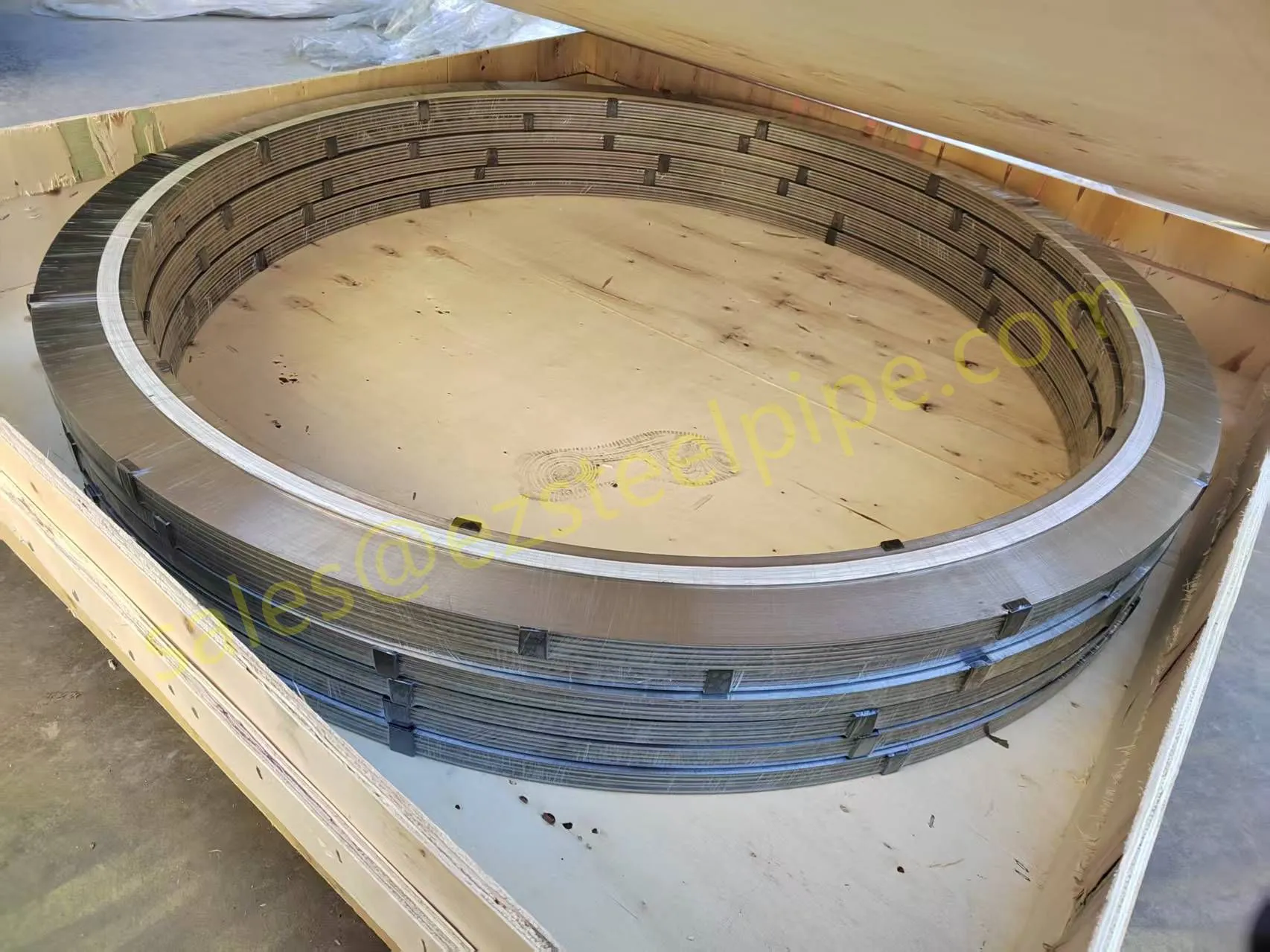
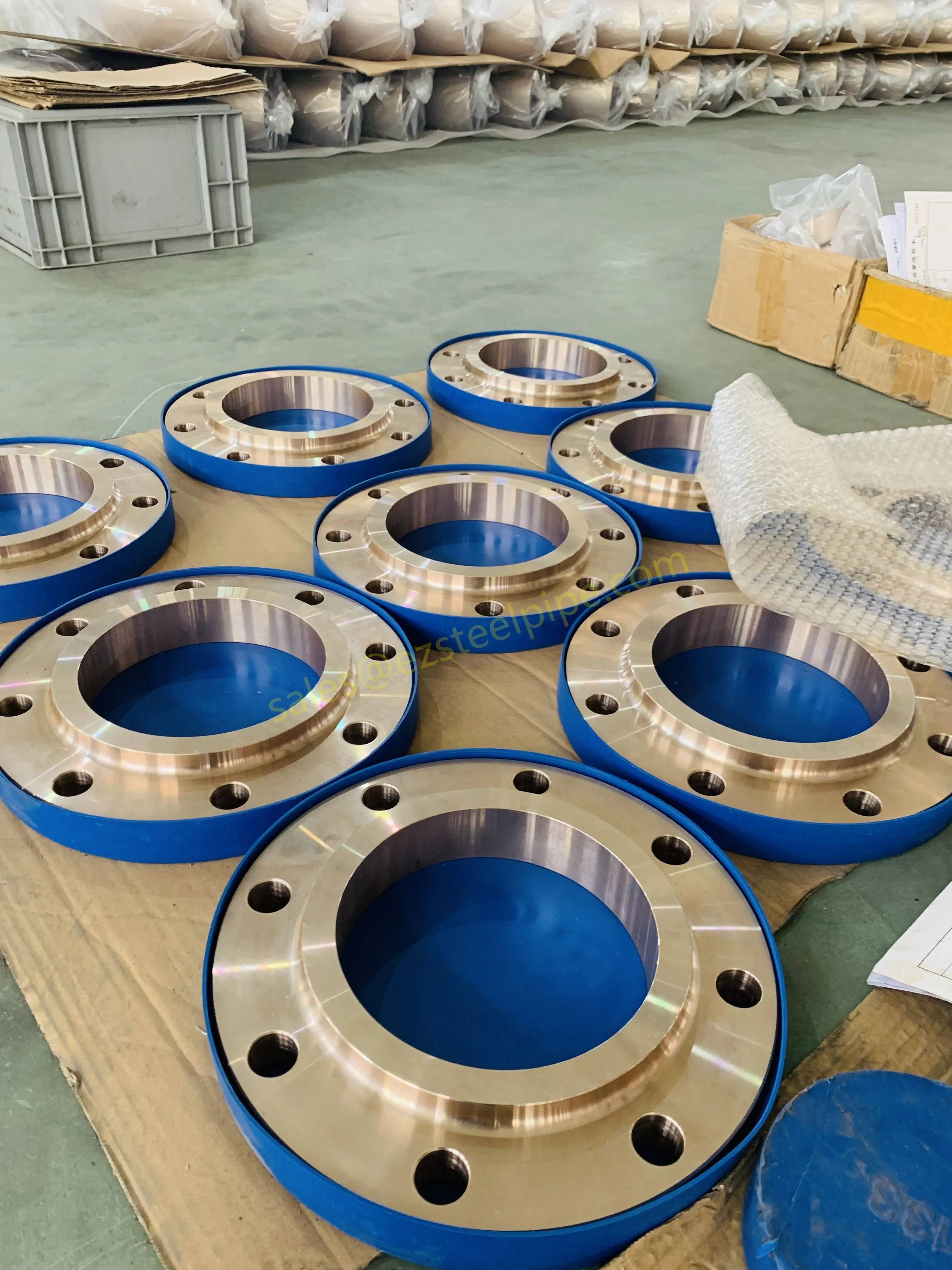
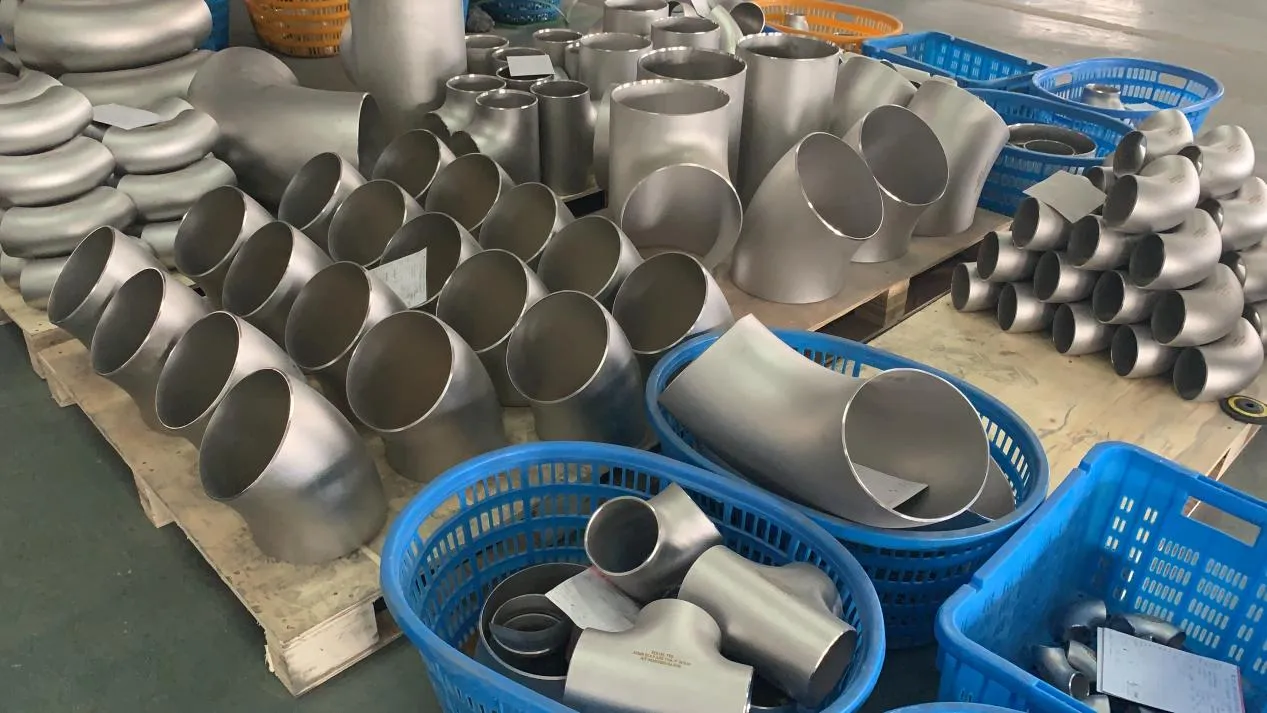
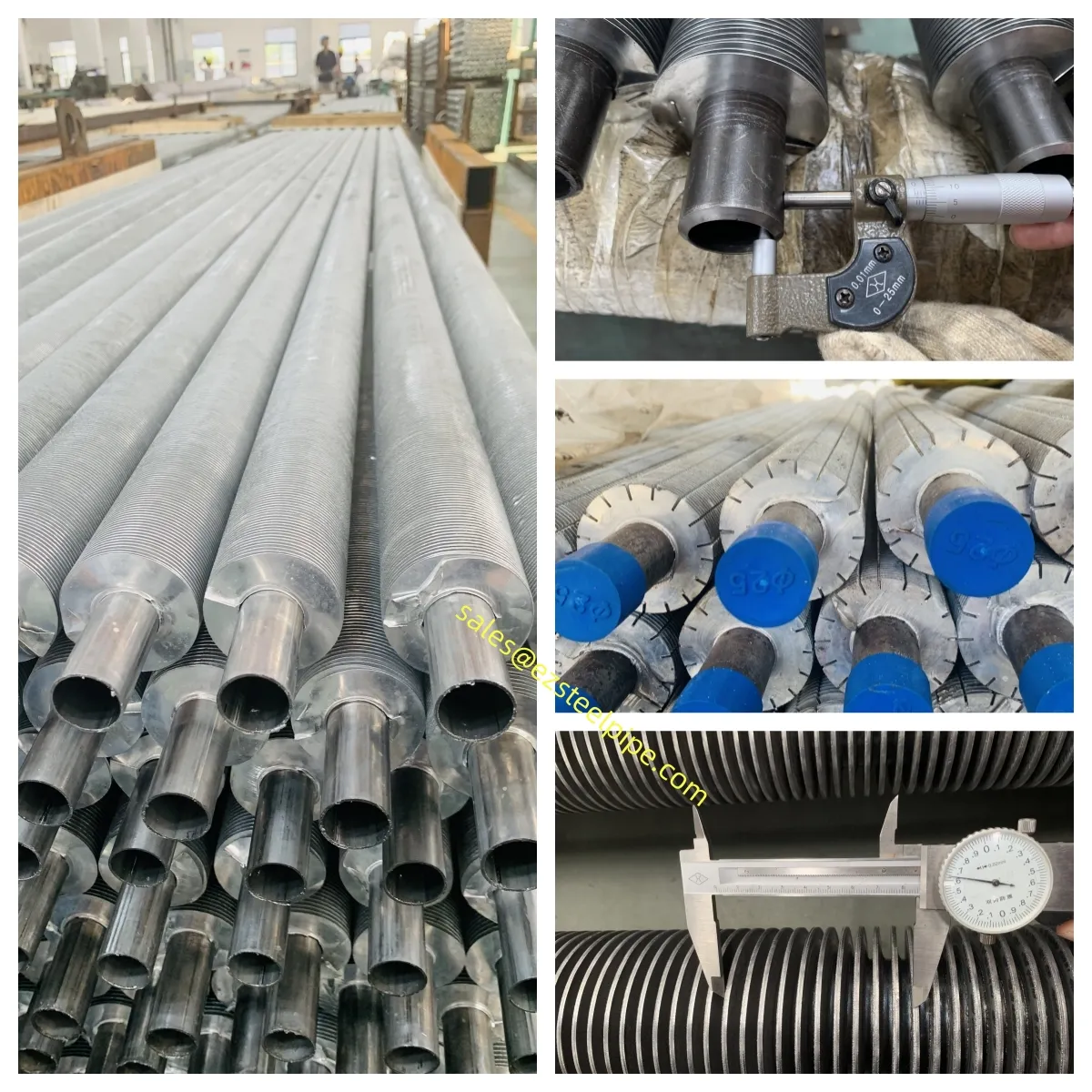
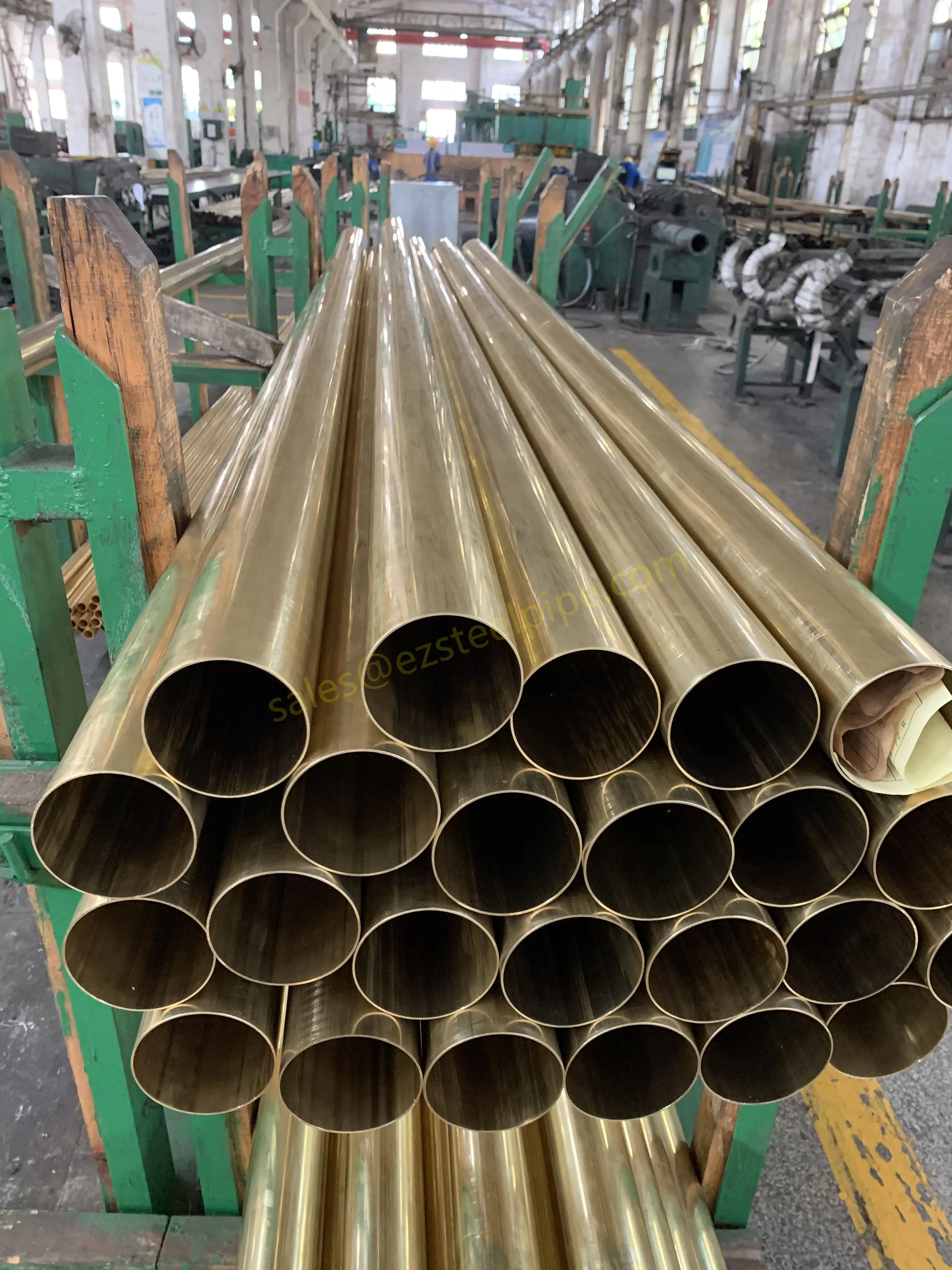
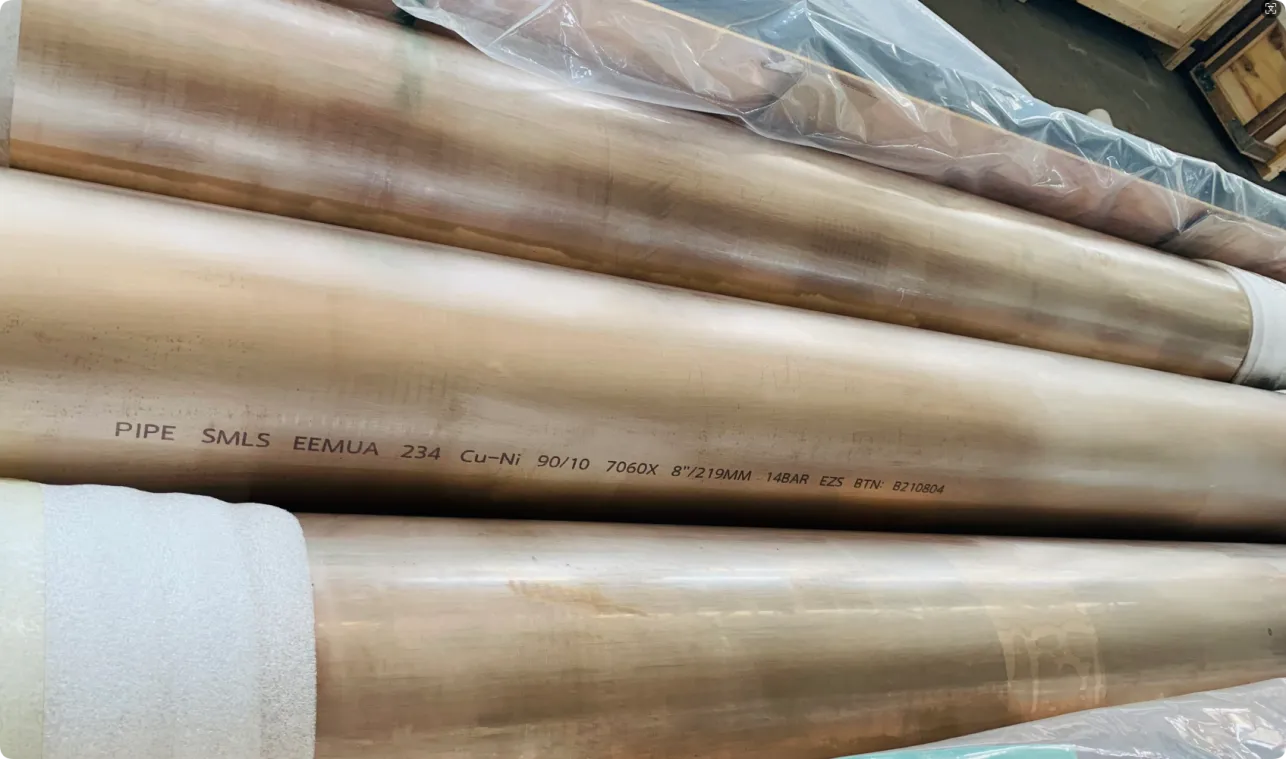
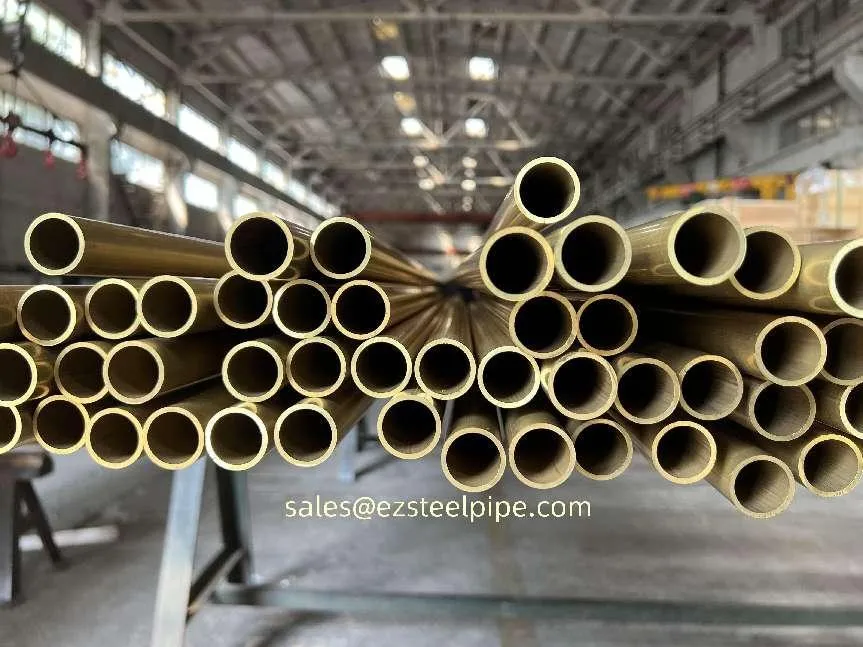
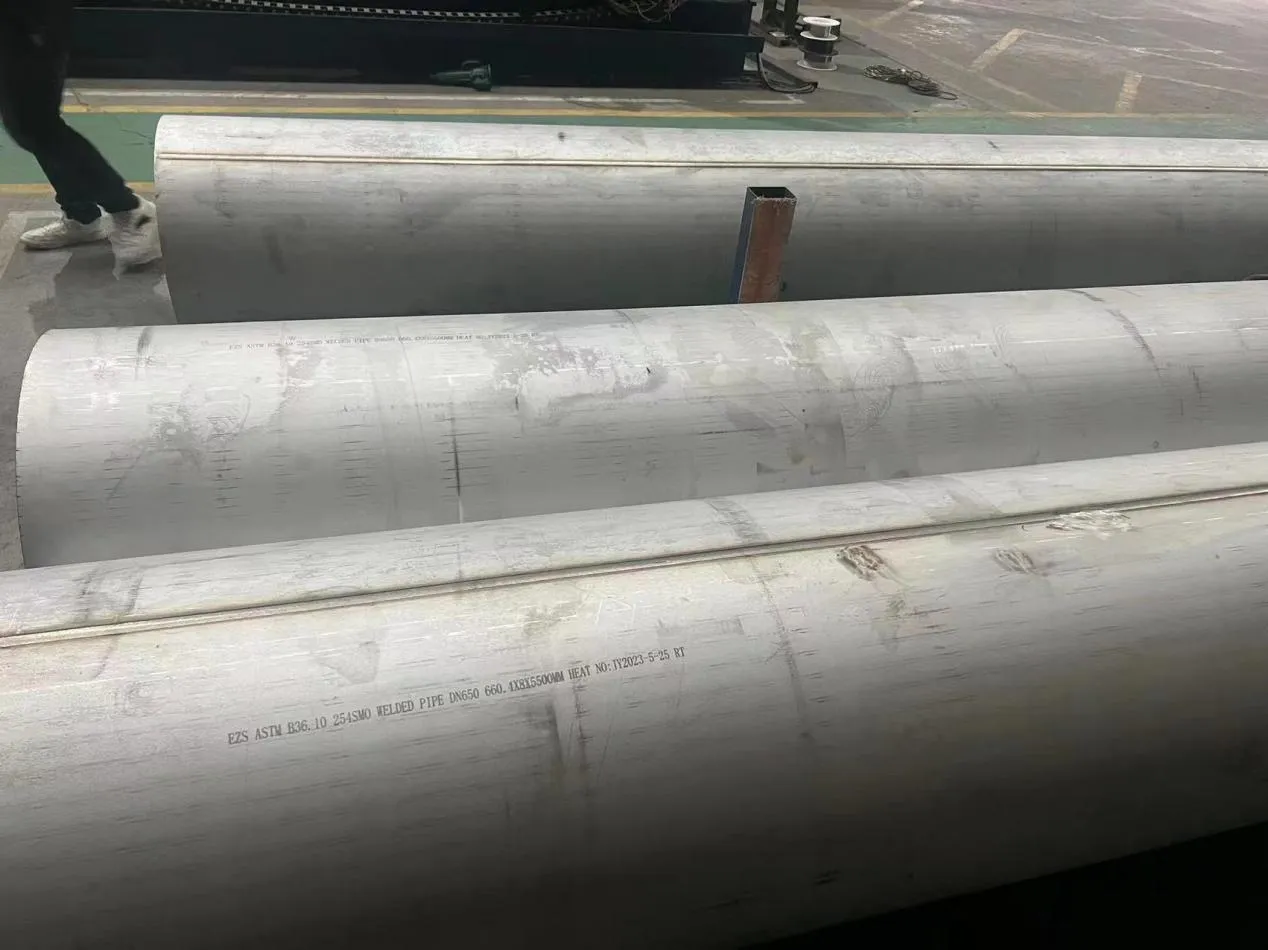
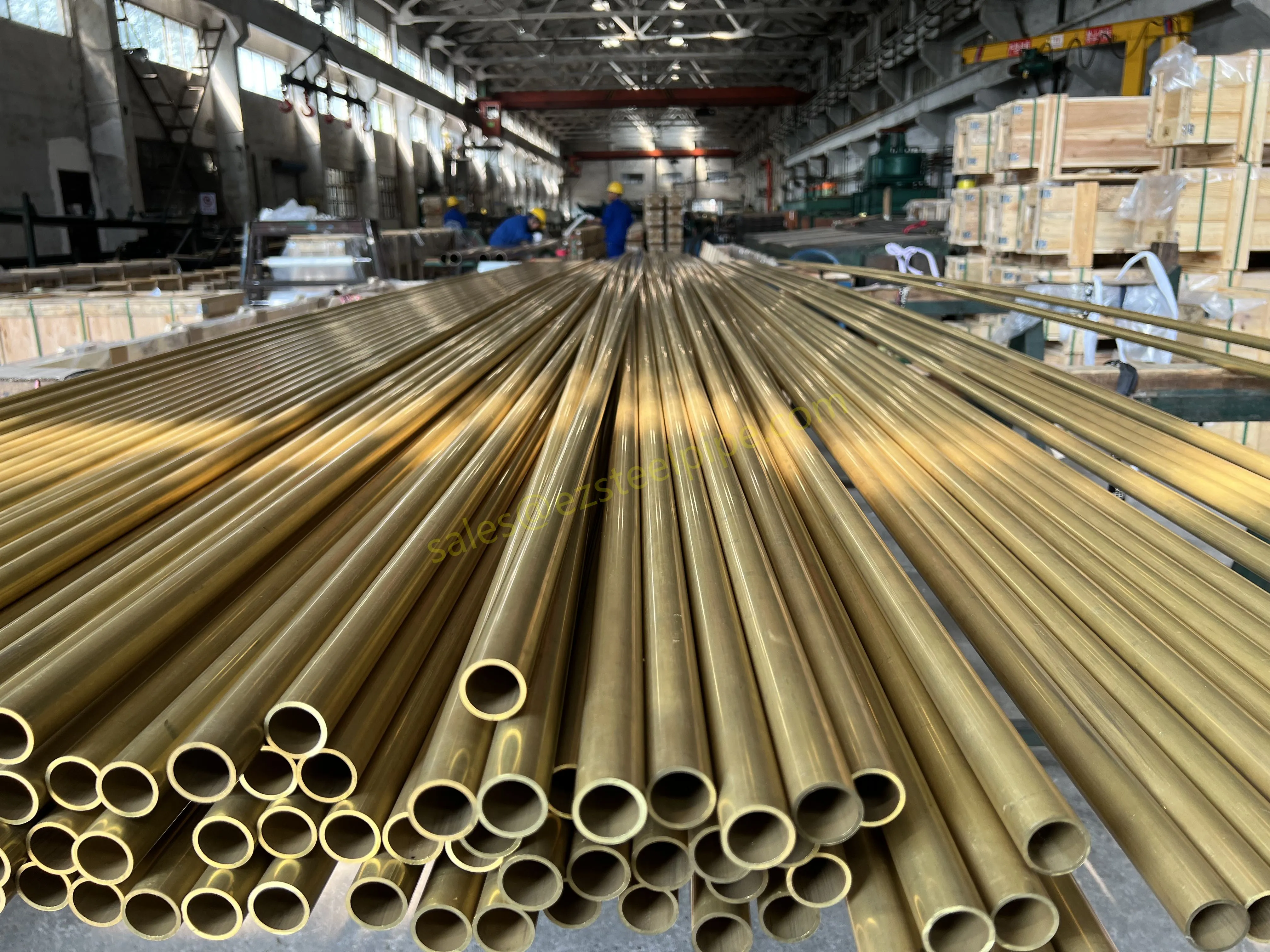
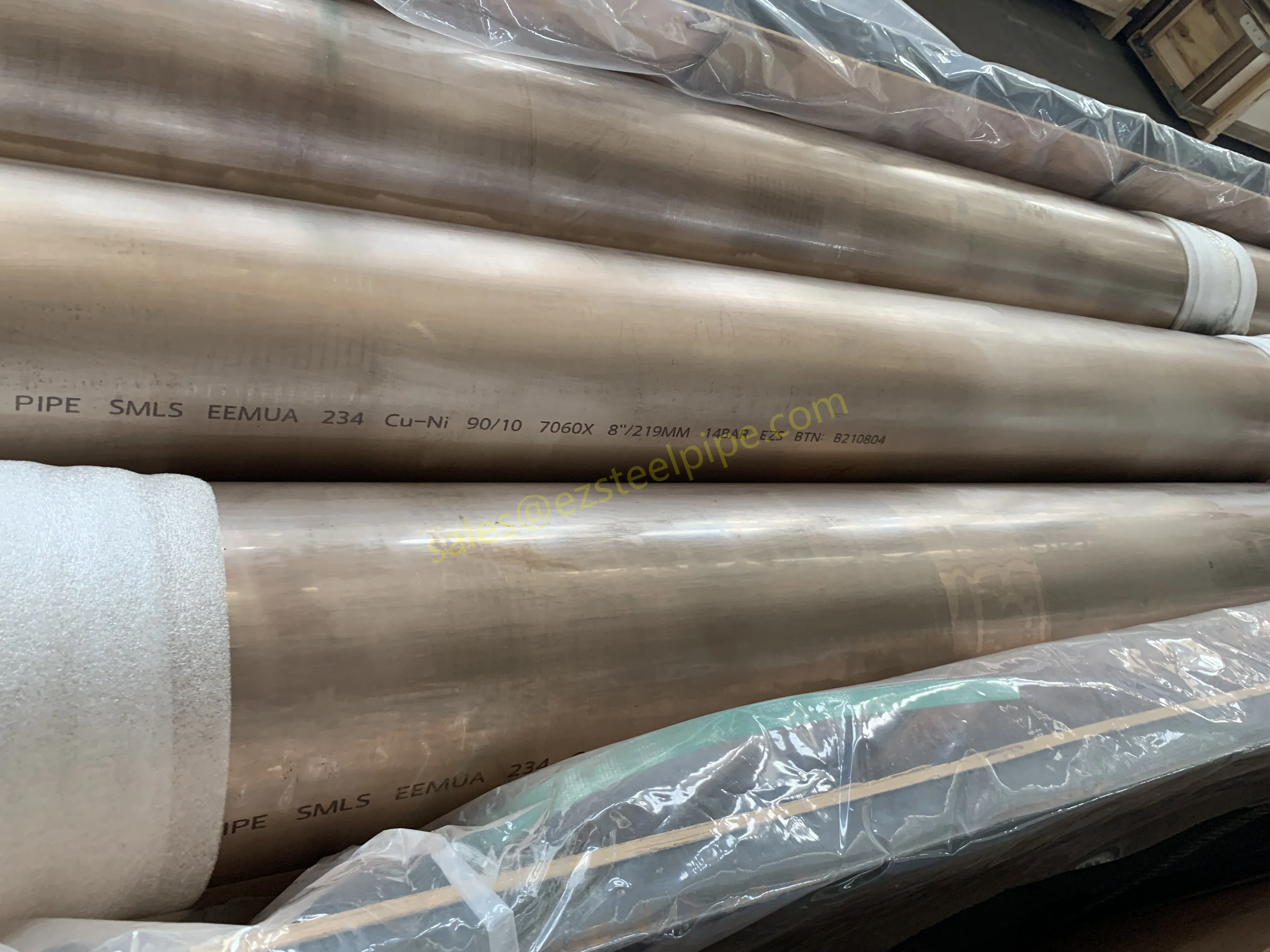
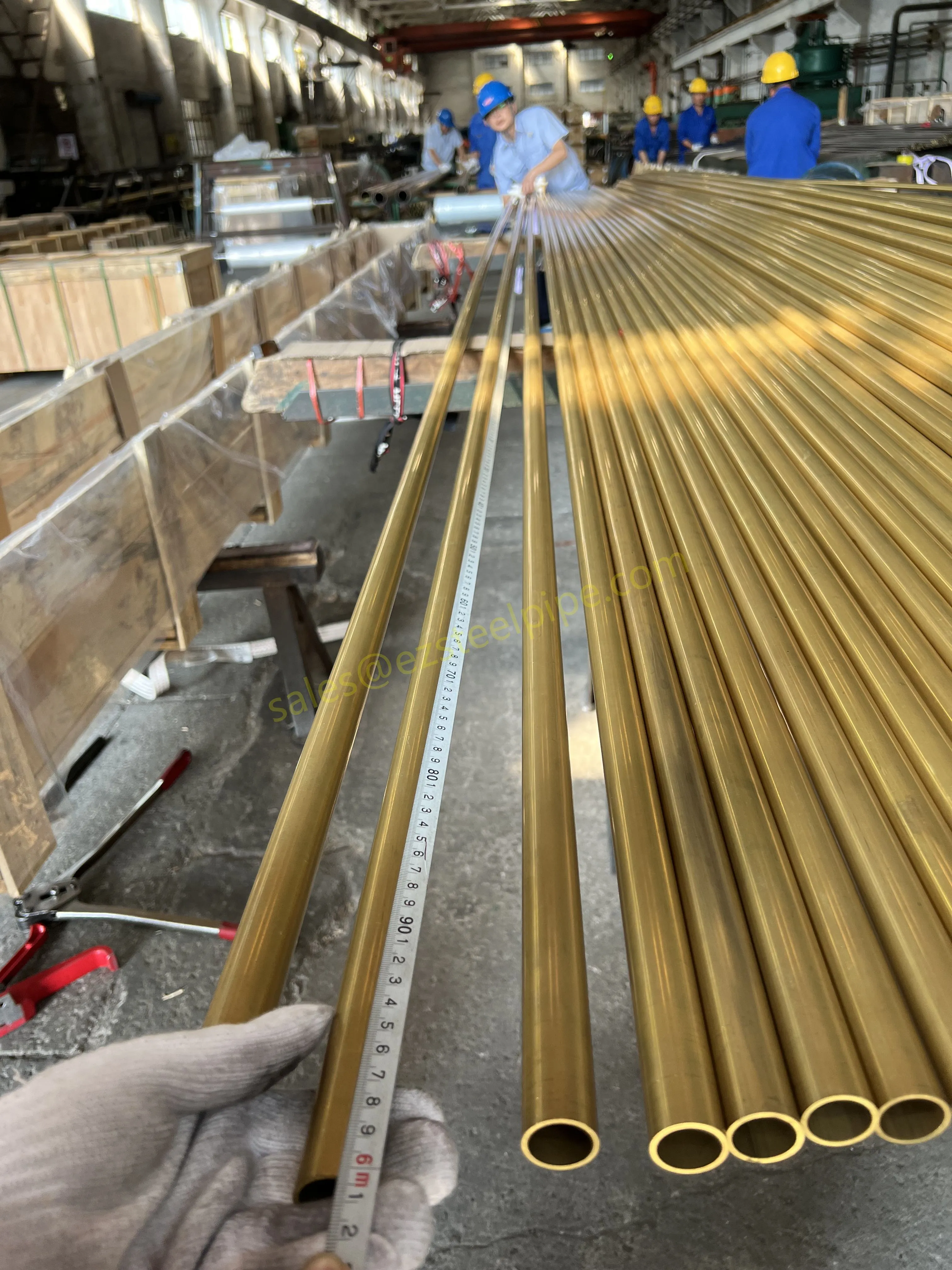
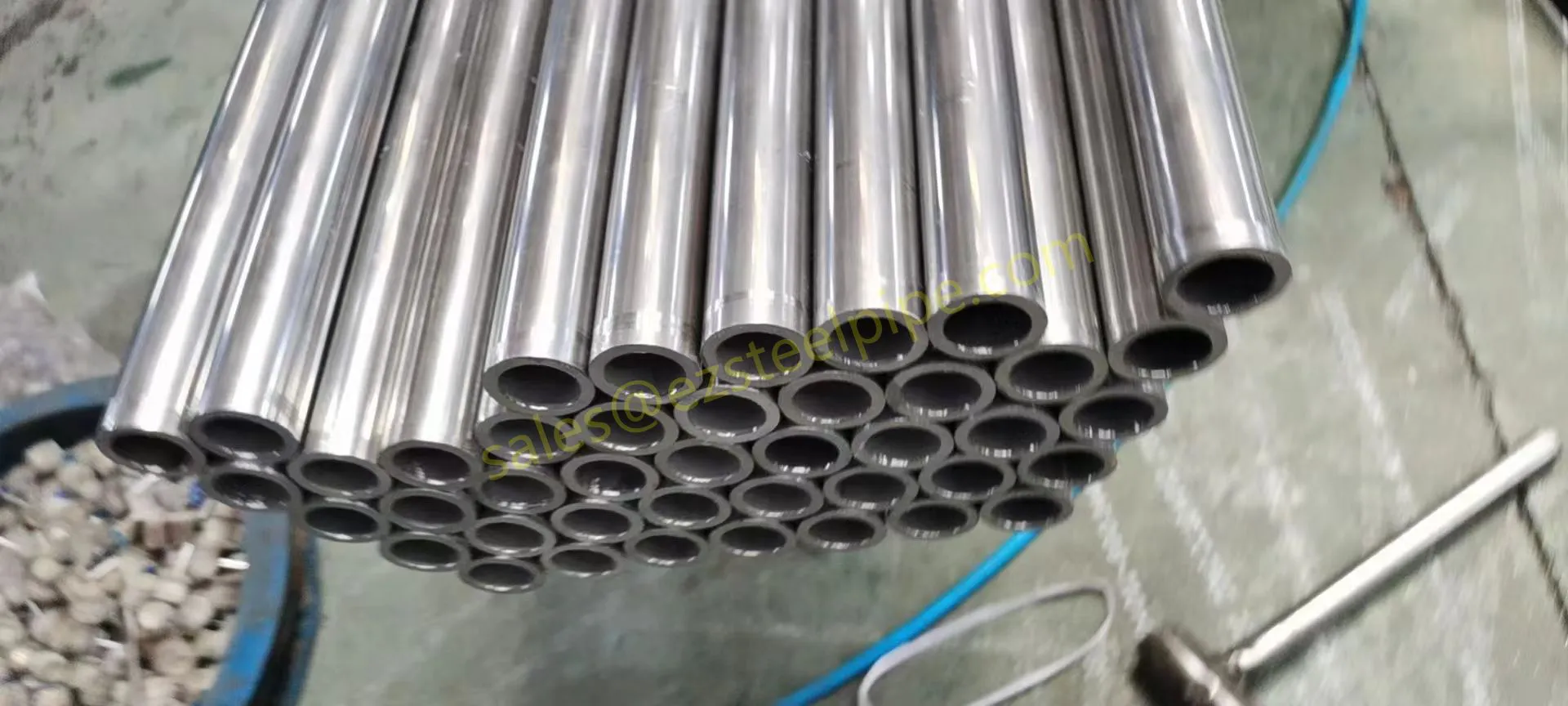
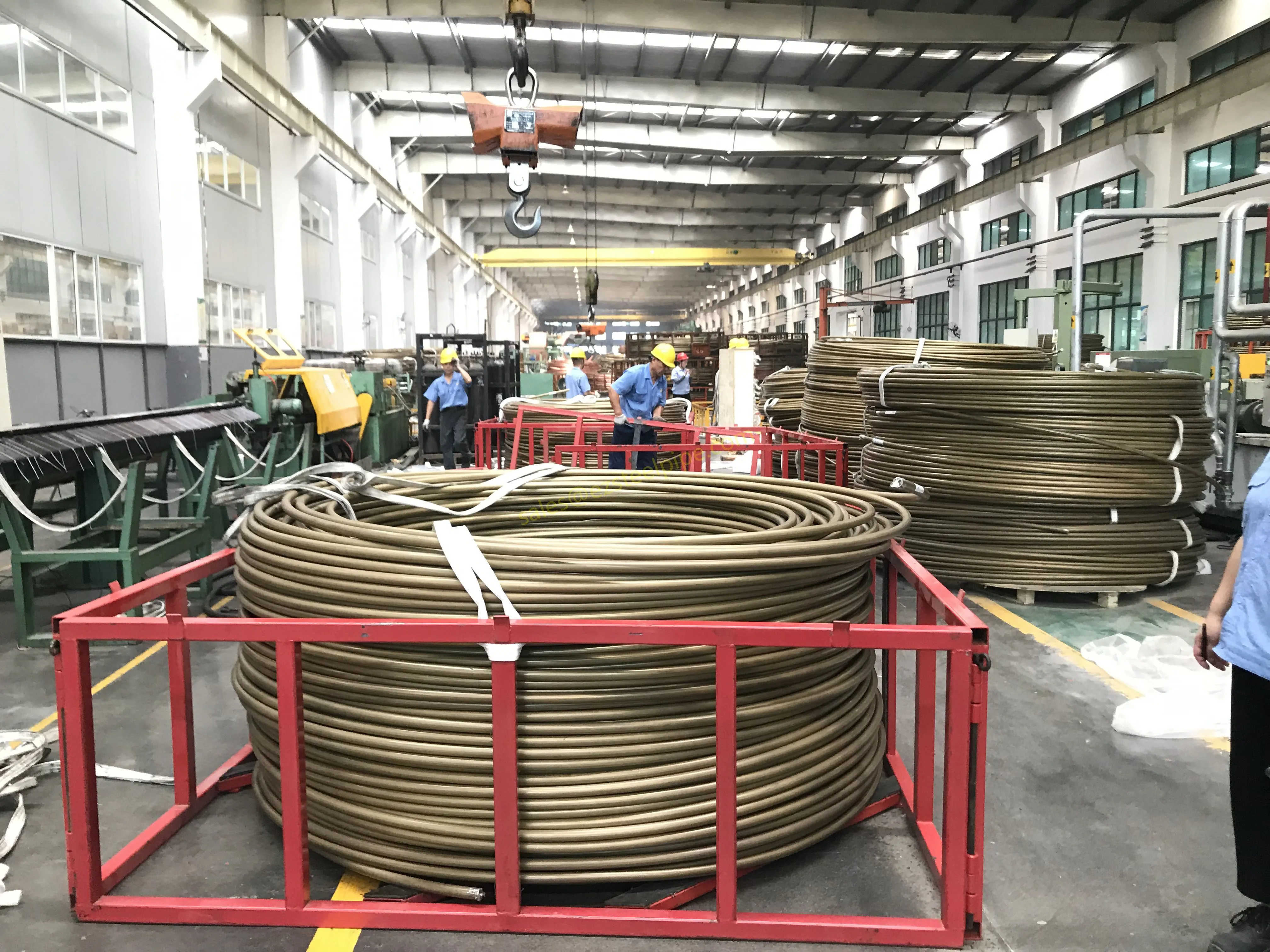
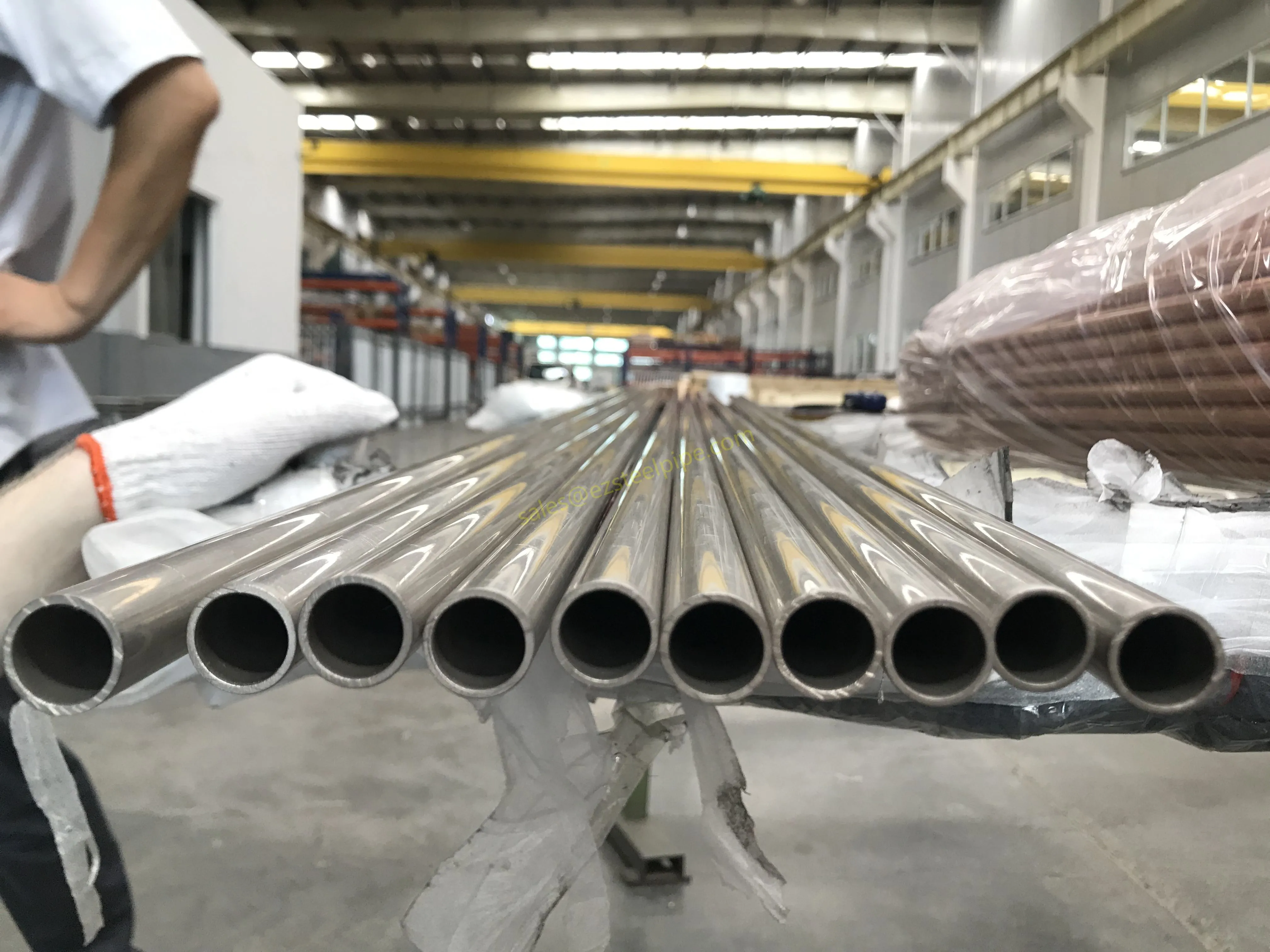
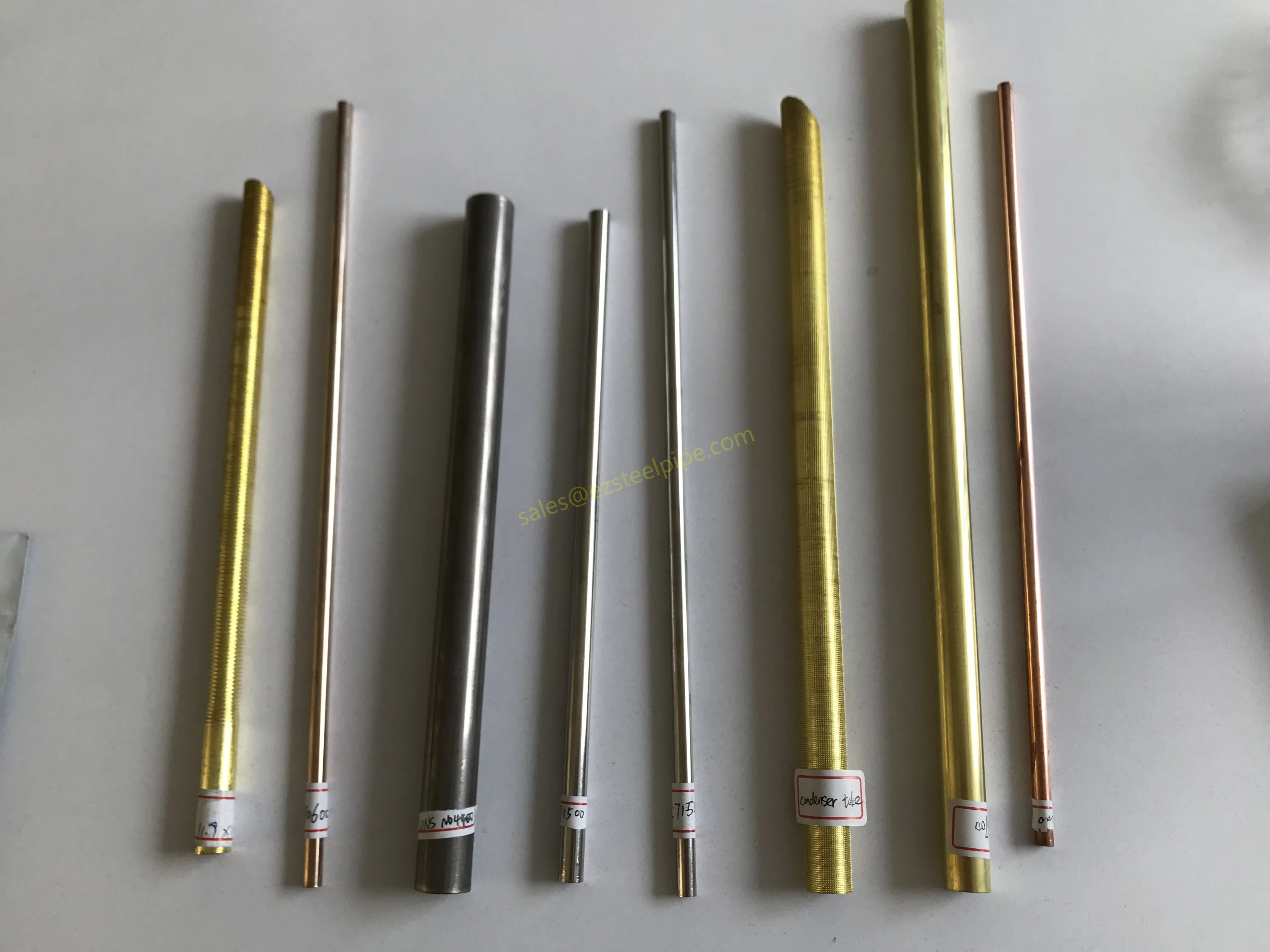
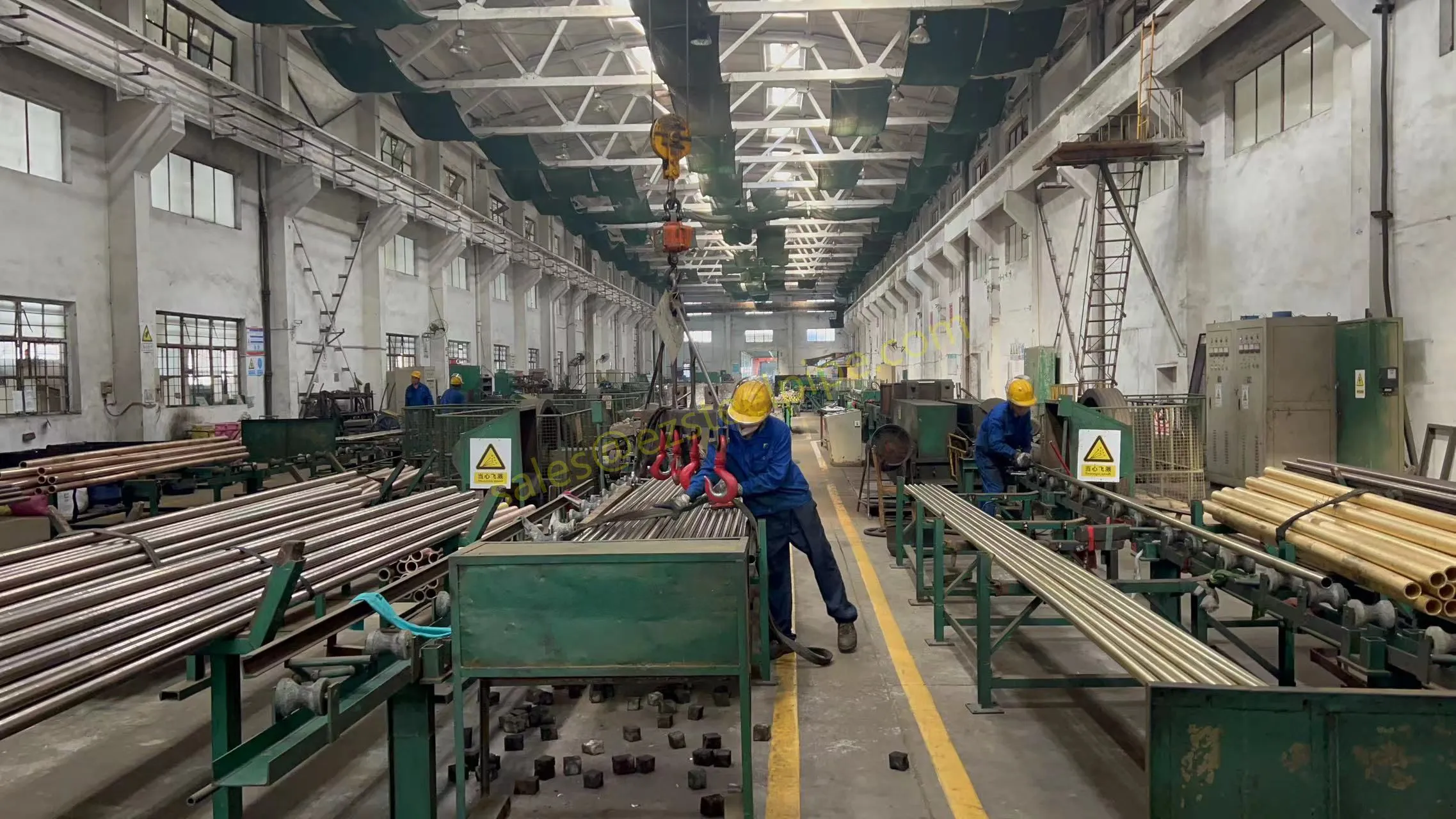
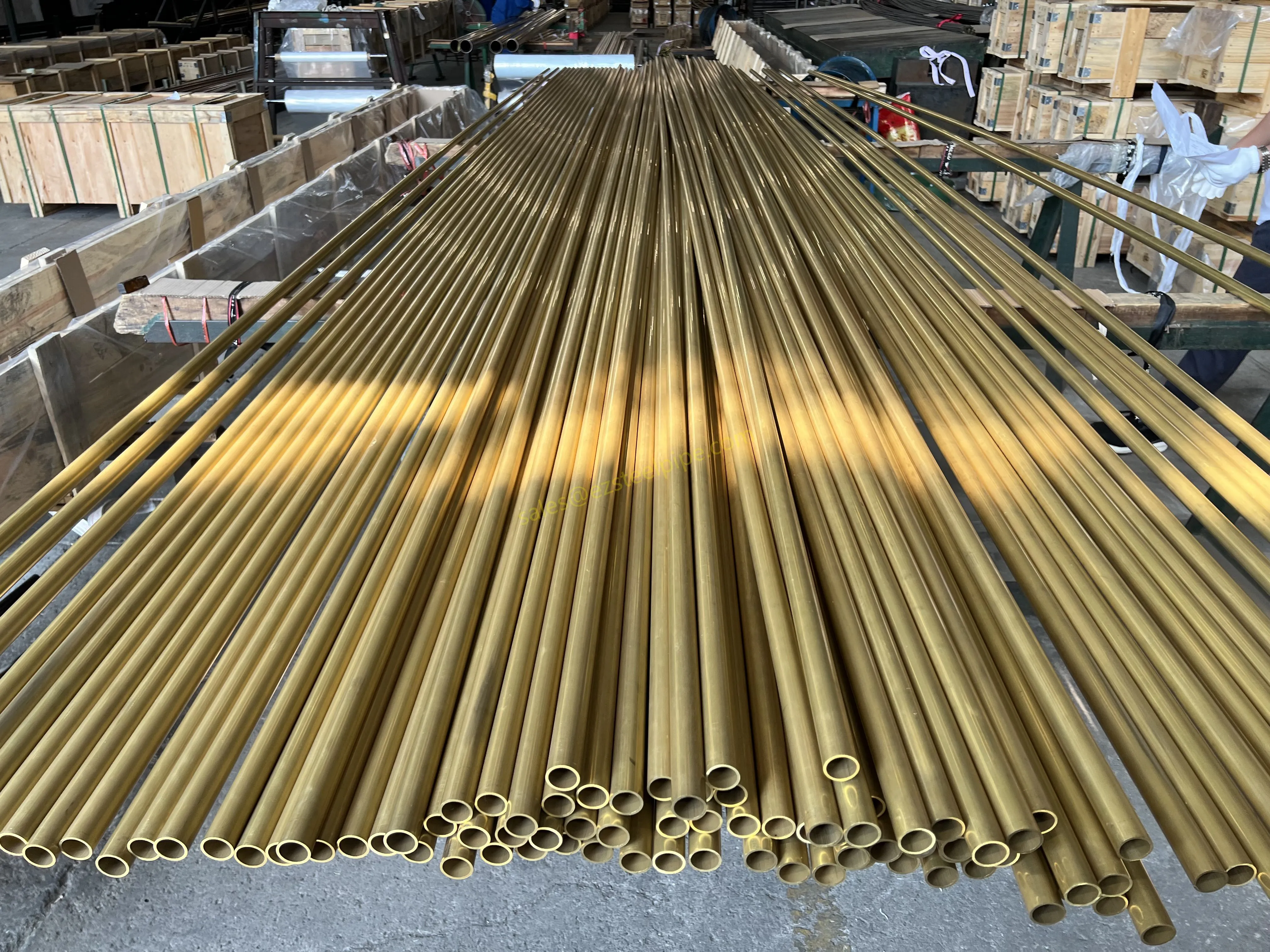
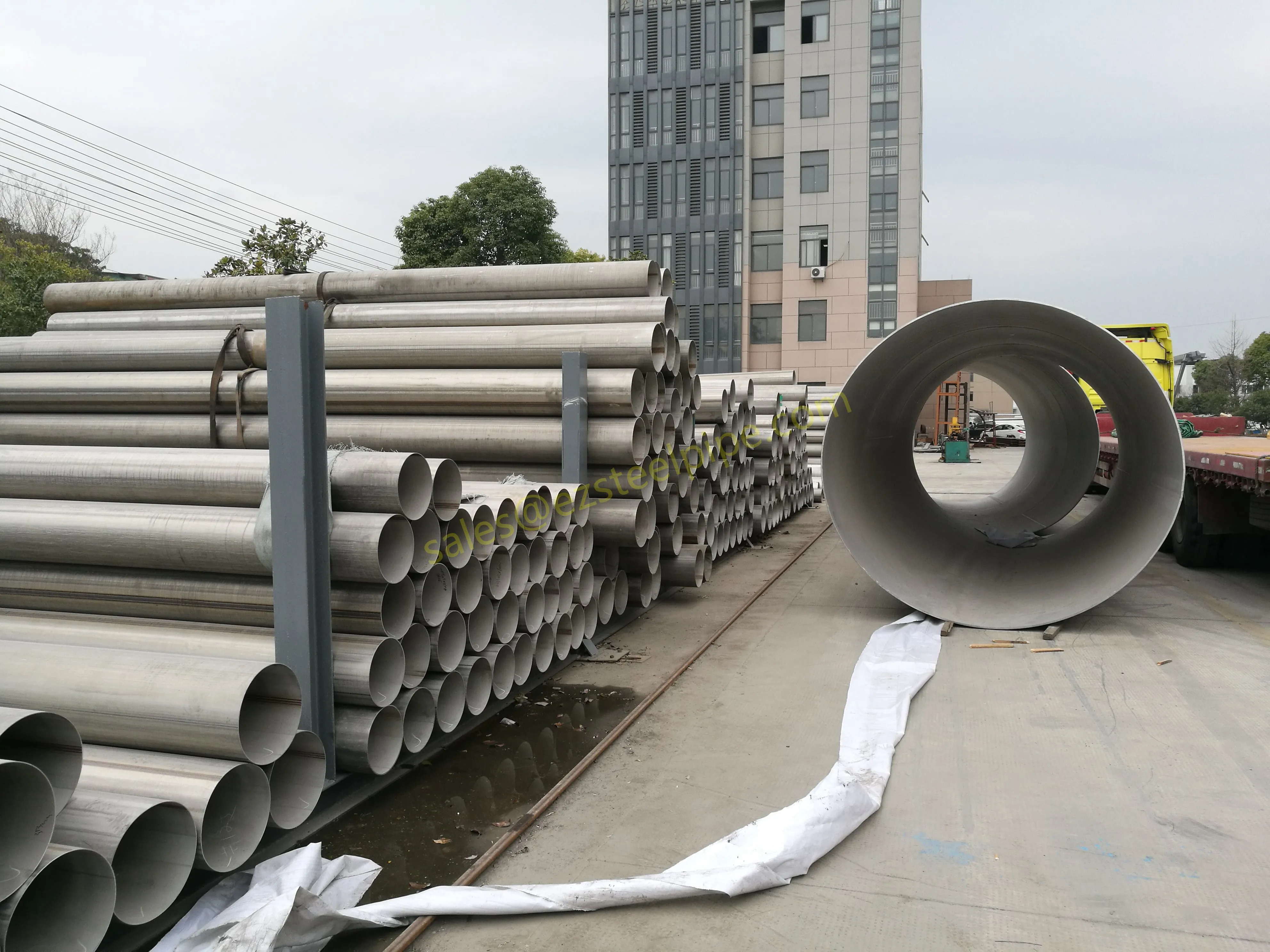
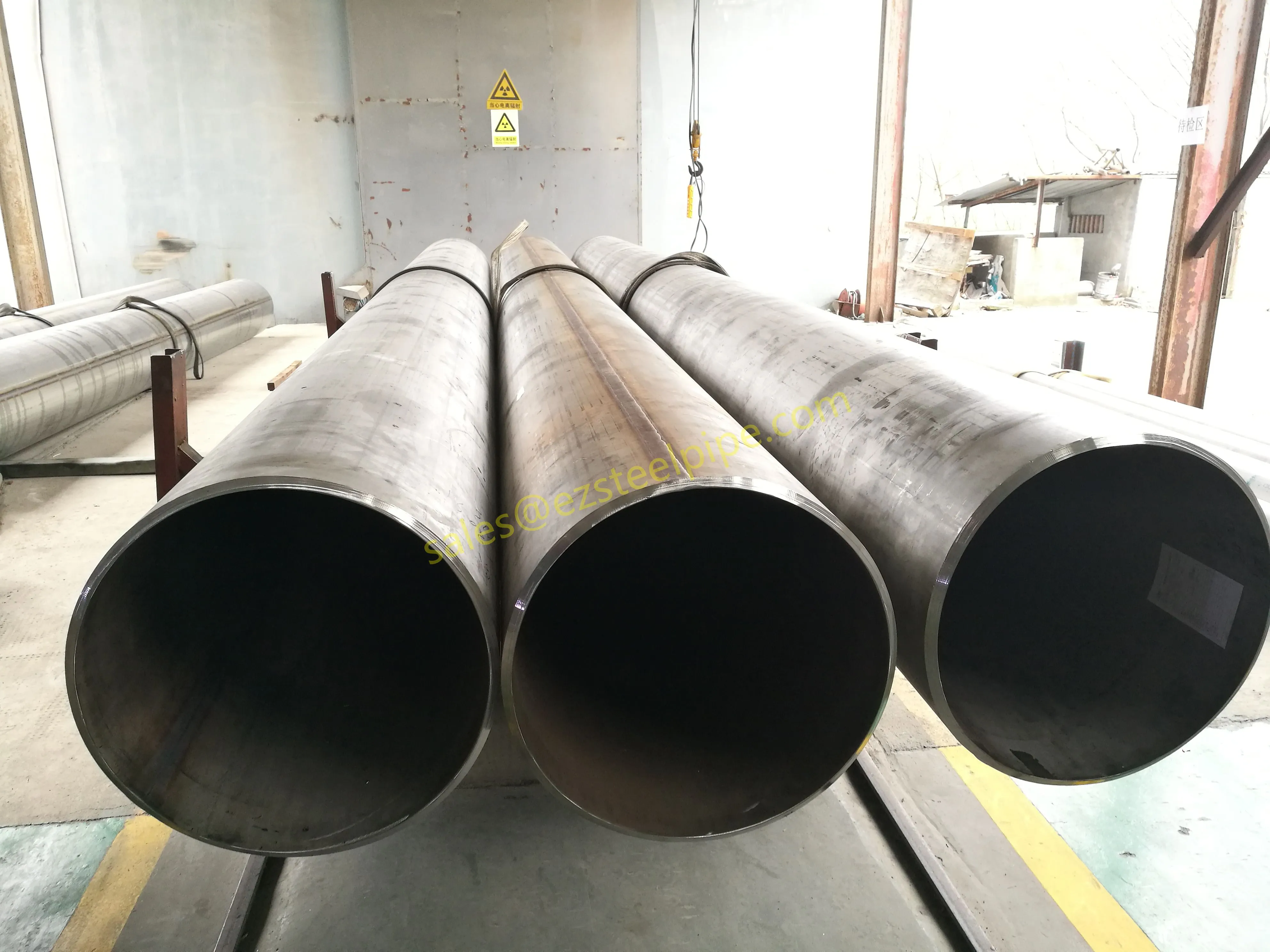
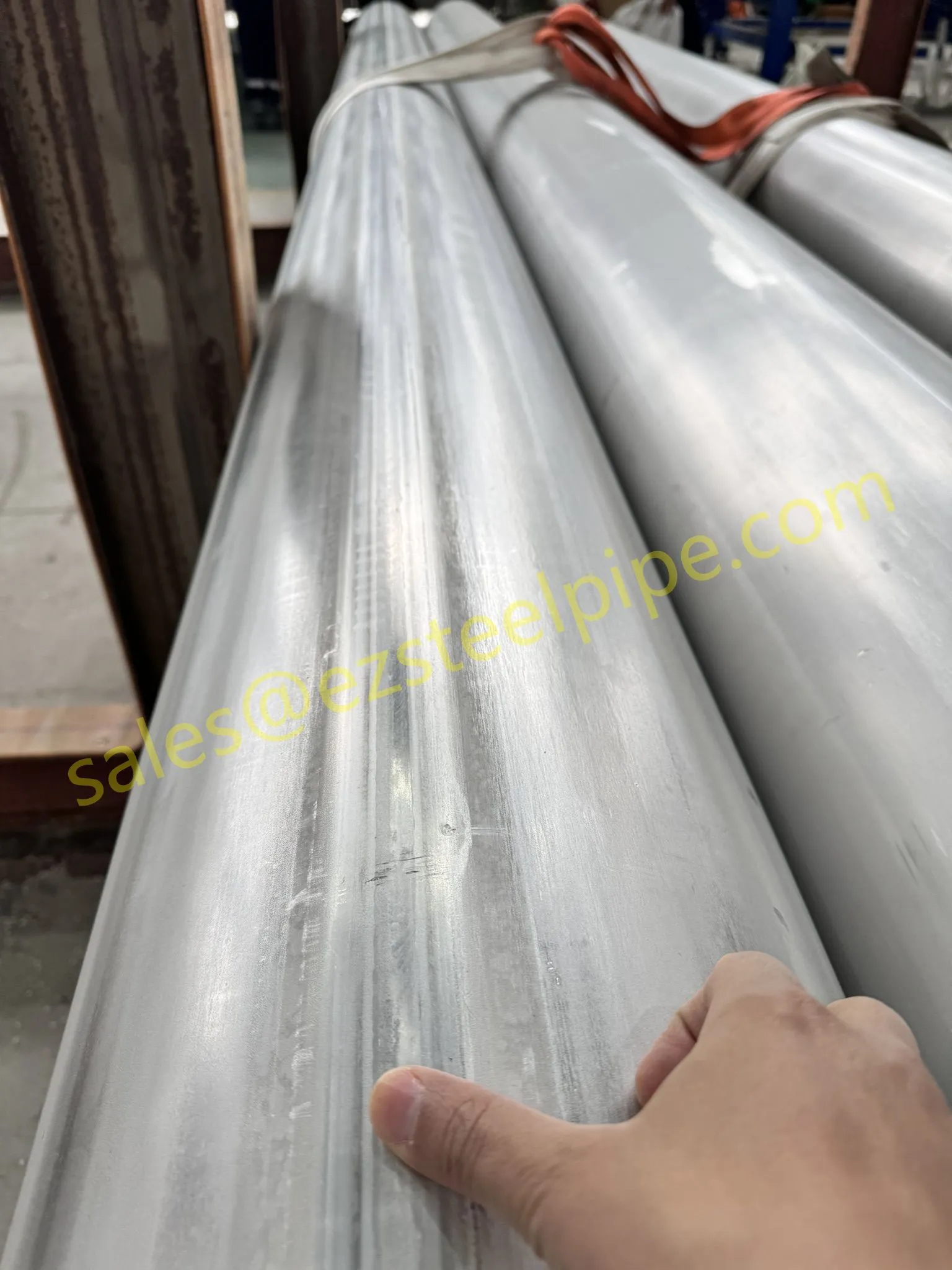
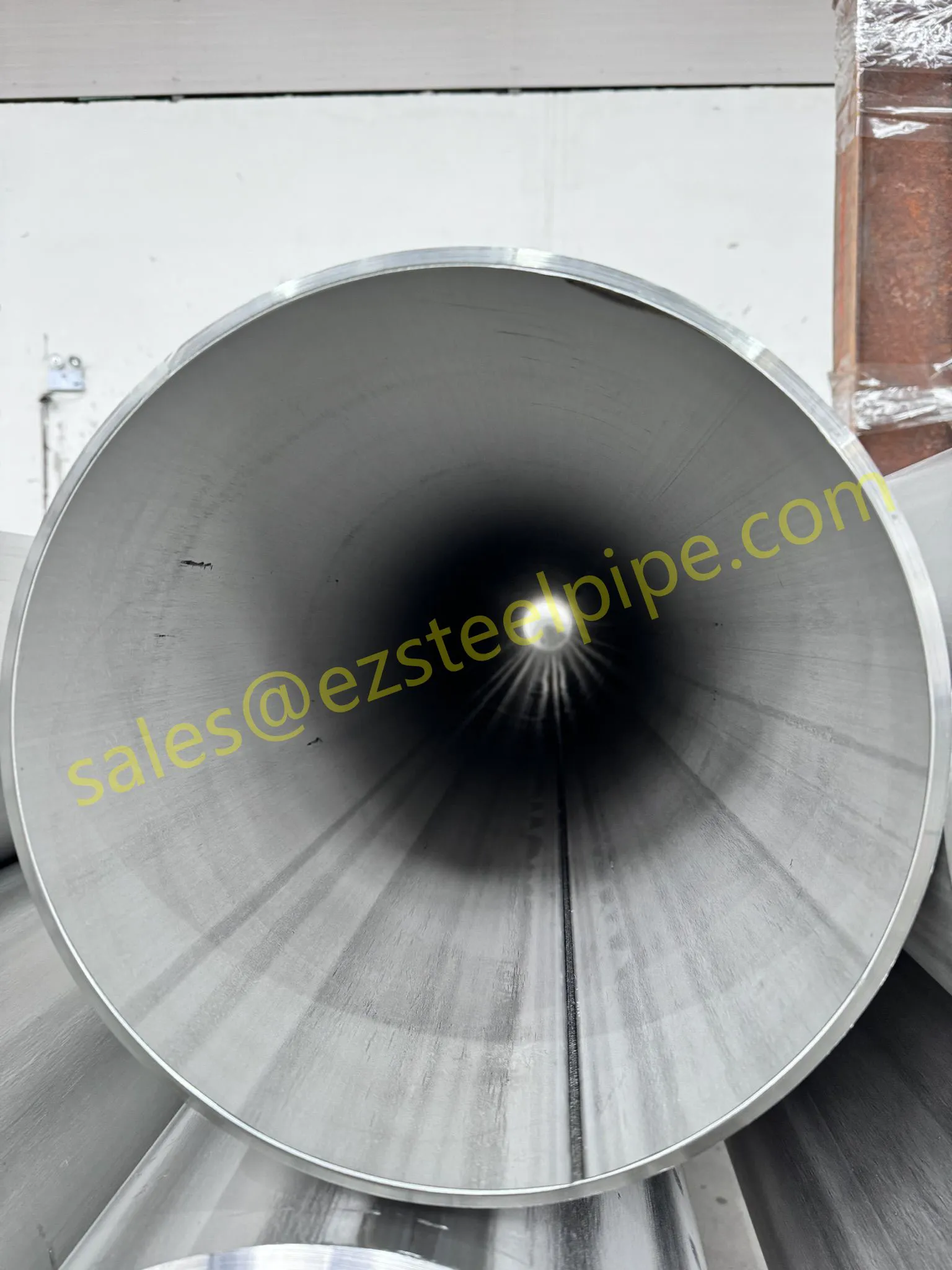
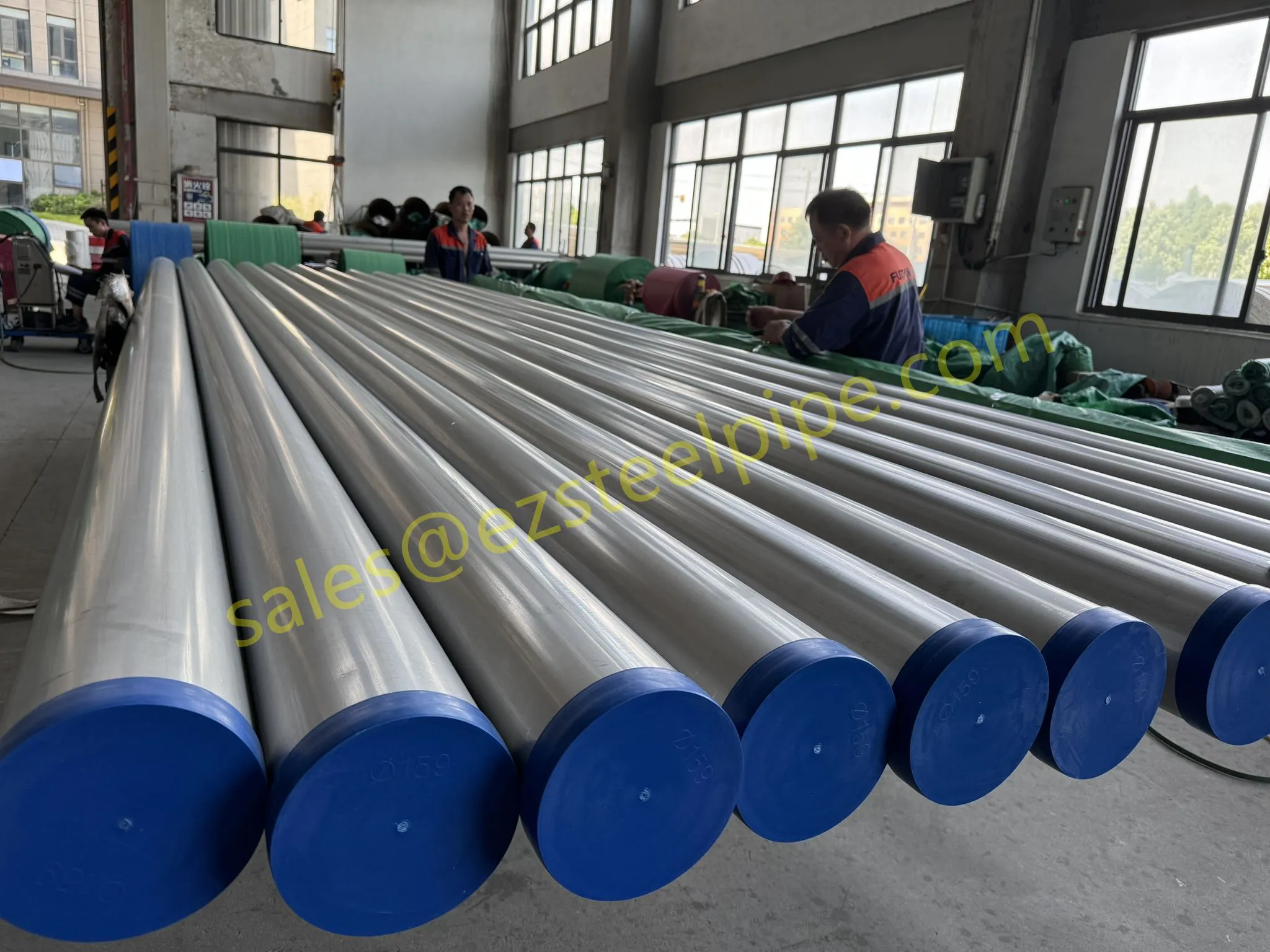
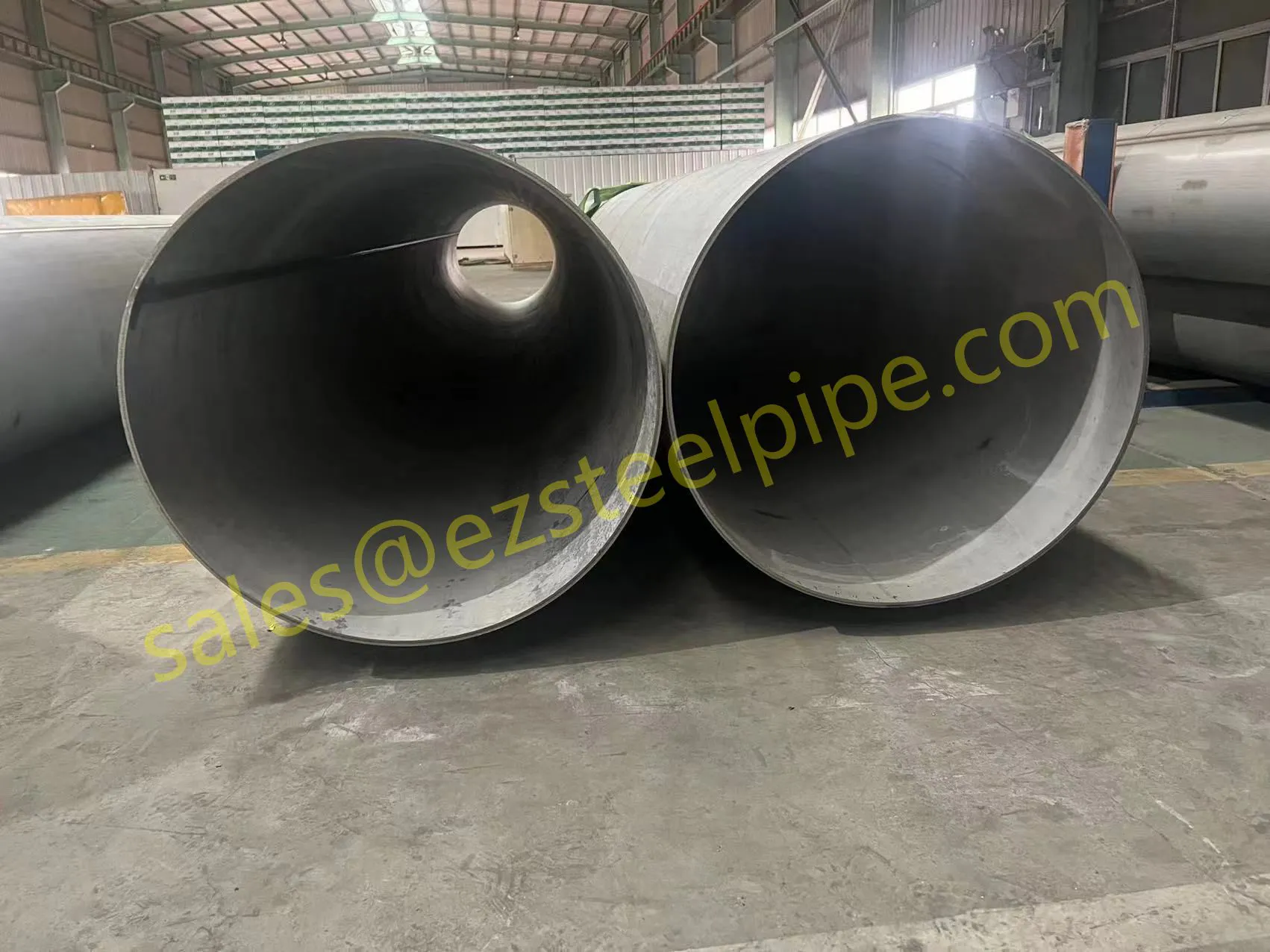
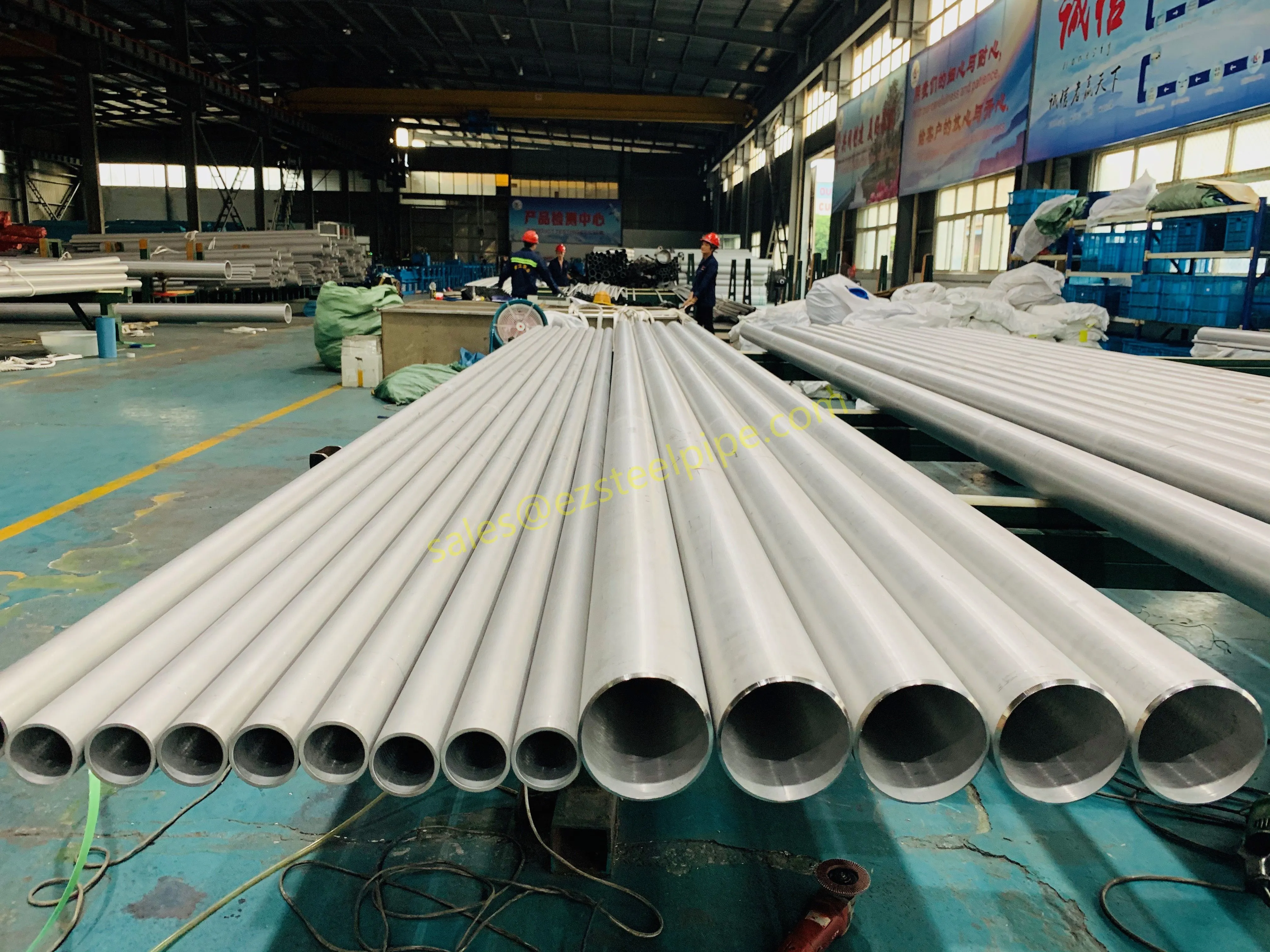
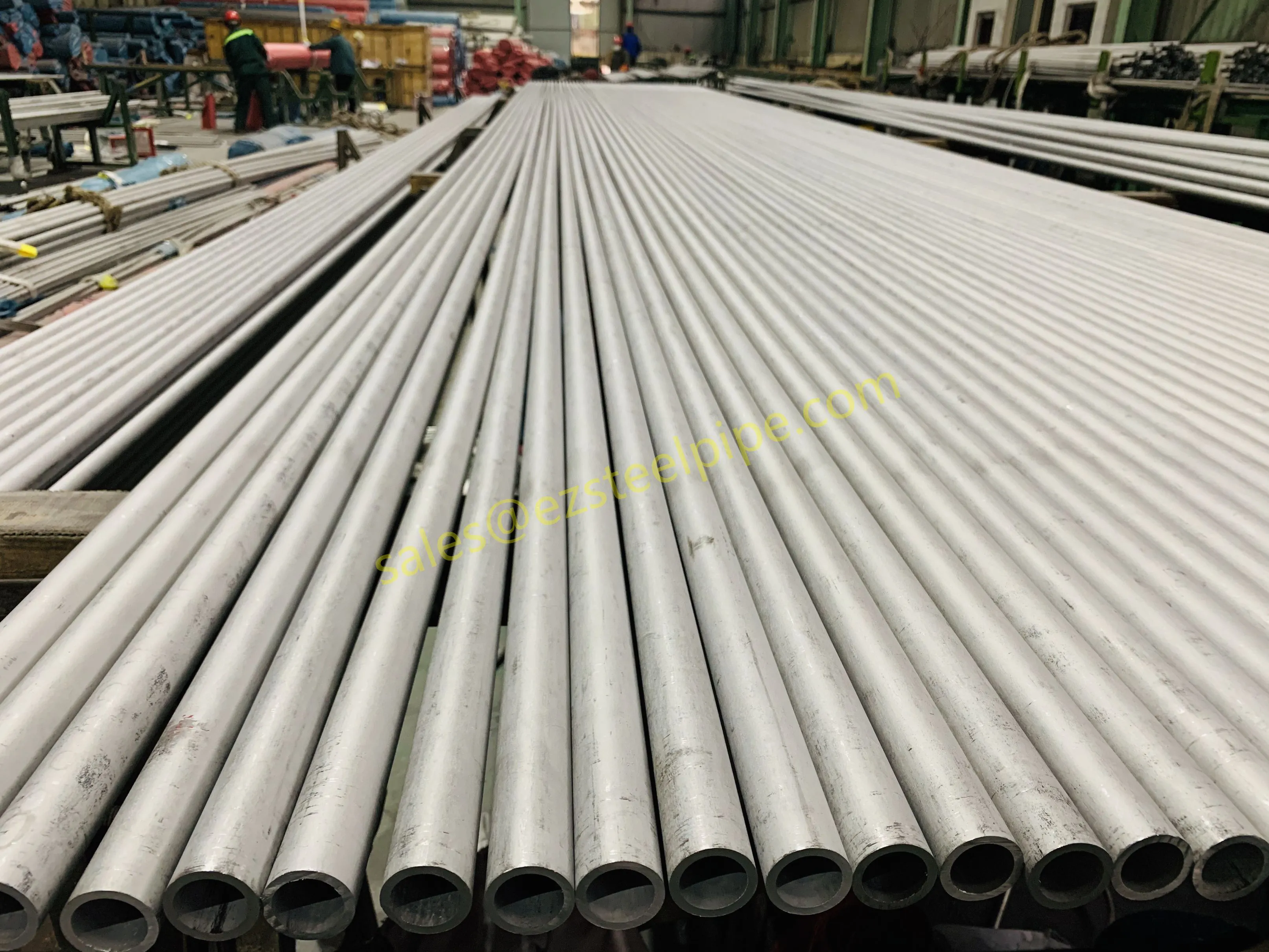
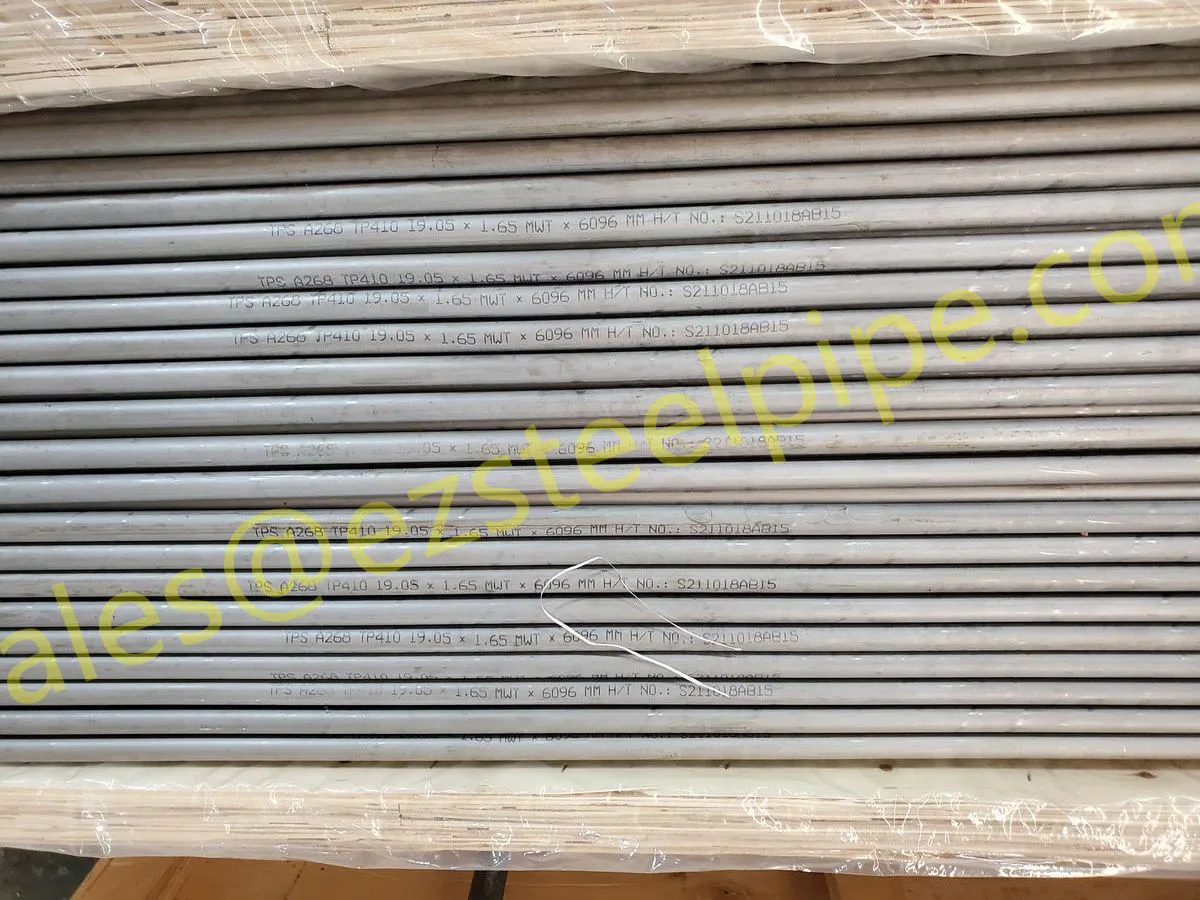
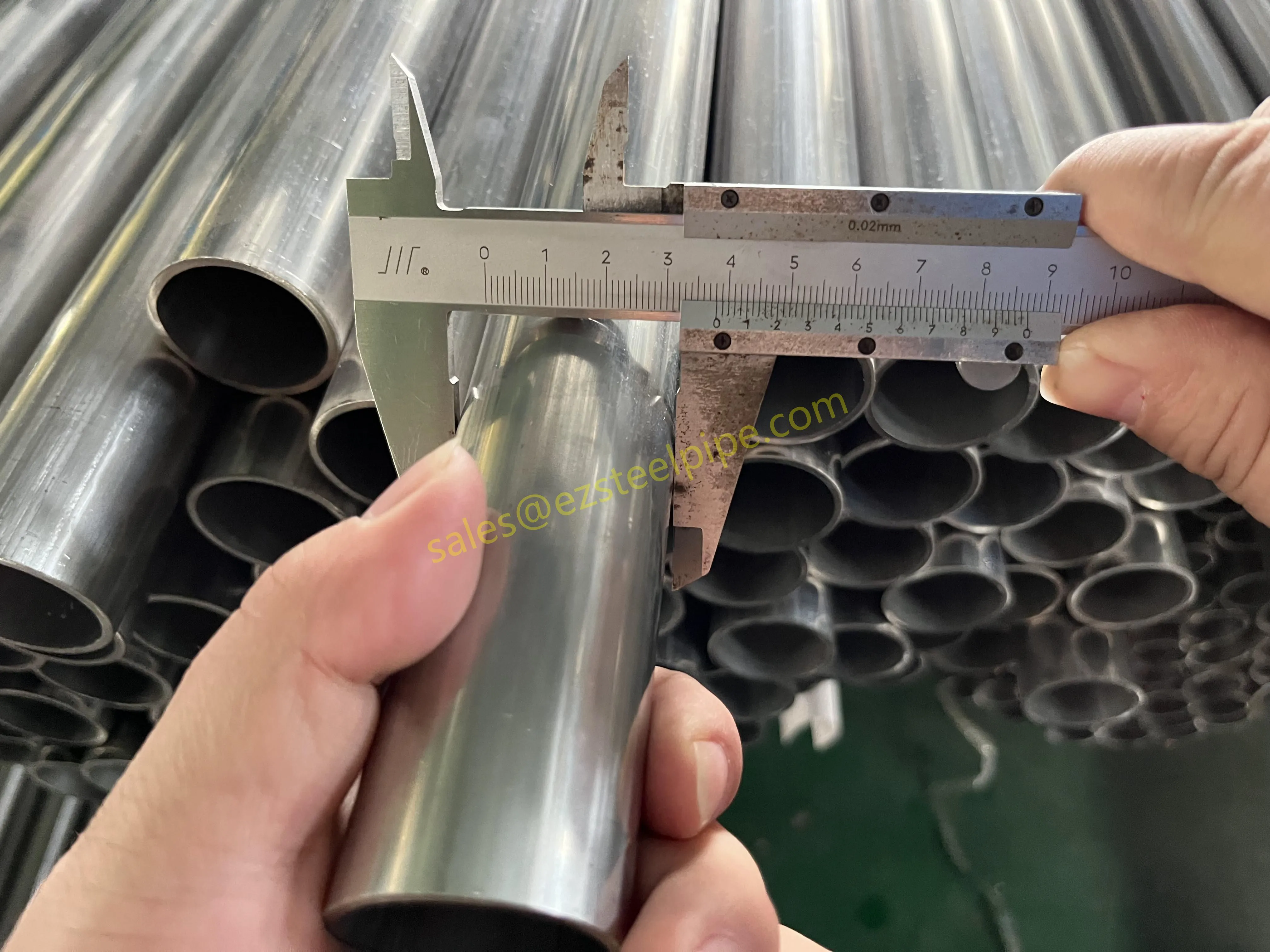
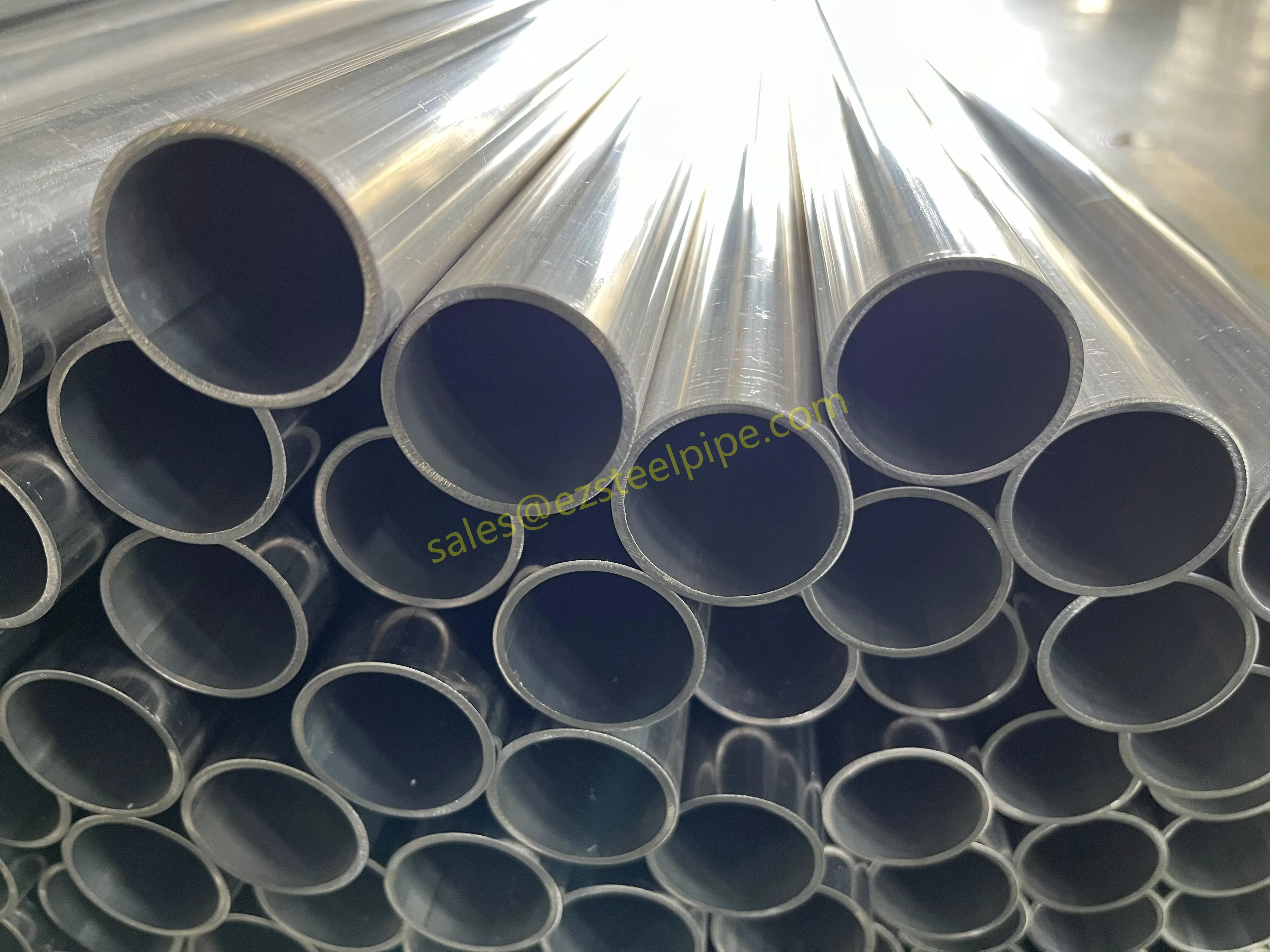
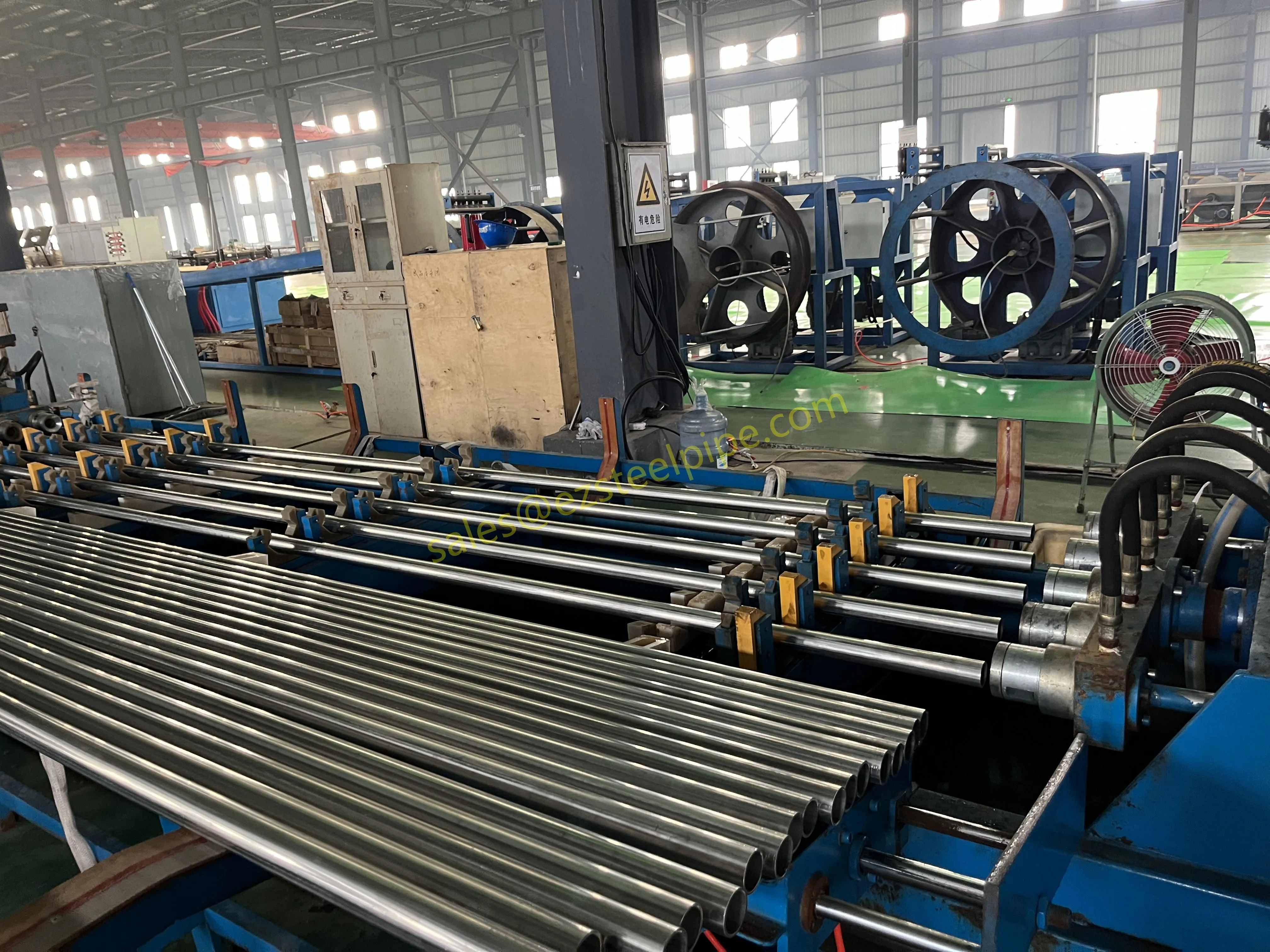
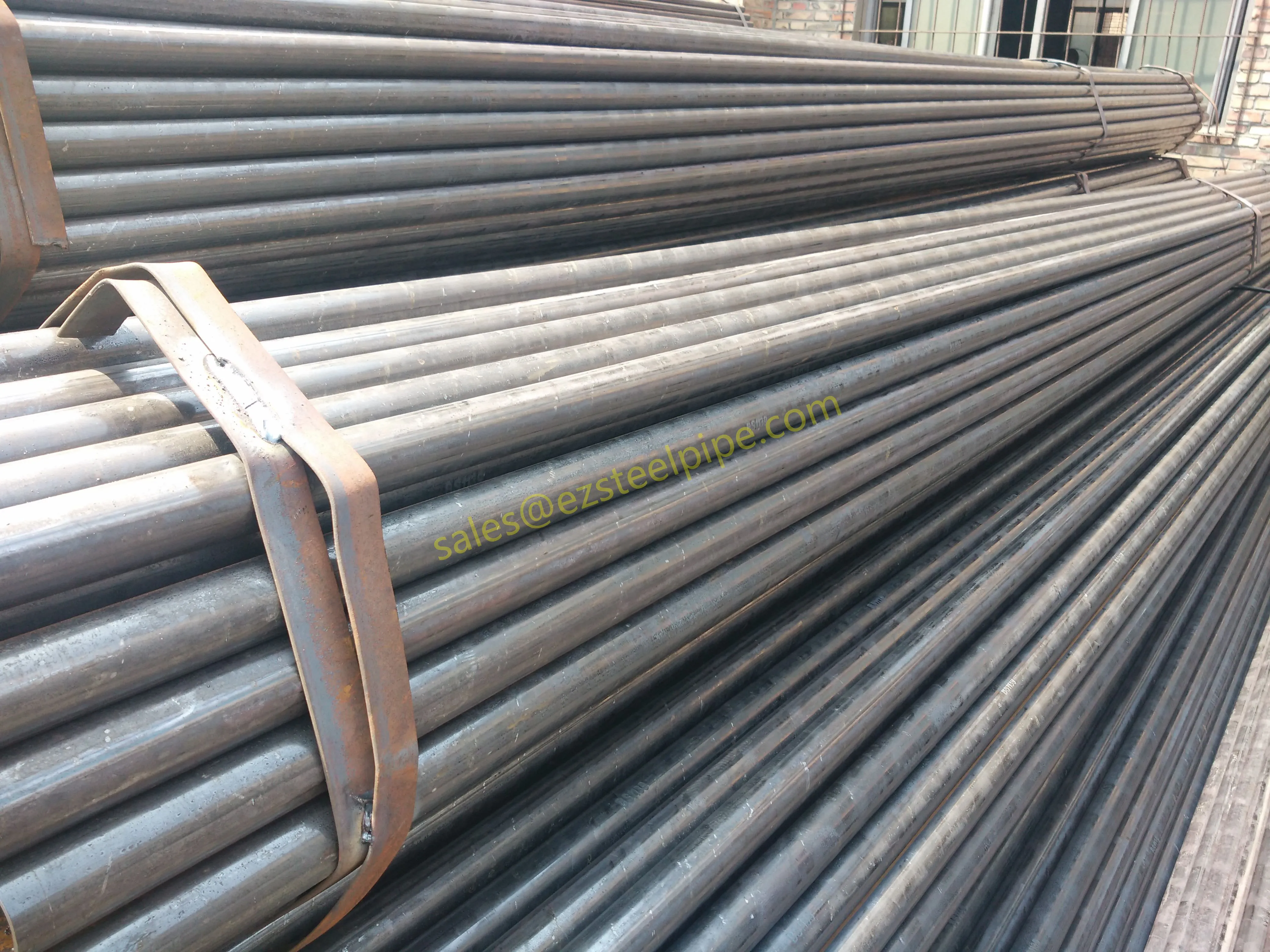
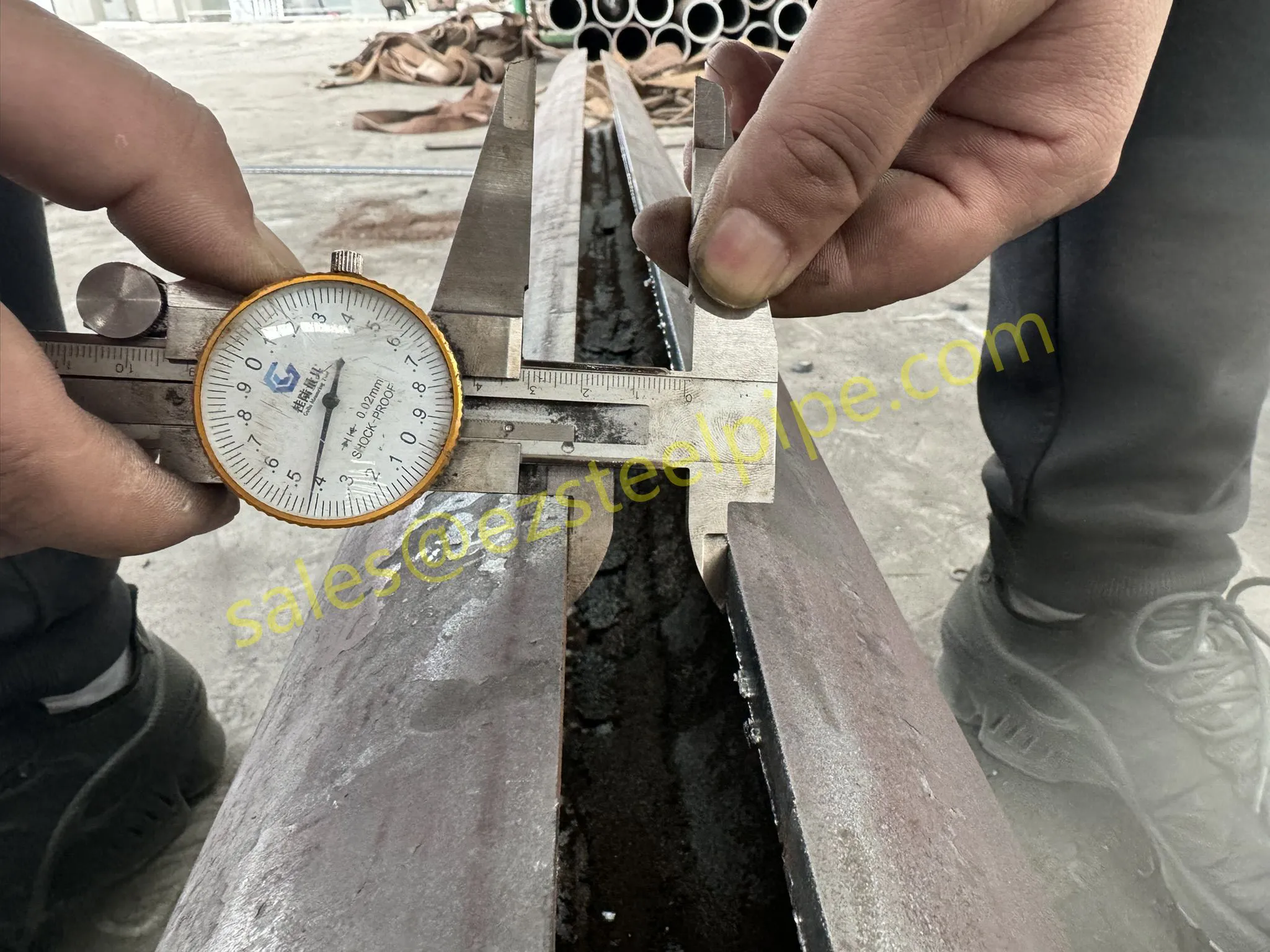
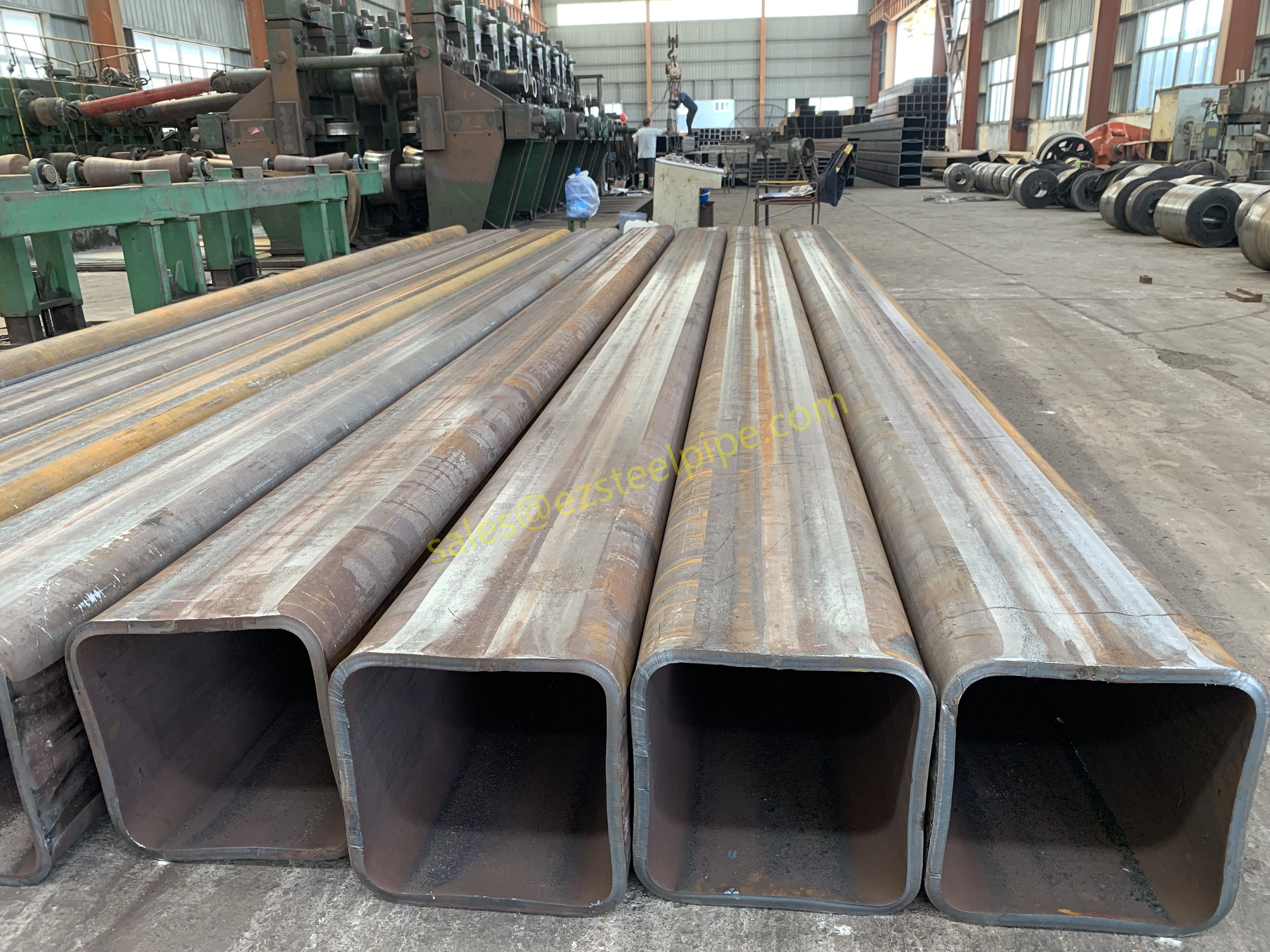
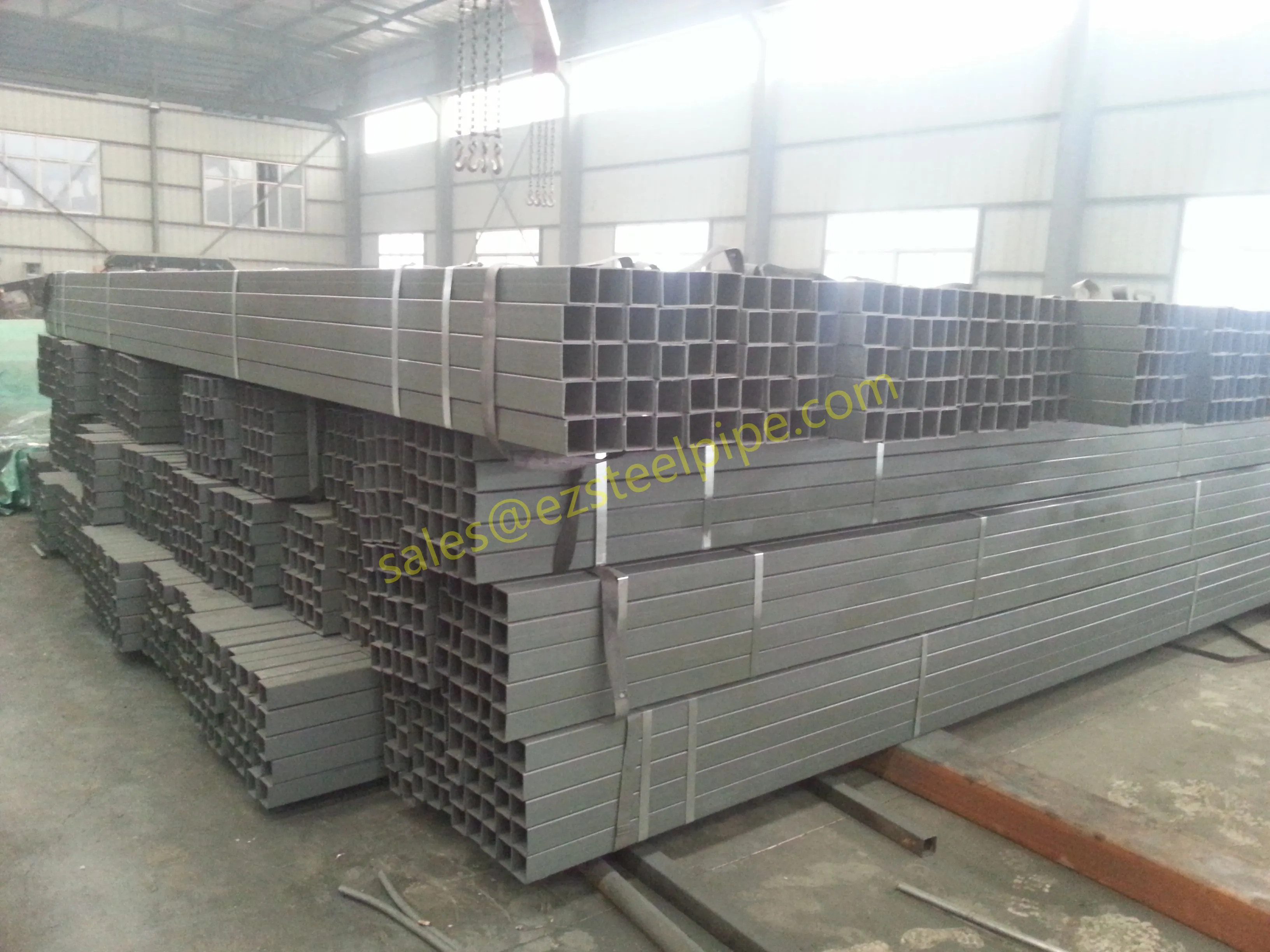
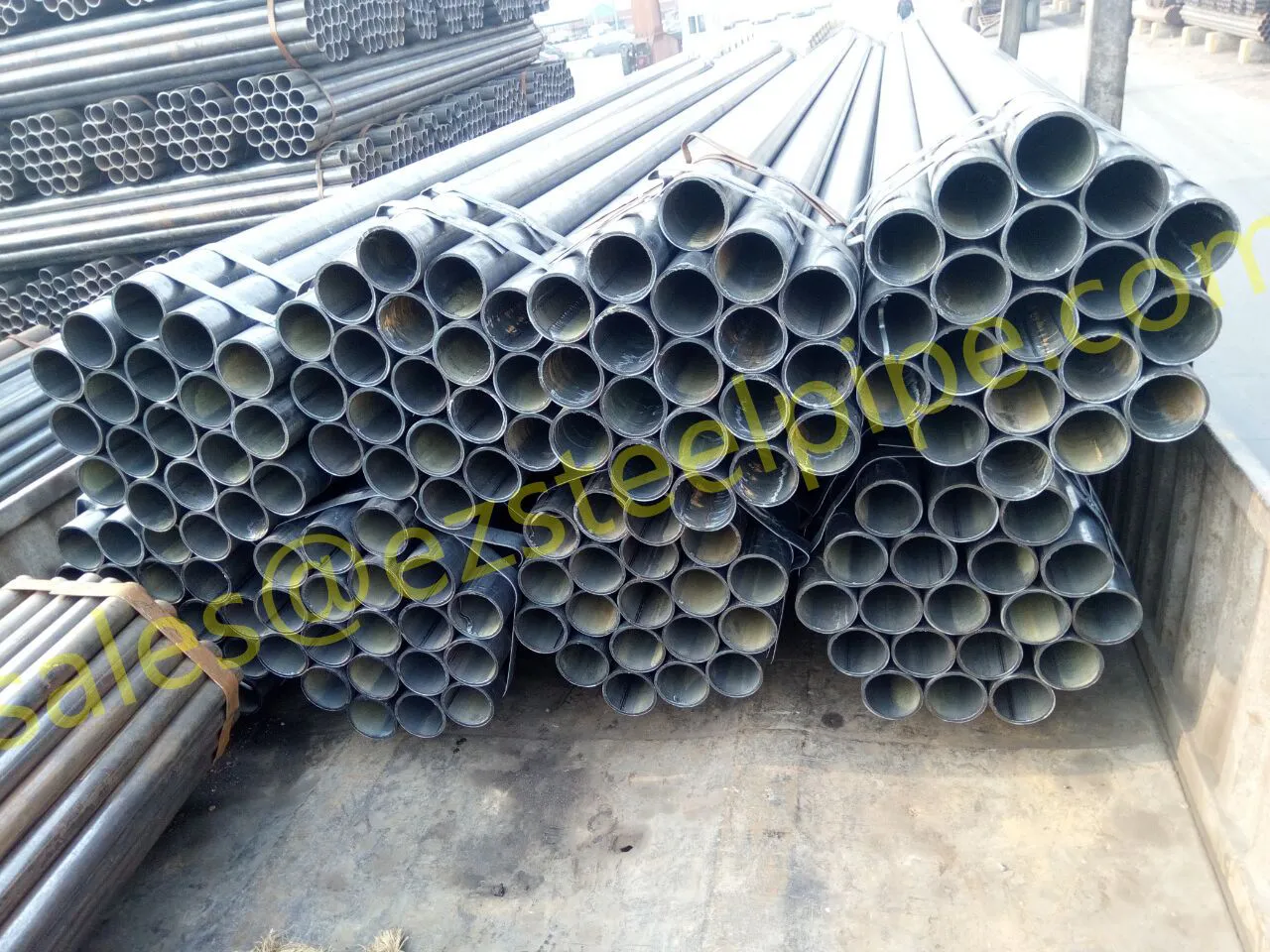
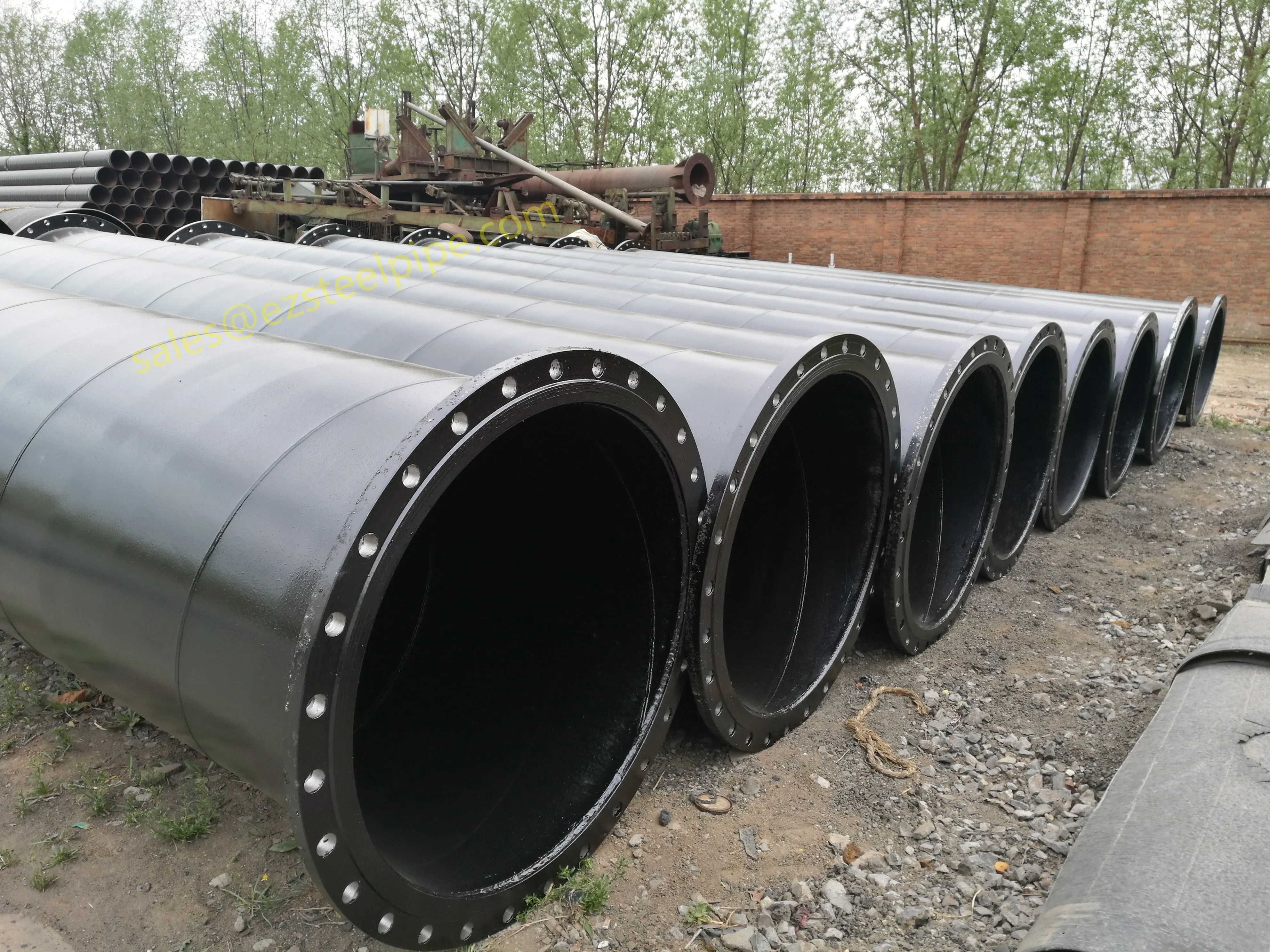
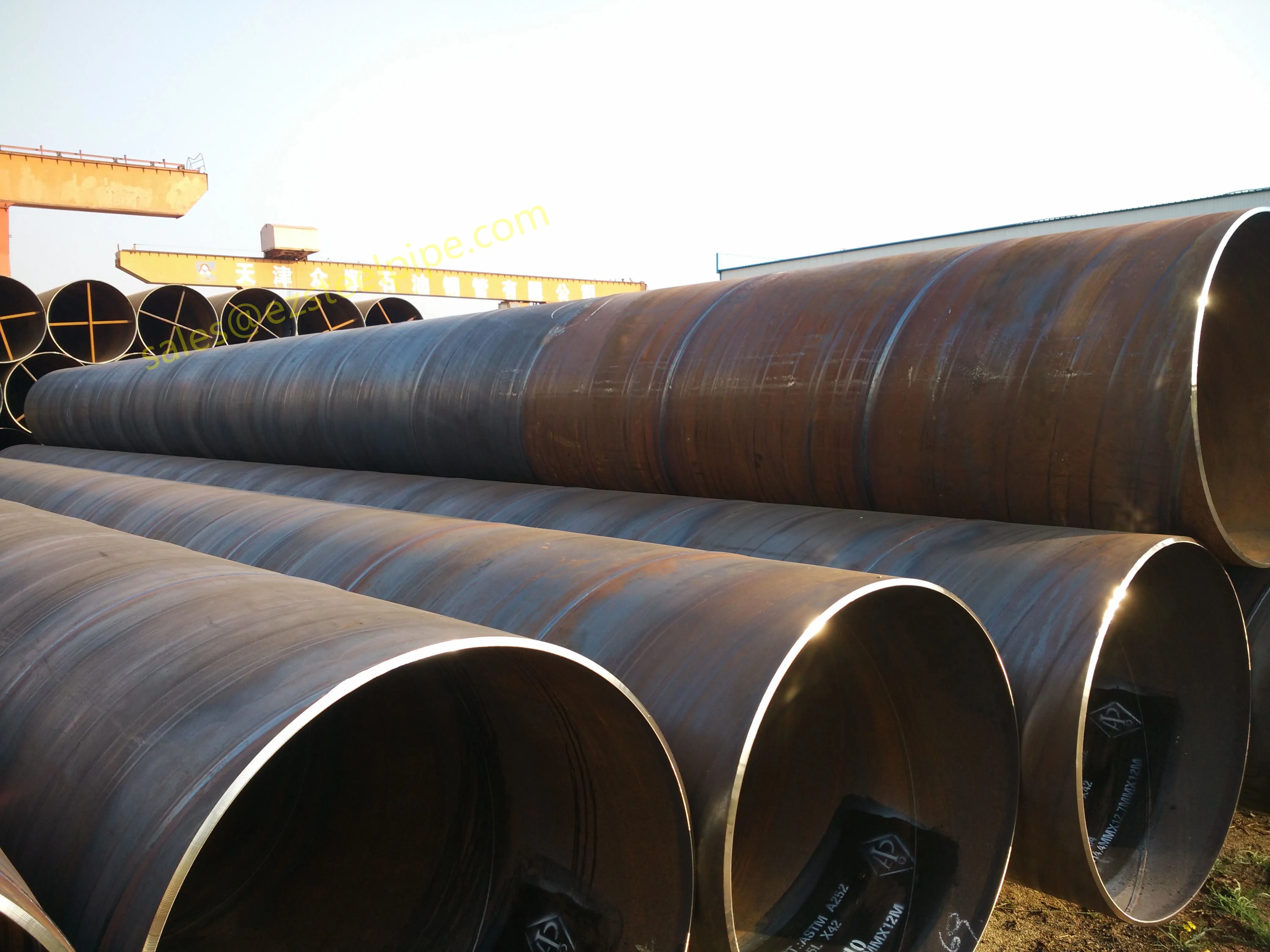
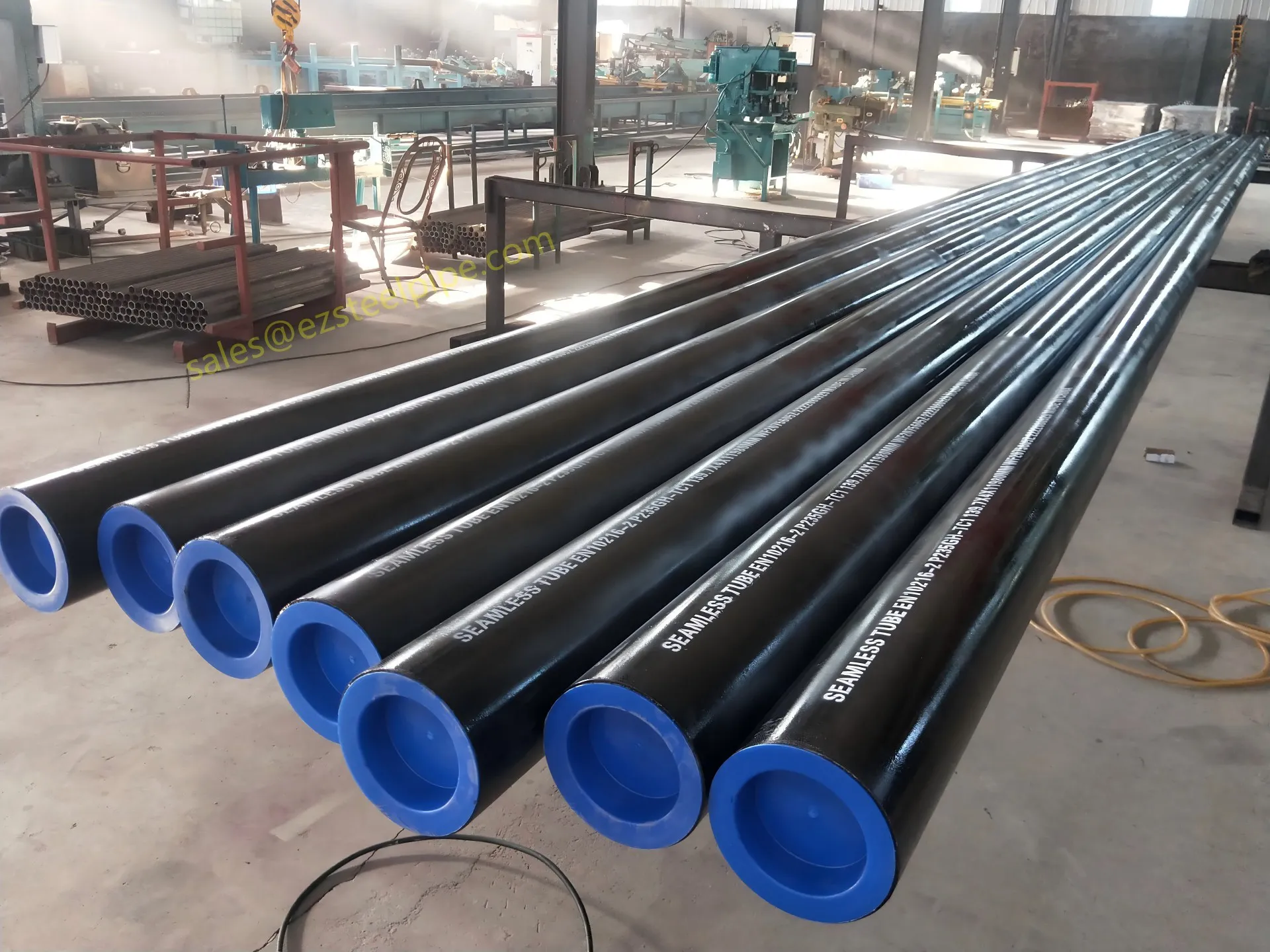
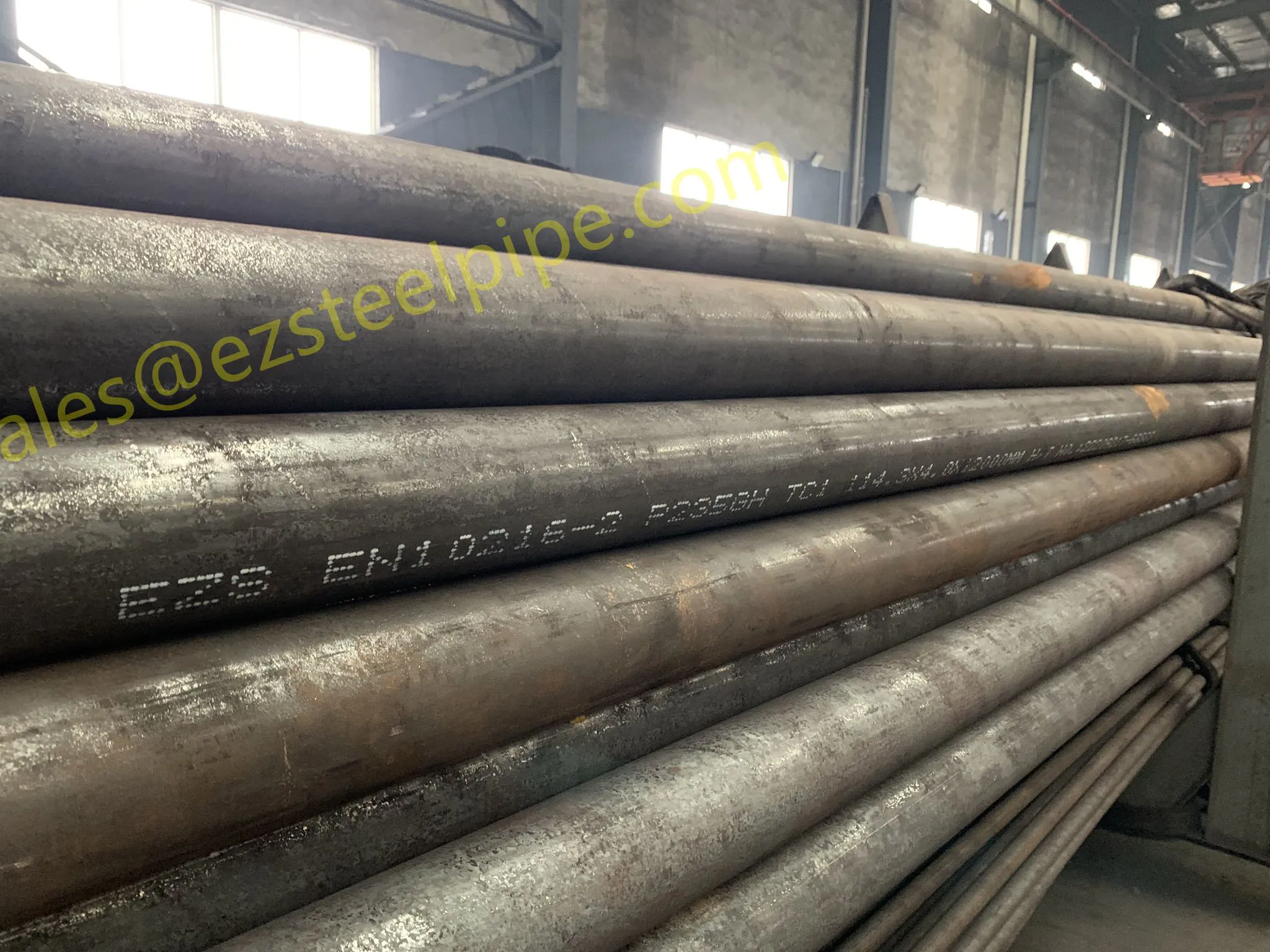
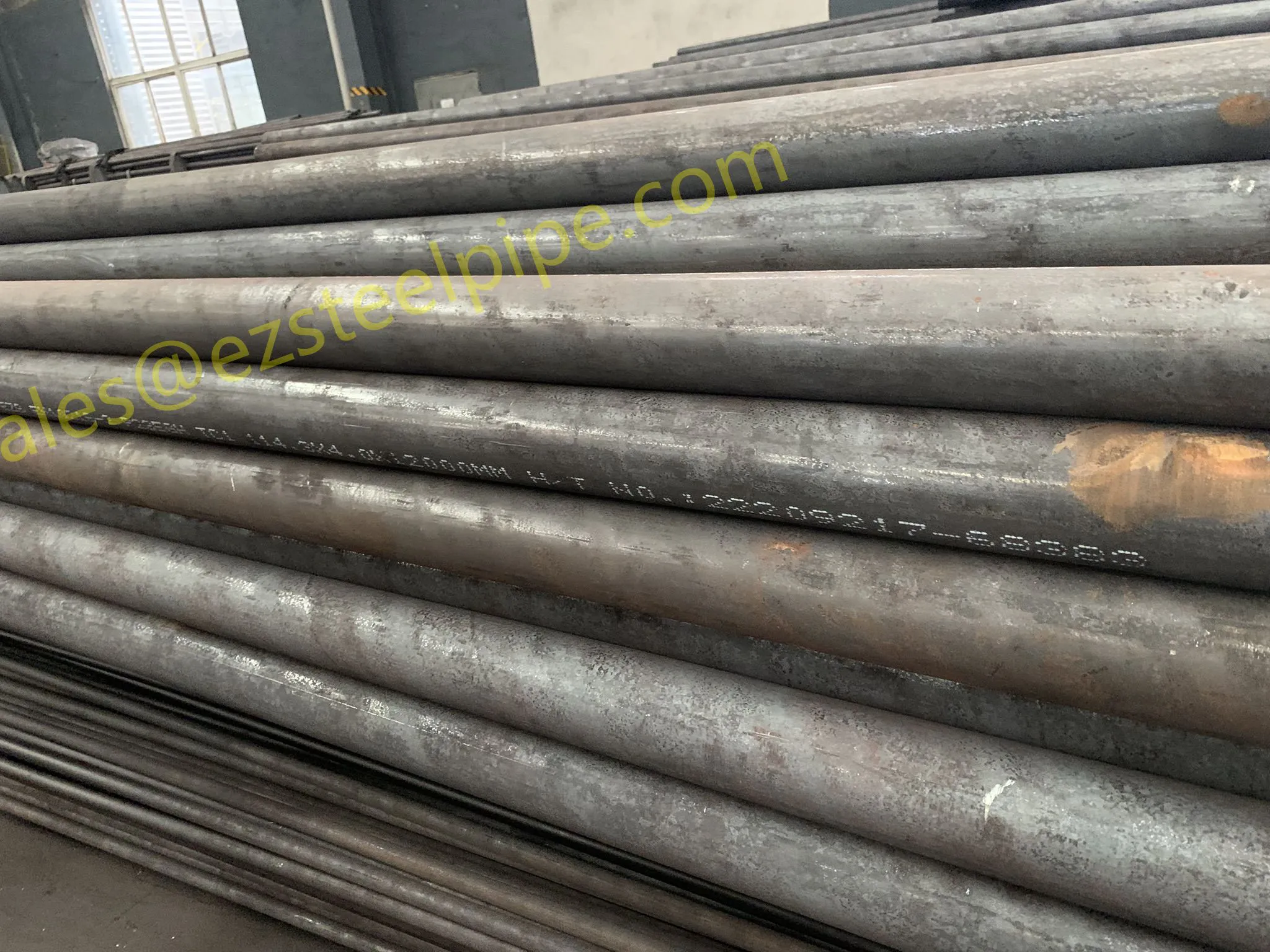
Before diving into inspection techniques, it's important to grasp what makes boiler tubing unique. Unlike standard pipes, these are pressure tubes designed to handle extreme conditions: think high temperatures (often exceeding 1,000°F), intense pressure (up to thousands of psi), and exposure to corrosive or abrasive fluids. They're typically made from robust materials like carbon & carbon alloy steel, stainless steel, or even copper & nickel alloy, depending on the application. For example, in power plants & aerospace, where reliability is non-negotiable, you might find specialized alloys that resist thermal fatigue. In marine & ship-building, corrosion resistance takes priority, leading to the use of copper-nickel blends.
What sets boiler tubing apart from, say, heat exchanger tubes (another workhorse in industrial settings) is its role in generating and transferring heat. While heat exchanger tubes focus on moving heat between fluids, boiler tubing is often at the heart of the heat source itself—boiling water to create steam for turbines, or heating process fluids in petrochemical facilities. This proximity to the "action" makes it more susceptible to wear and tear, from scaling on the inside to oxidation on the outside.
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































