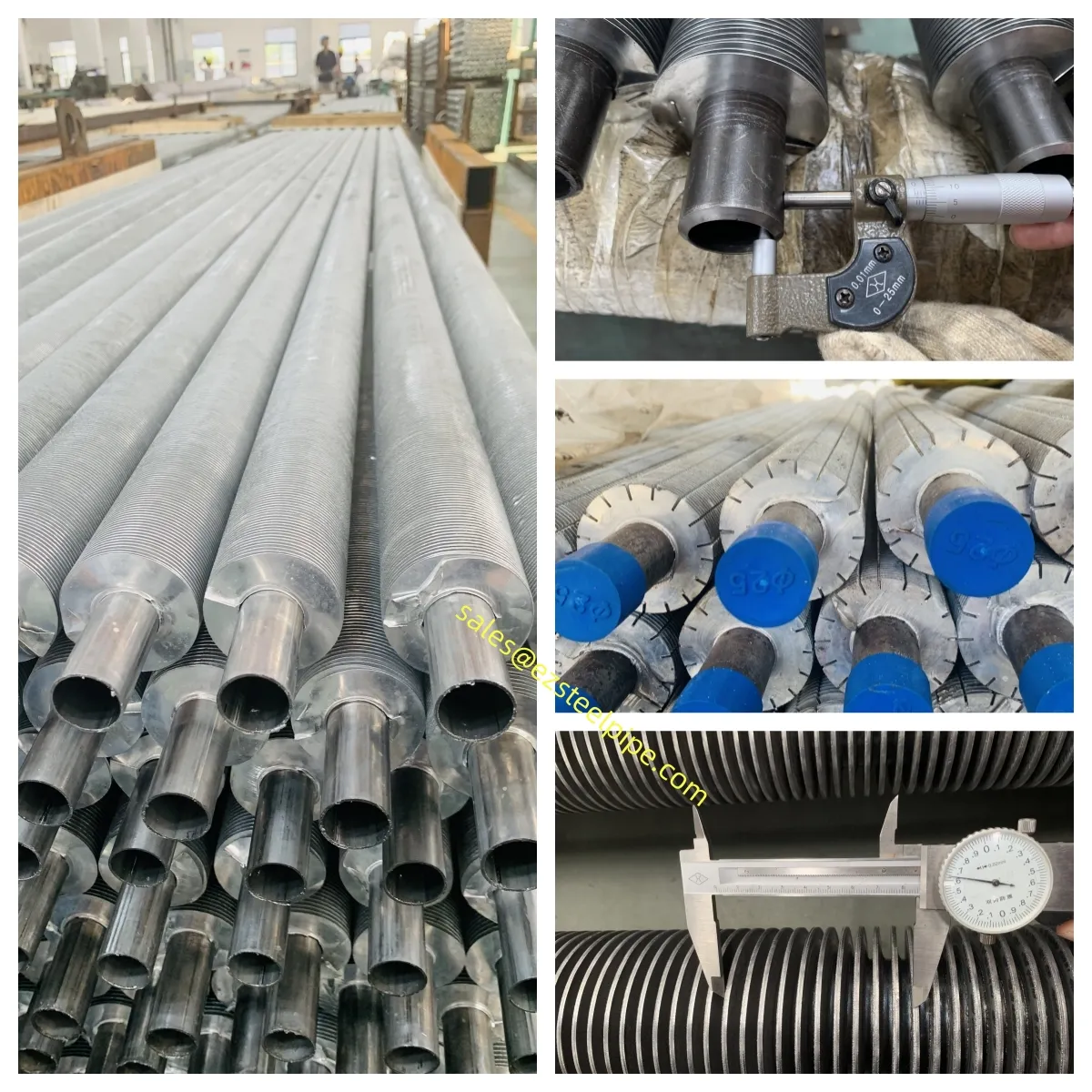
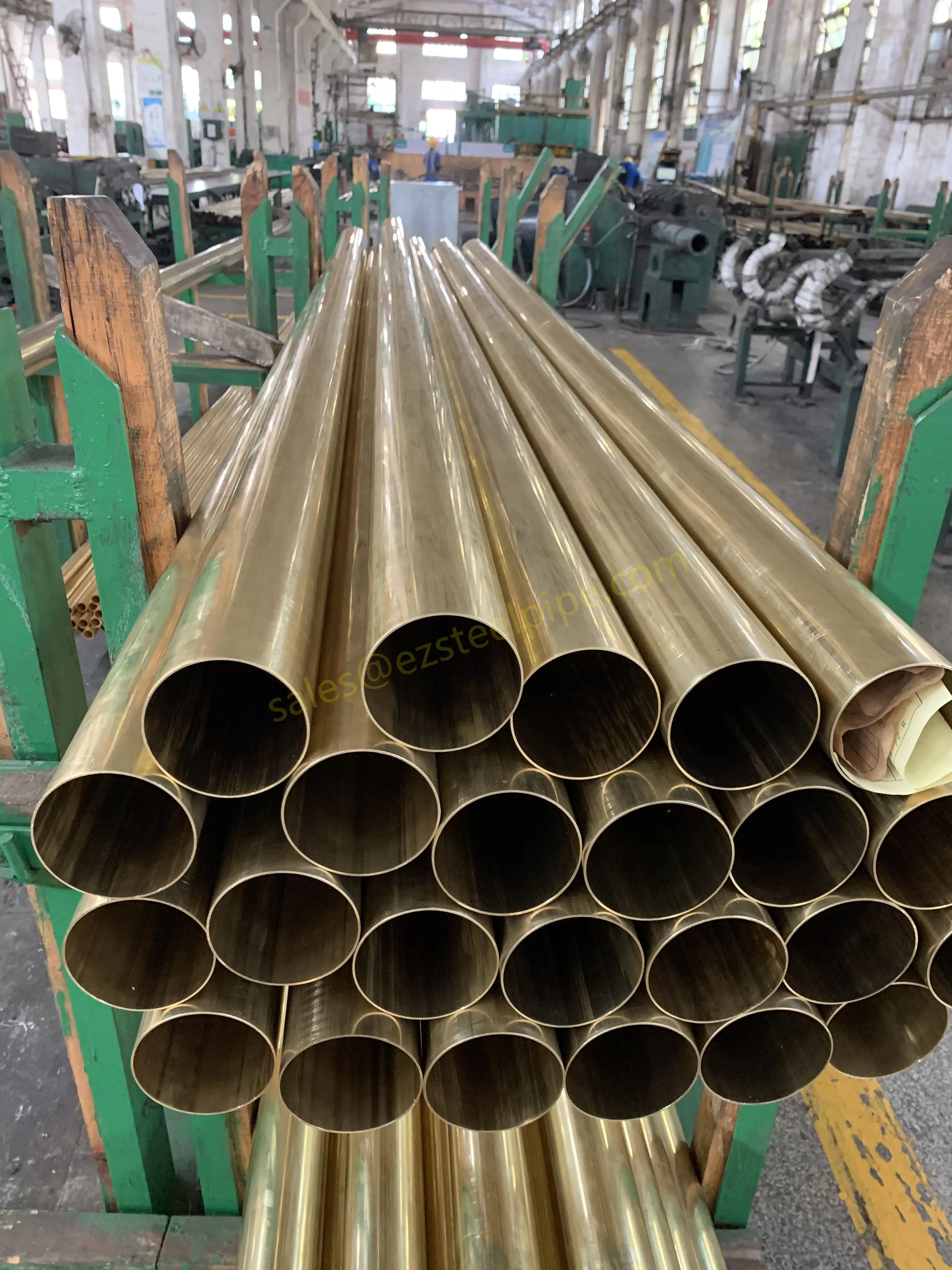
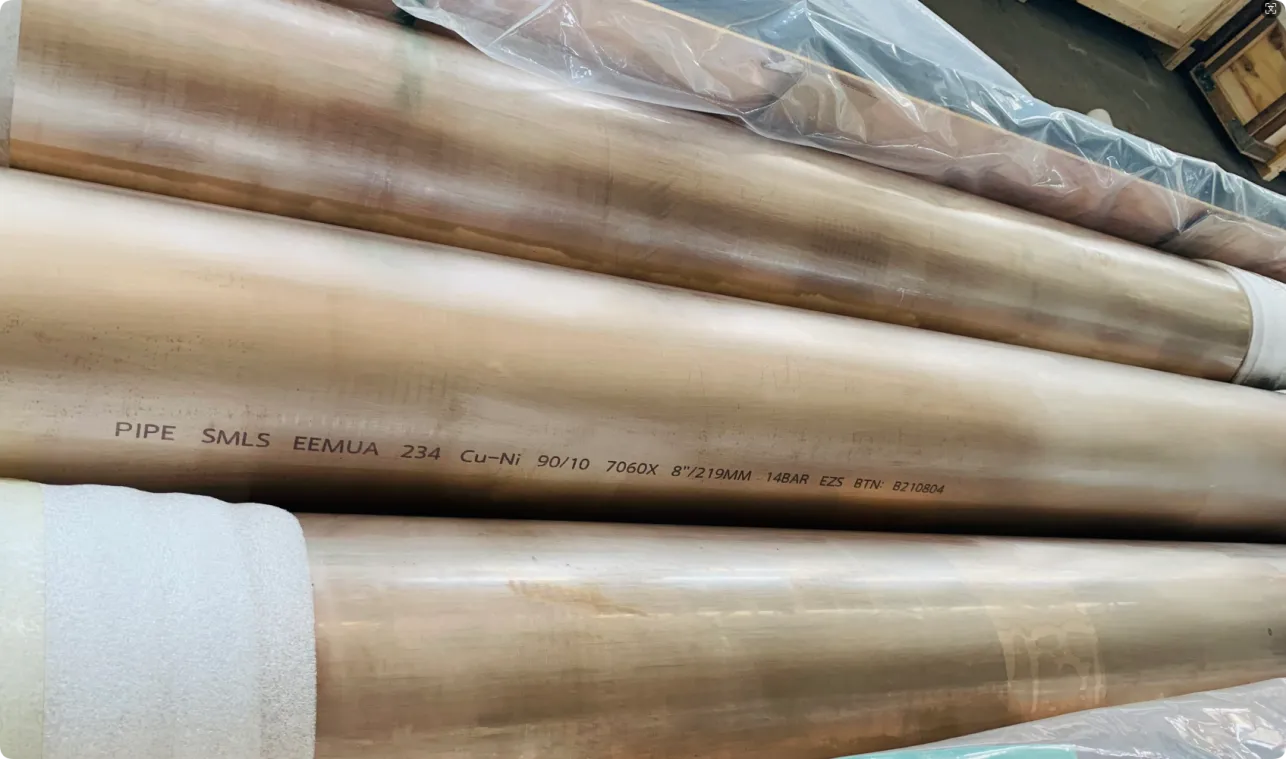
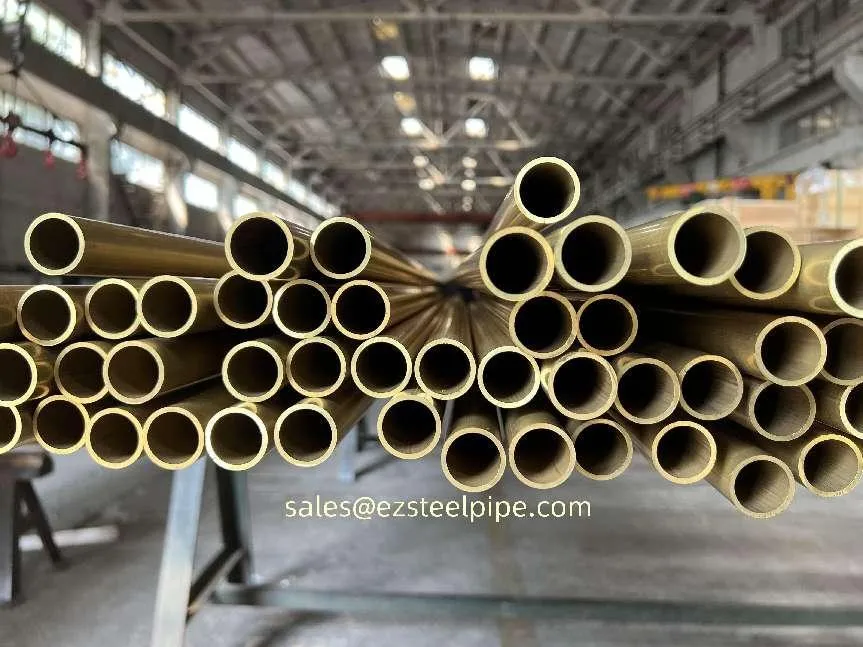
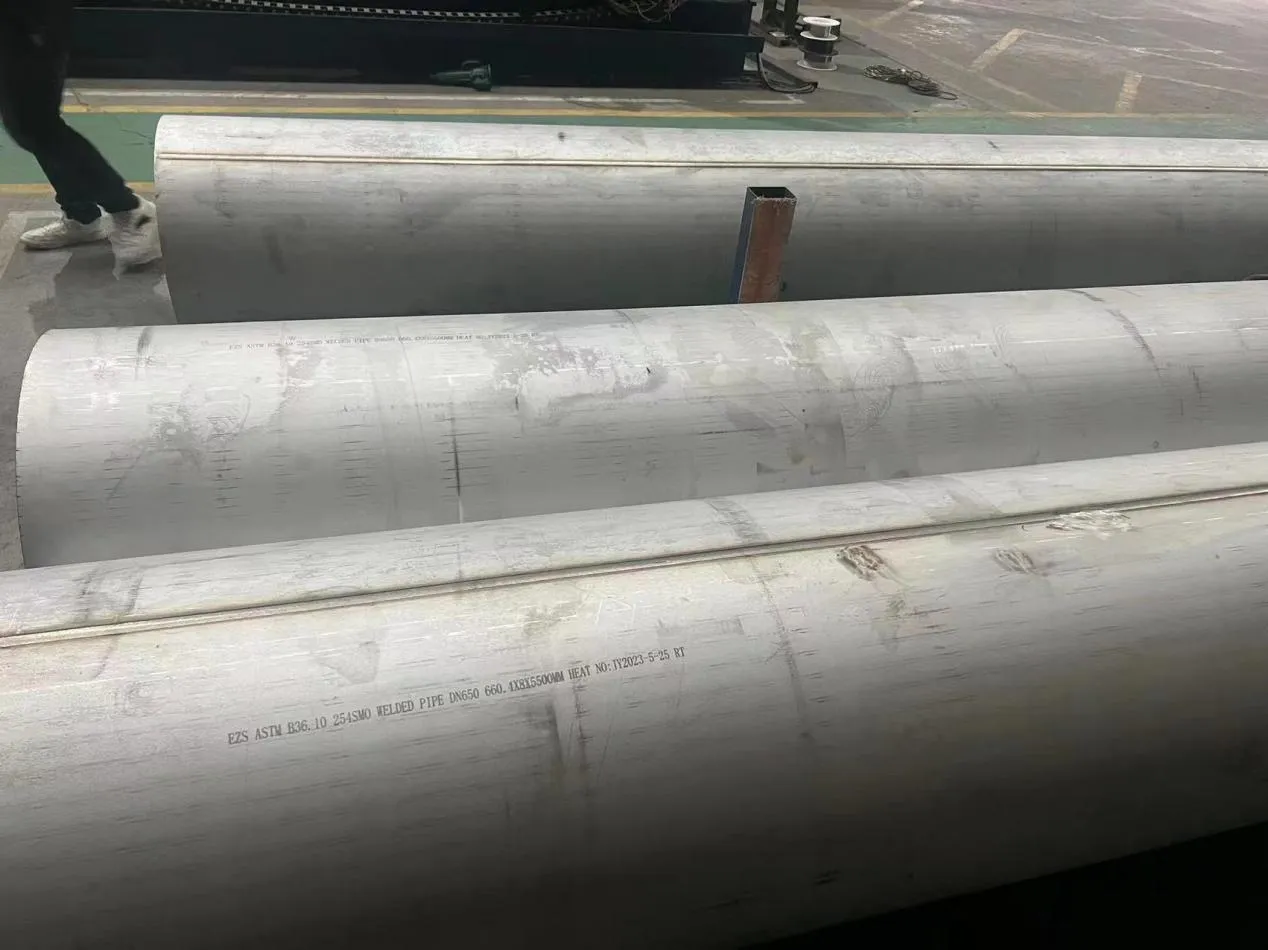
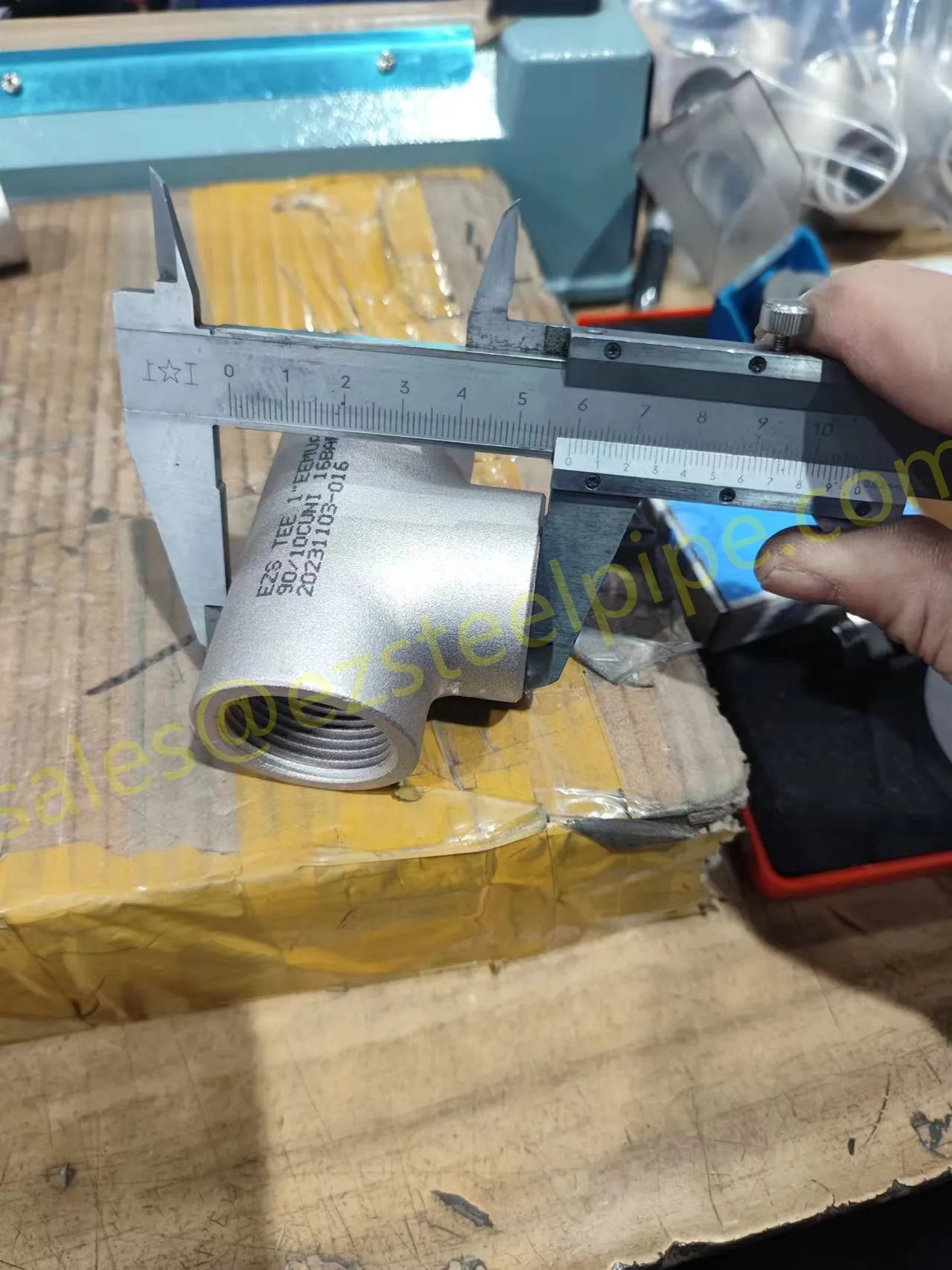
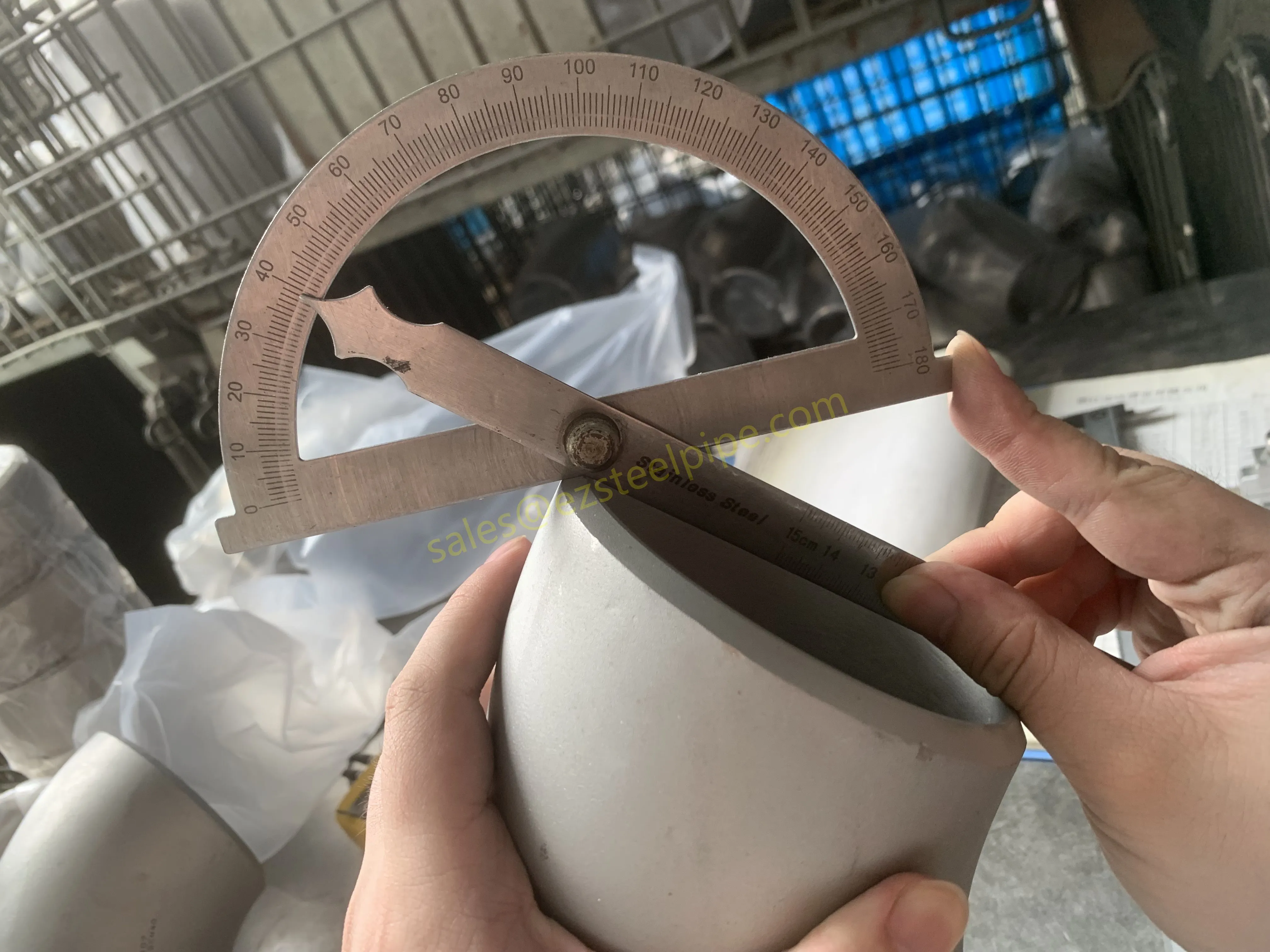
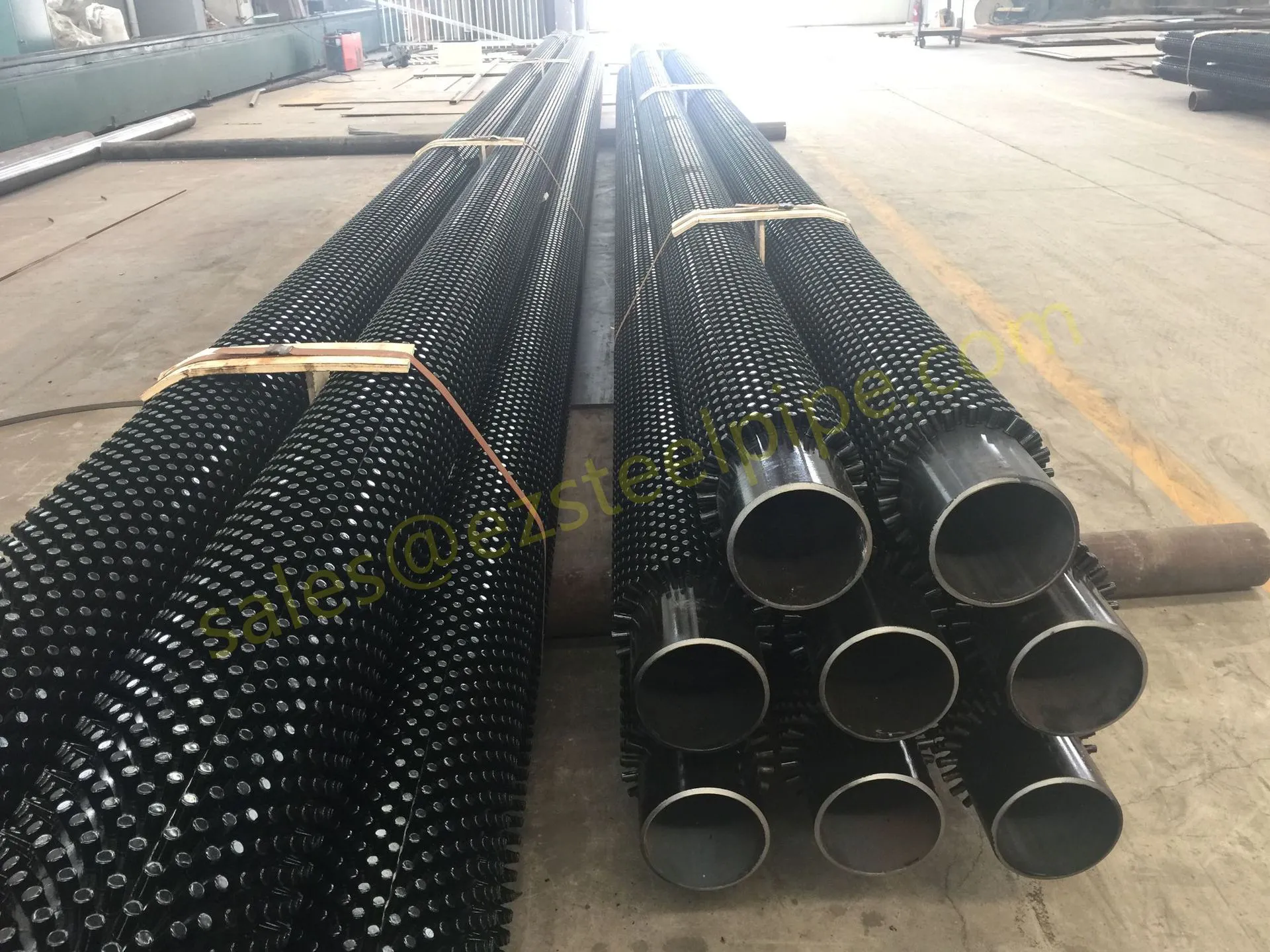
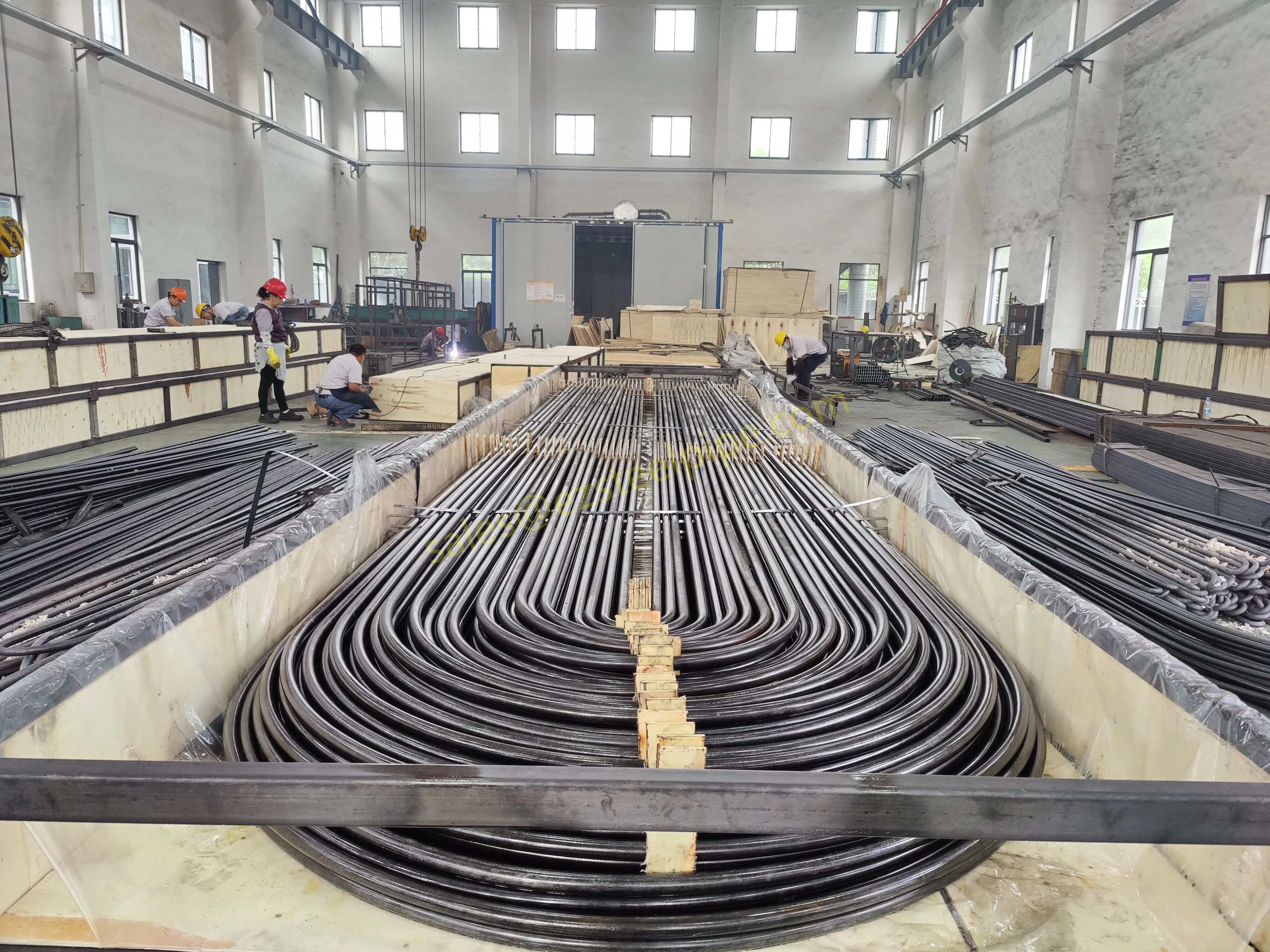
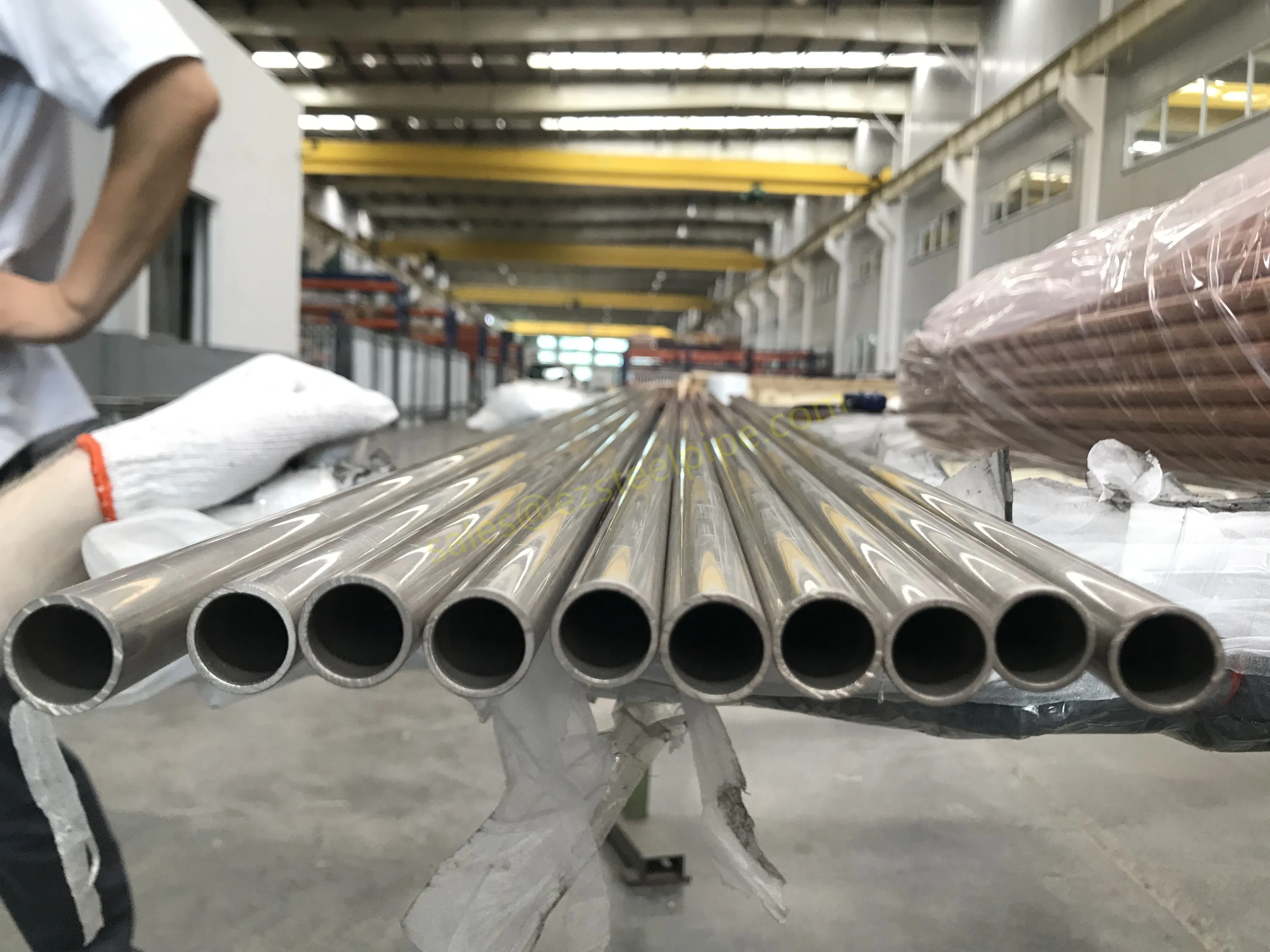
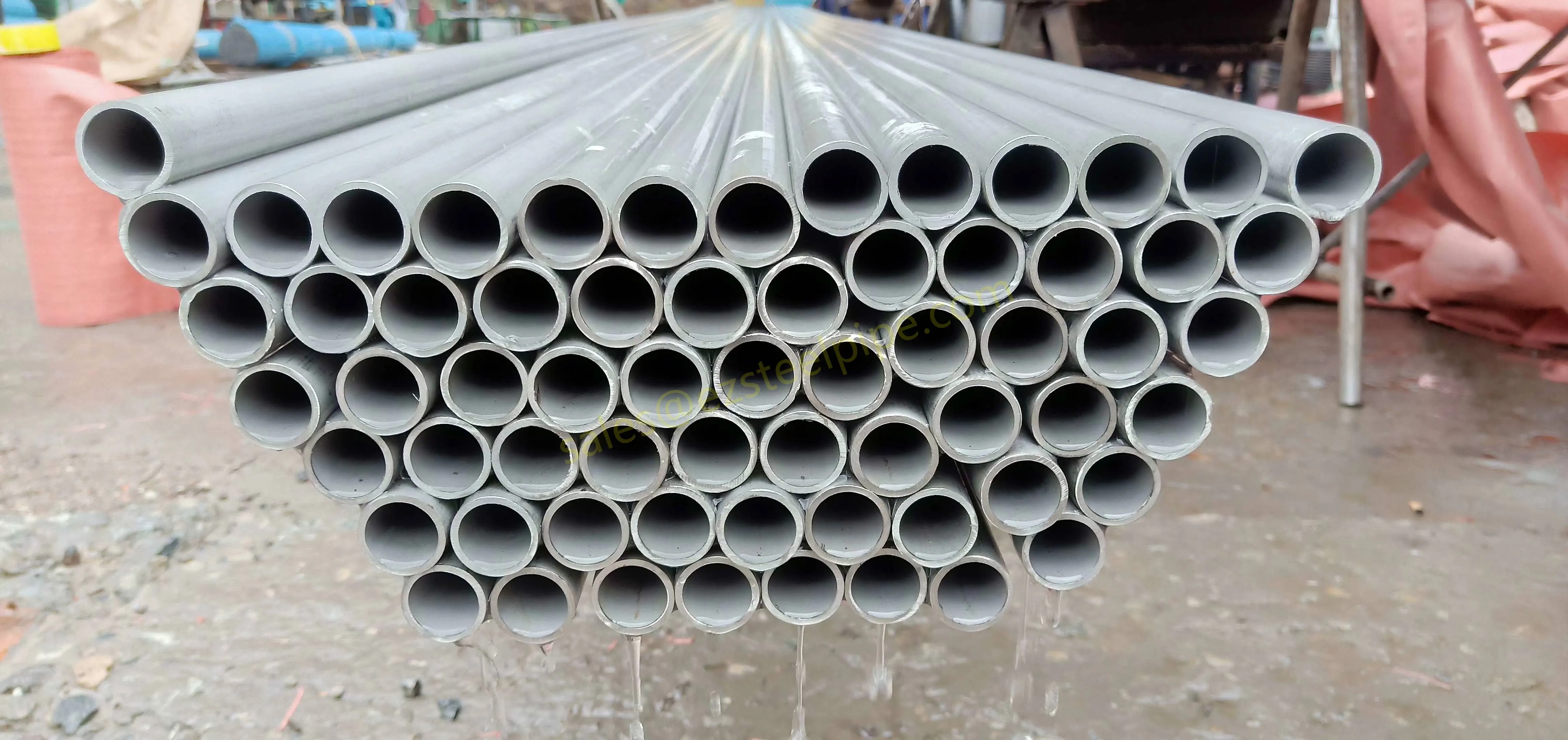
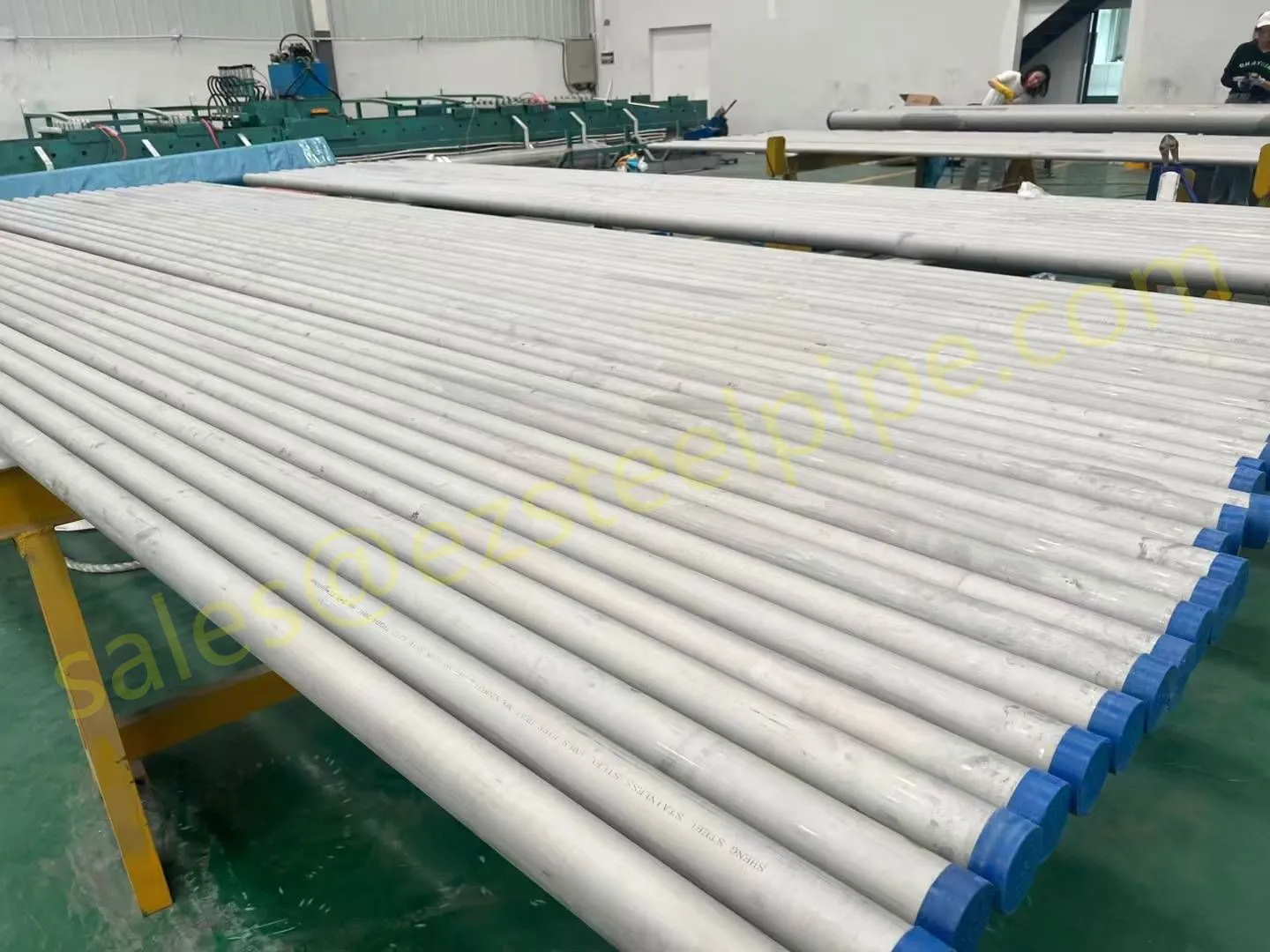
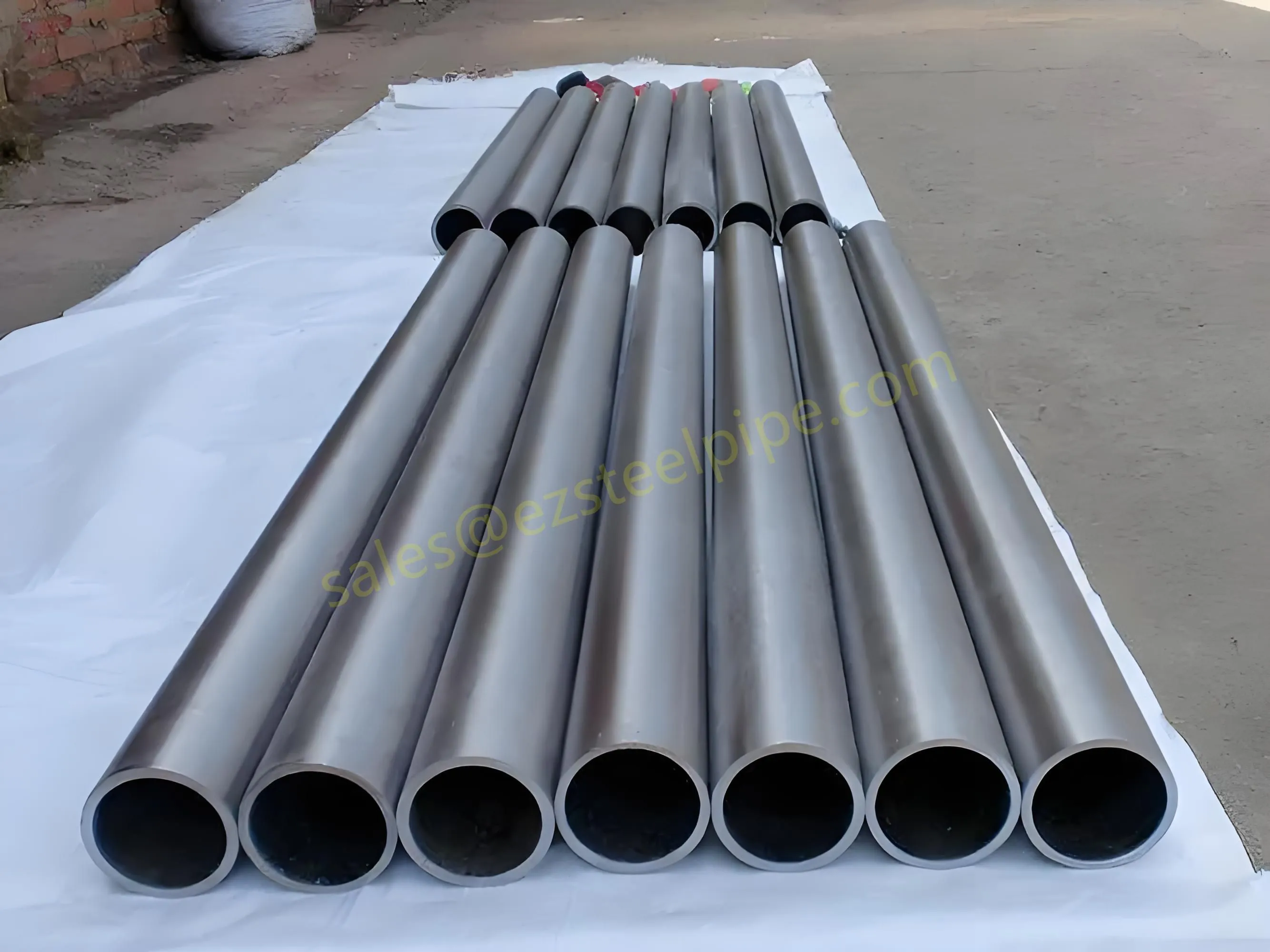
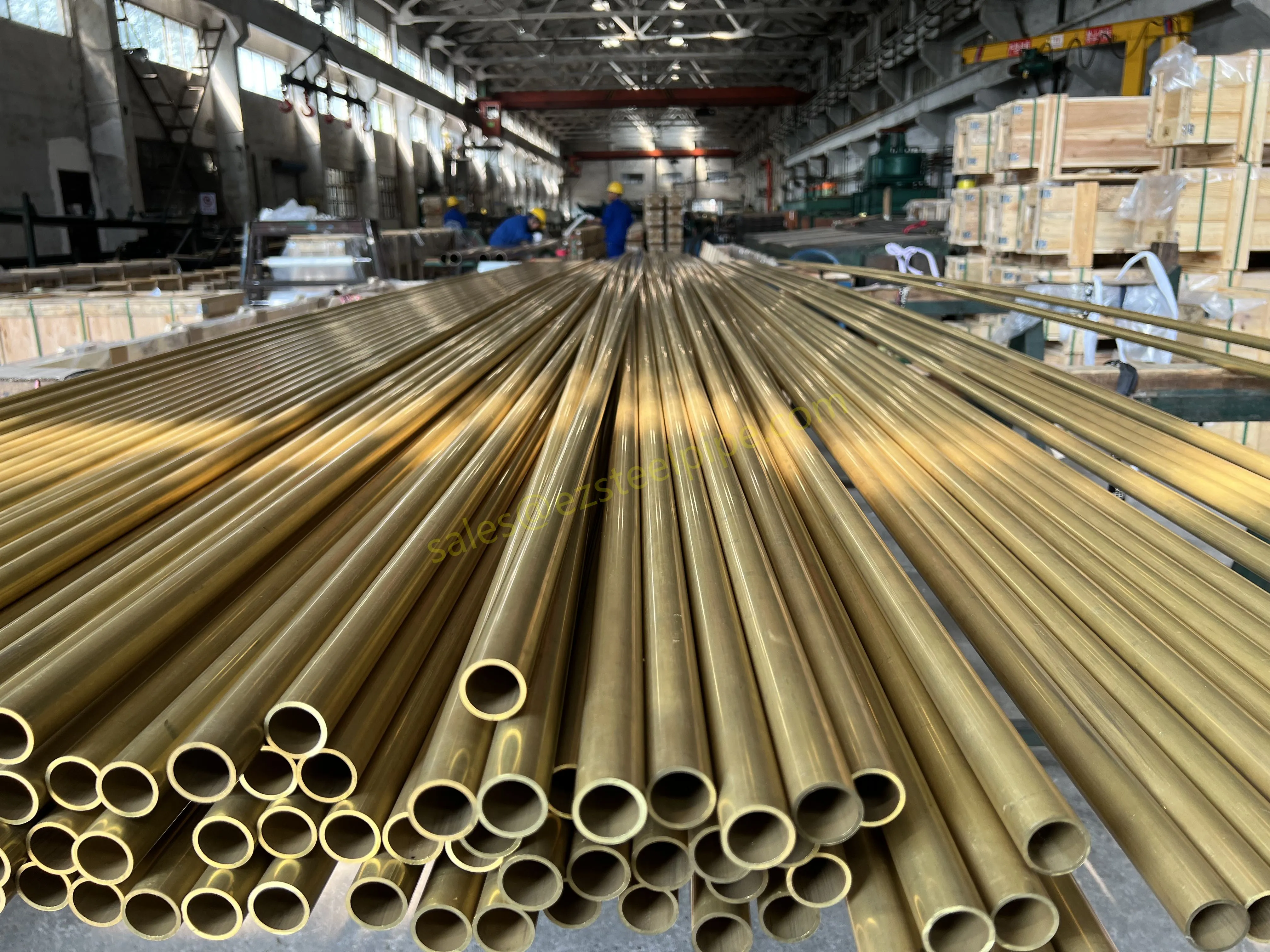
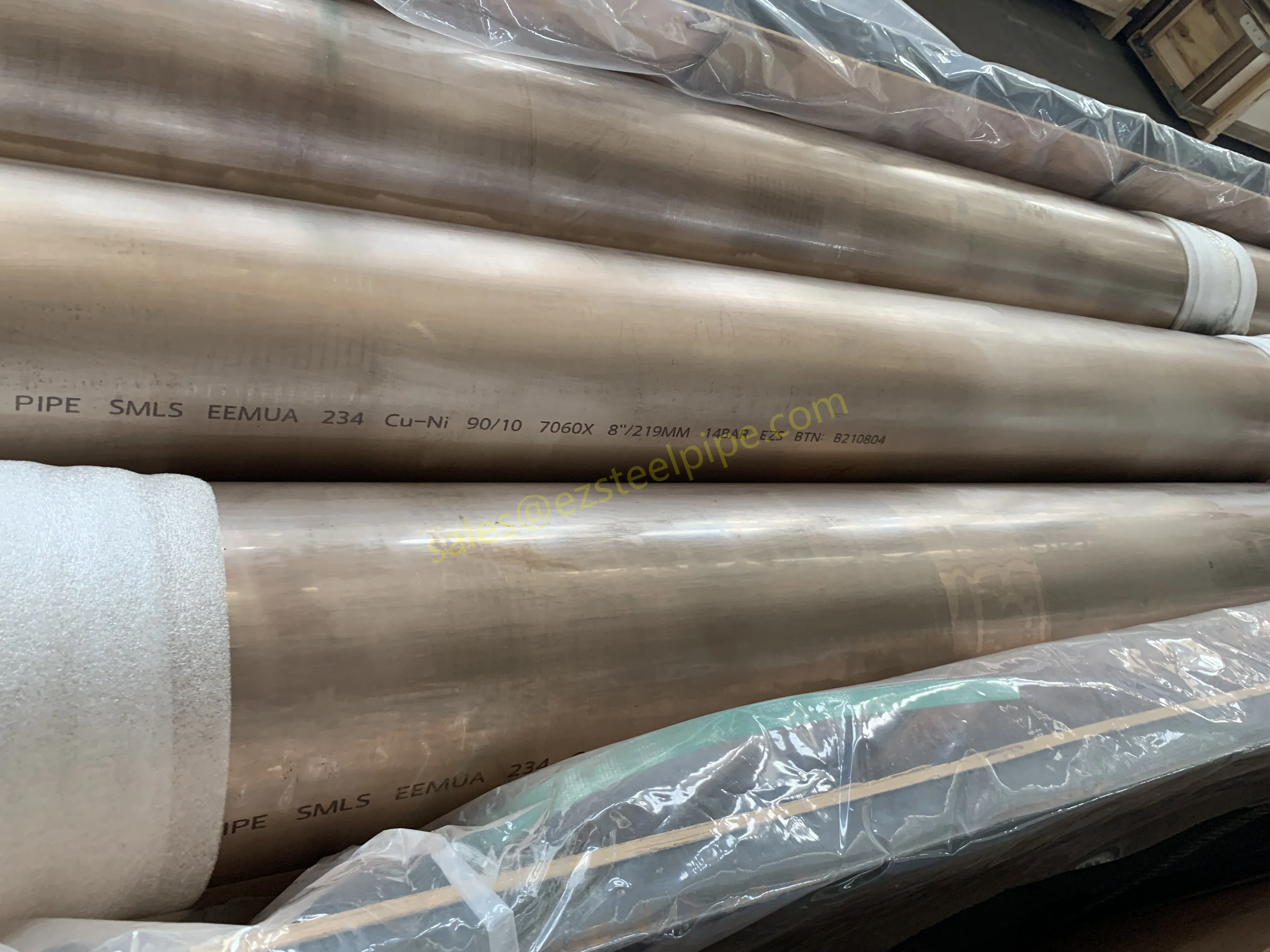
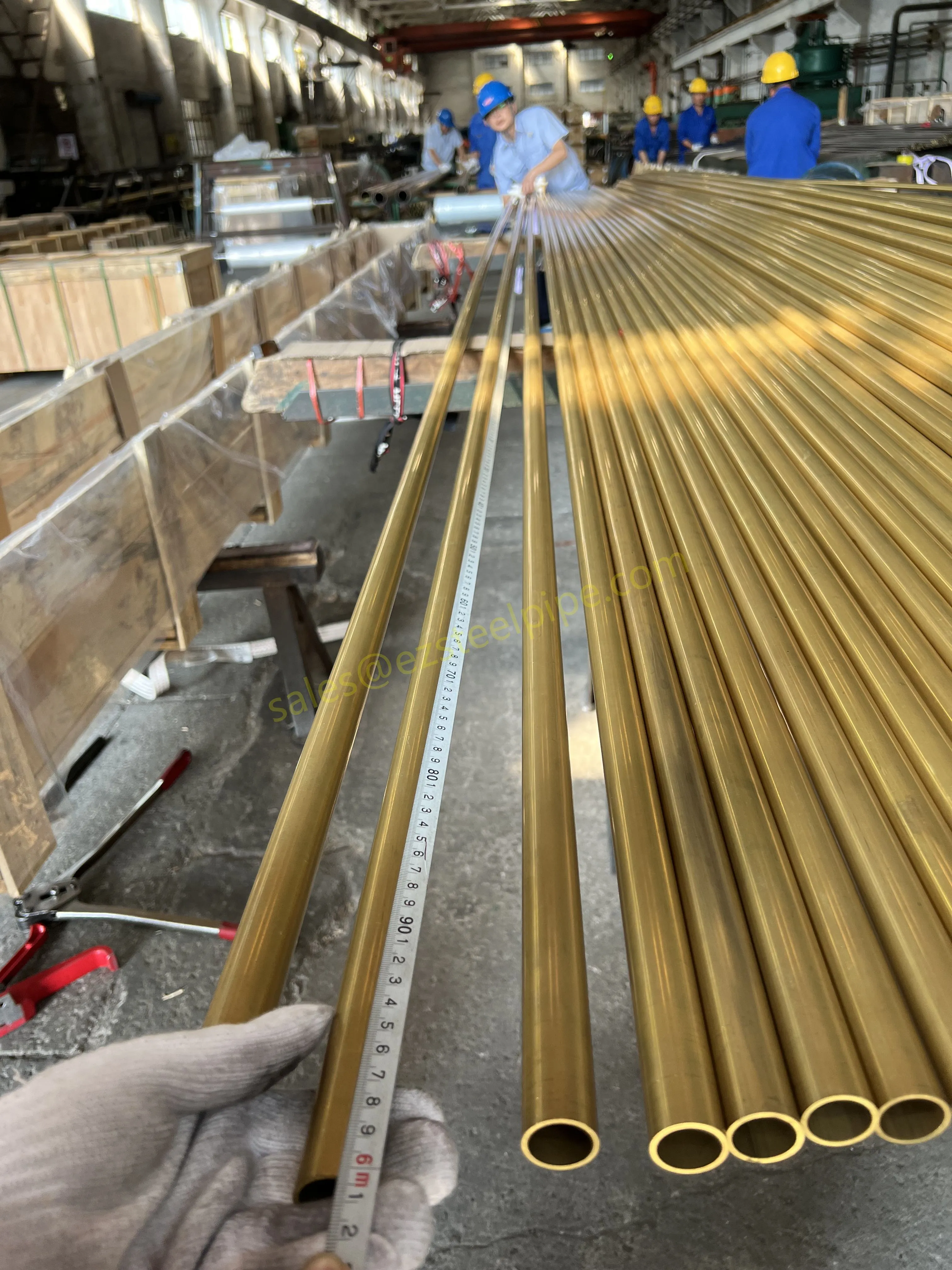
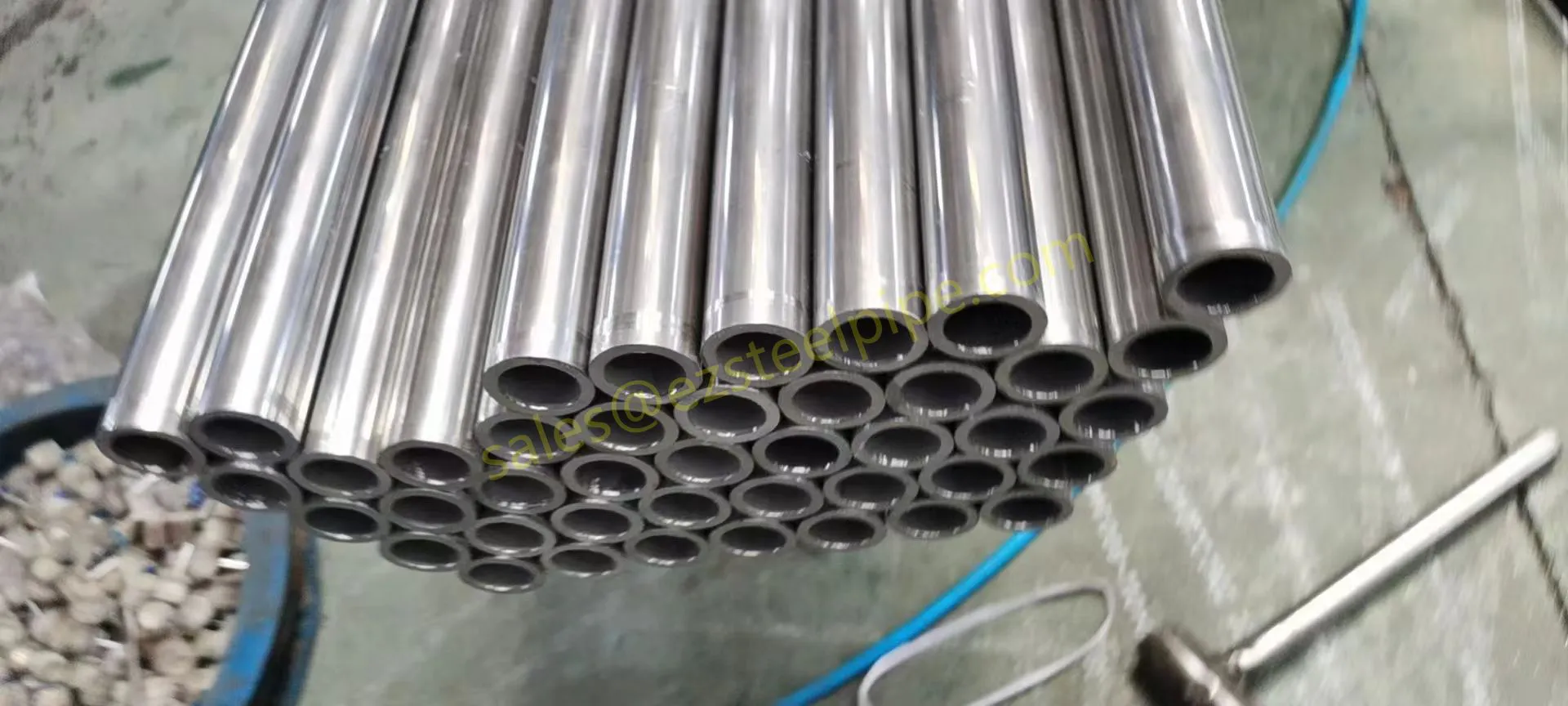
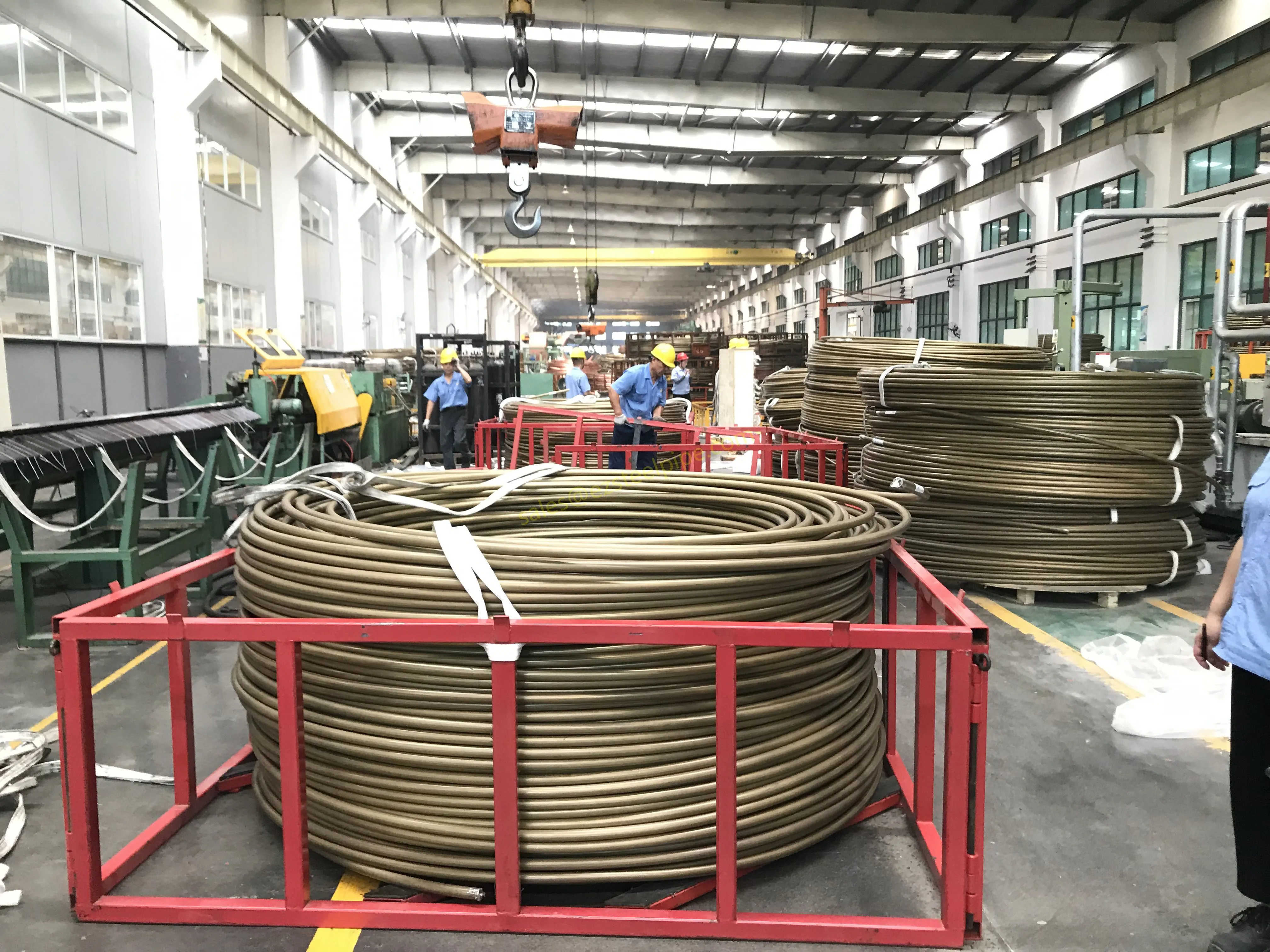
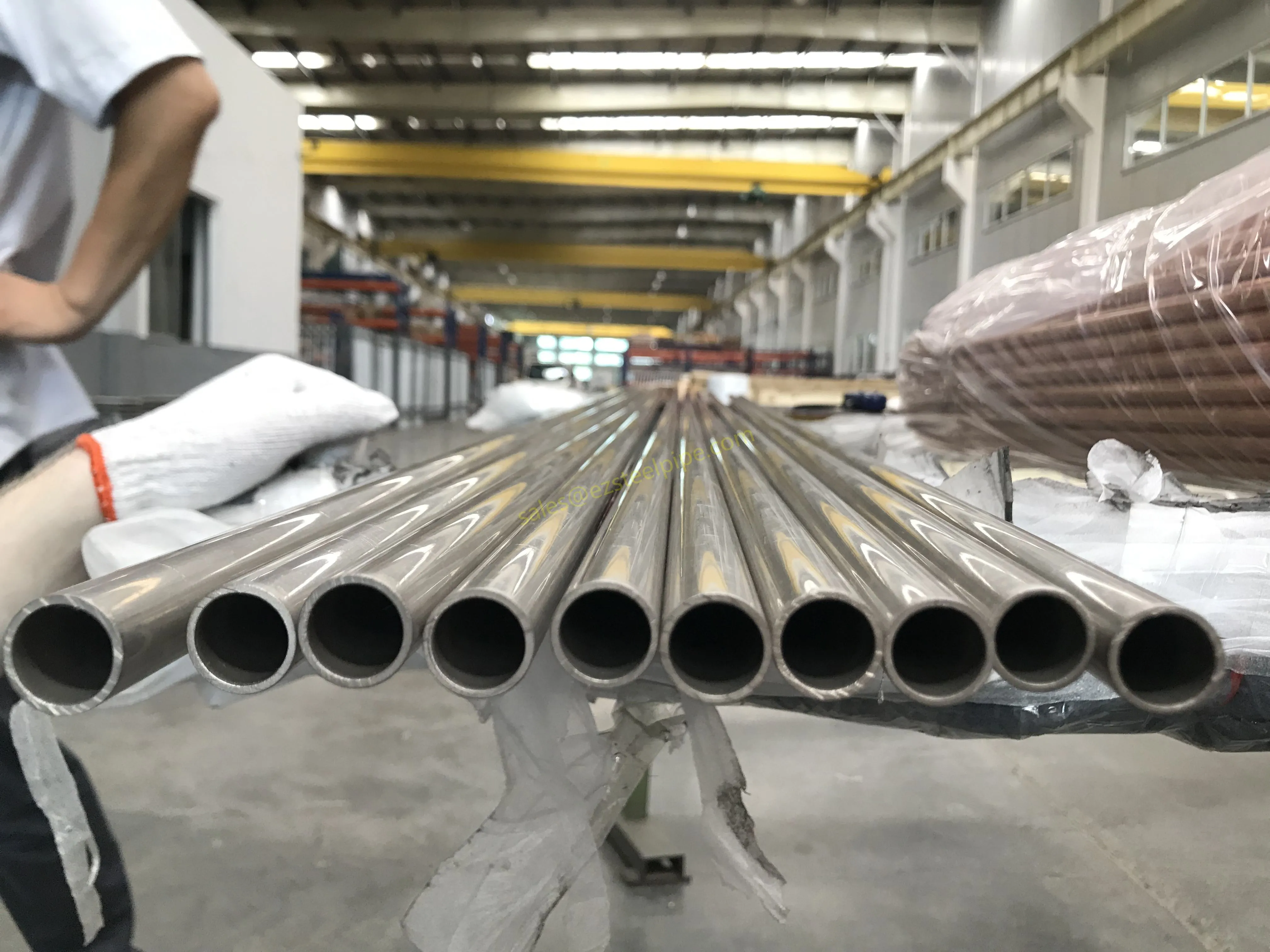
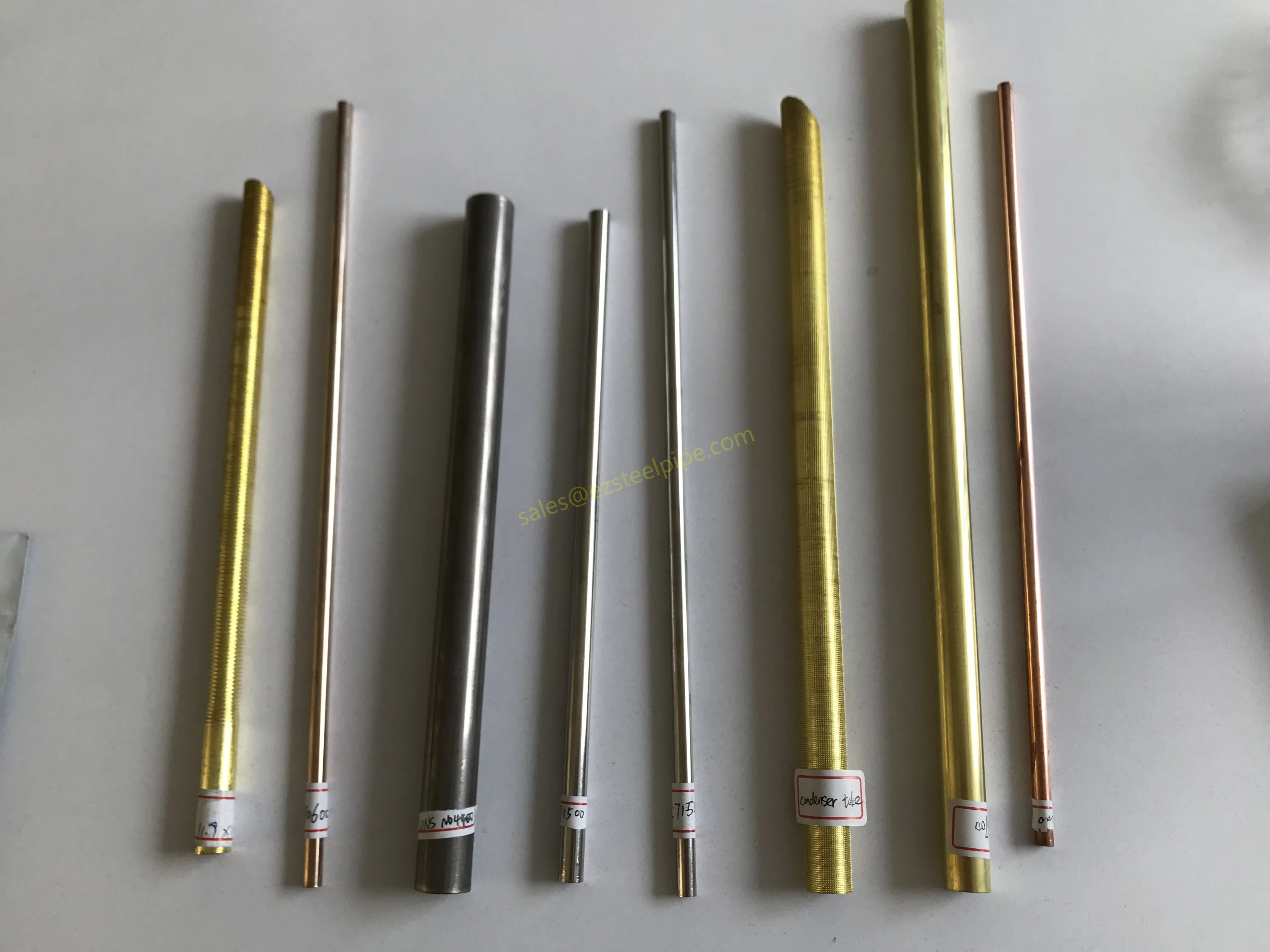
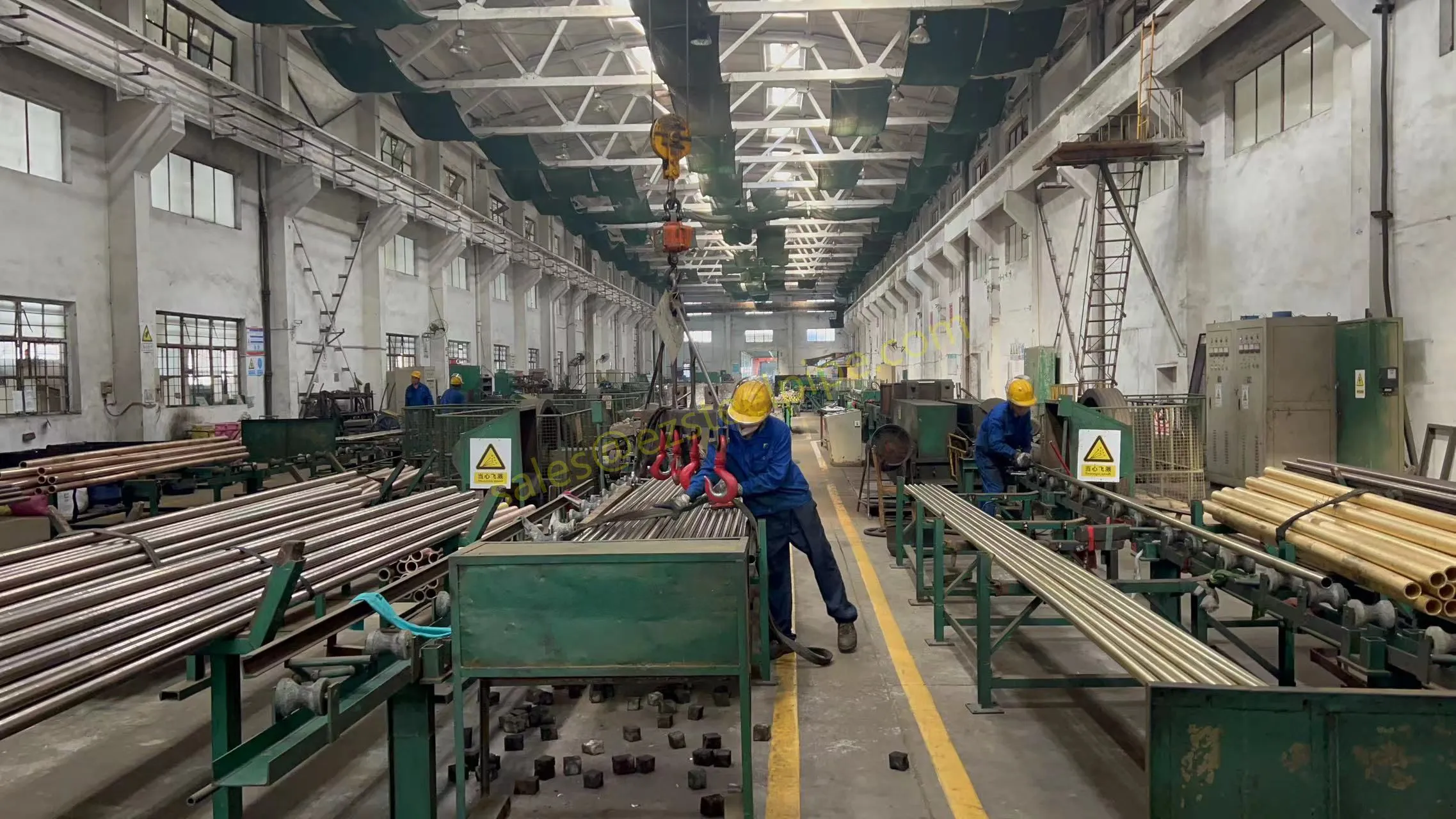
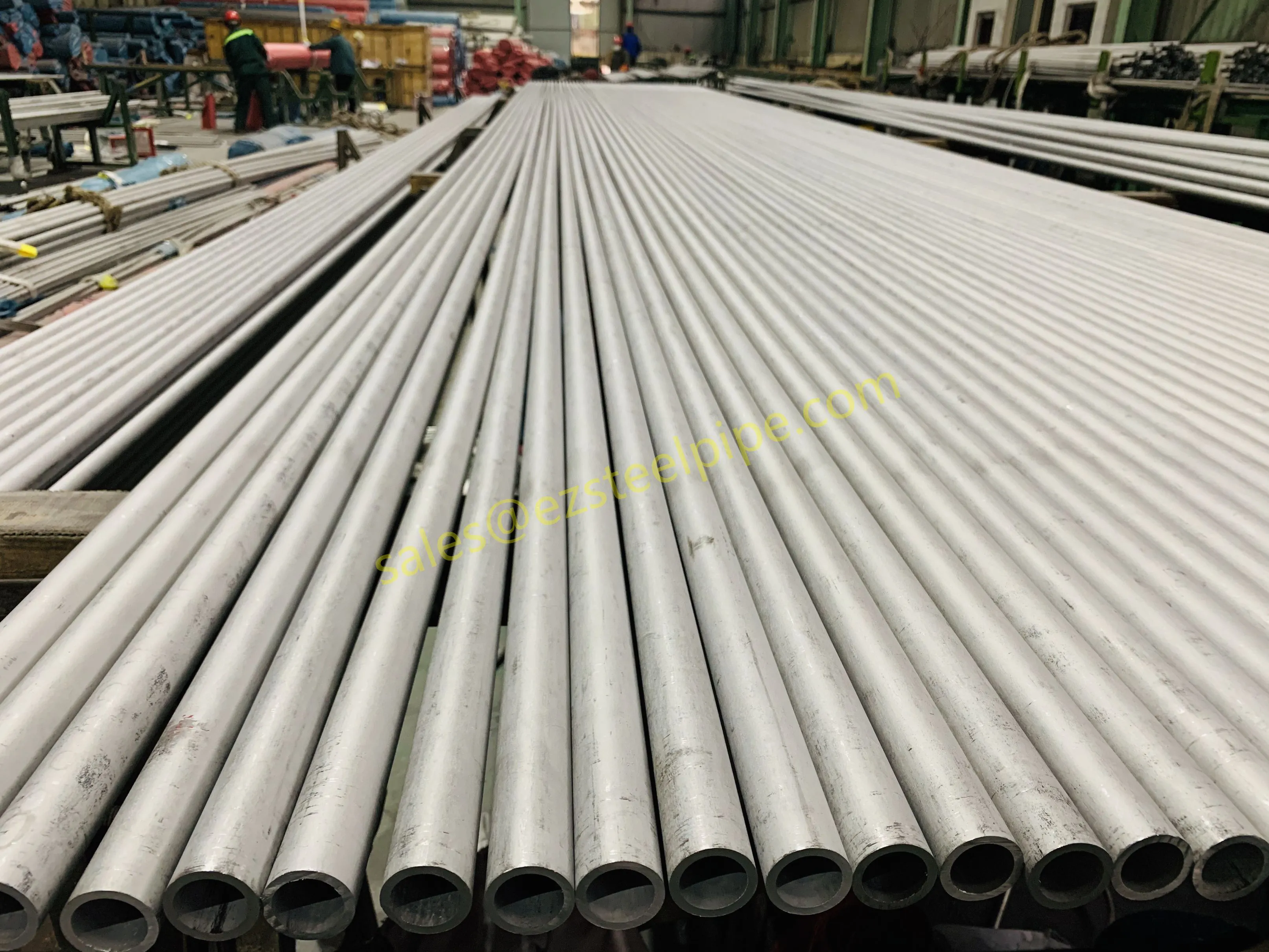
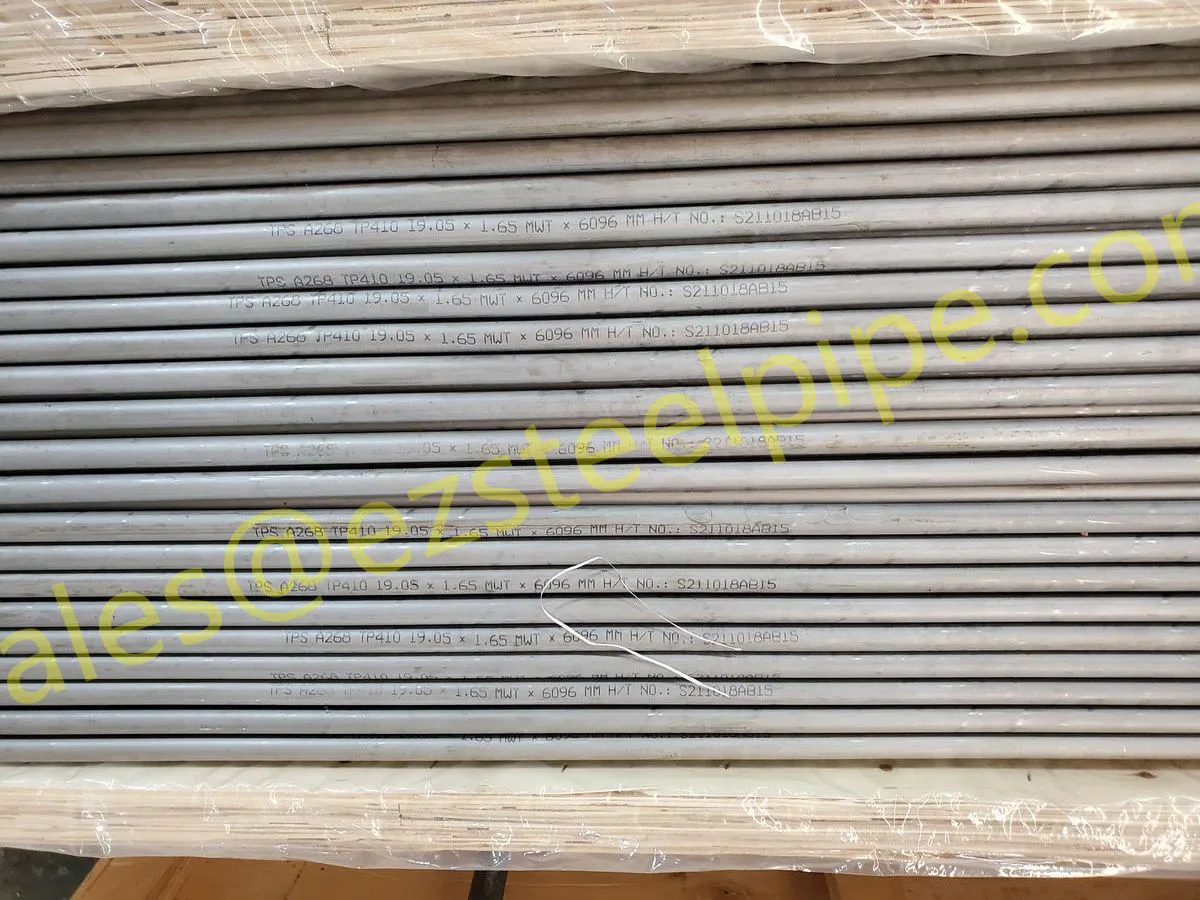
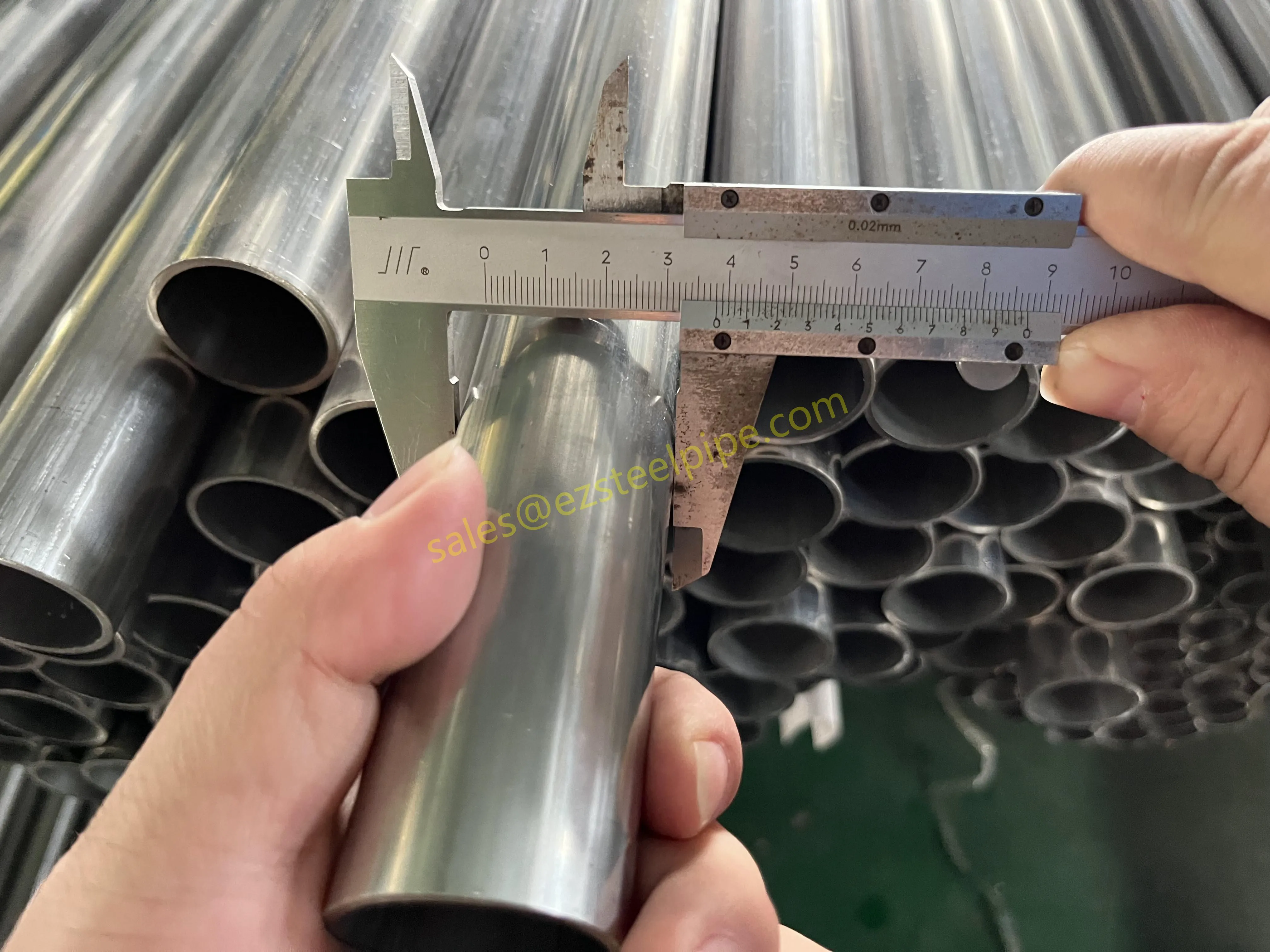
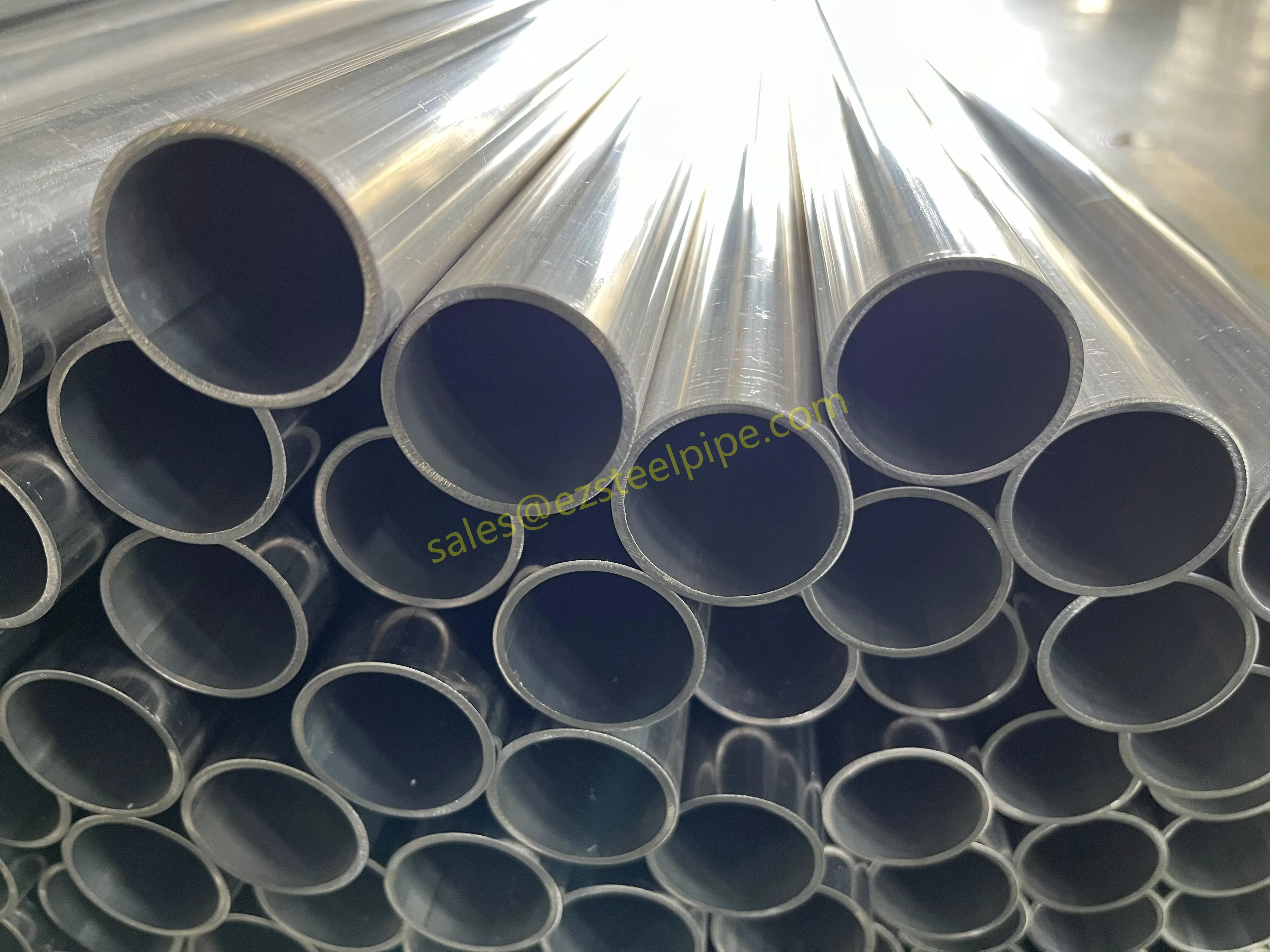
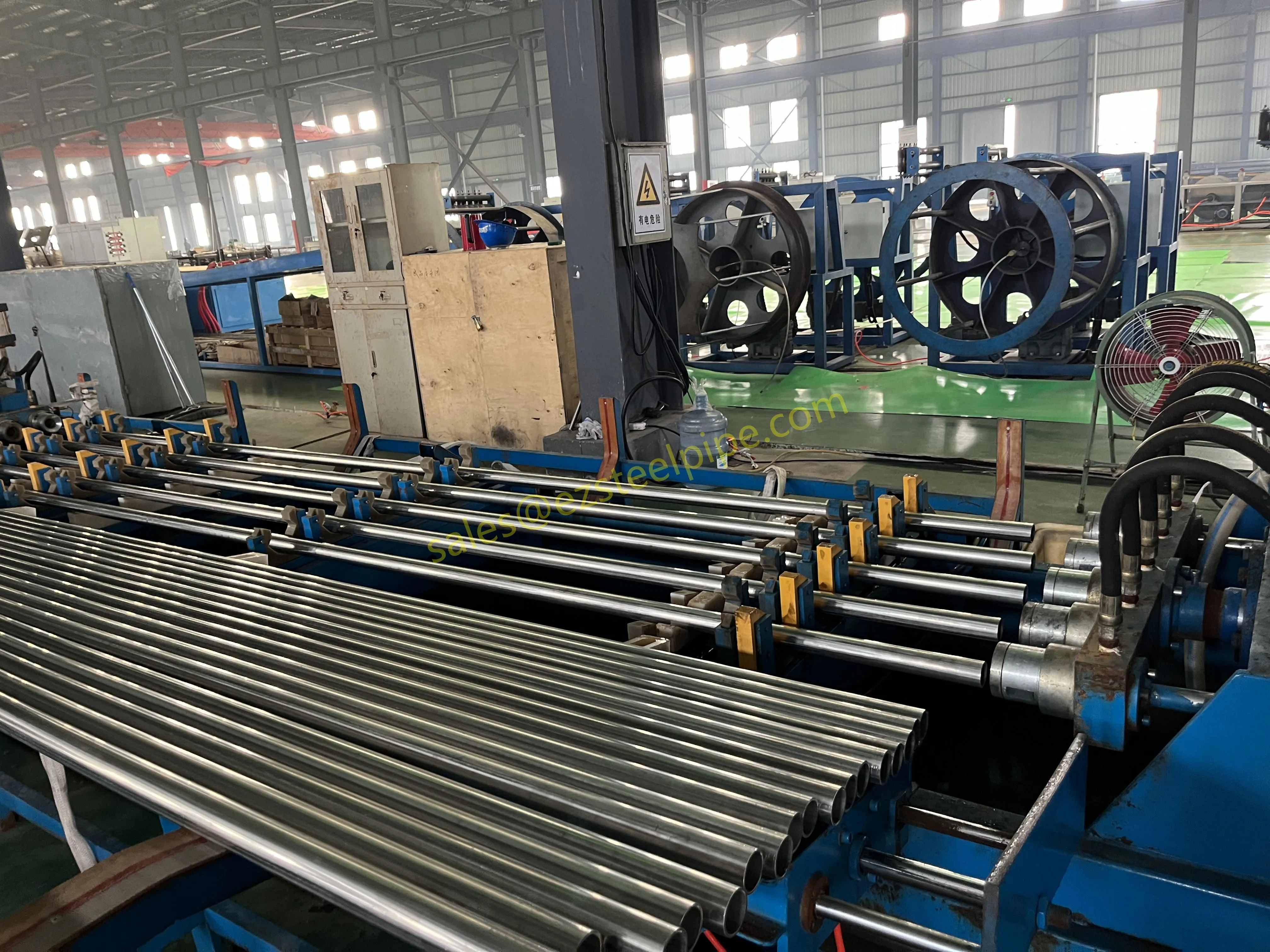
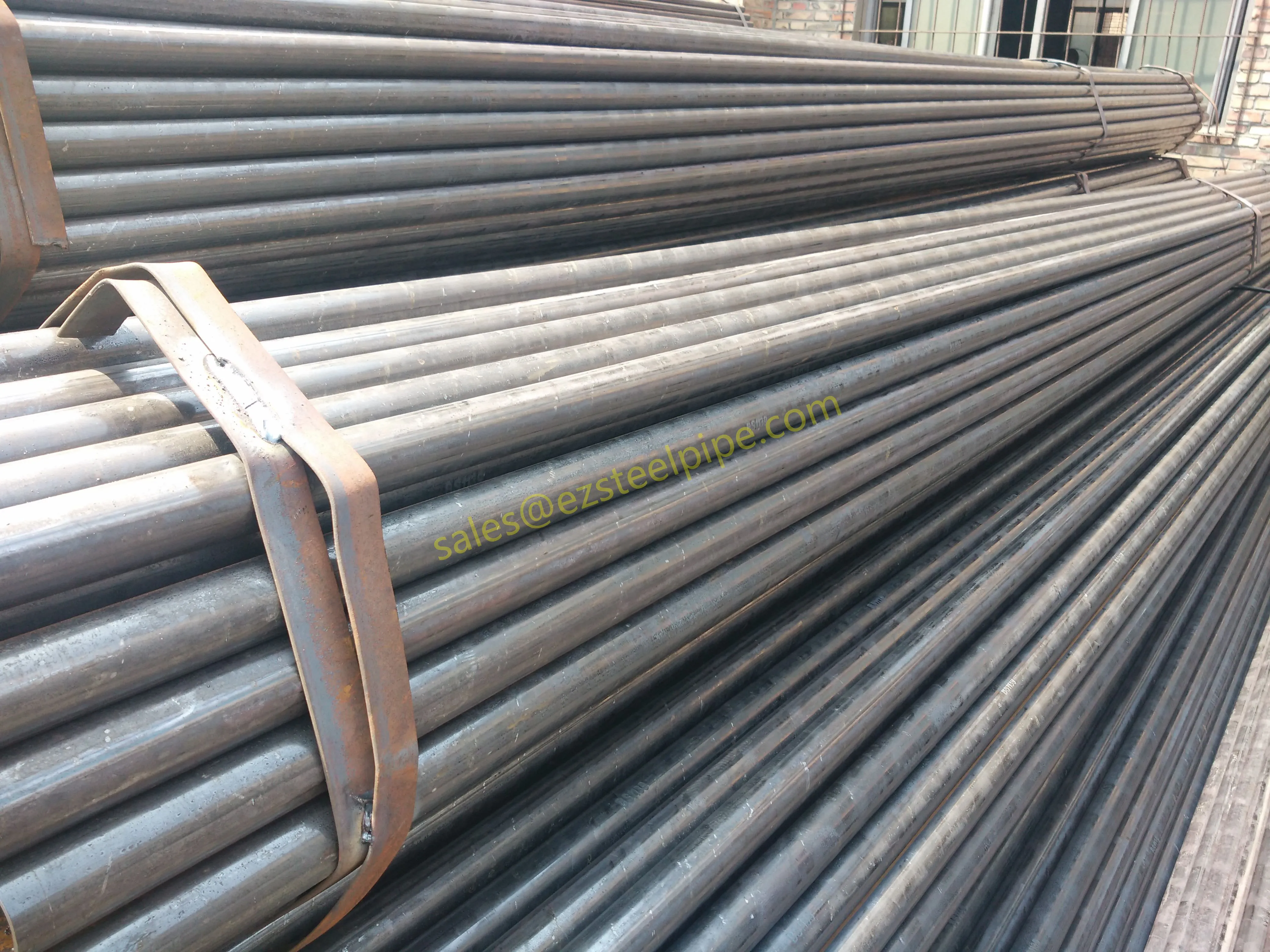
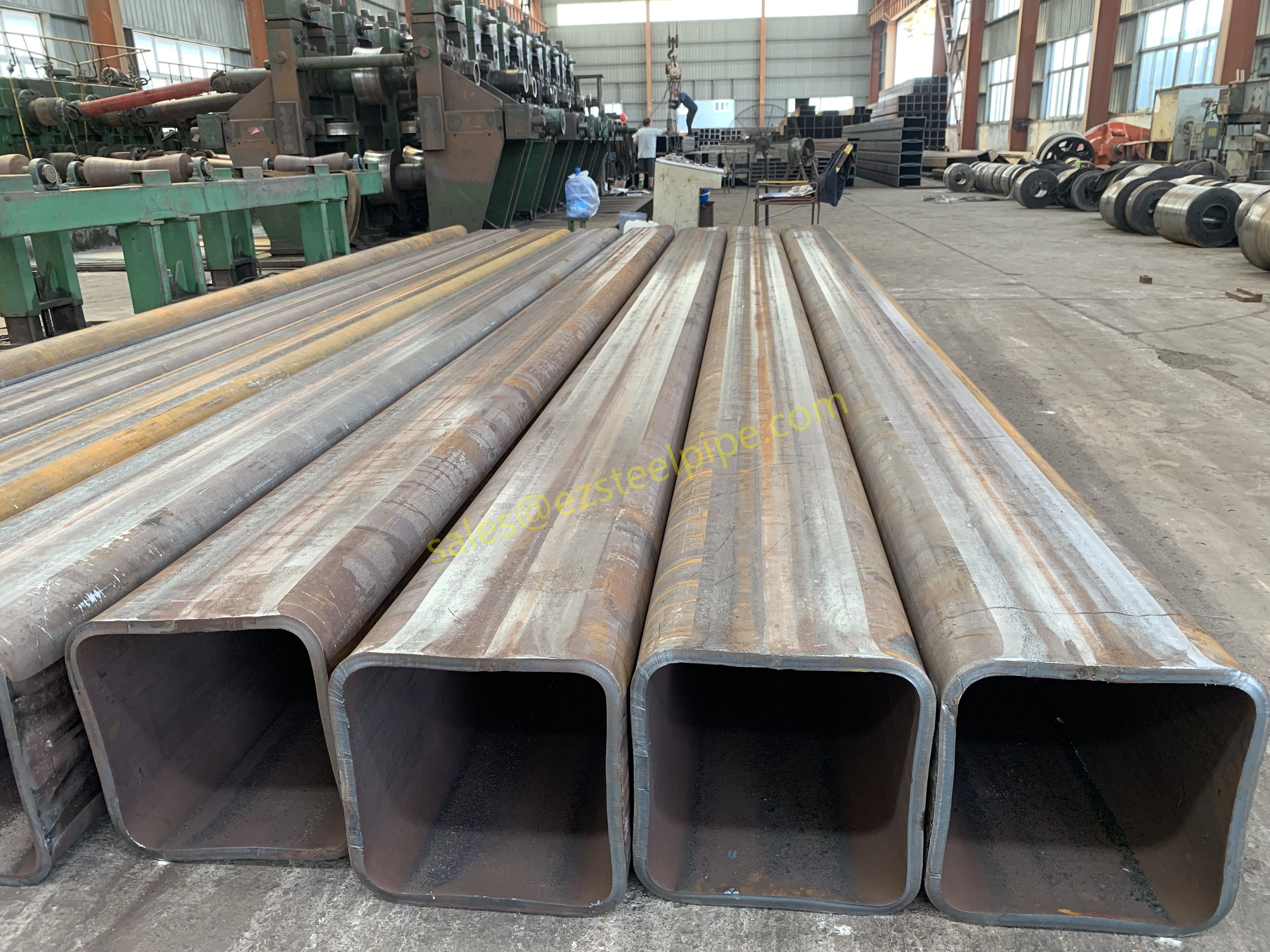
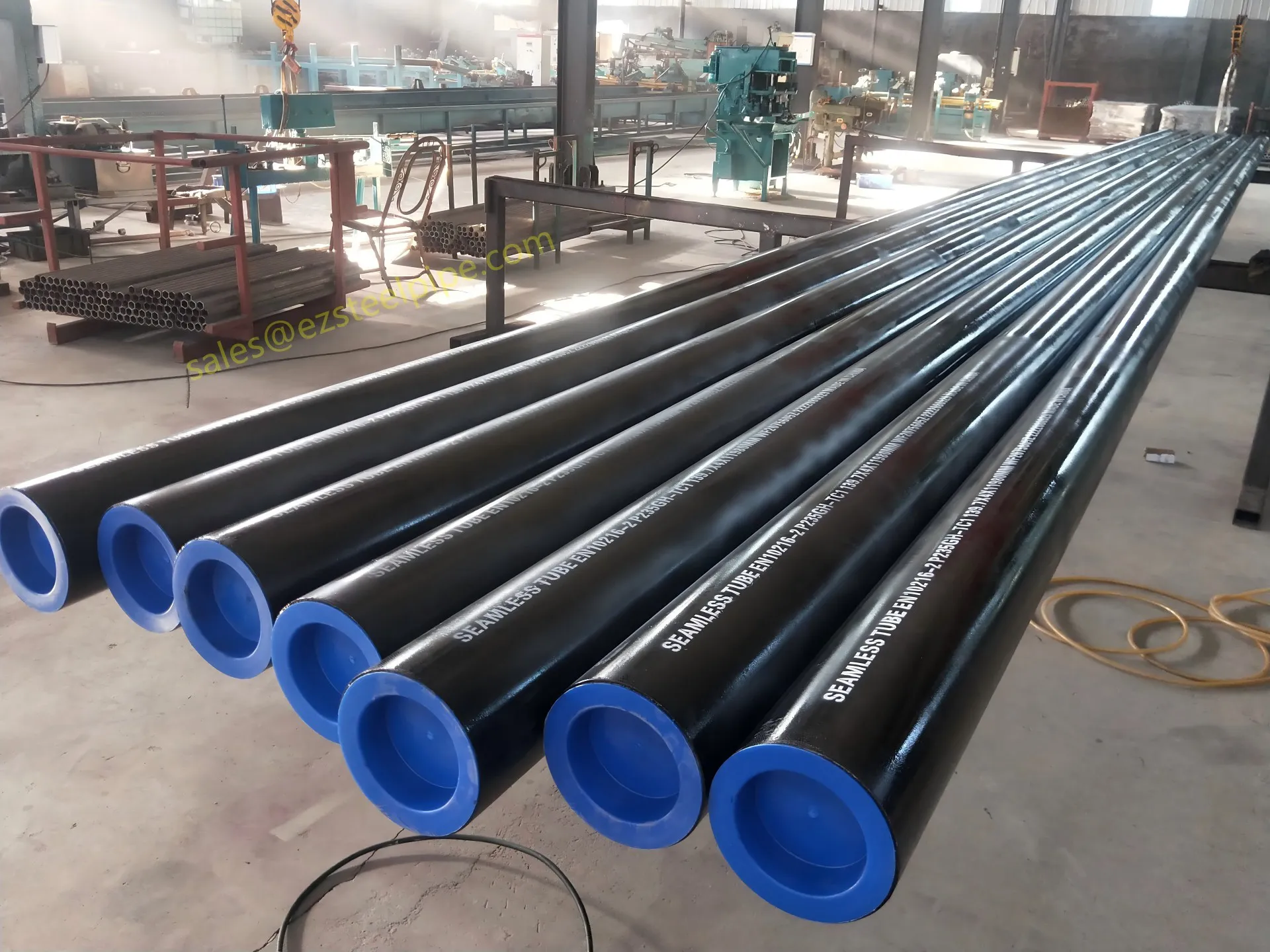
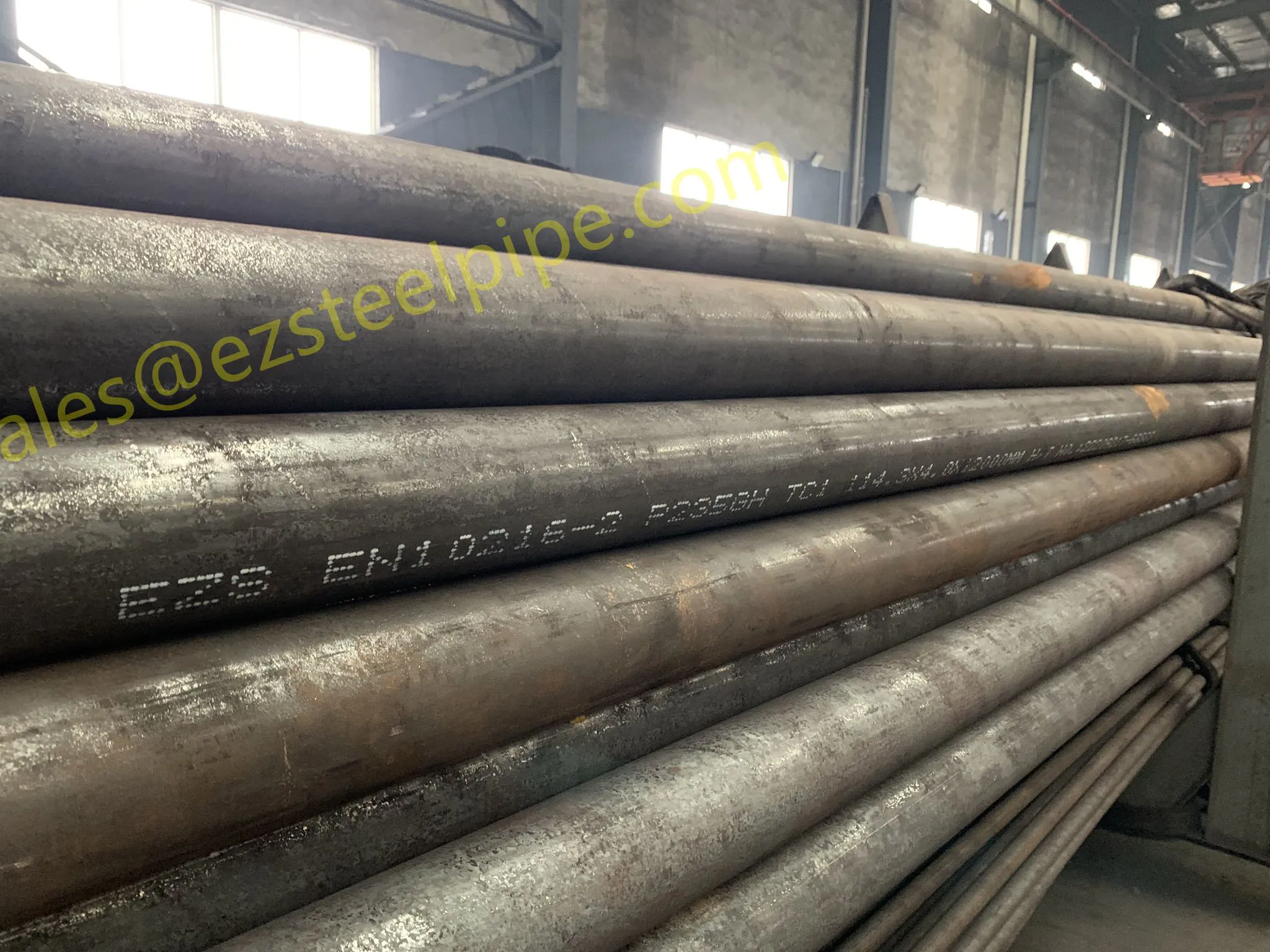
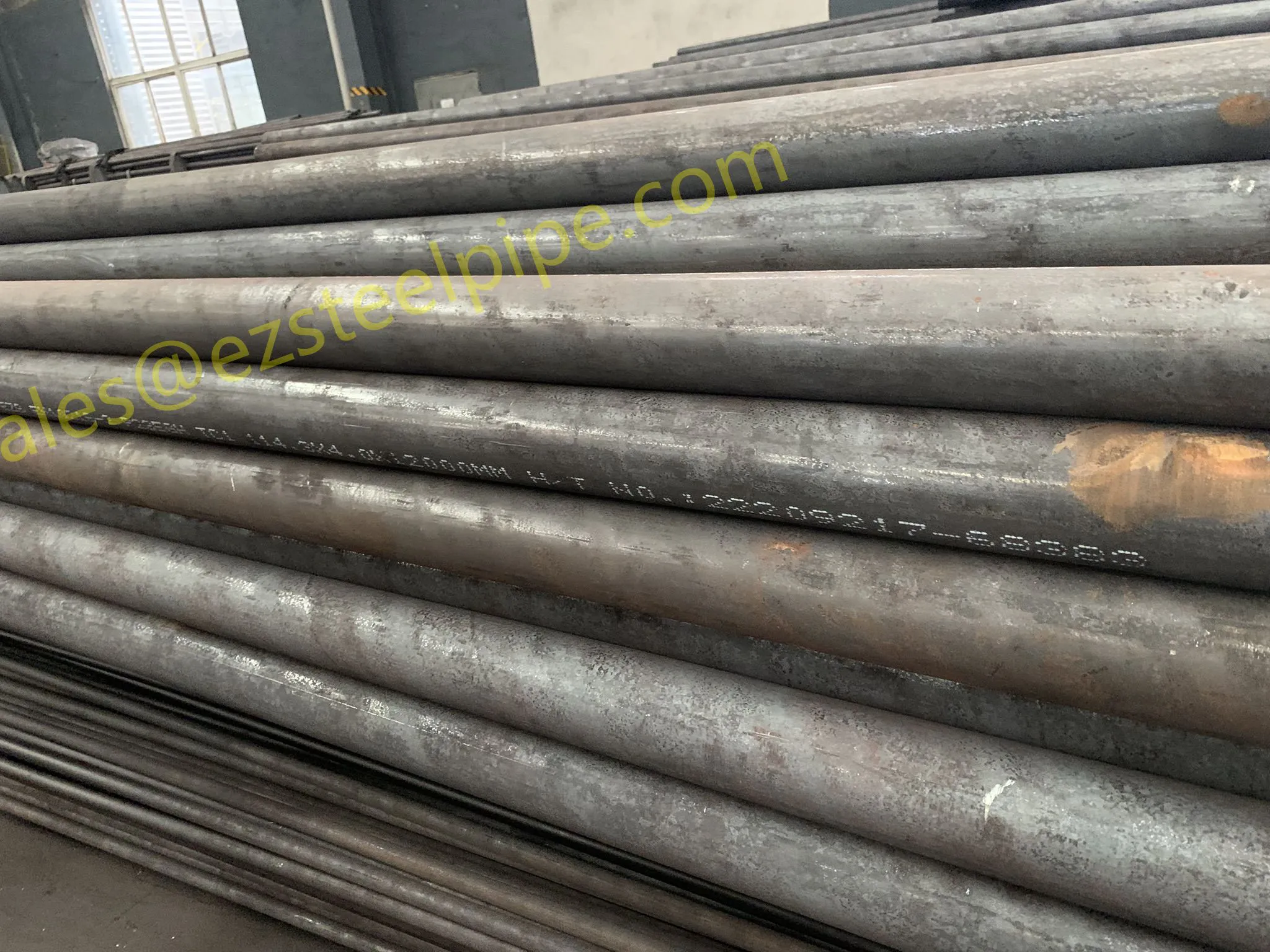
Nuclear power plants stand as beacons of clean, reliable energy, powering millions of homes and businesses while reducing carbon footprints. Yet, behind their towering reactors and humming turbines lies a network of components working tirelessly to ensure safety and efficiency. Among these, heat exchanger tubes are the unsung heroes—quietly transferring heat, withstanding extreme conditions, and acting as a critical barrier between radioactive materials and the environment. In nuclear facilities, where precision and durability are non-negotiable, these tubes are not just metal; they are guardians of public safety and energy stability.
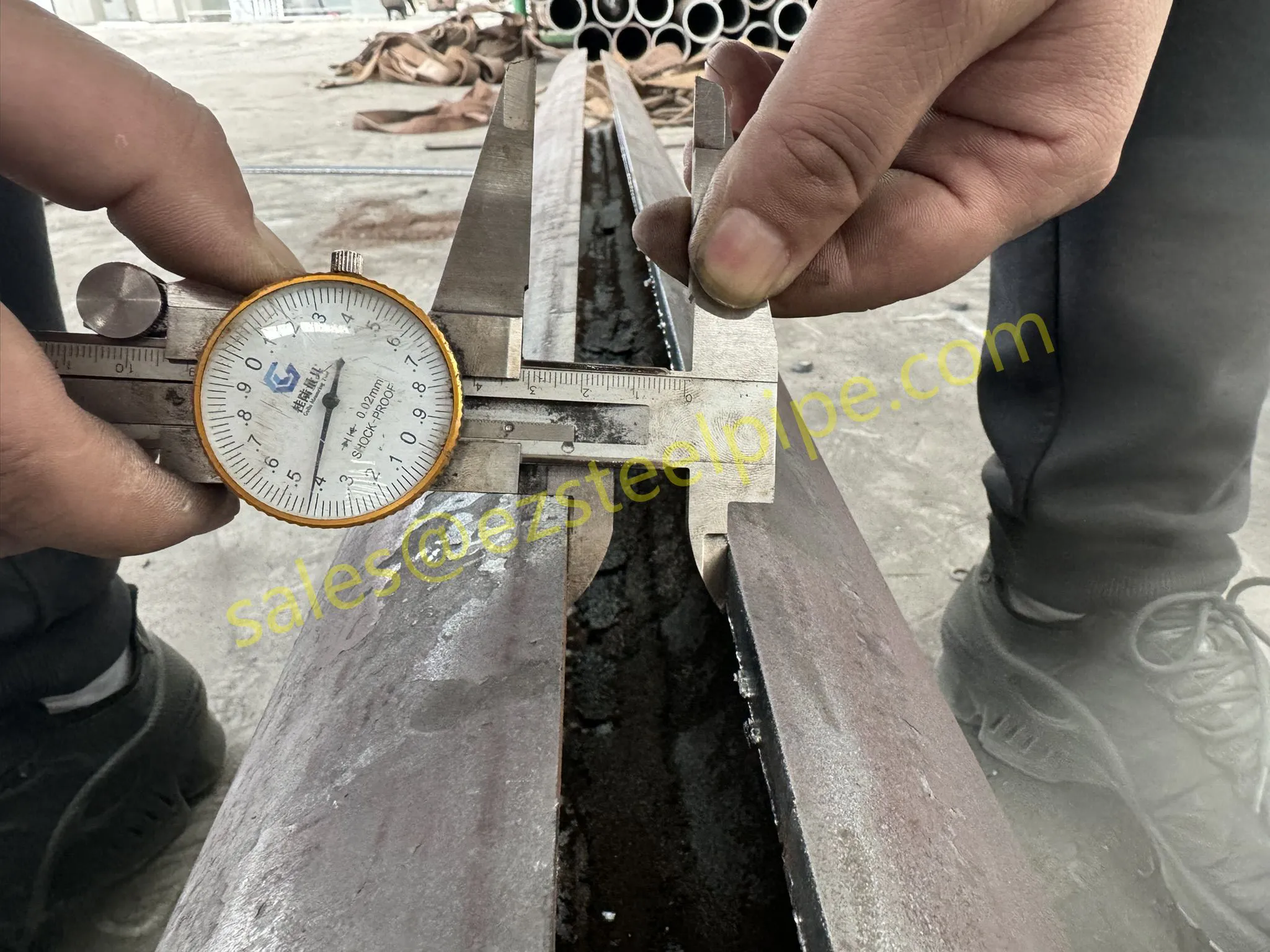
Consider the role of a heat exchanger in a nuclear plant: it's responsible for transferring heat from the reactor core to generate steam, which then drives turbines to produce electricity. This process demands tubes that can handle intense heat, high pressure, and constant exposure to radiation—all while maintaining structural integrity for decades. The stakes couldn't be higher: a single flaw in these tubes could compromise the entire system, risking environmental contamination and endangering lives. That's why the design, materials, and manufacturing of these tubes are governed by some of the strictest standards in the industrial world.
In this article, we'll explore the world of heat exchanger tubes for nuclear power plants, focusing on two critical aspects: their ability to resist radiation and the rigorous safety standards that ensure their reliability. We'll dive into the materials that make this possible, the standards that guide their production, and the human expertise that brings these components to life. Because when it comes to nuclear energy, every detail matters—and these tubes are where precision meets purpose.
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































