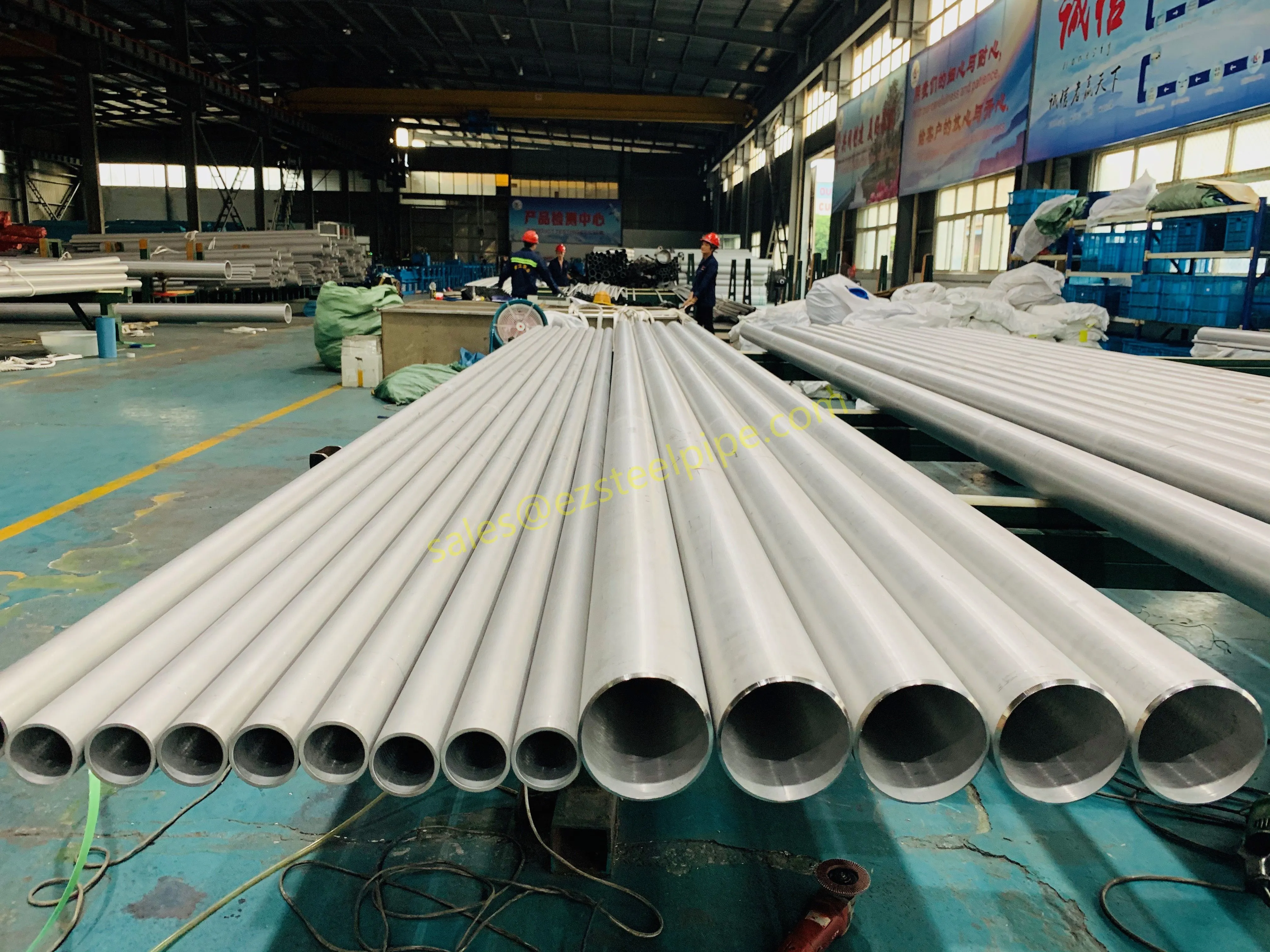
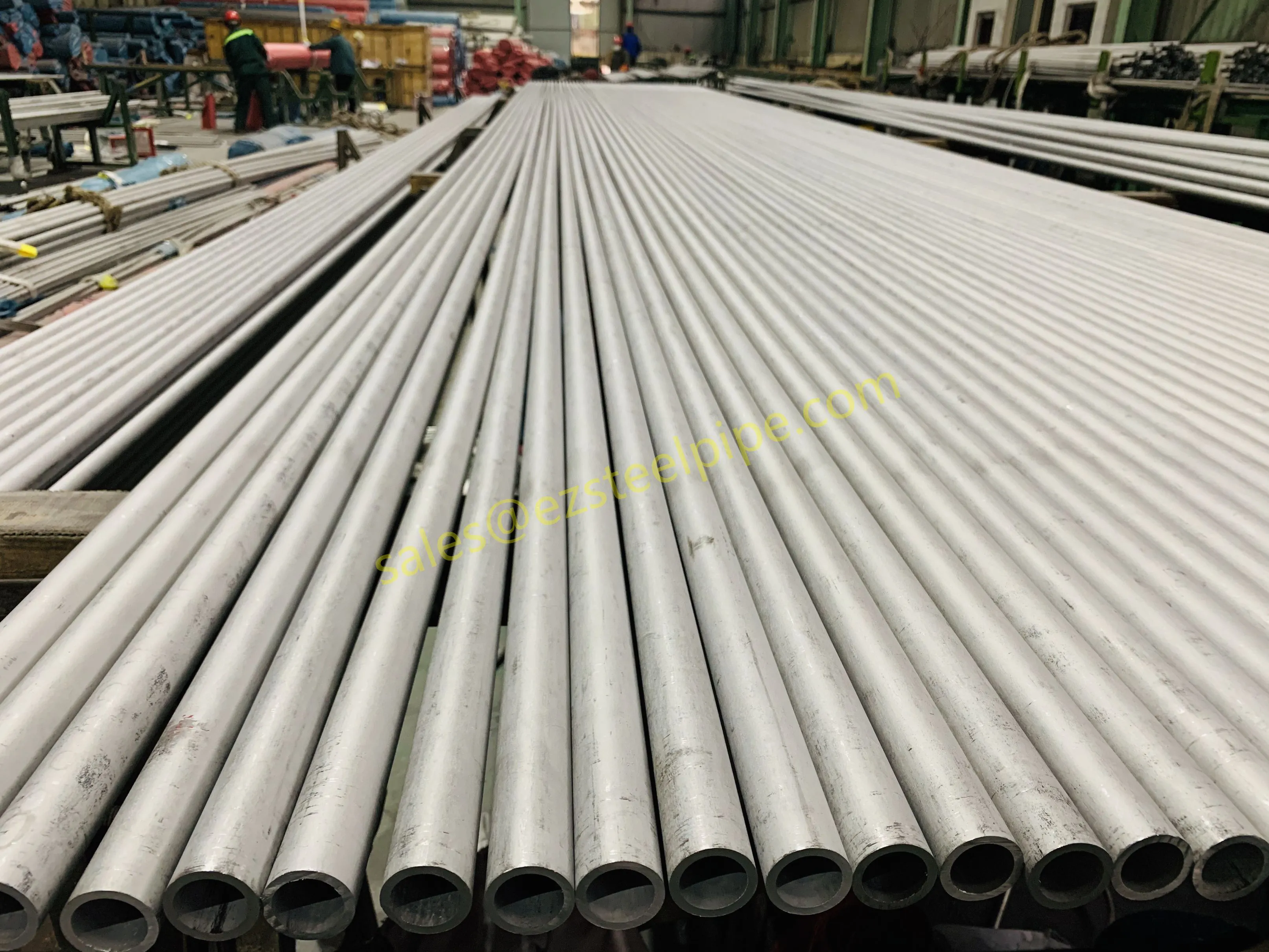
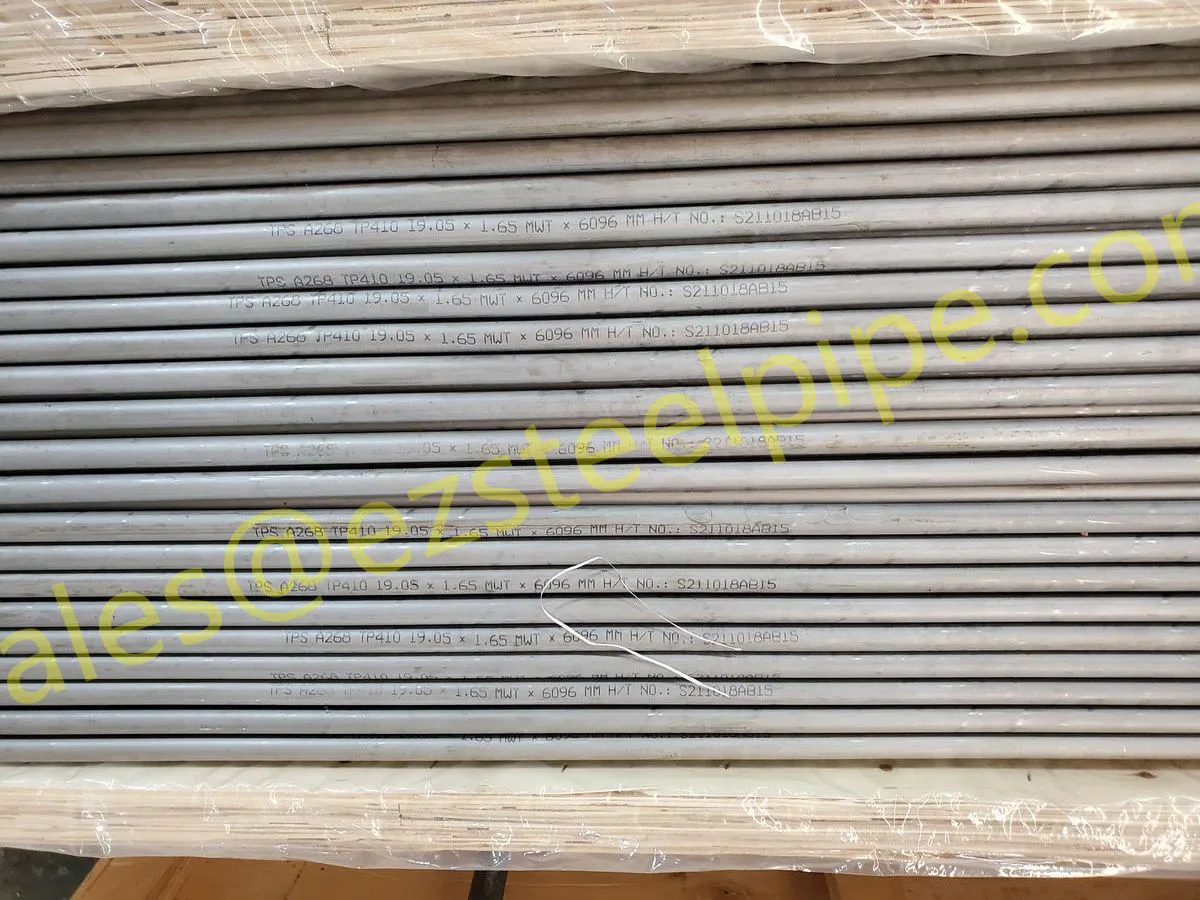
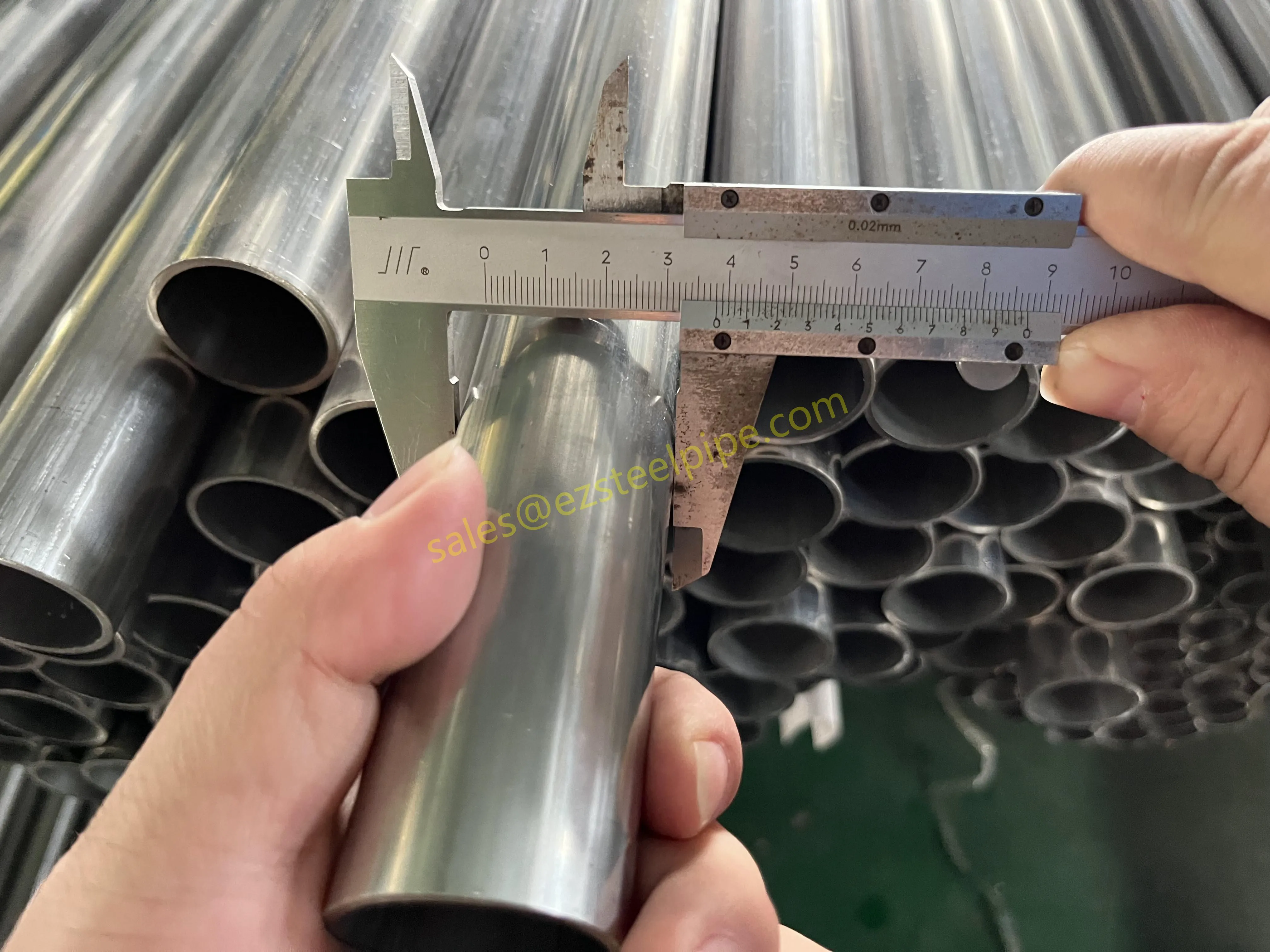
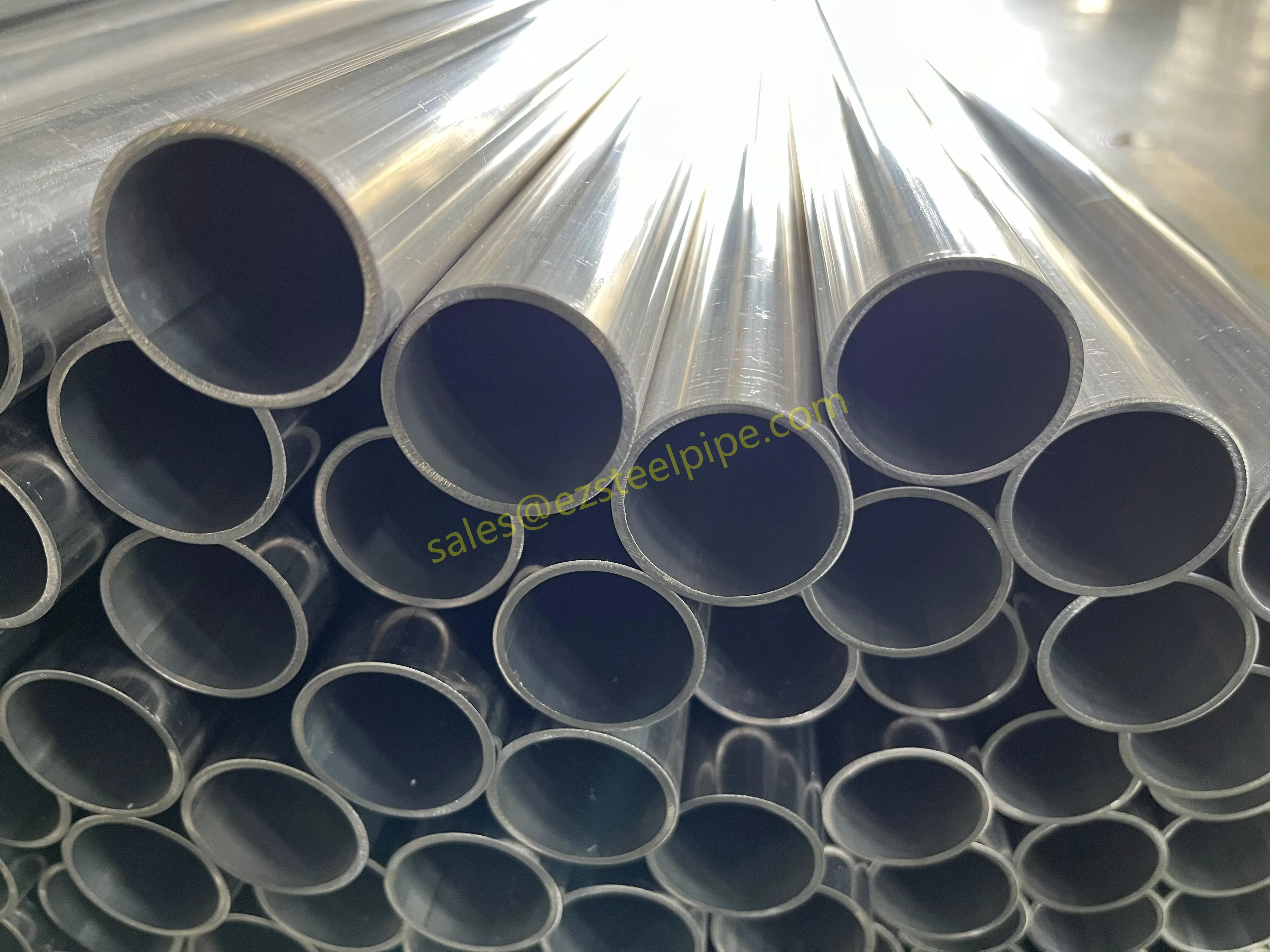
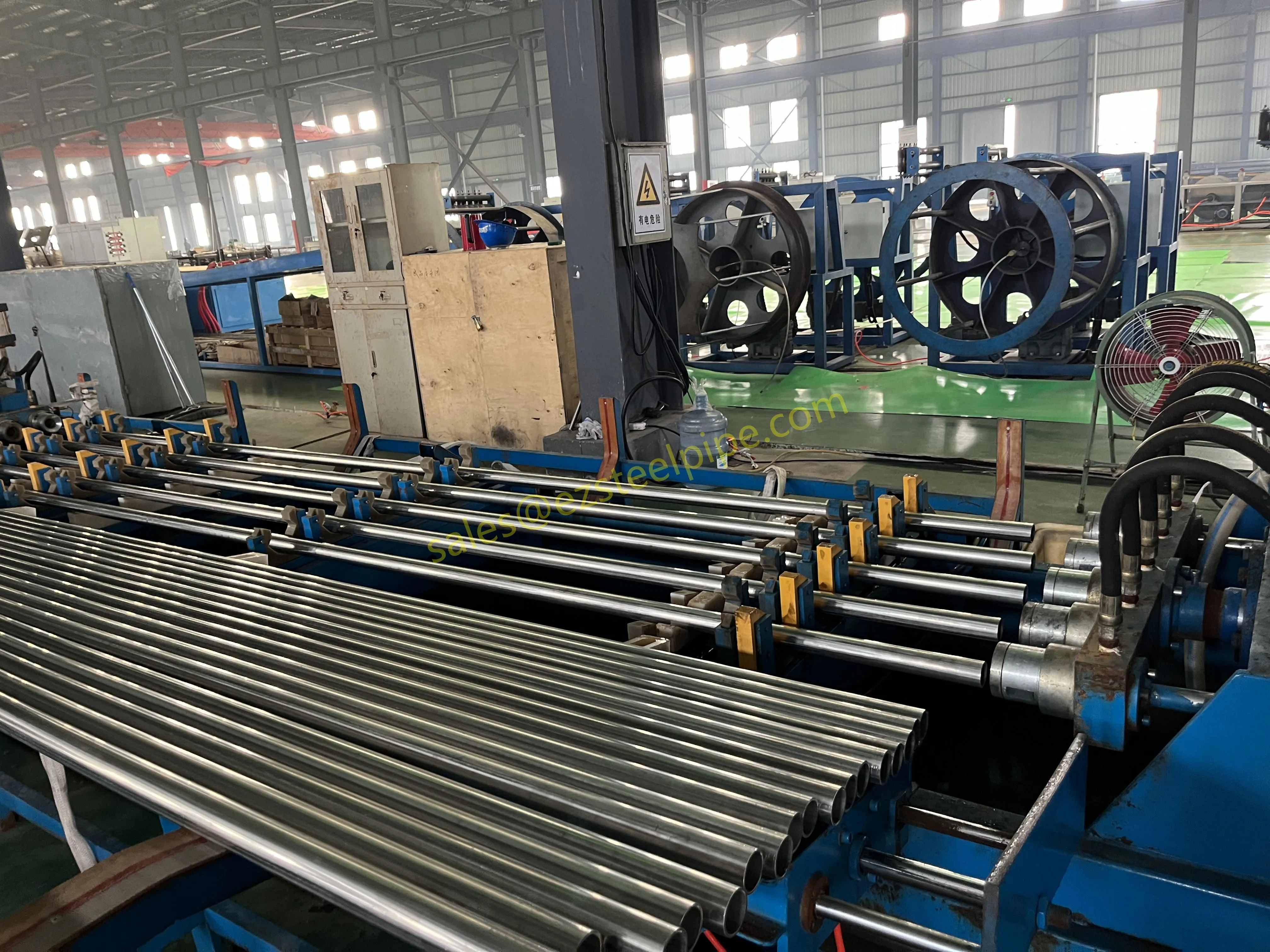
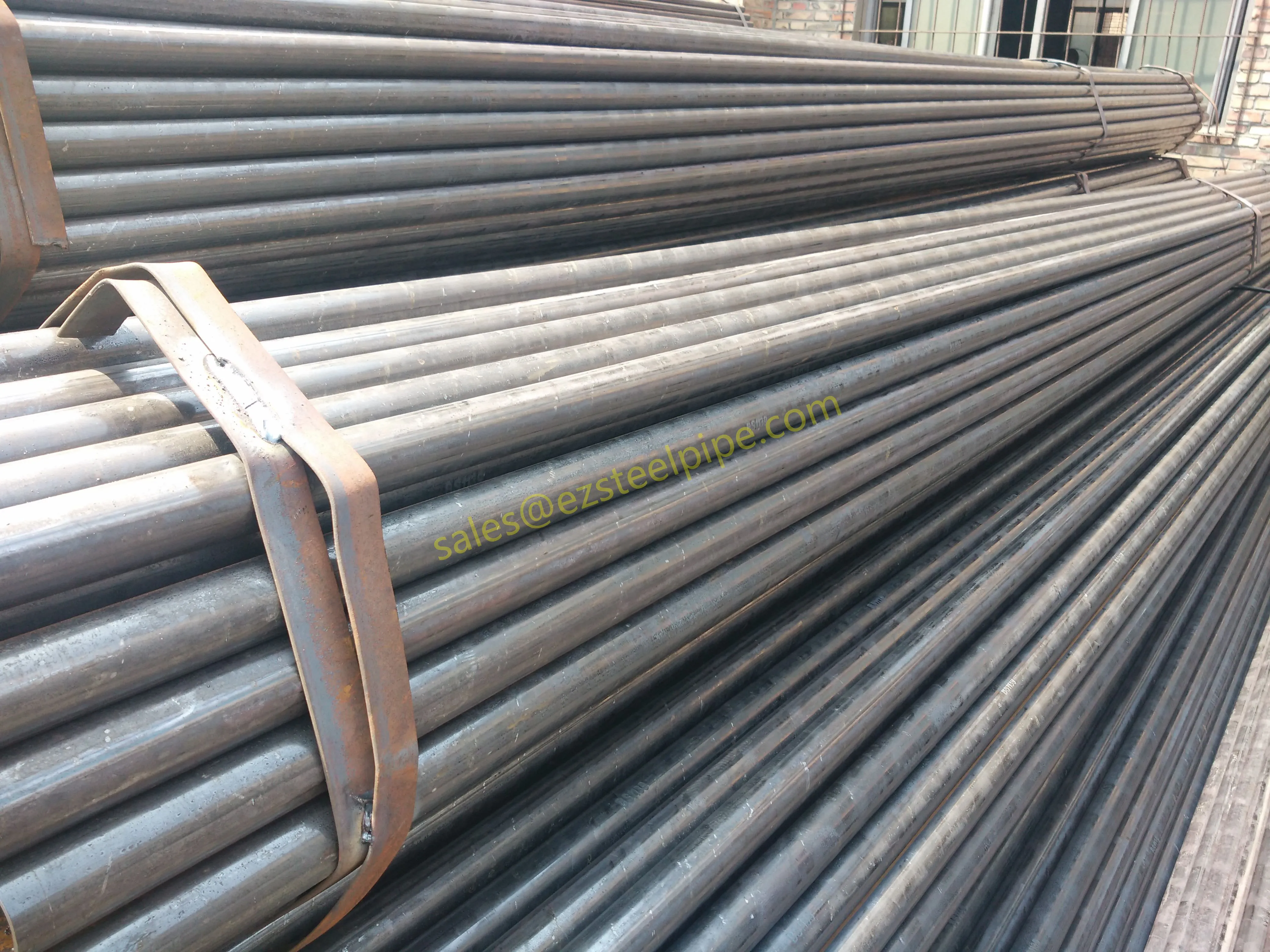
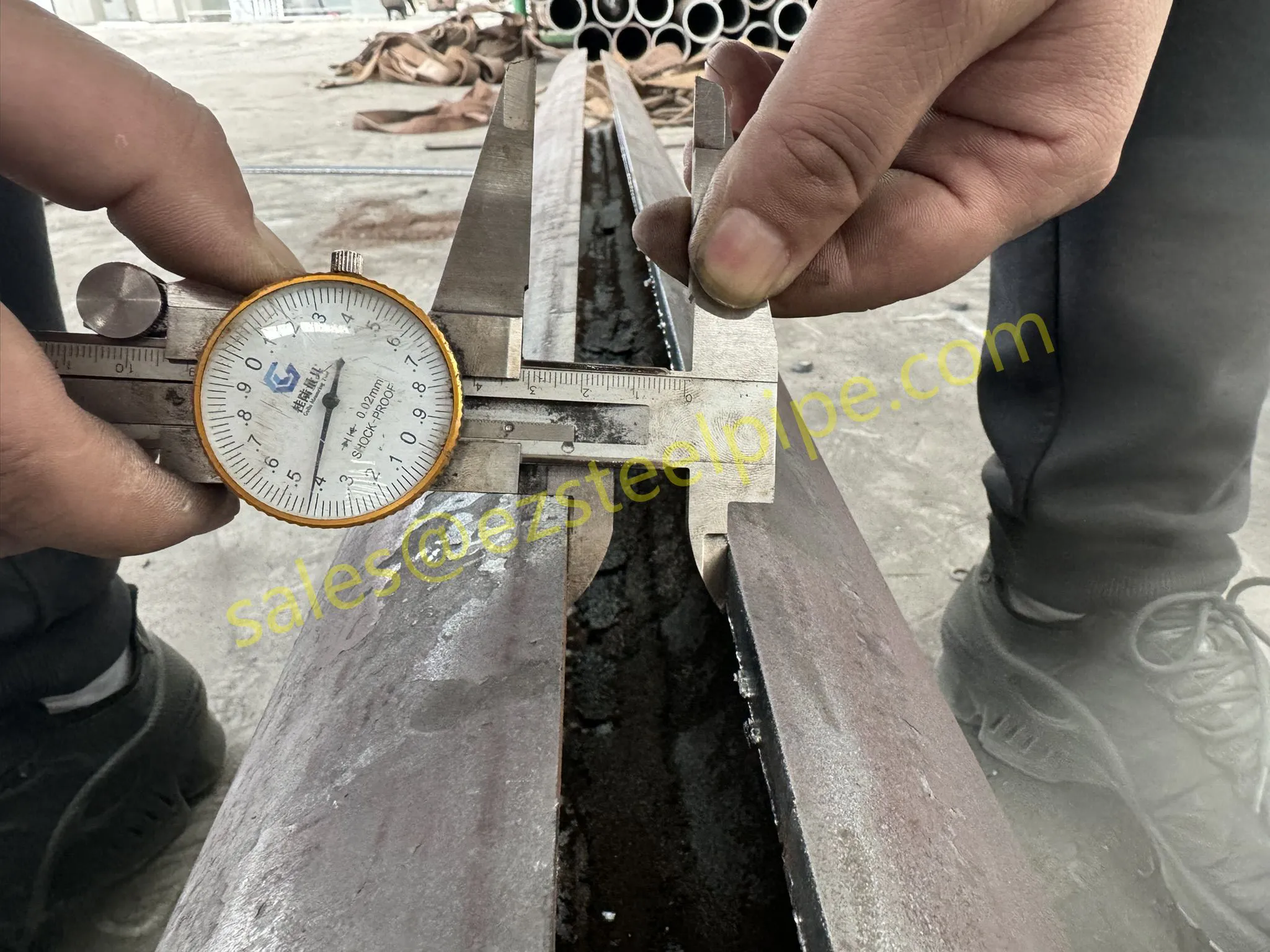
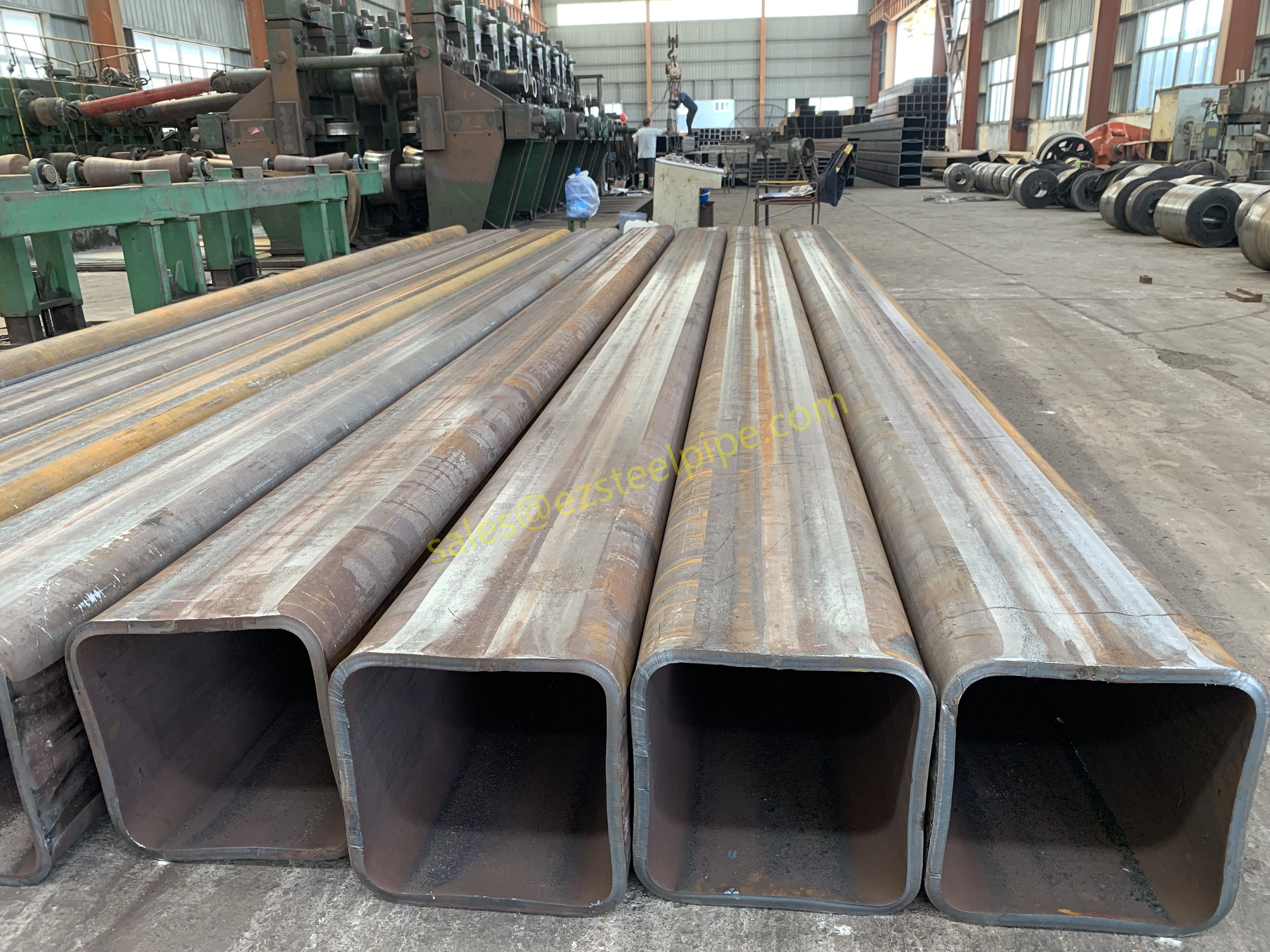
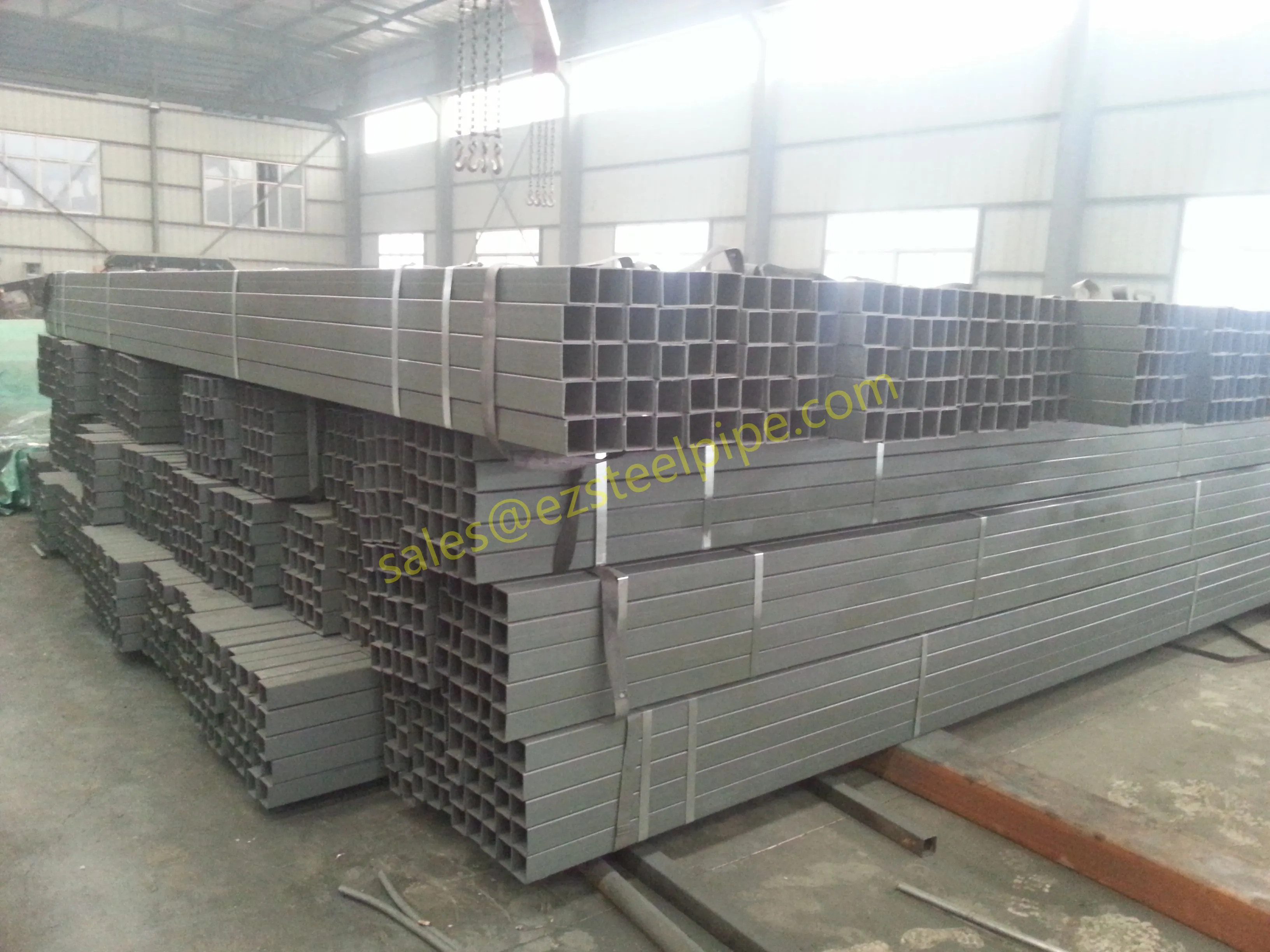
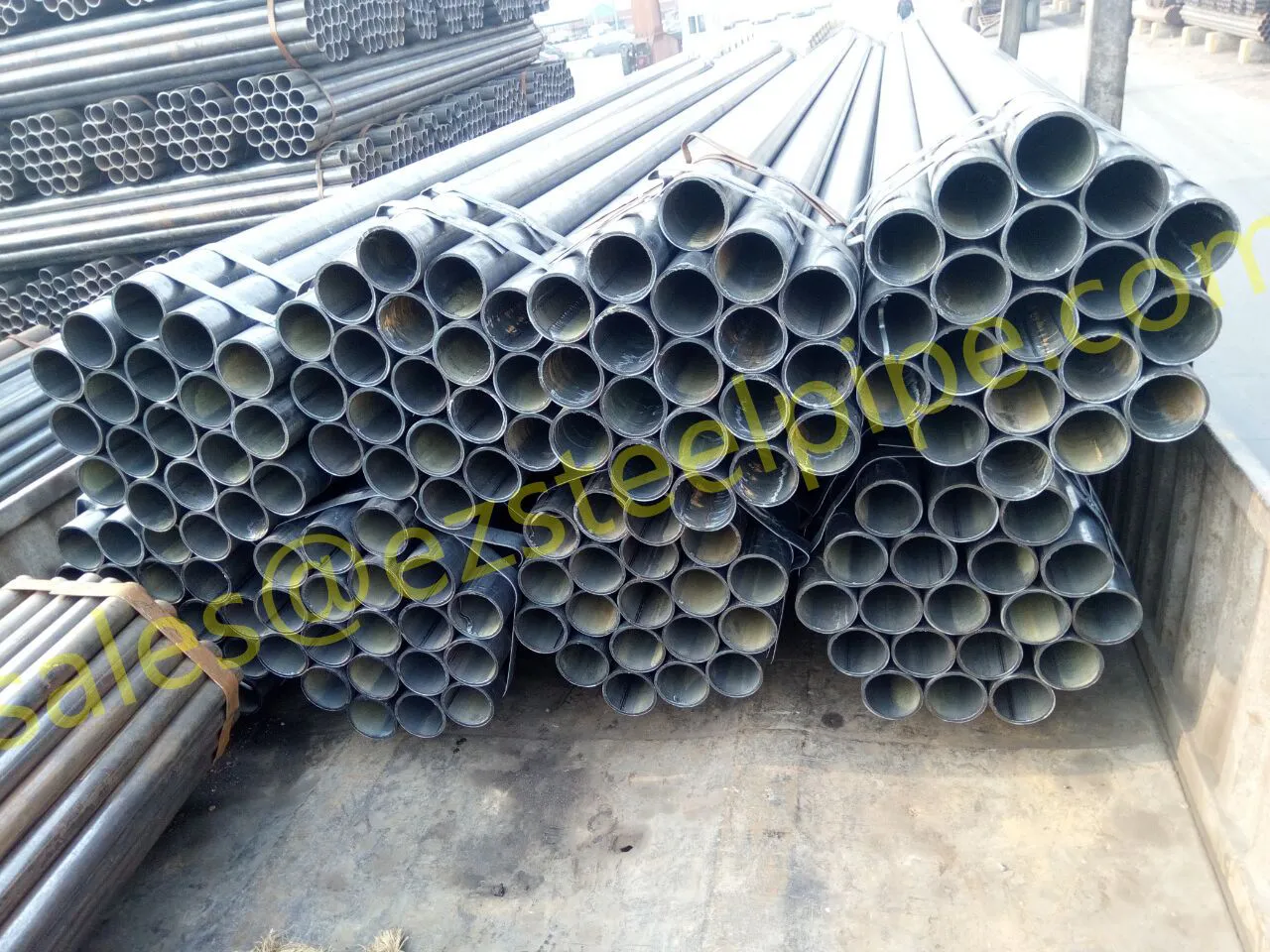
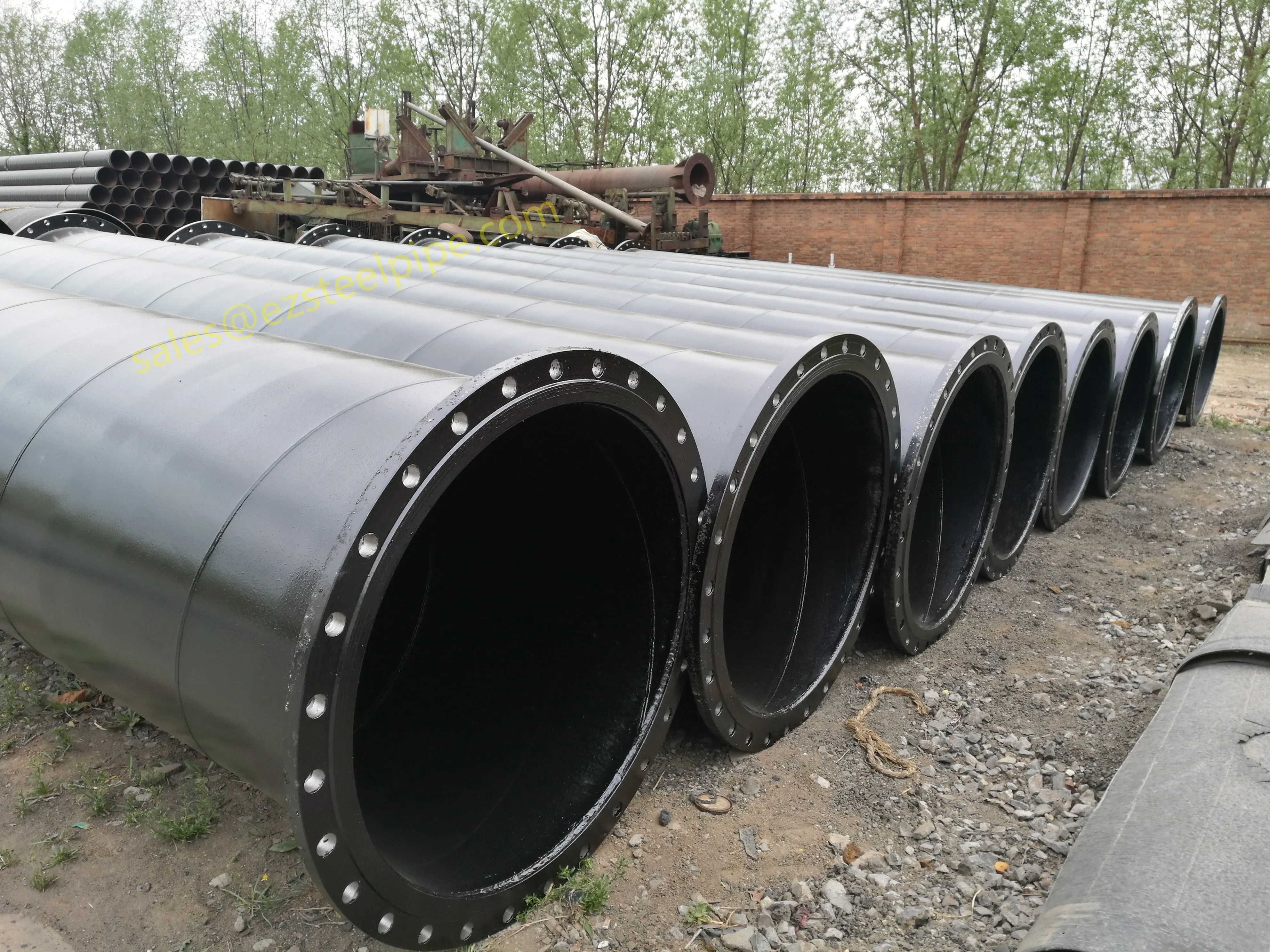
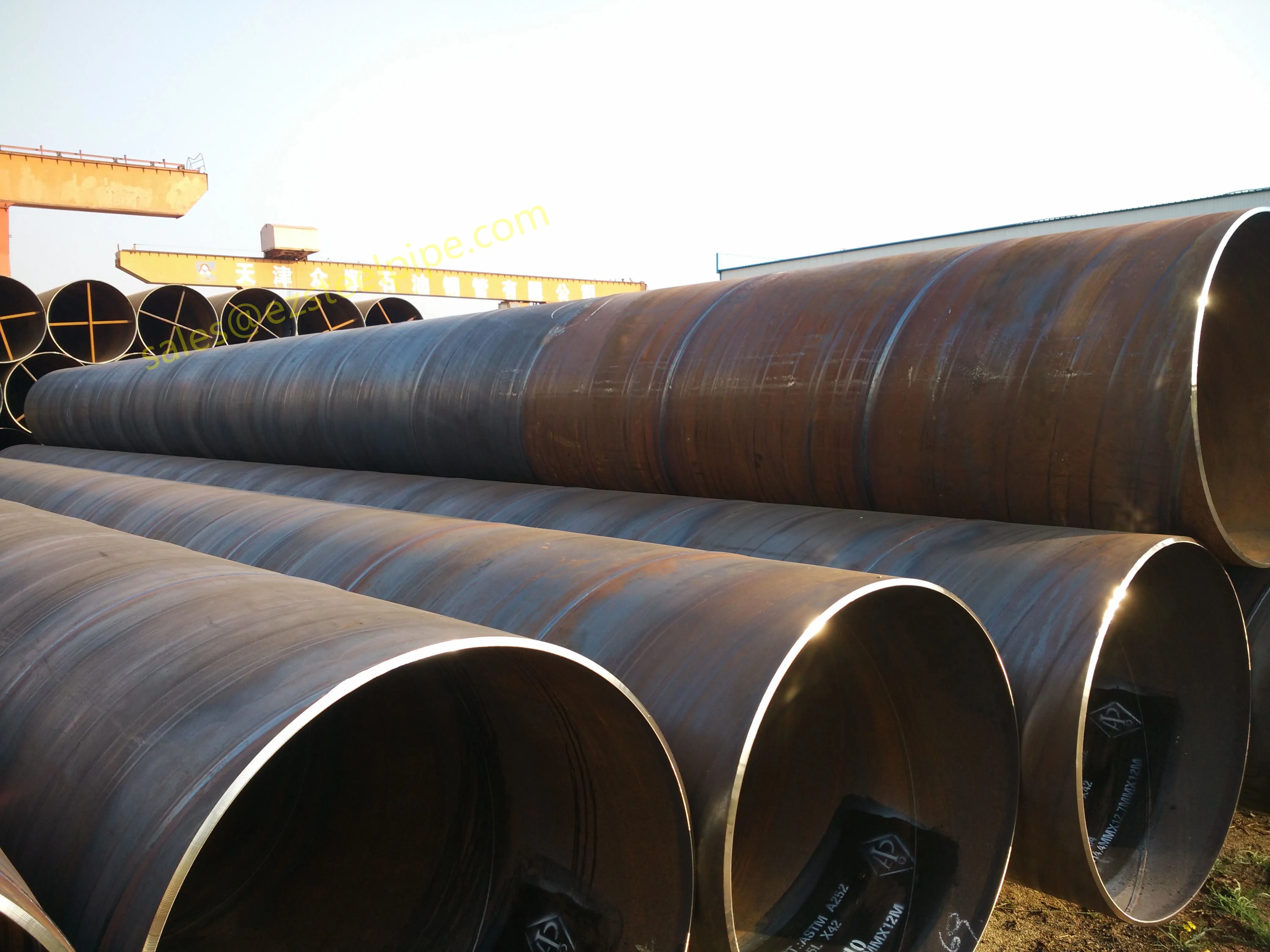
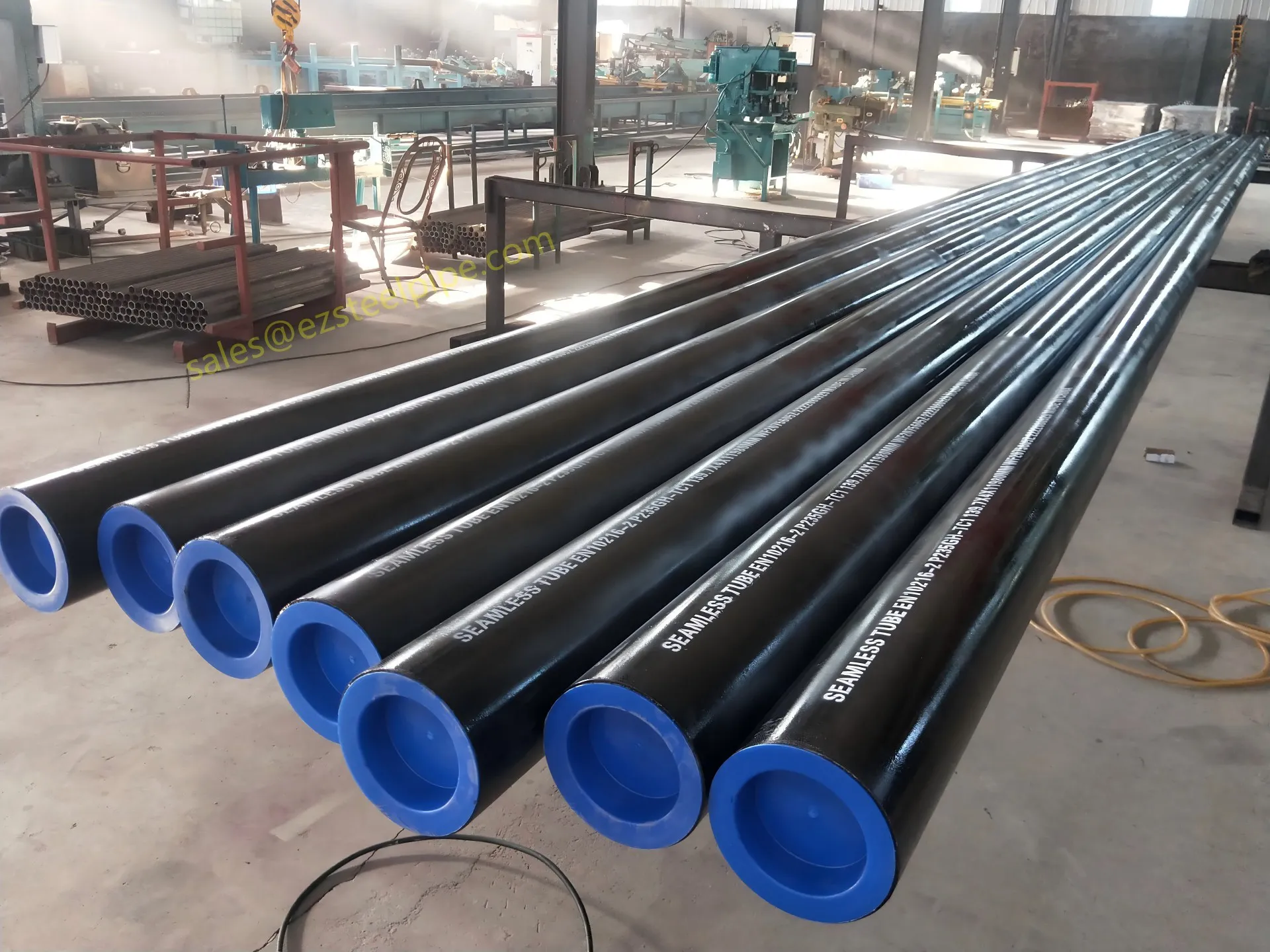
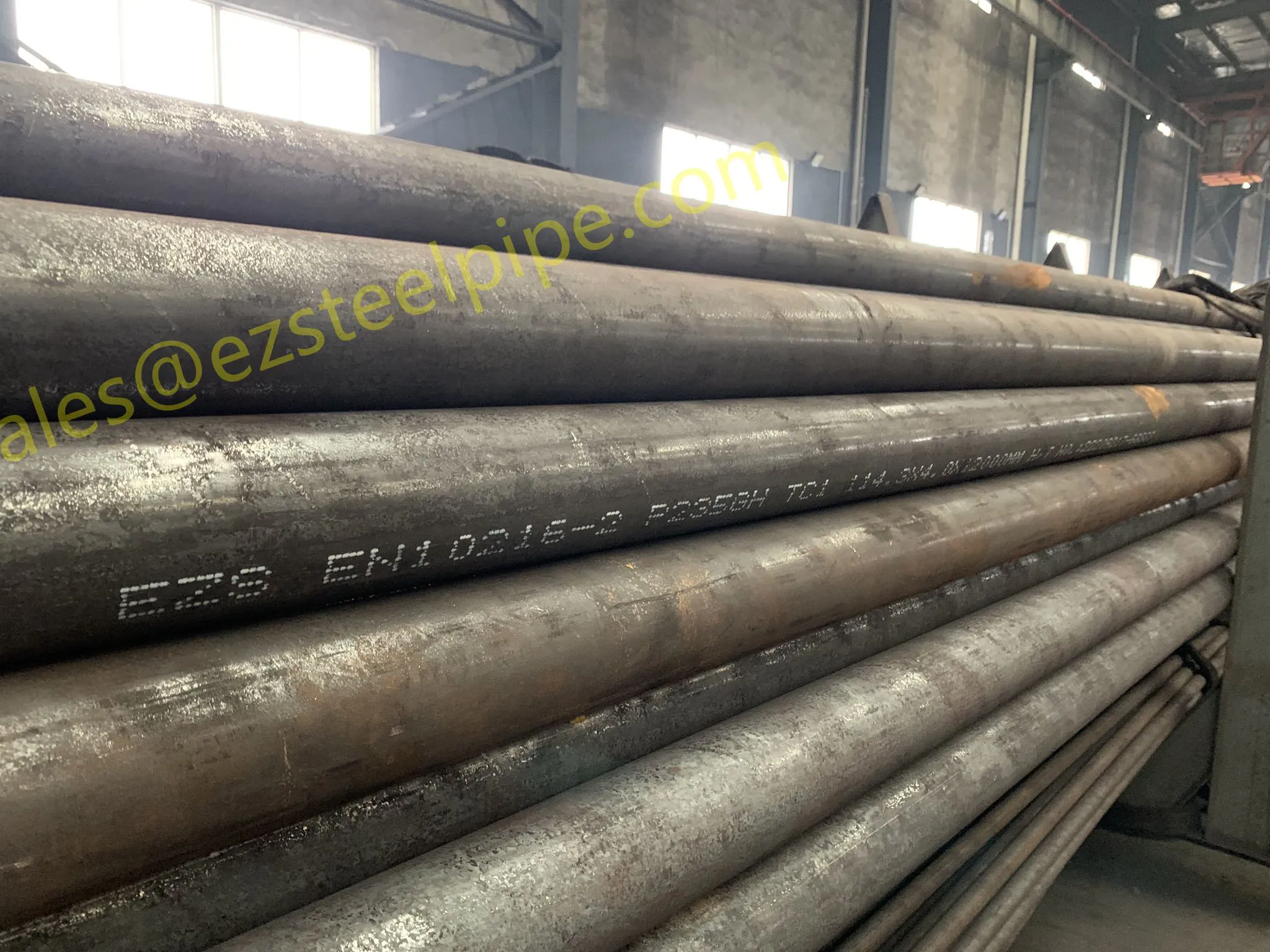
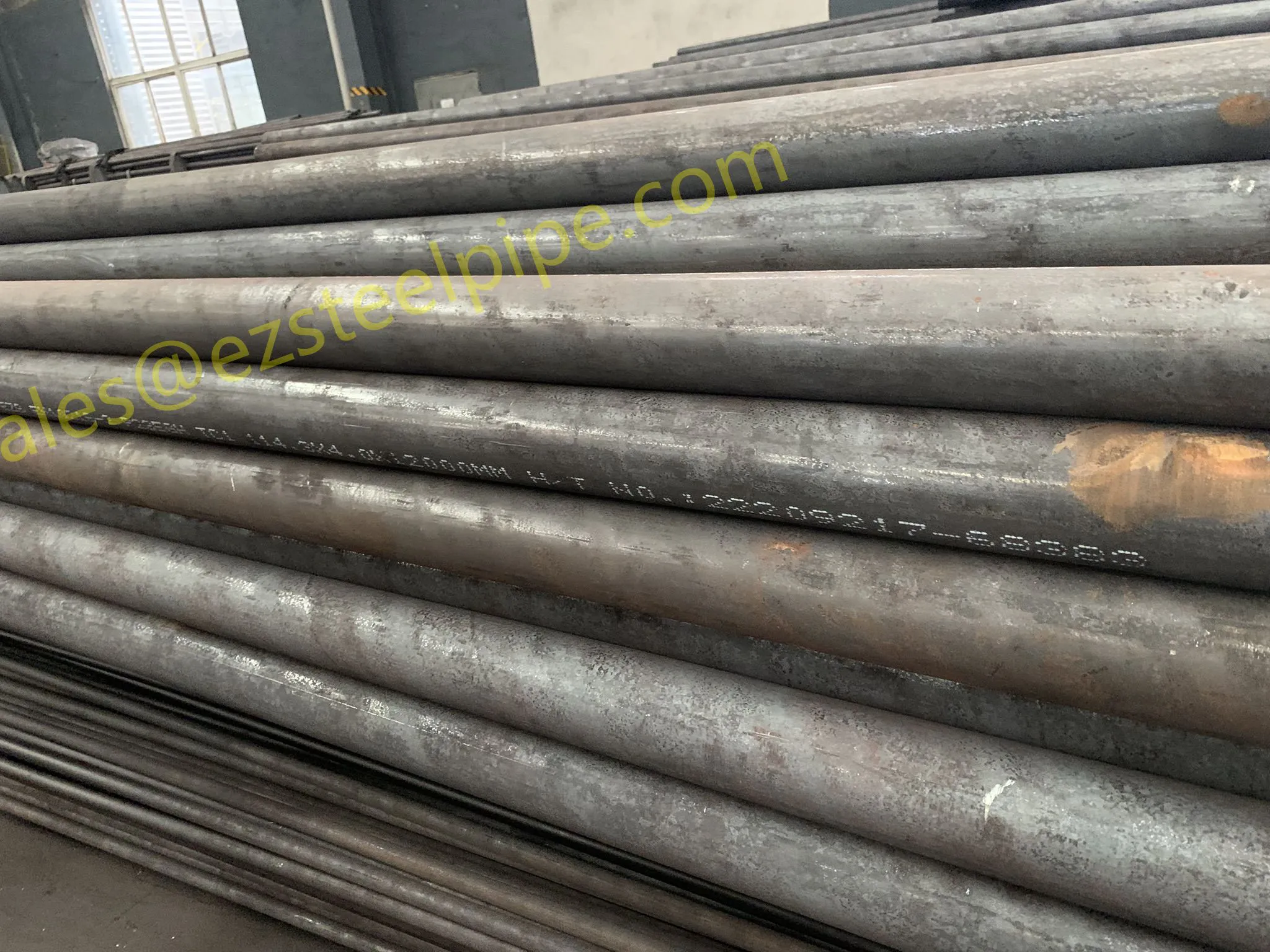
Before we pit these two materials against each other, let's get clear on what we're actually talking about. Butt-welded (BW) fittings are the workhorses of industrial piping systems. Unlike threaded or socket-welded fittings, they're joined by welding the ends of the pipes directly to the fitting, creating a seamless, leak-resistant connection that can handle high pressure and temperature. They're the backbone of pipelines in everything from oil rigs to power plants.
Now, the stars of our show:
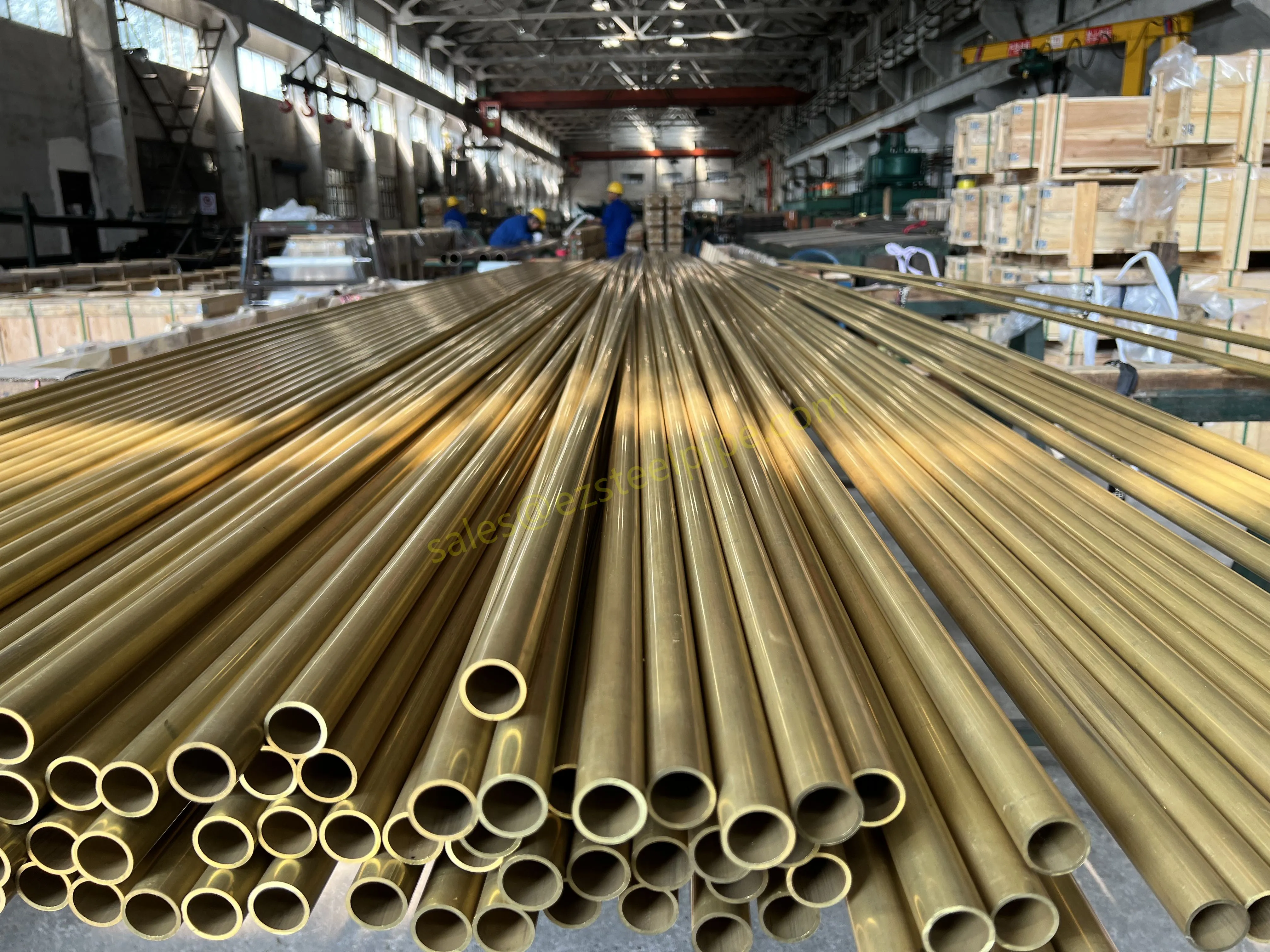
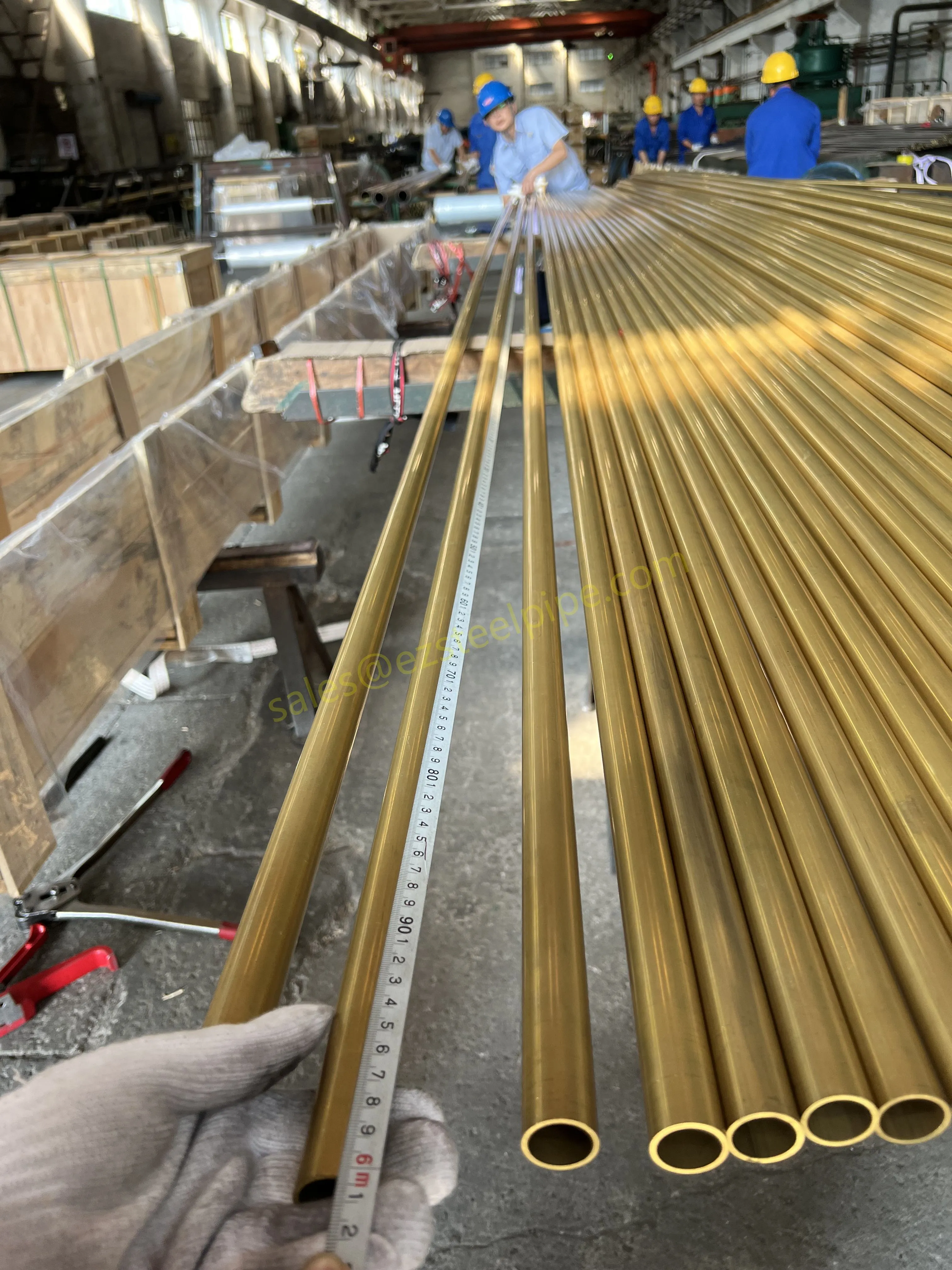
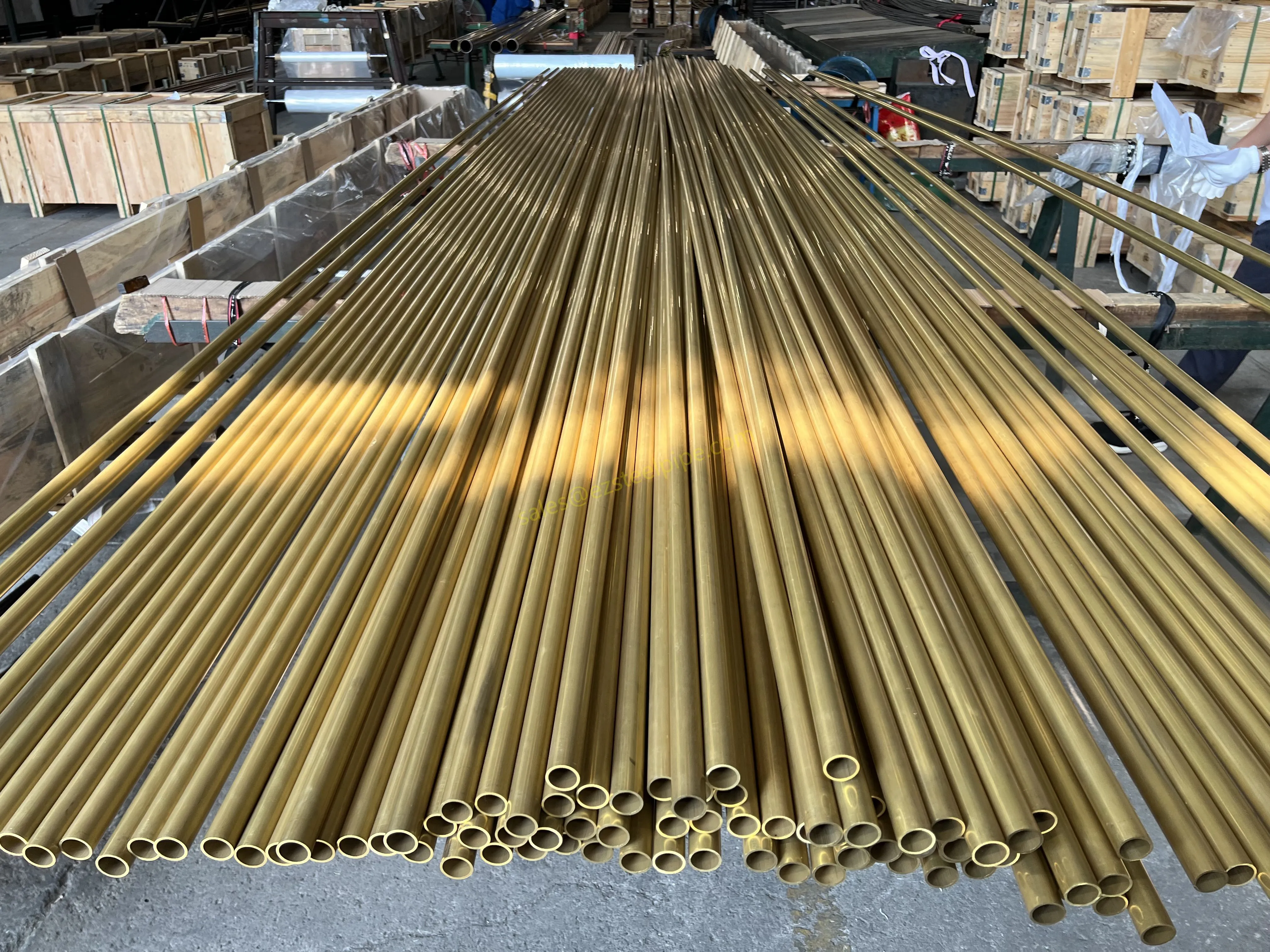
Copper-Nickel (Cu-Ni) Alloys : These are exactly what they sound like—alloys of copper and nickel, often blended with small amounts of iron, manganese, or other elements to boost specific properties. The most common grades are 90/10 (90% copper, 10% nickel) and 70/30 (70% copper, 30% nickel), each tailored for different environments. Think of them as the champions of the marine world.
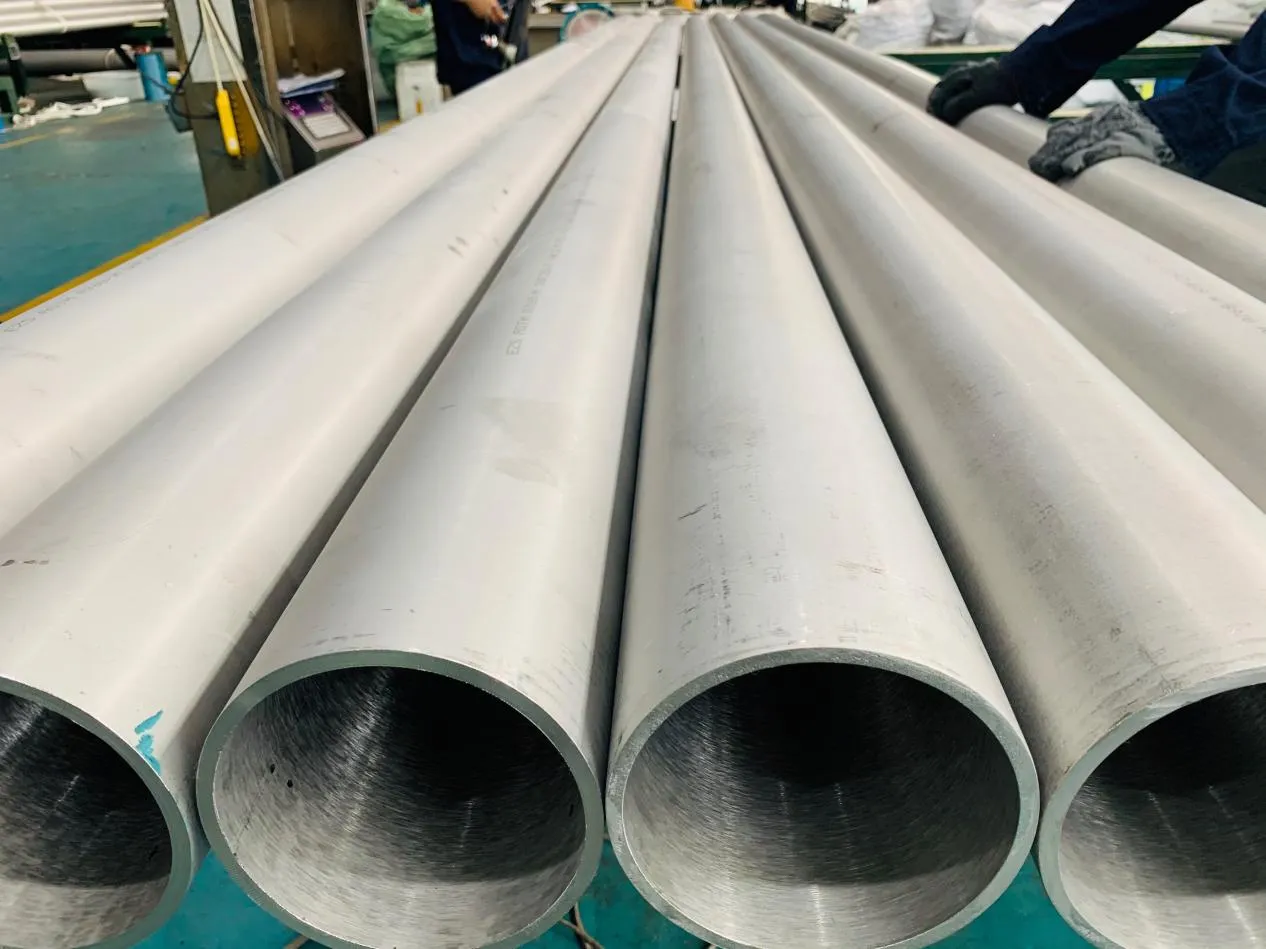
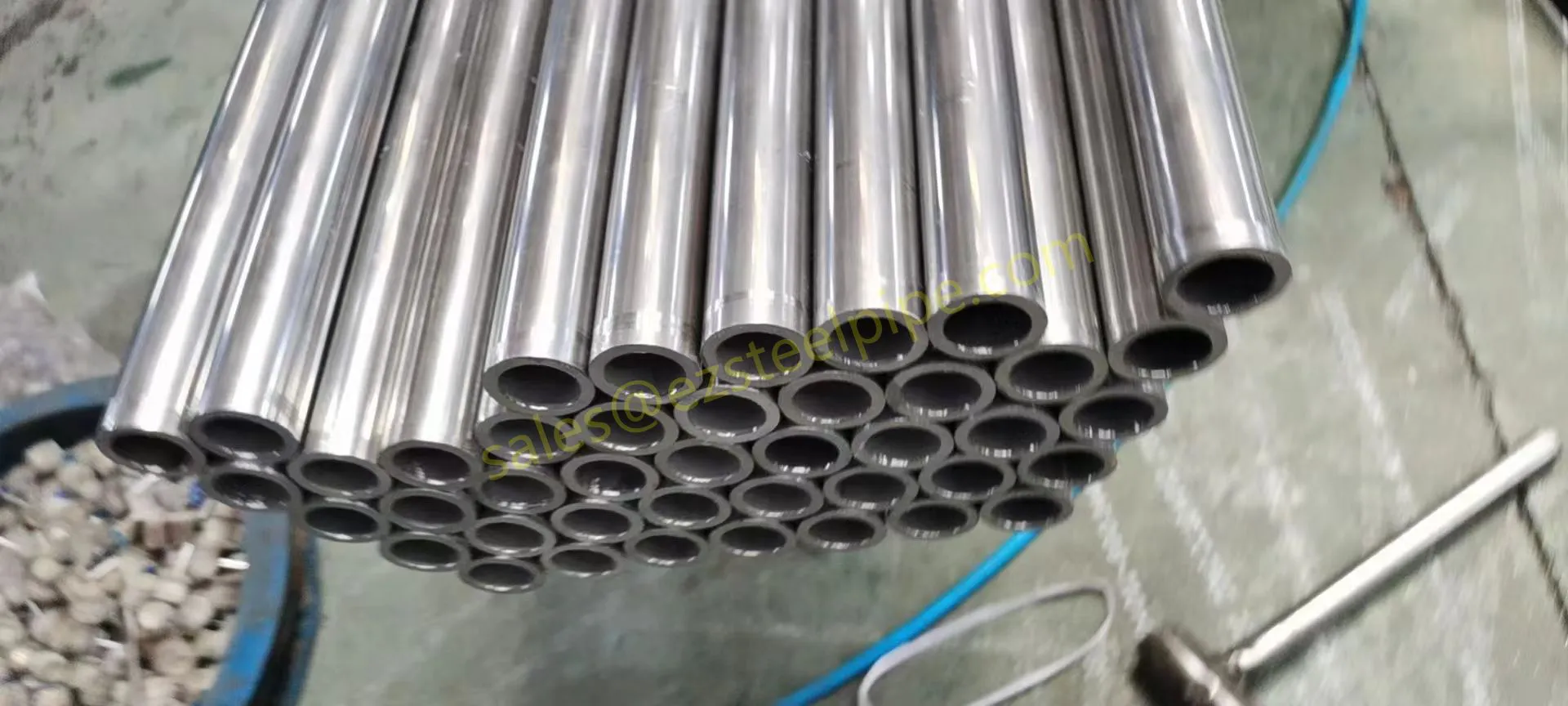
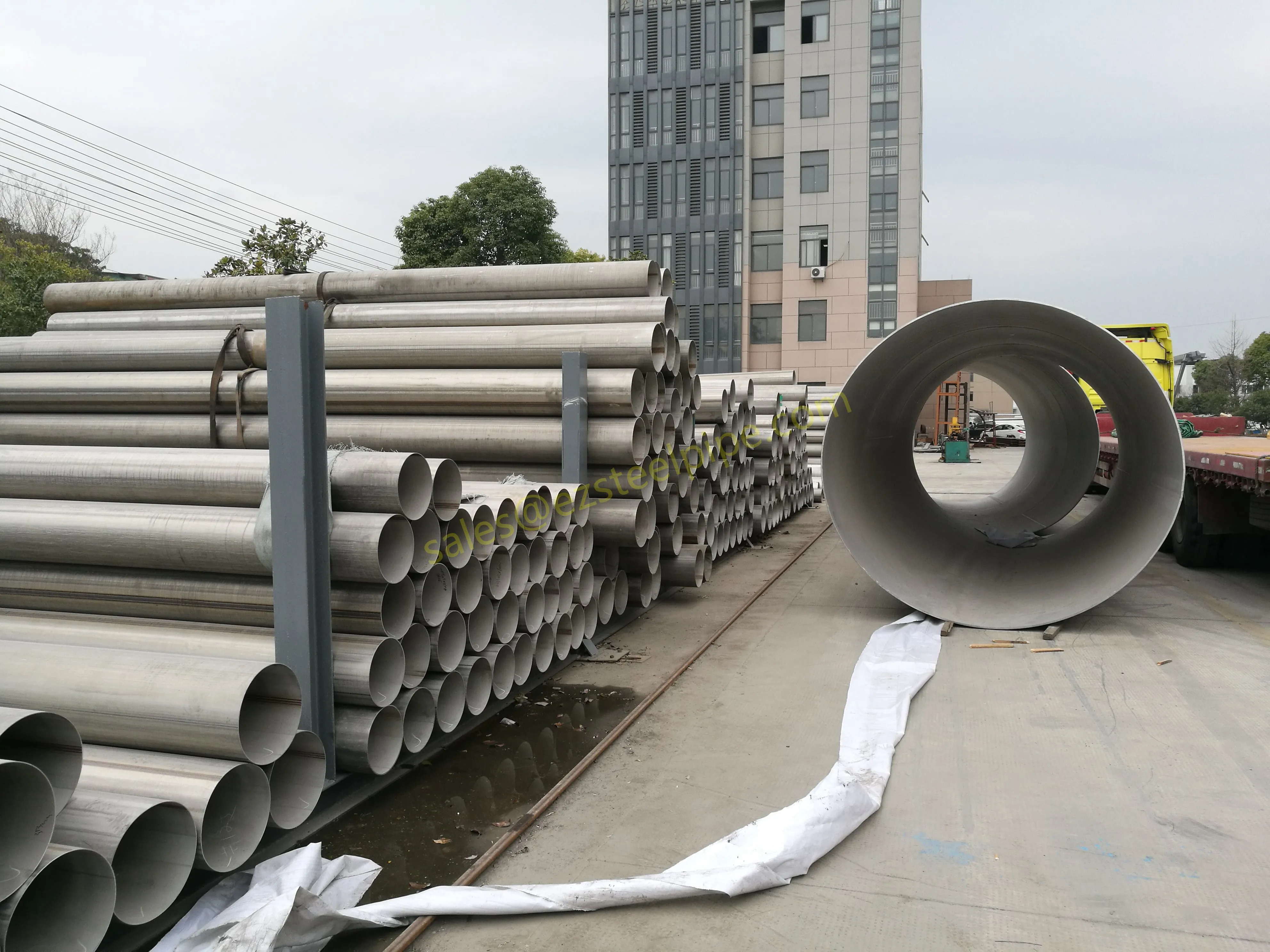
Stainless Steel : A family of iron-based alloys containing at least 10.5% chromium, which forms a protective oxide layer that resists rust. Grades like 304 (the "workhorse"), 316 (with molybdenum for extra corrosion resistance), and 316L (low carbon for better weldability) dominate industrial spaces. They're the Swiss Army knife of materials—versatile, strong, and reliable across countless applications.
Real-World Relevance : Imagine a petrochemical plant where a single fitting failure could lead to toxic leaks, or a ship at sea where corrosion eats through a pipe, endangering the crew. The choice between copper-nickel and stainless steel isn't just technical—it's about protecting people, assets, and operations.
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































