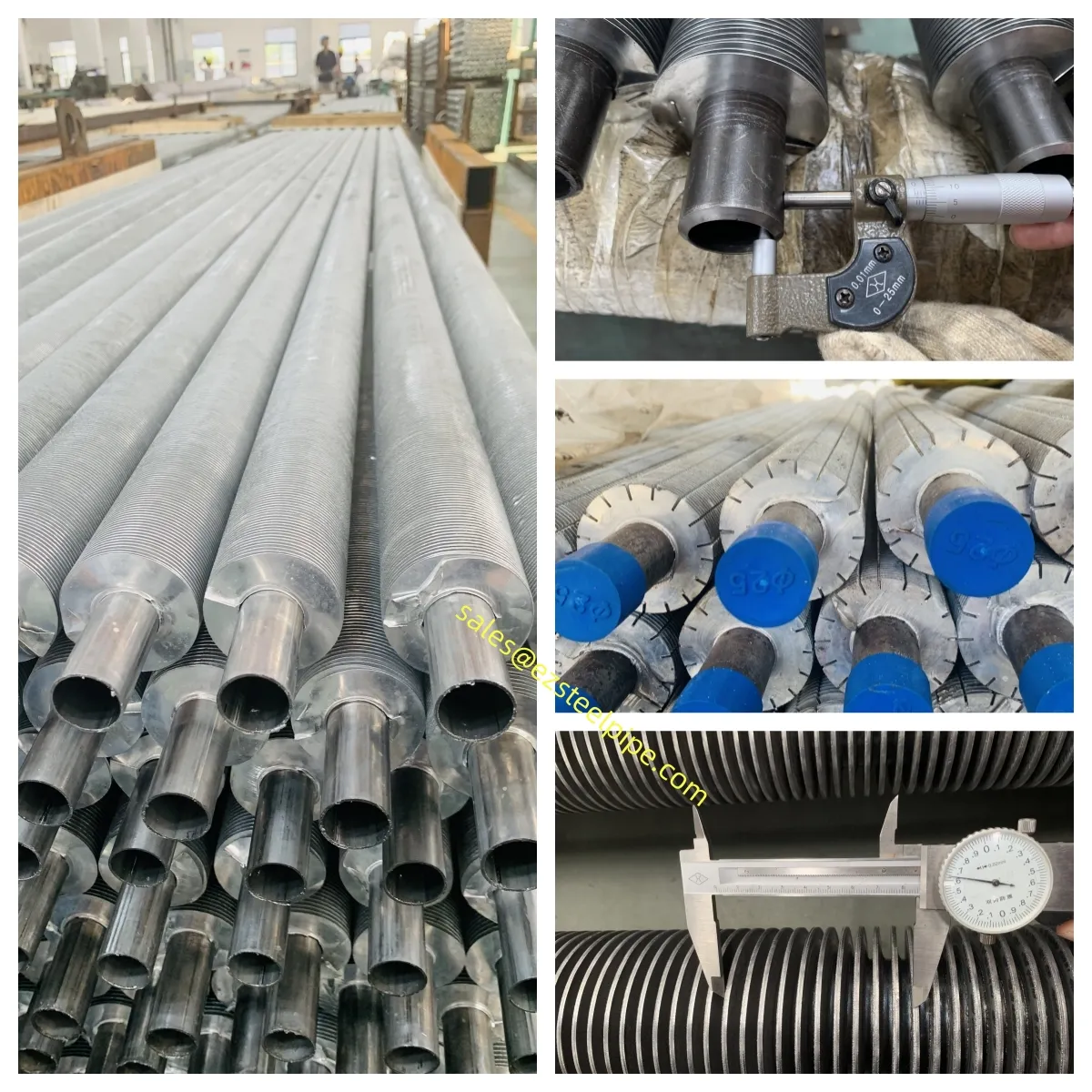
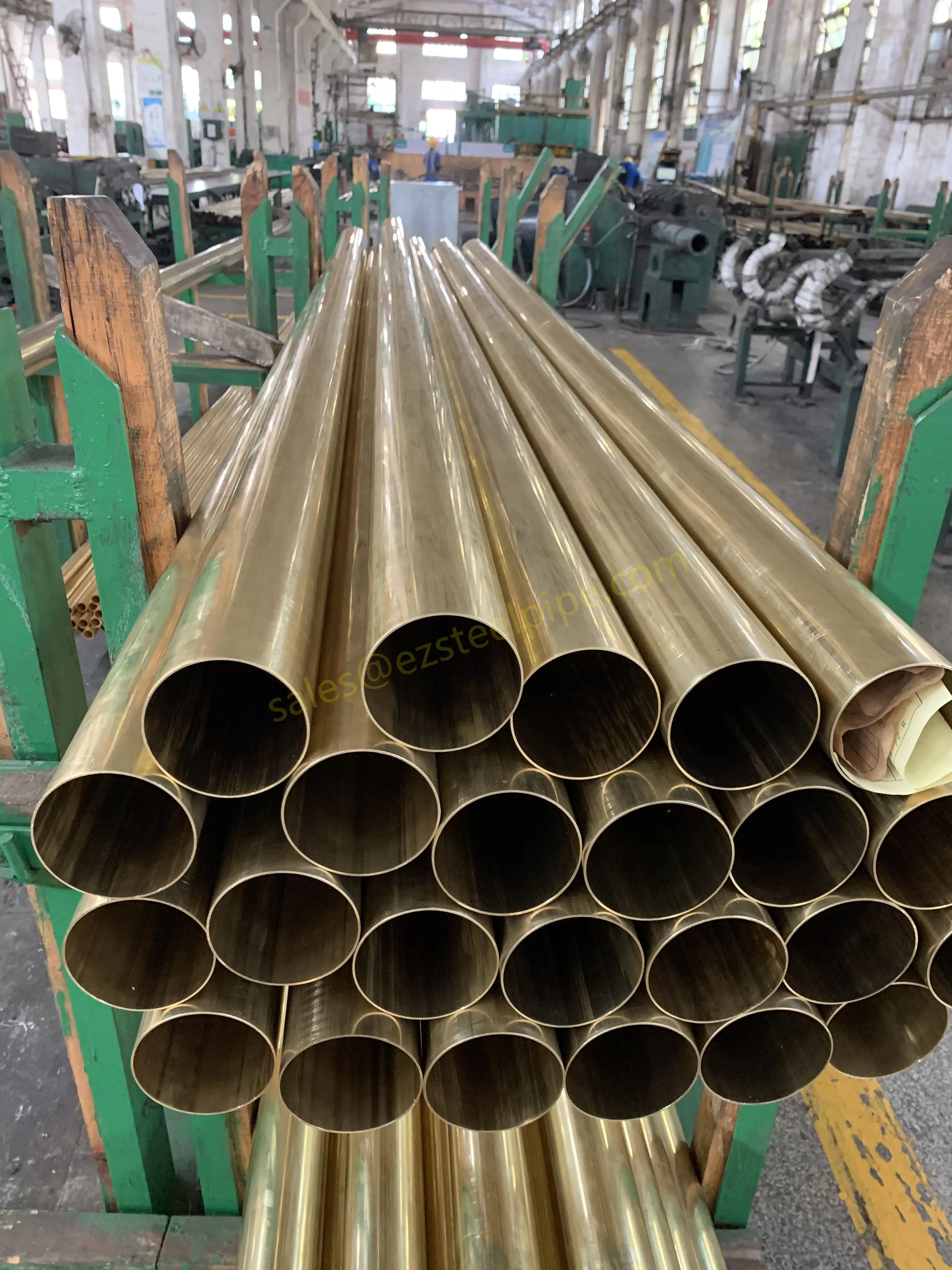
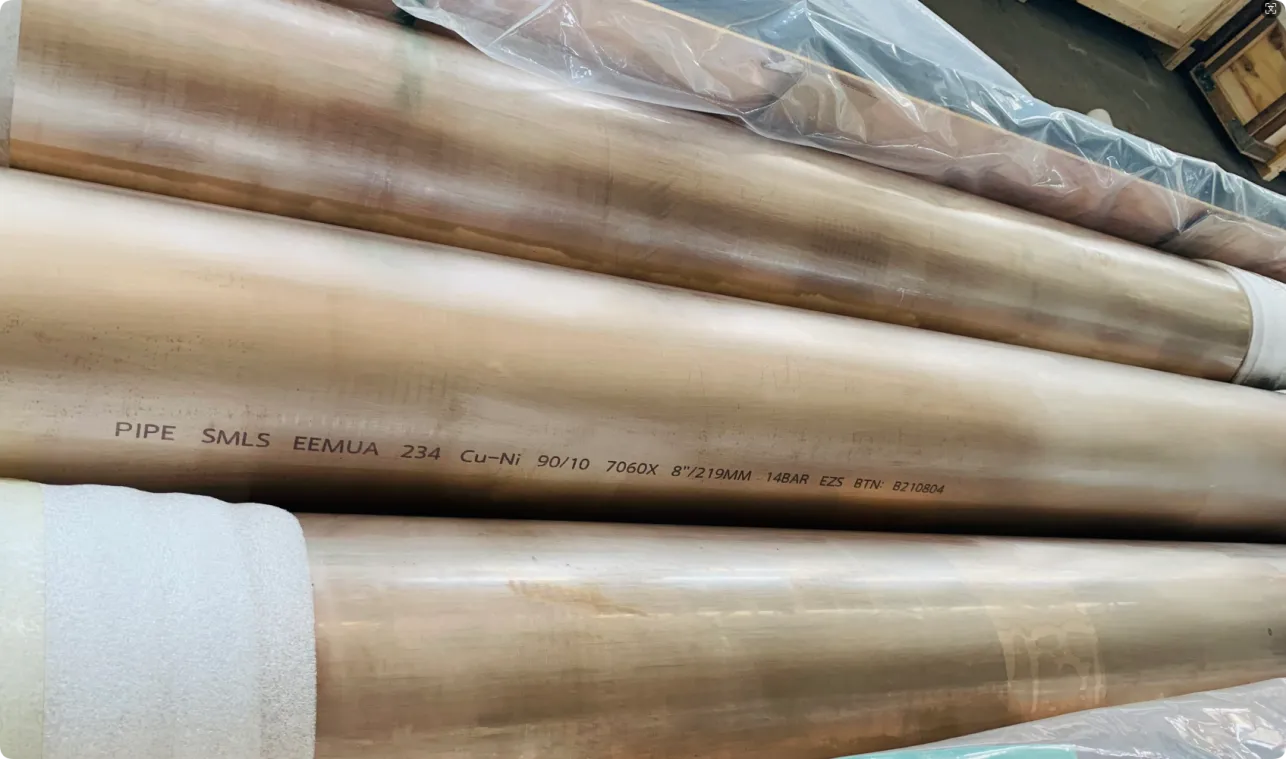
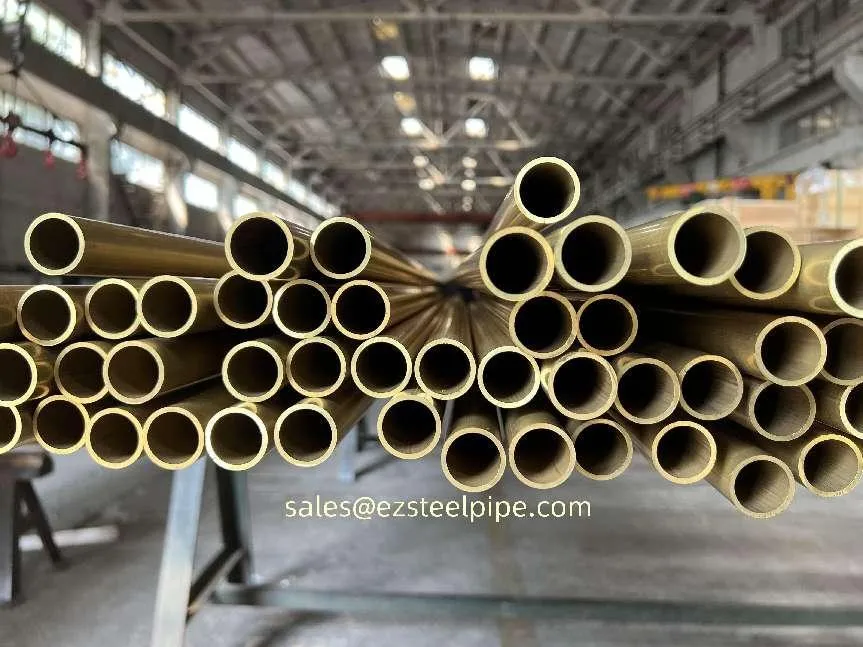
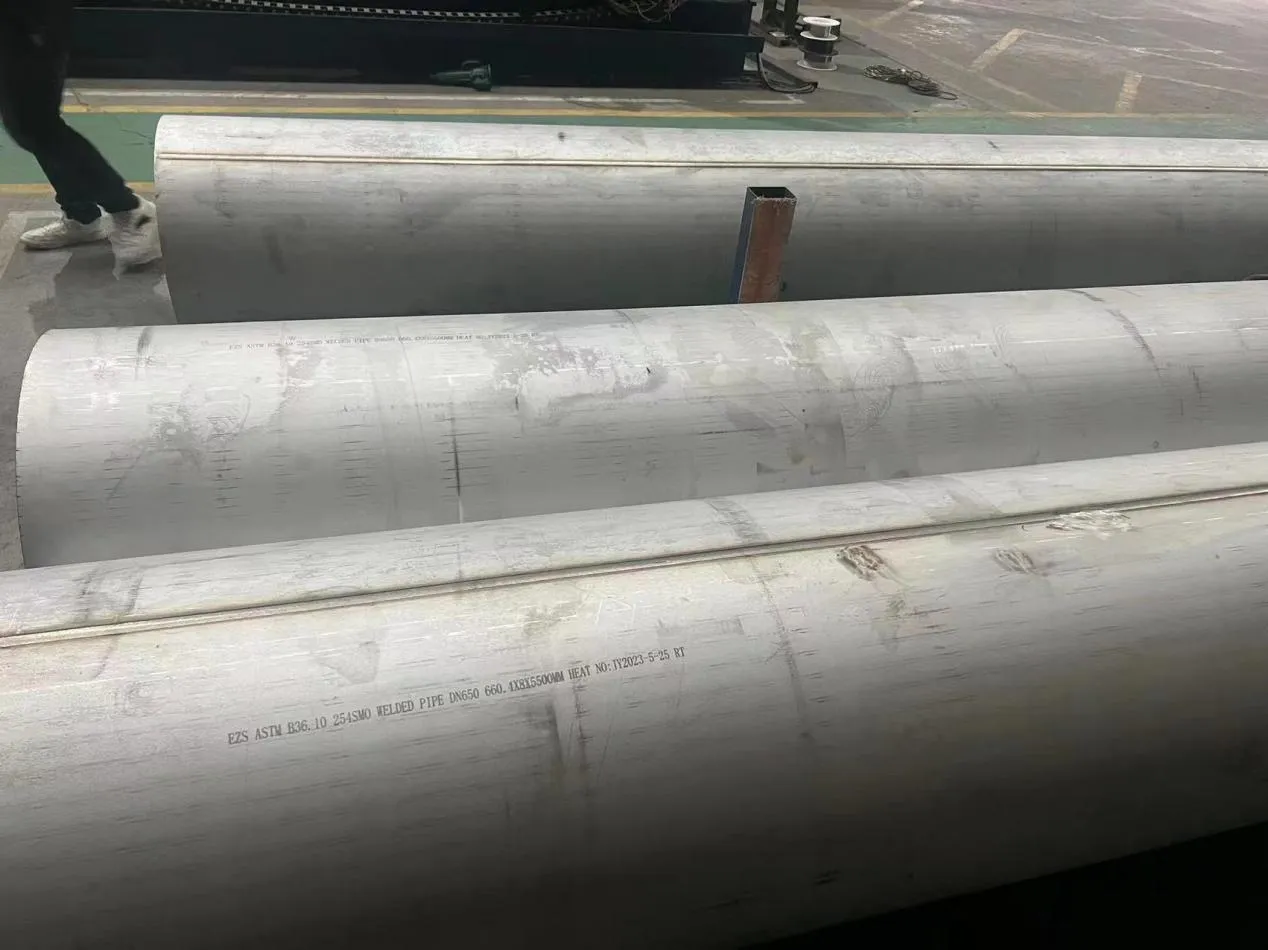
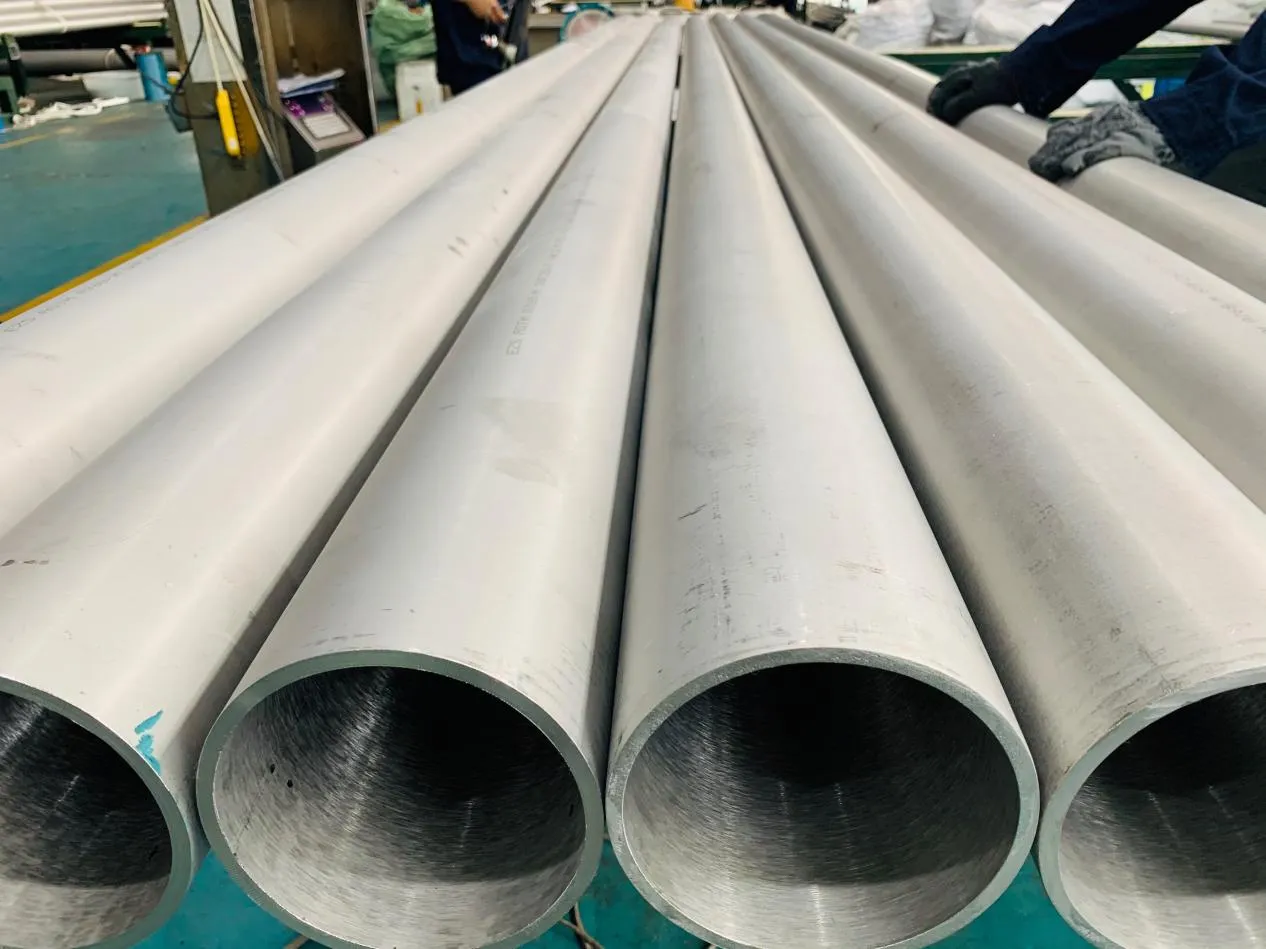
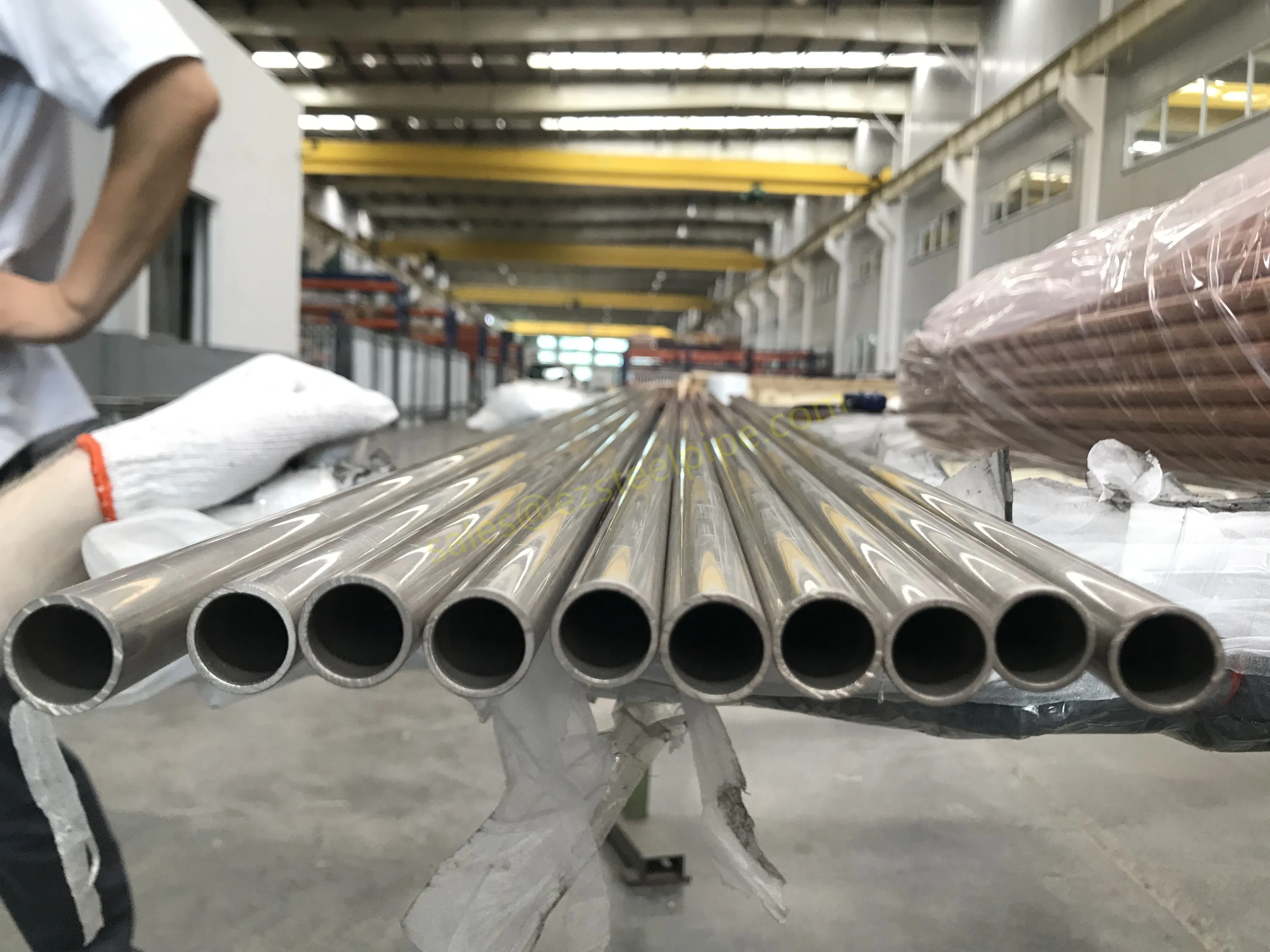
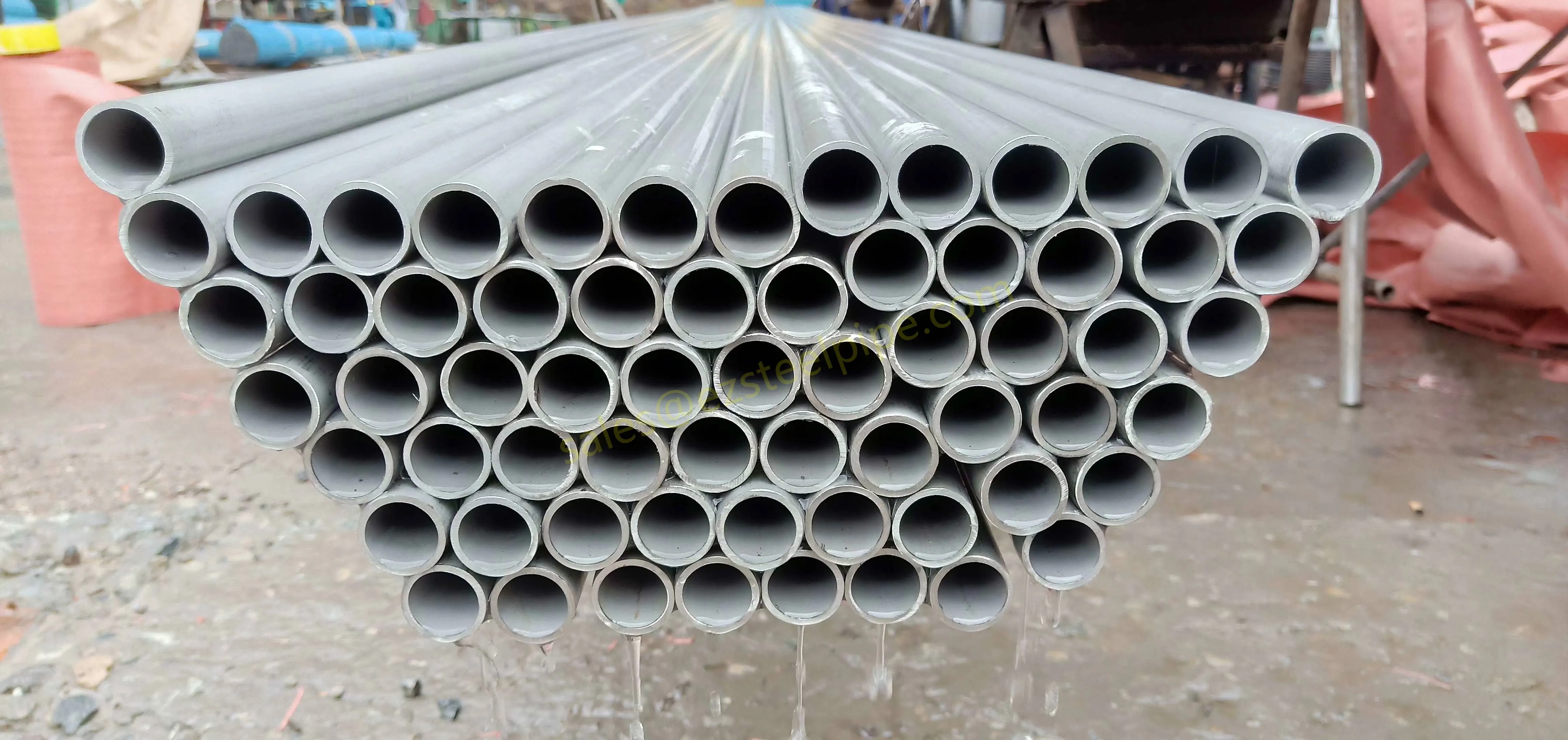
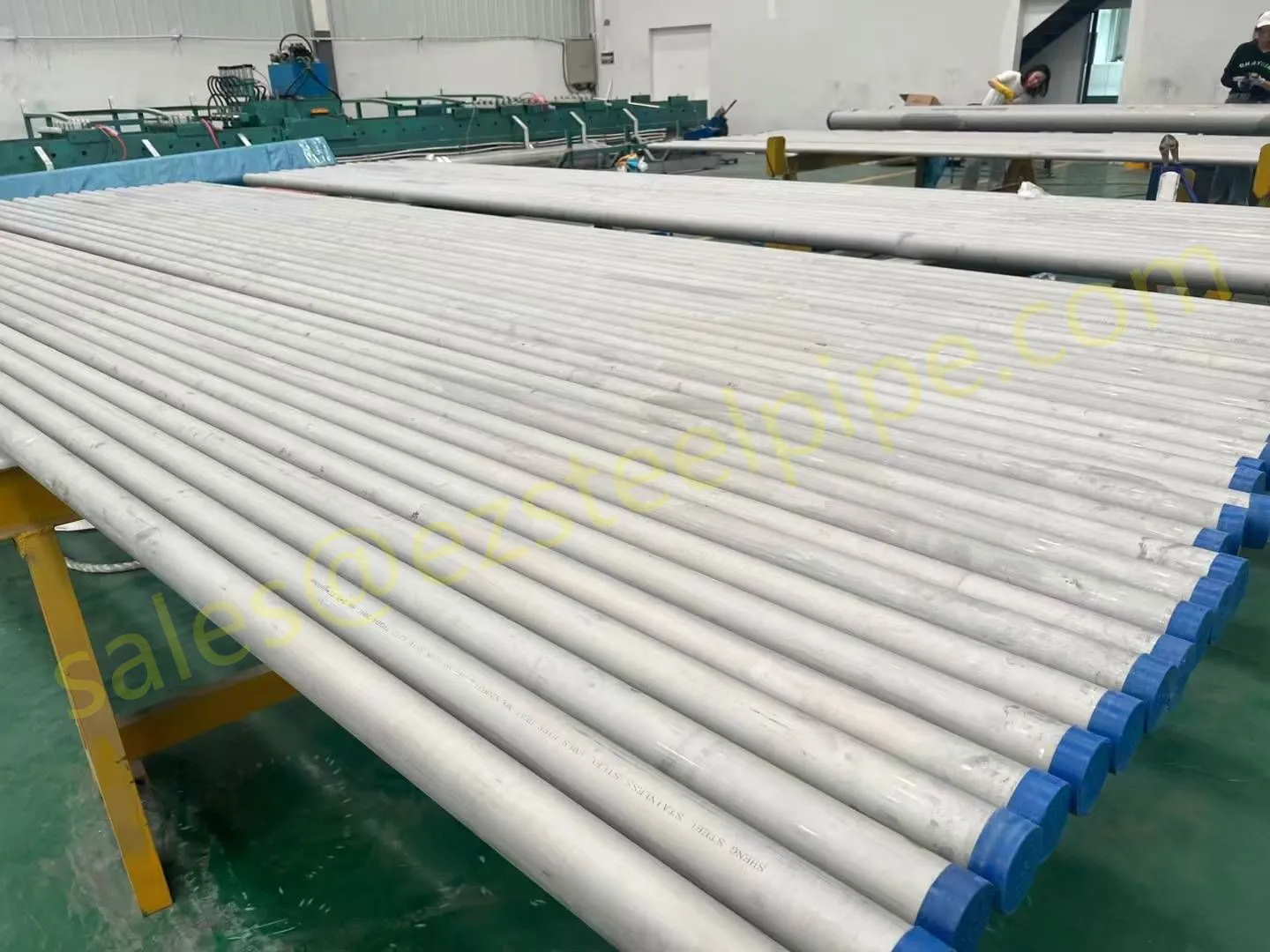
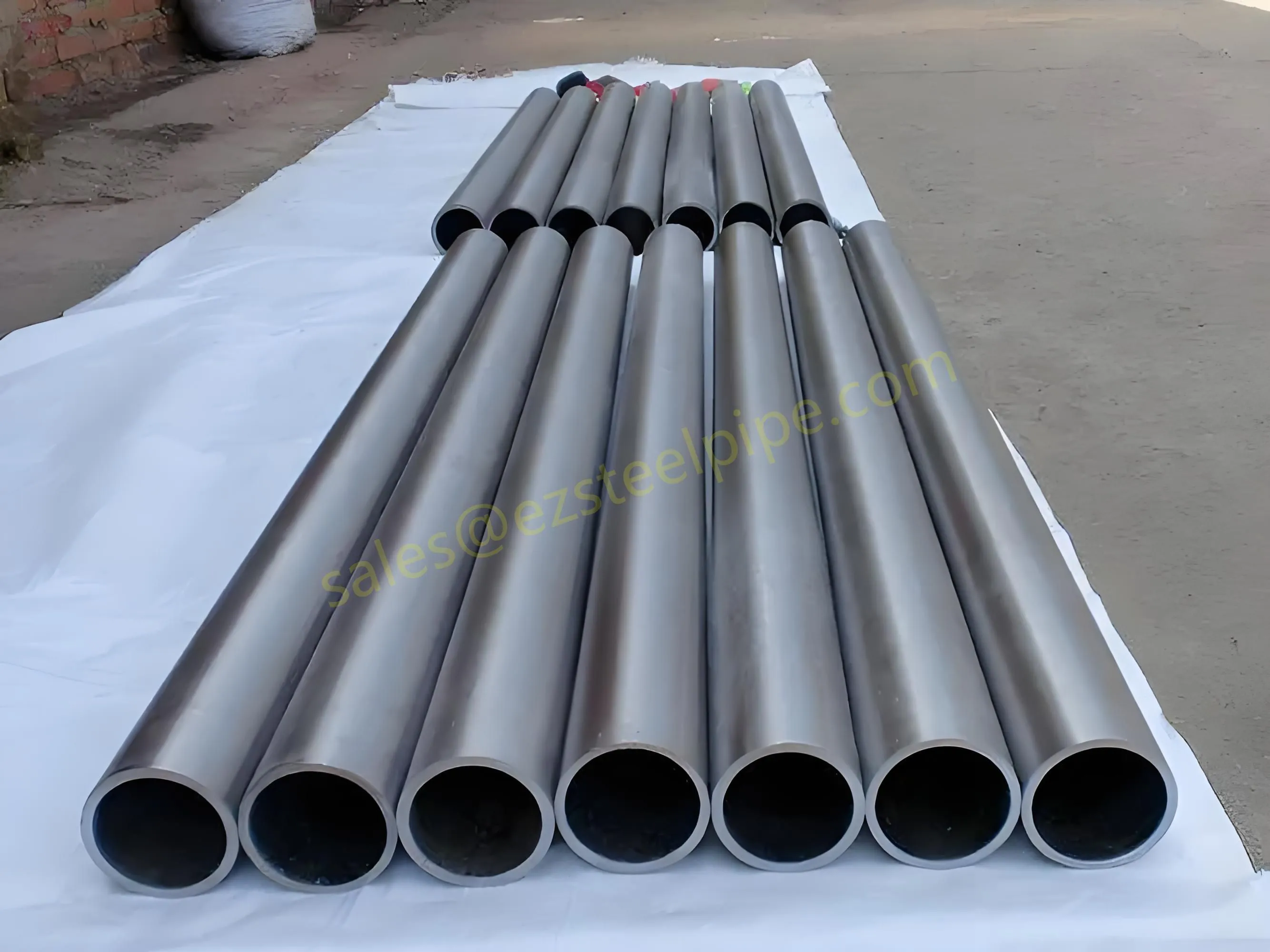
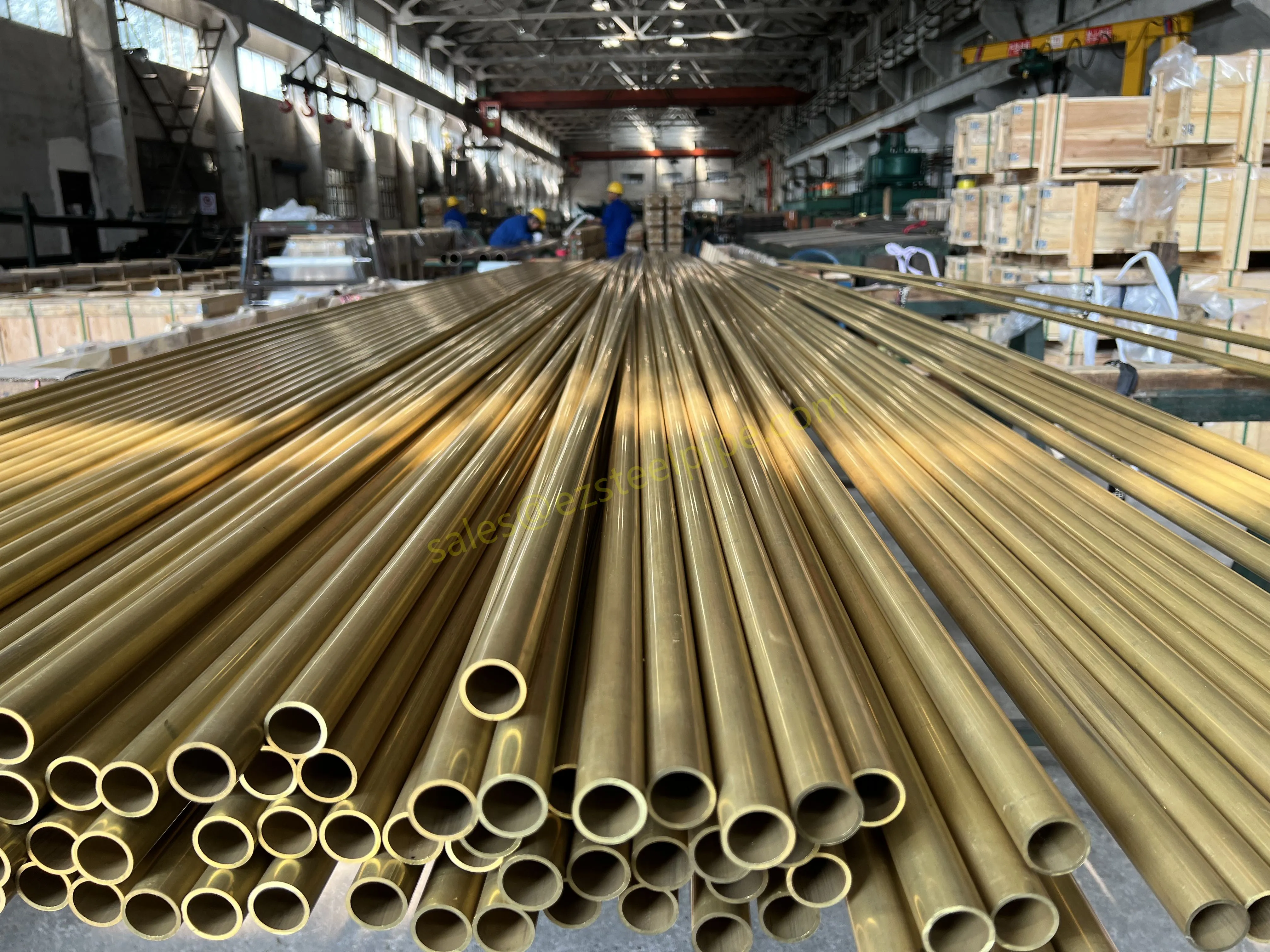
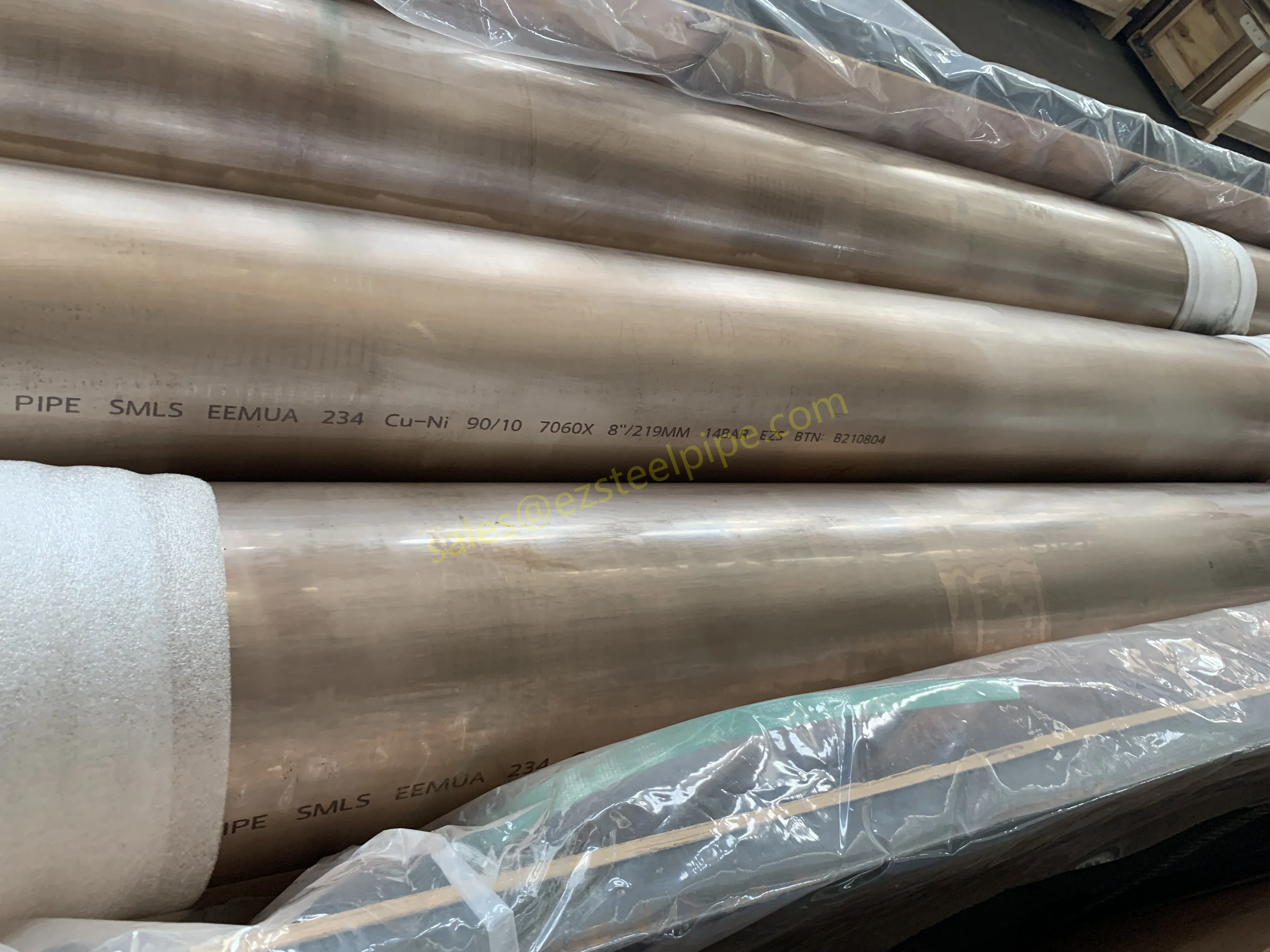
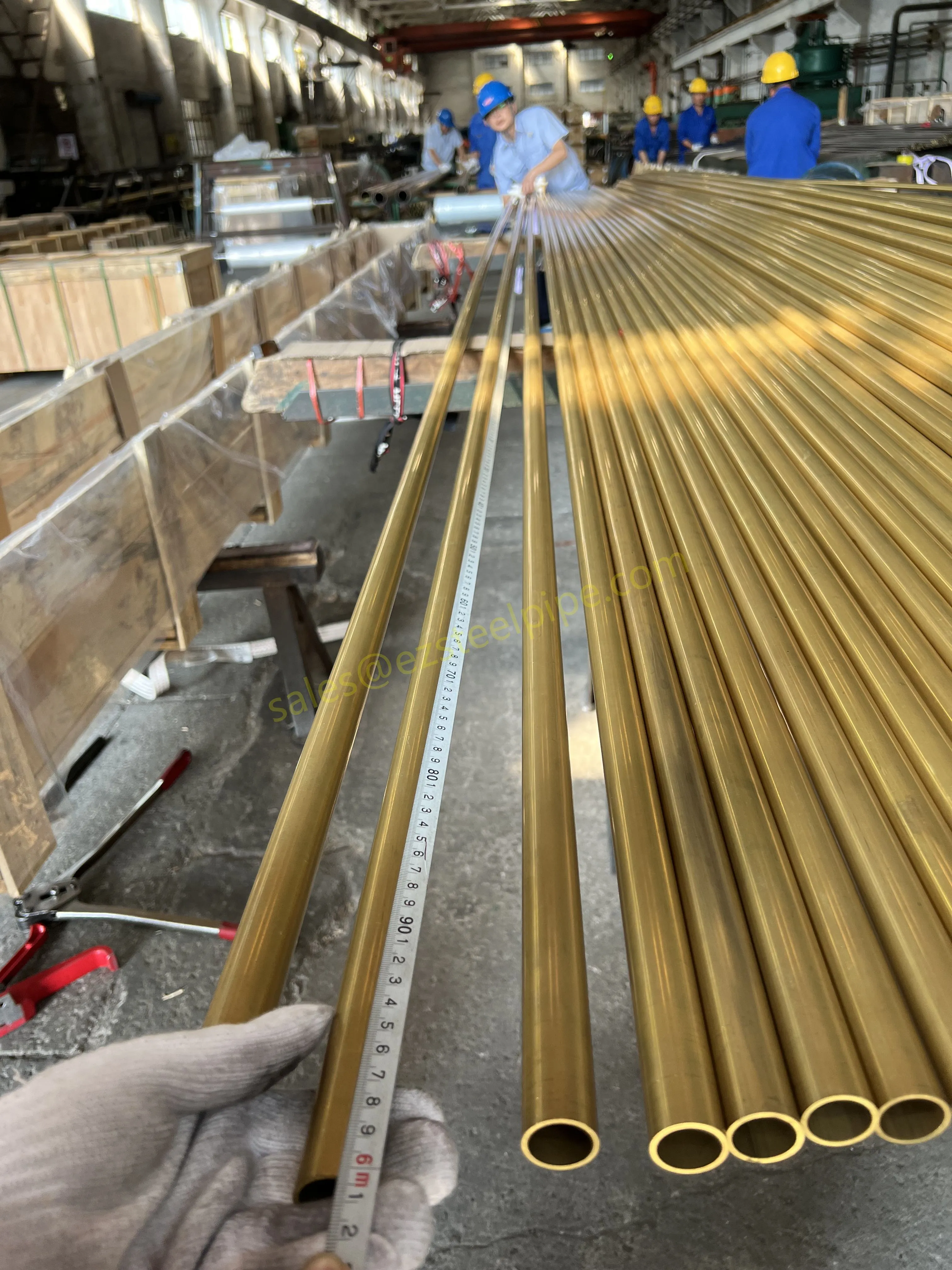
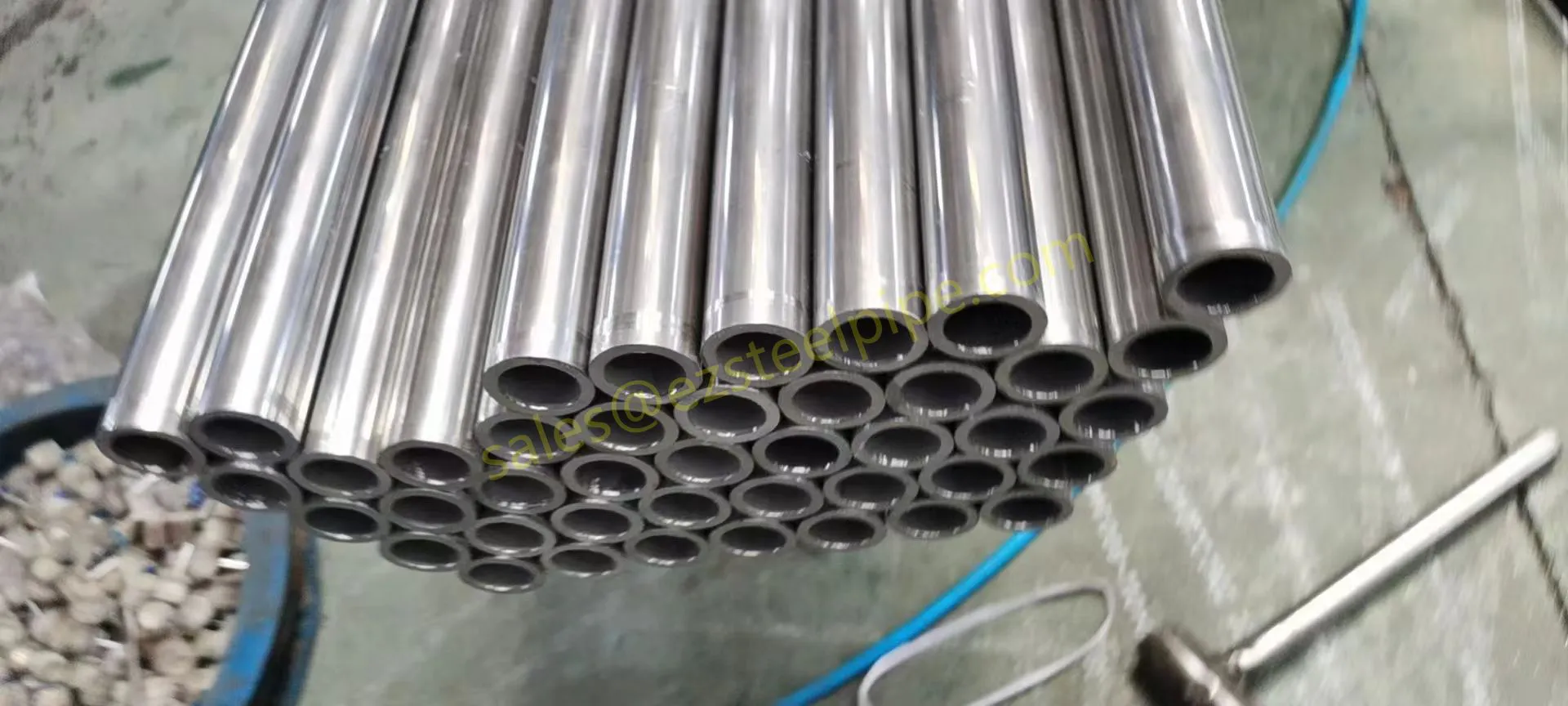
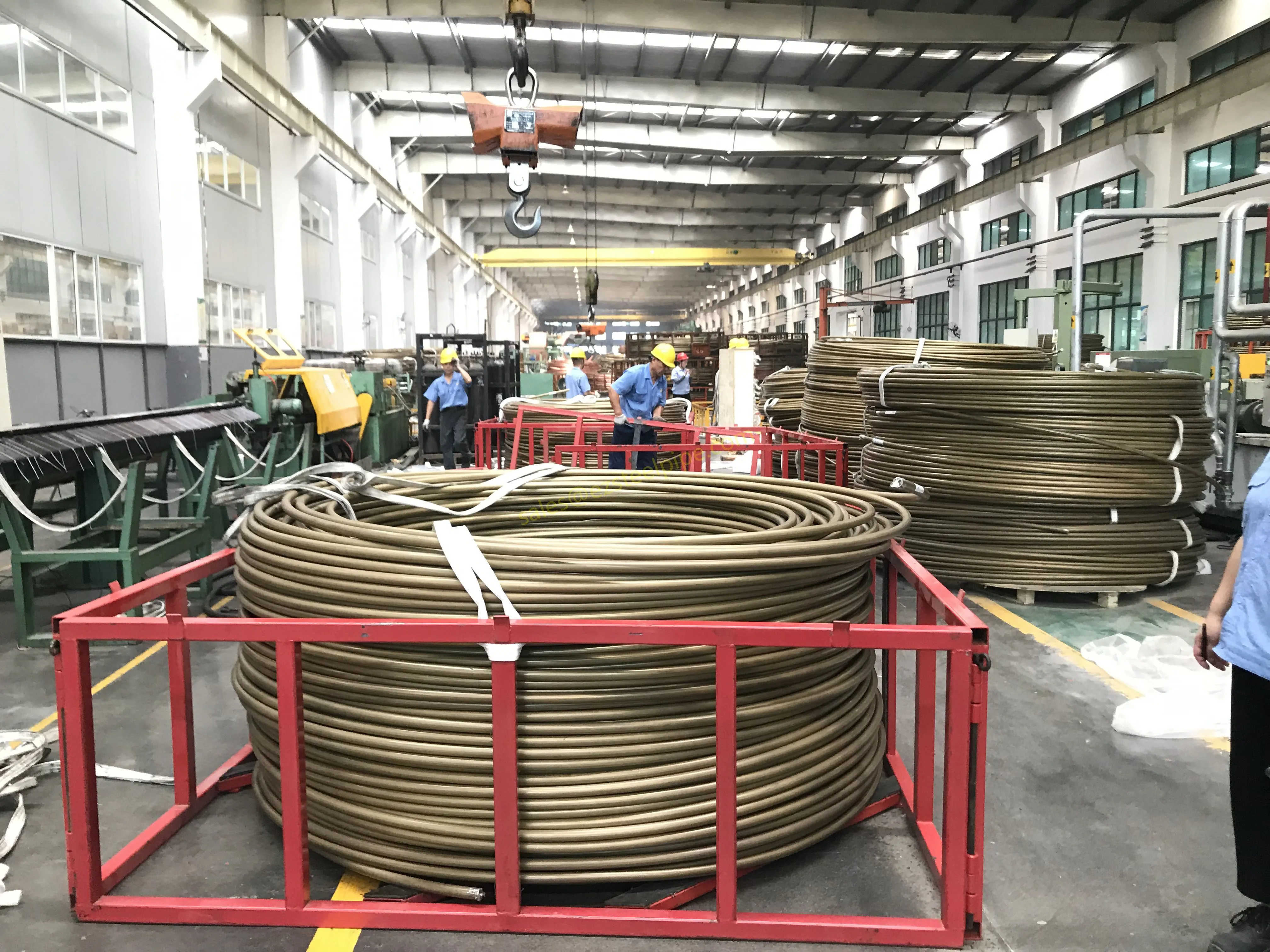
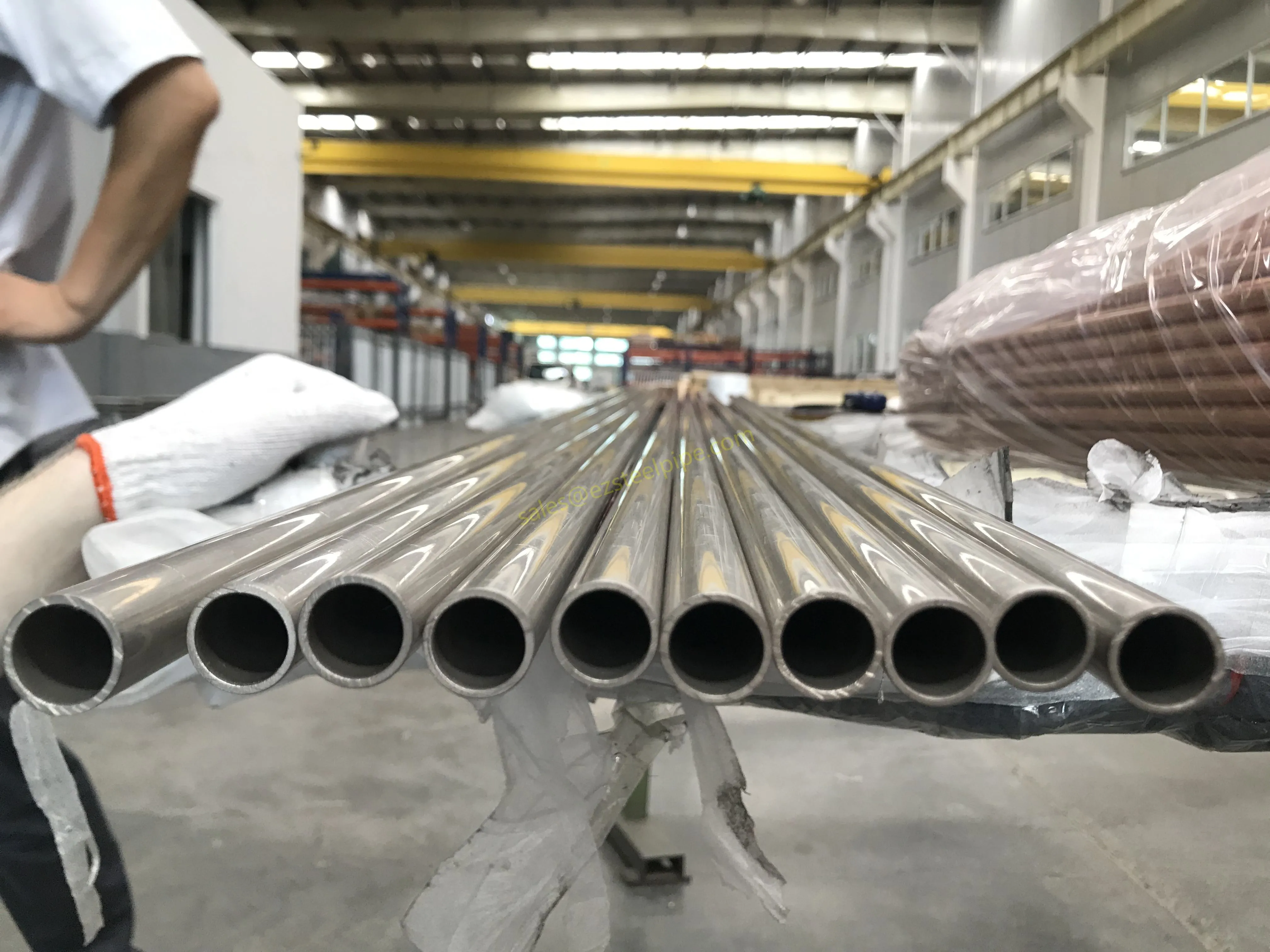
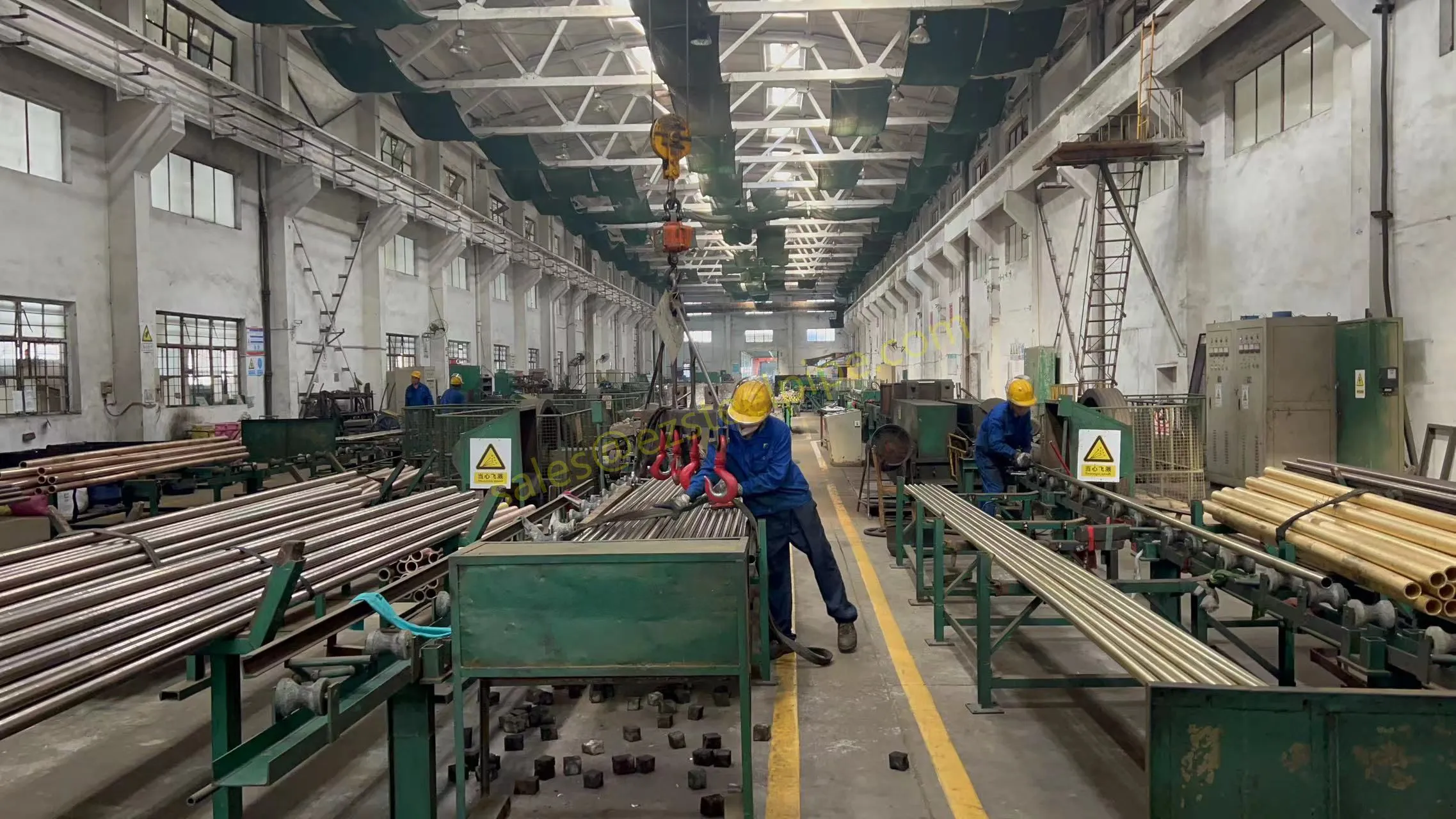
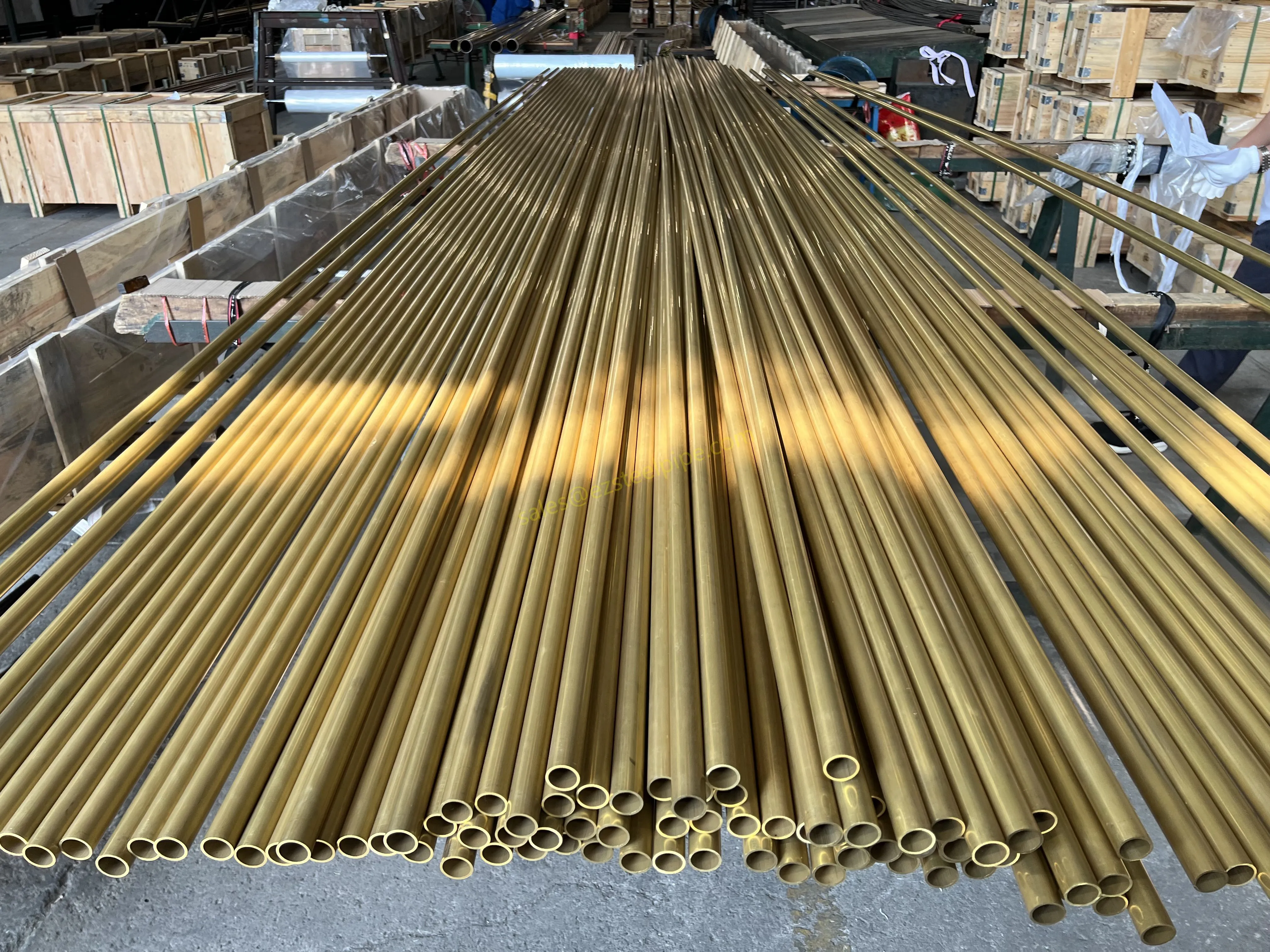
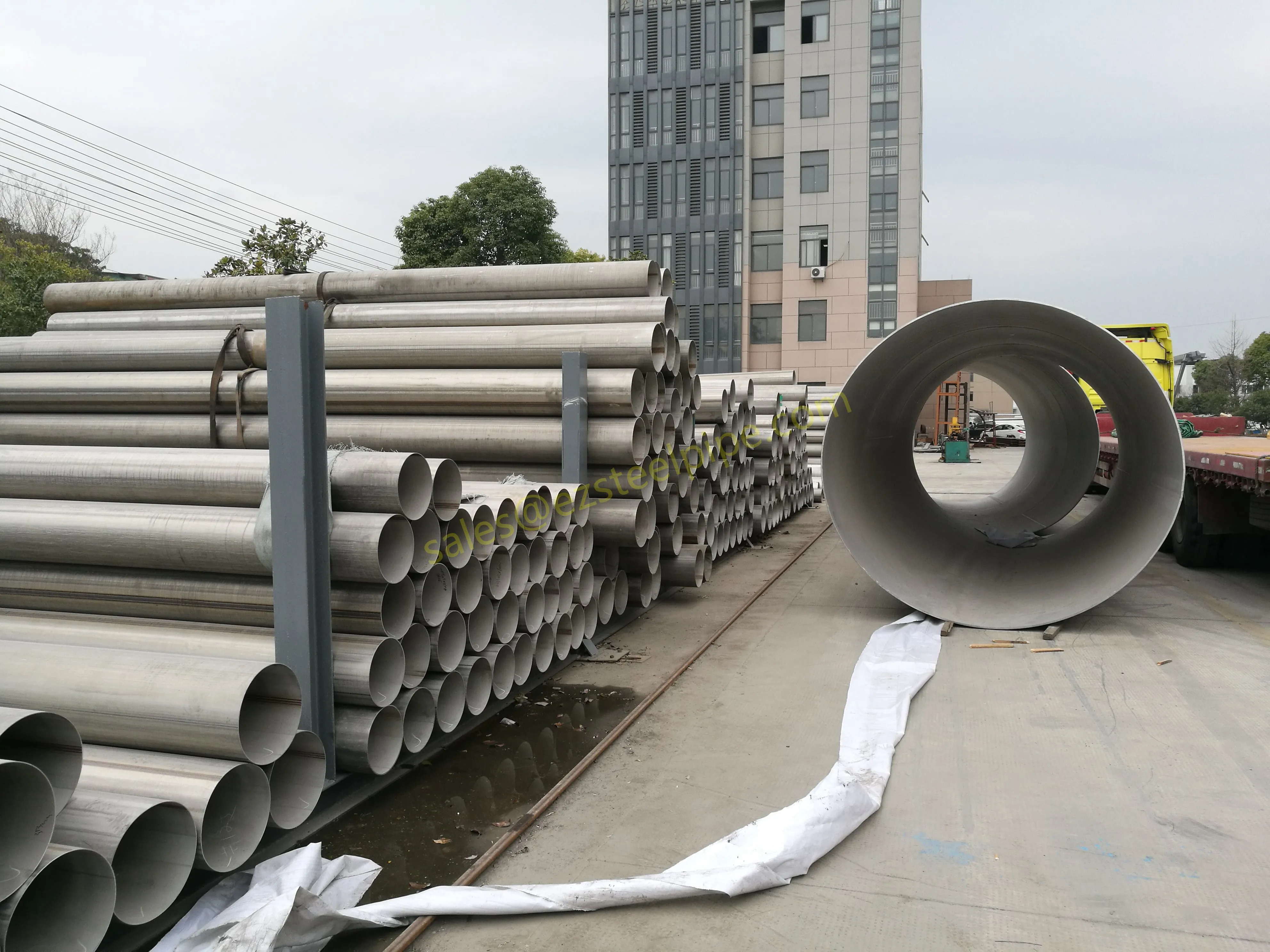
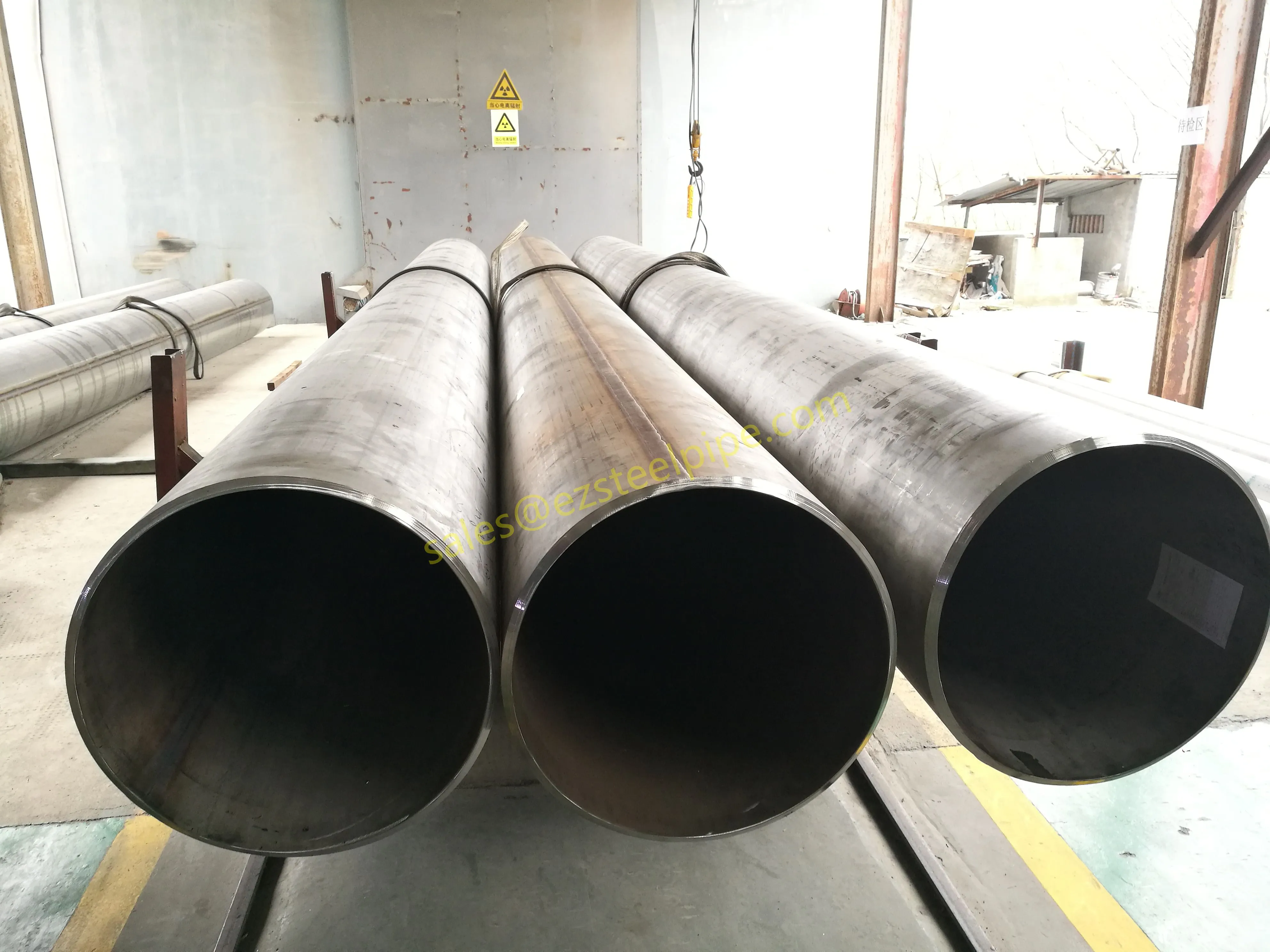
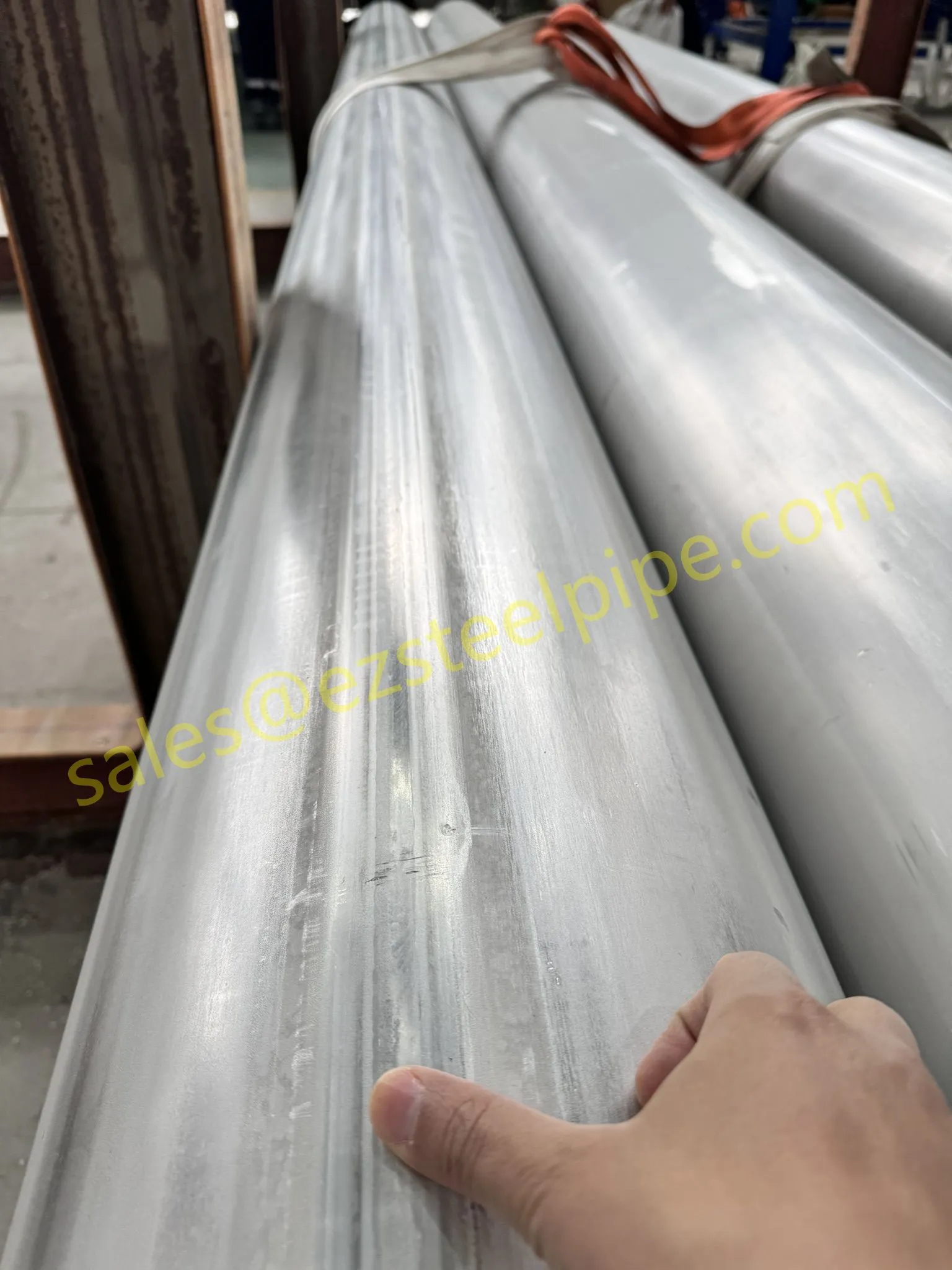
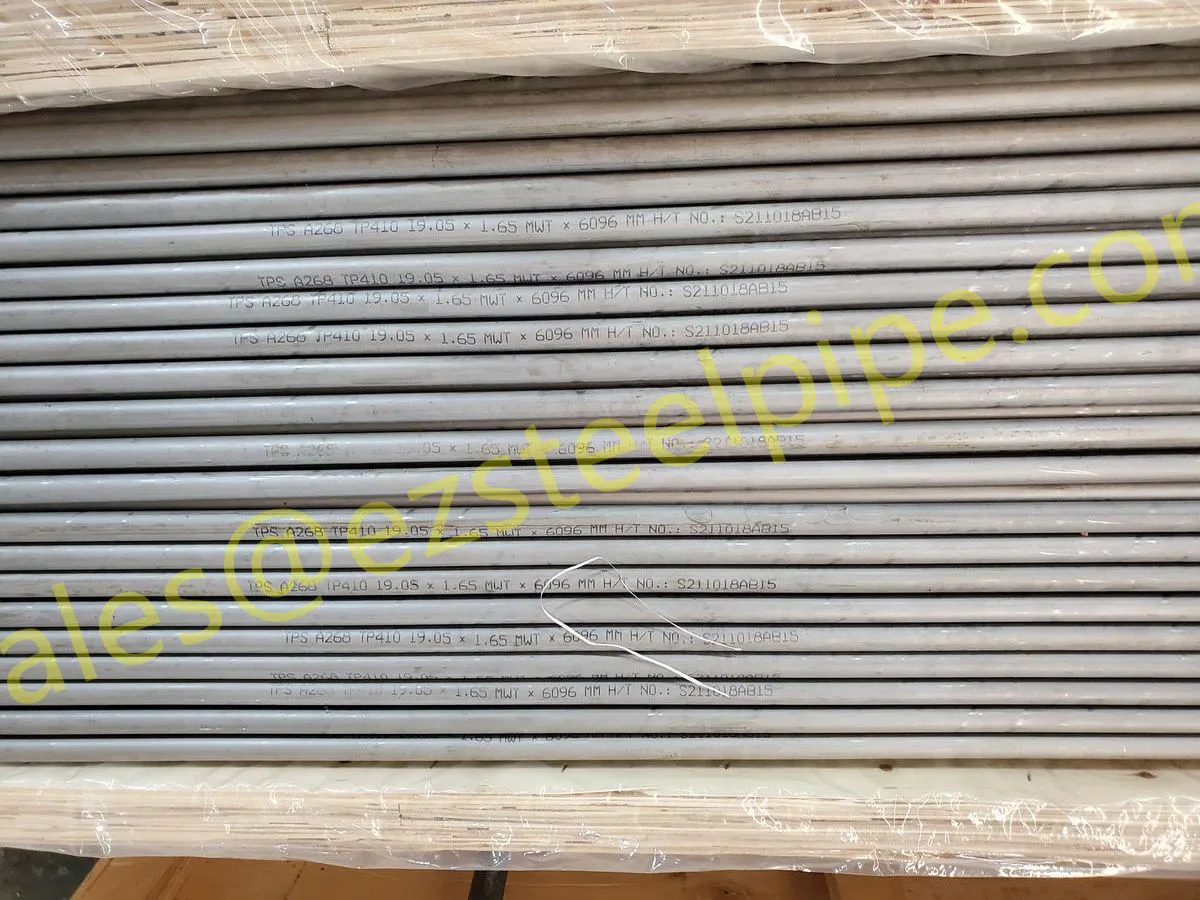
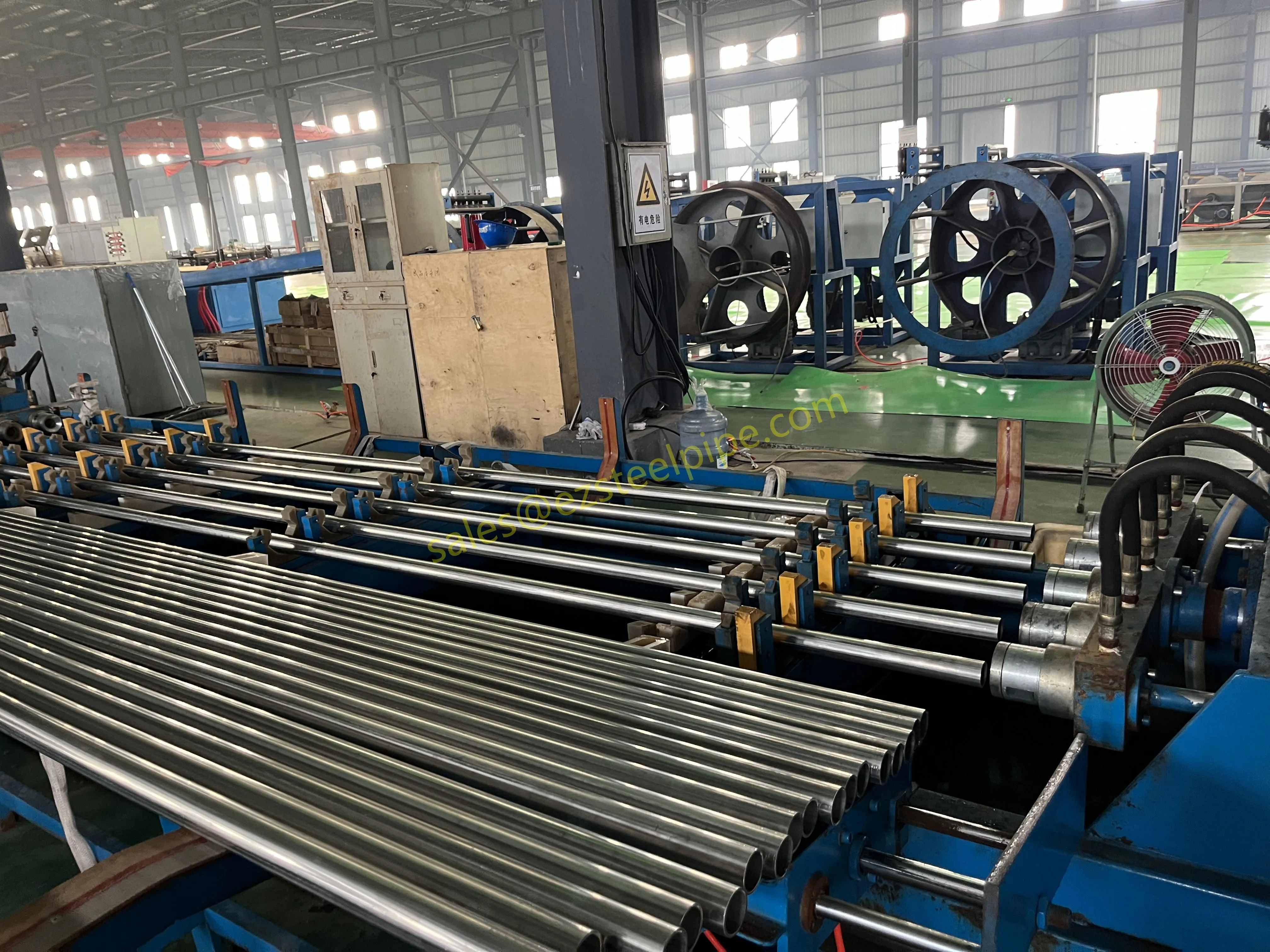
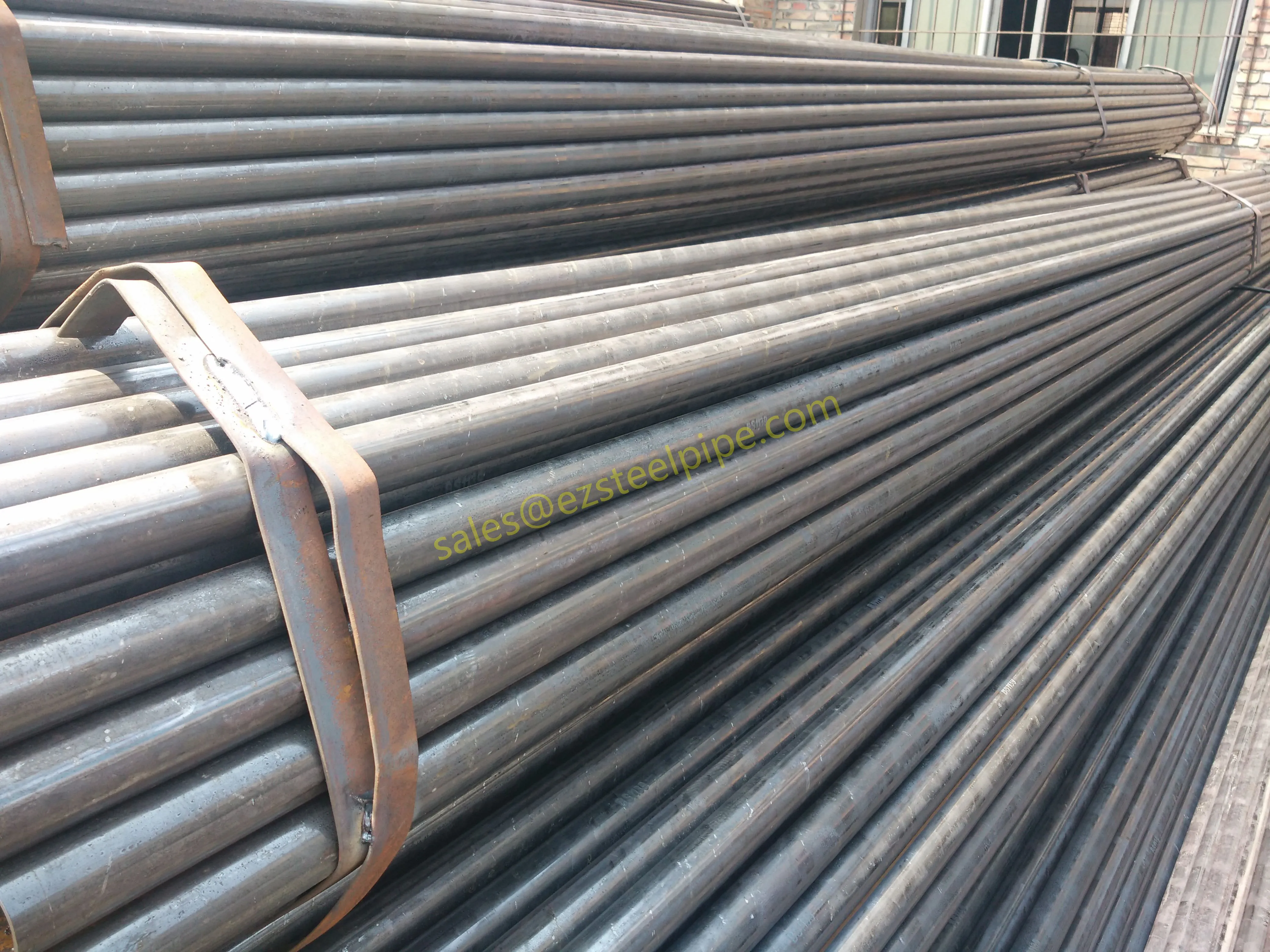
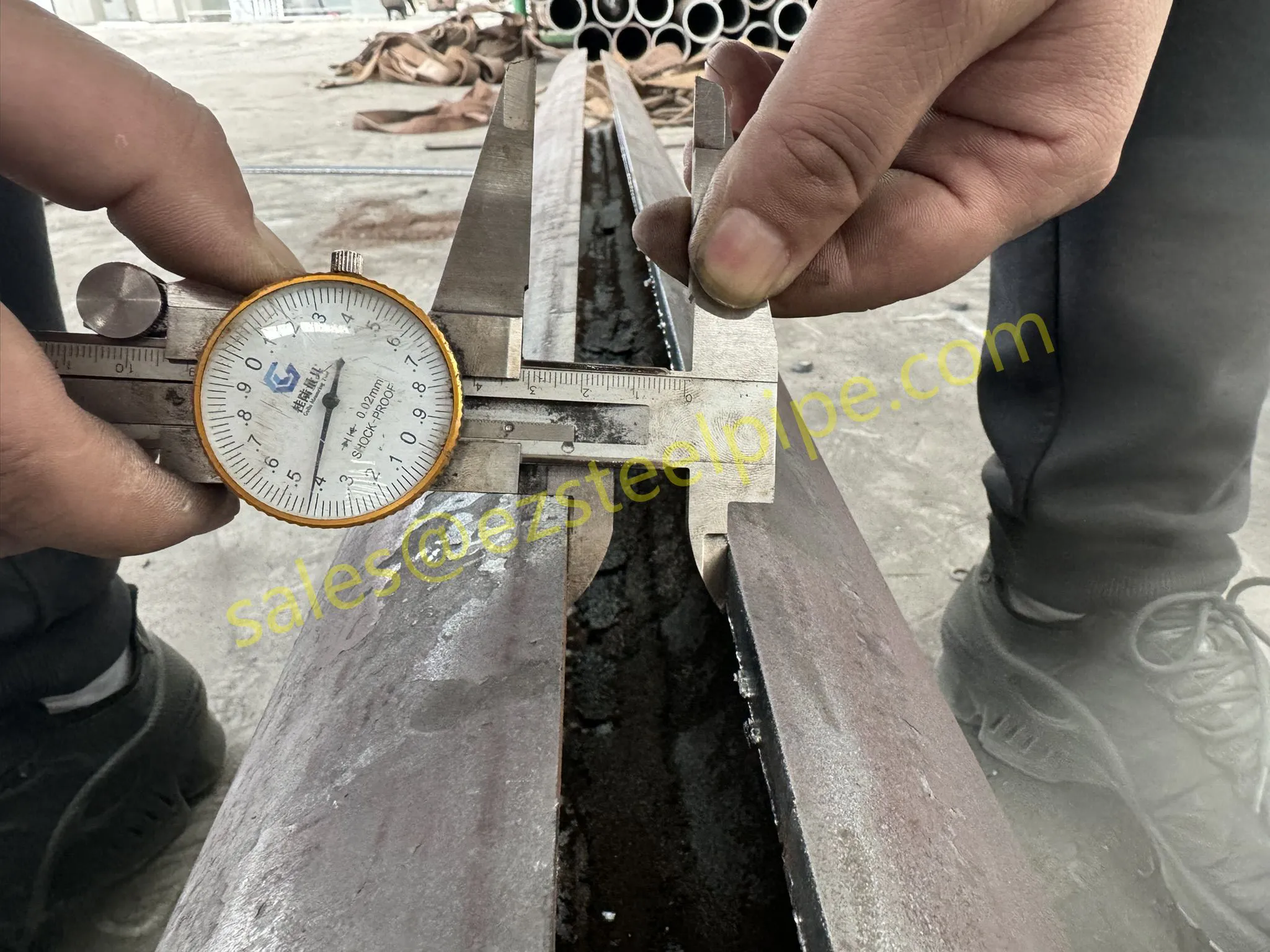
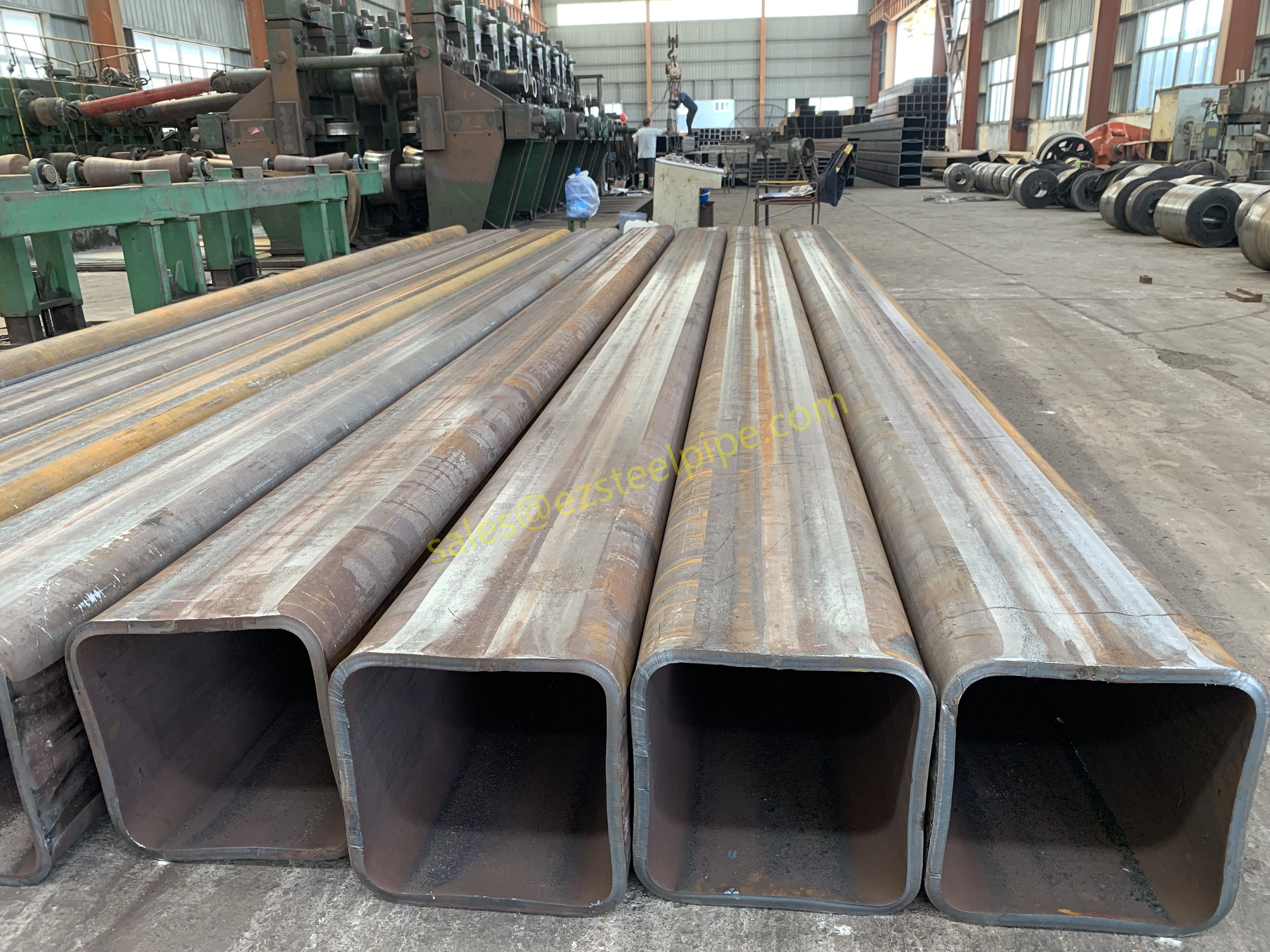
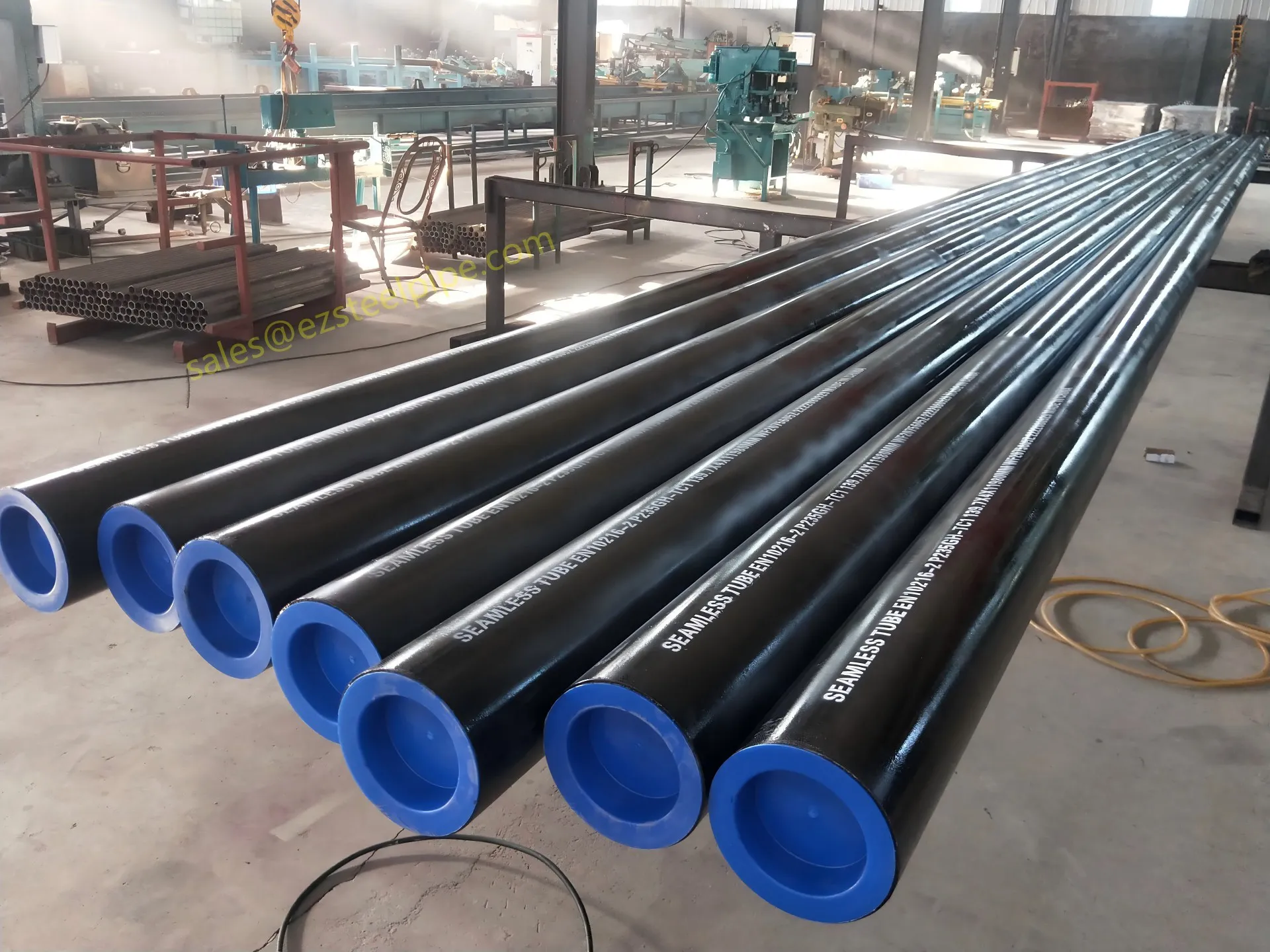
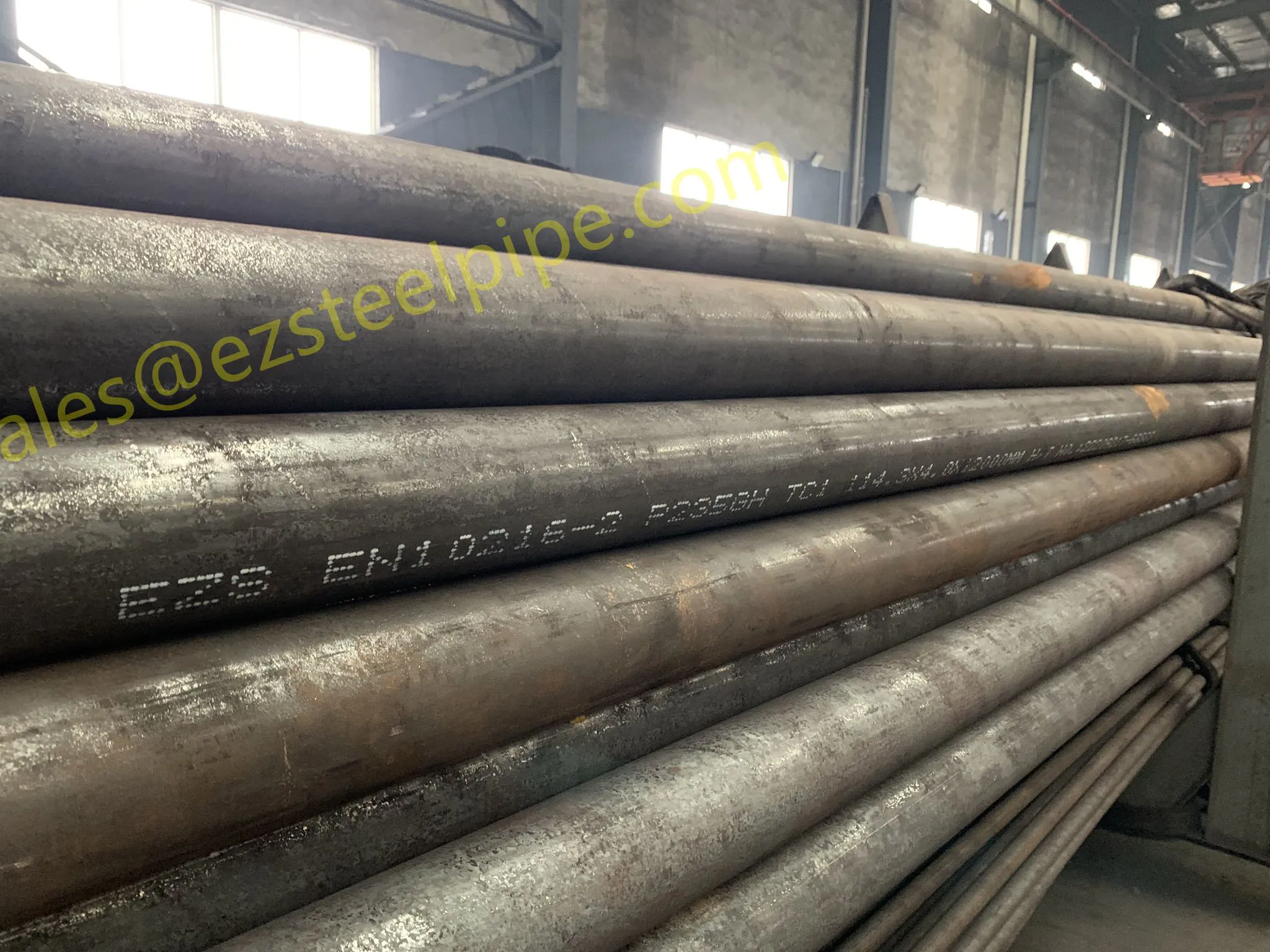
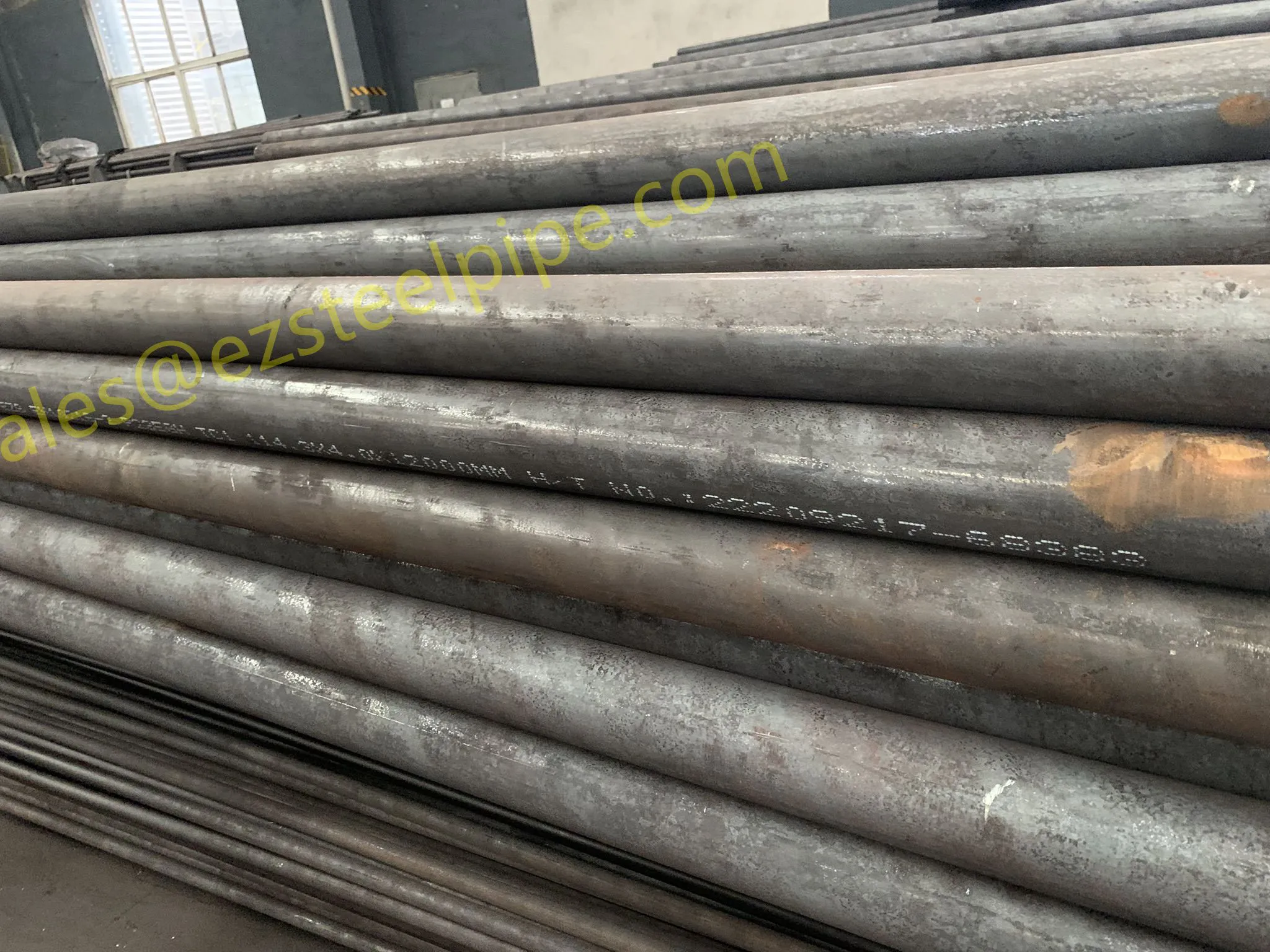
At their core, heat exchanger tubes are cylindrical structures designed to facilitate the transfer of heat from one medium (like water, steam, or oil) to another without the two media mixing. Think of them as the "veins" of industrial systems: in a power plant, they might transfer heat from hot exhaust gases to water, turning it into steam to drive turbines. In a chemical plant, they could cool down reactive fluids to prevent overheating. In aerospace, they might regulate temperatures in jet engines to ensure safe, efficient operation.
But here's the catch: traditional heat exchanger tubes often lose a significant amount of energy during this transfer process. Inefficient heat transfer means systems have to work harder—burning more fuel, consuming more electricity, and releasing more emissions—to achieve the same results. That's where sustainability comes in. By optimizing heat exchanger tubes for better performance, industries can reduce the energy they waste, lower their operational costs, and shrink their environmental impact. It's a win-win: better business for companies, better planet for all of us.
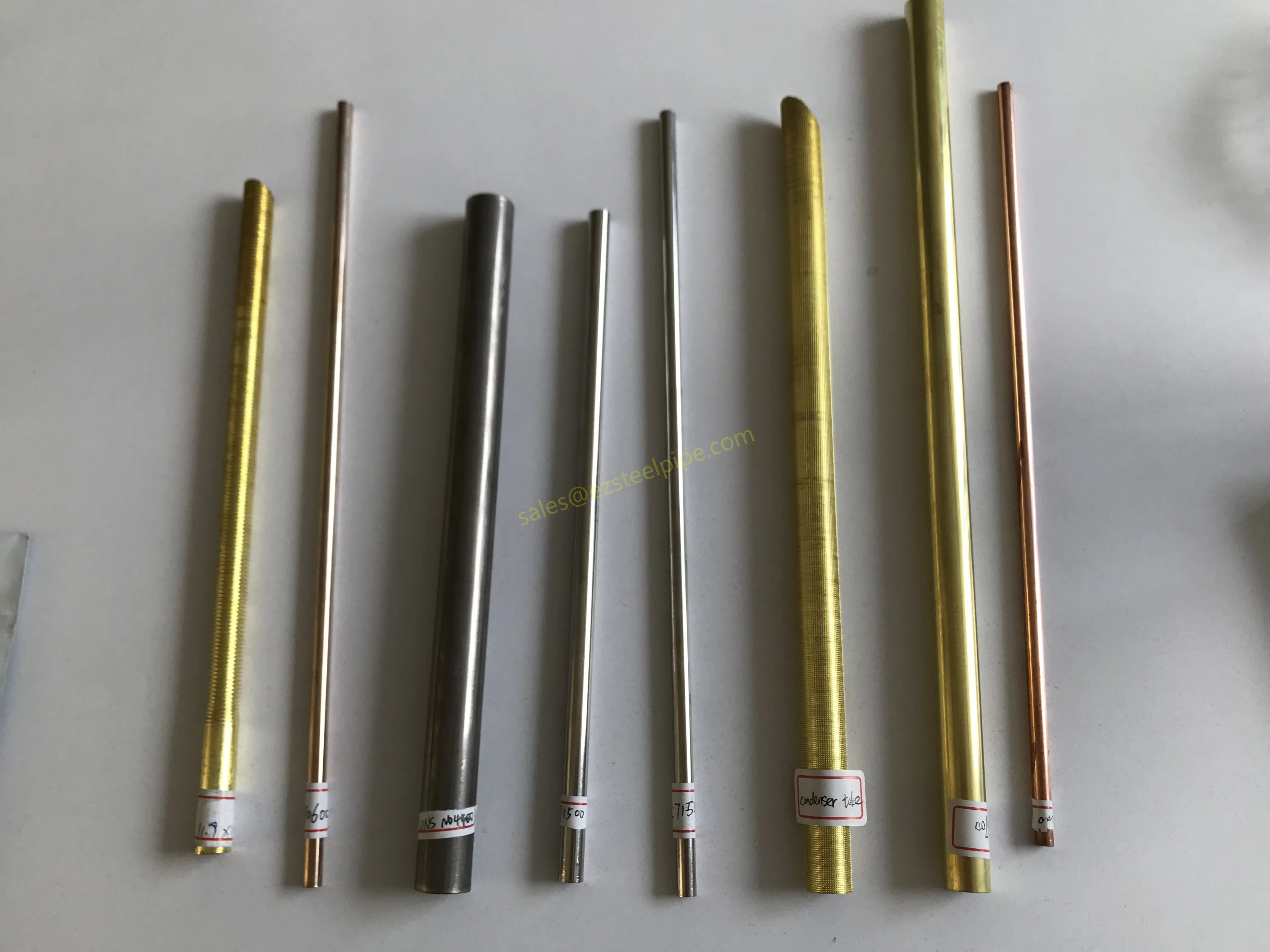
The key to this optimization lies in three areas: materials, design, and customization . Let's start with materials—because what a tube is made of directly impacts how well it transfers heat, how long it lasts, and how sustainably it can be produced and maintained.
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































