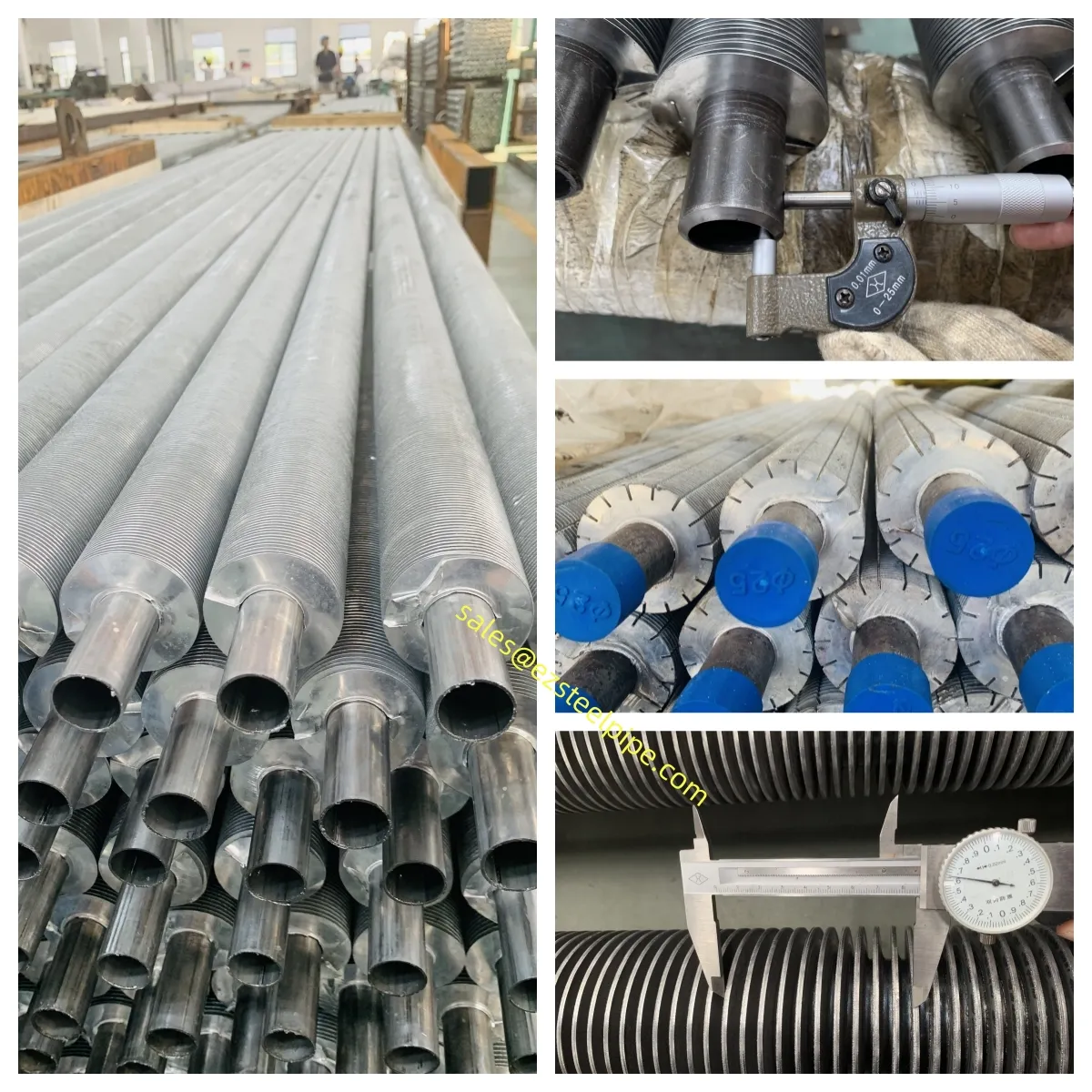
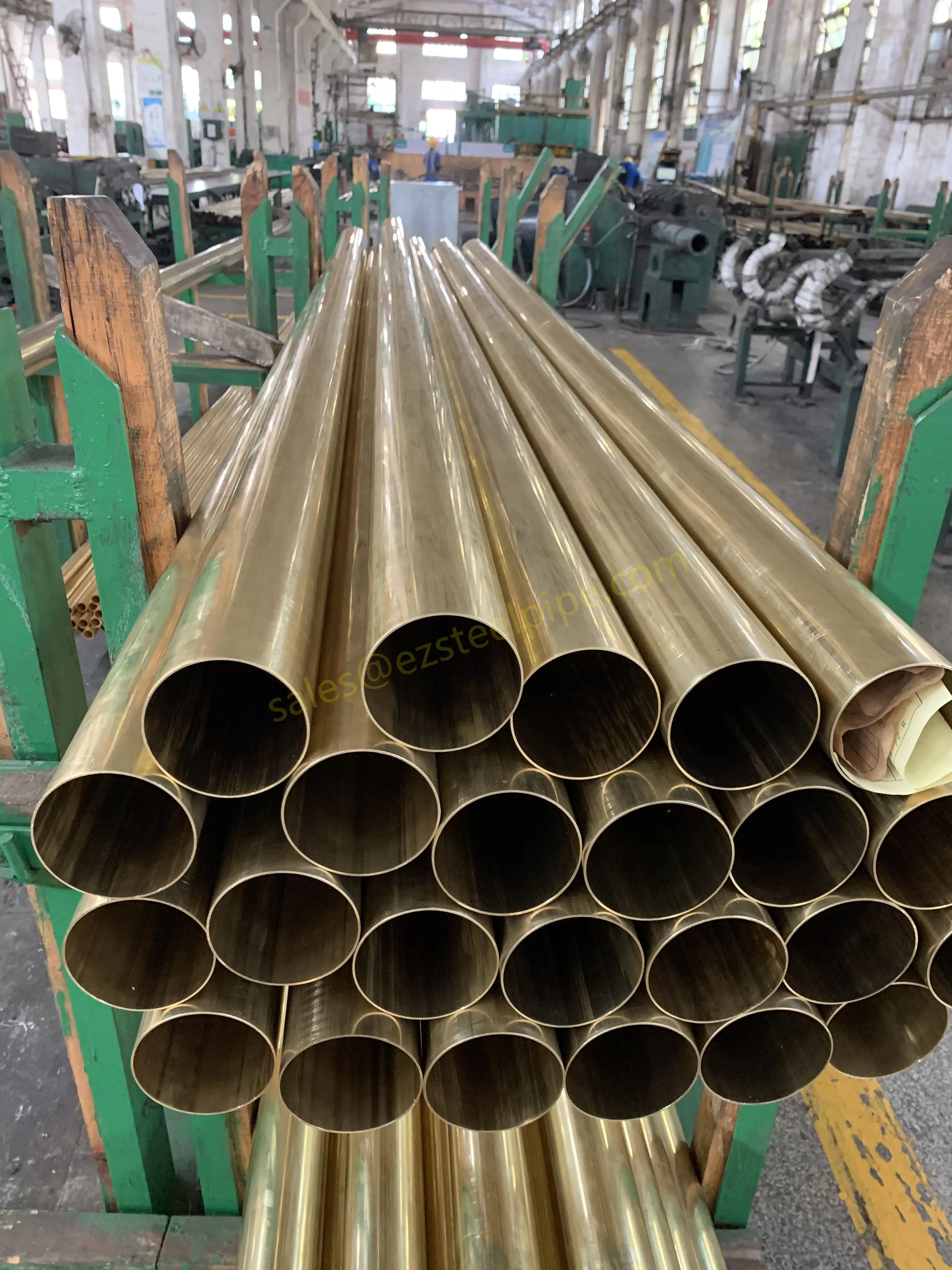
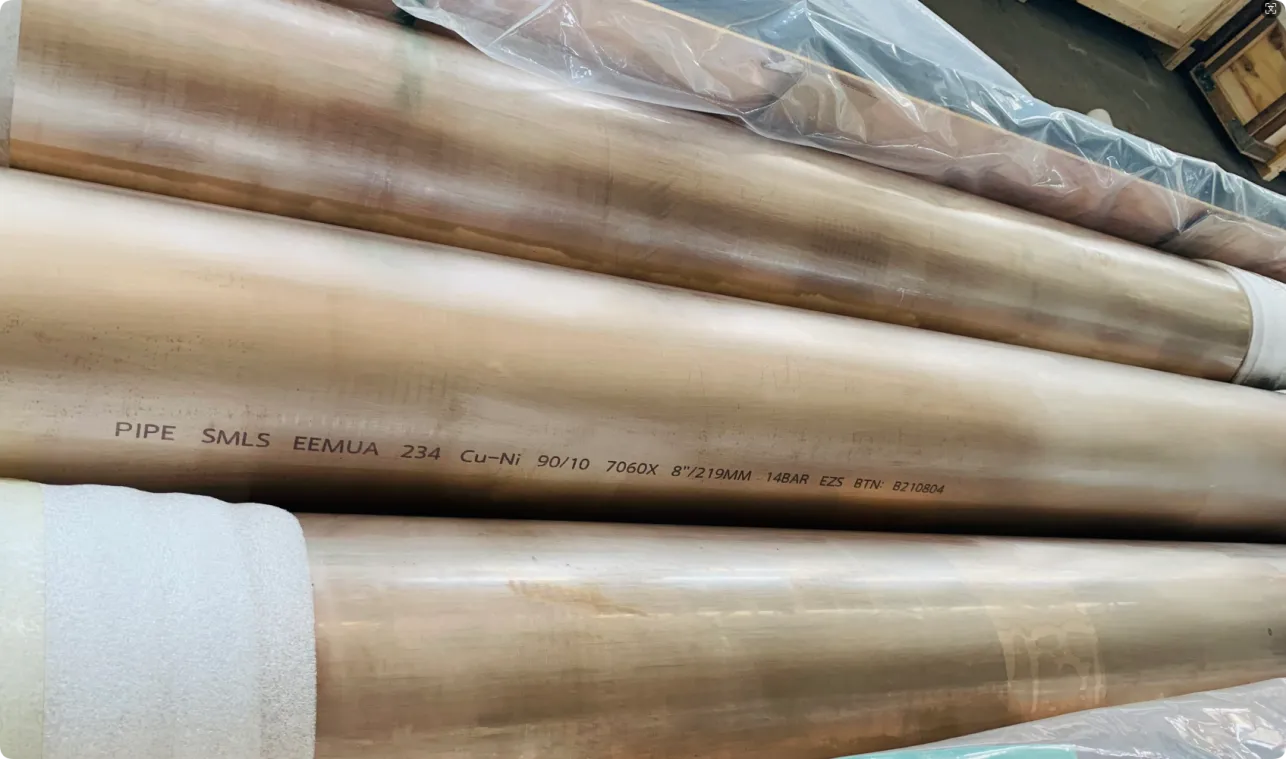
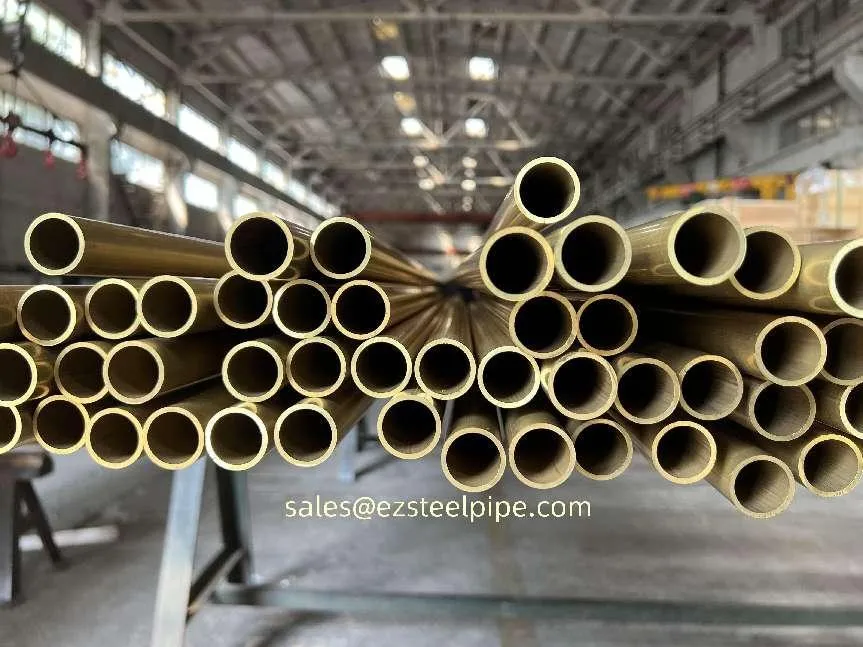
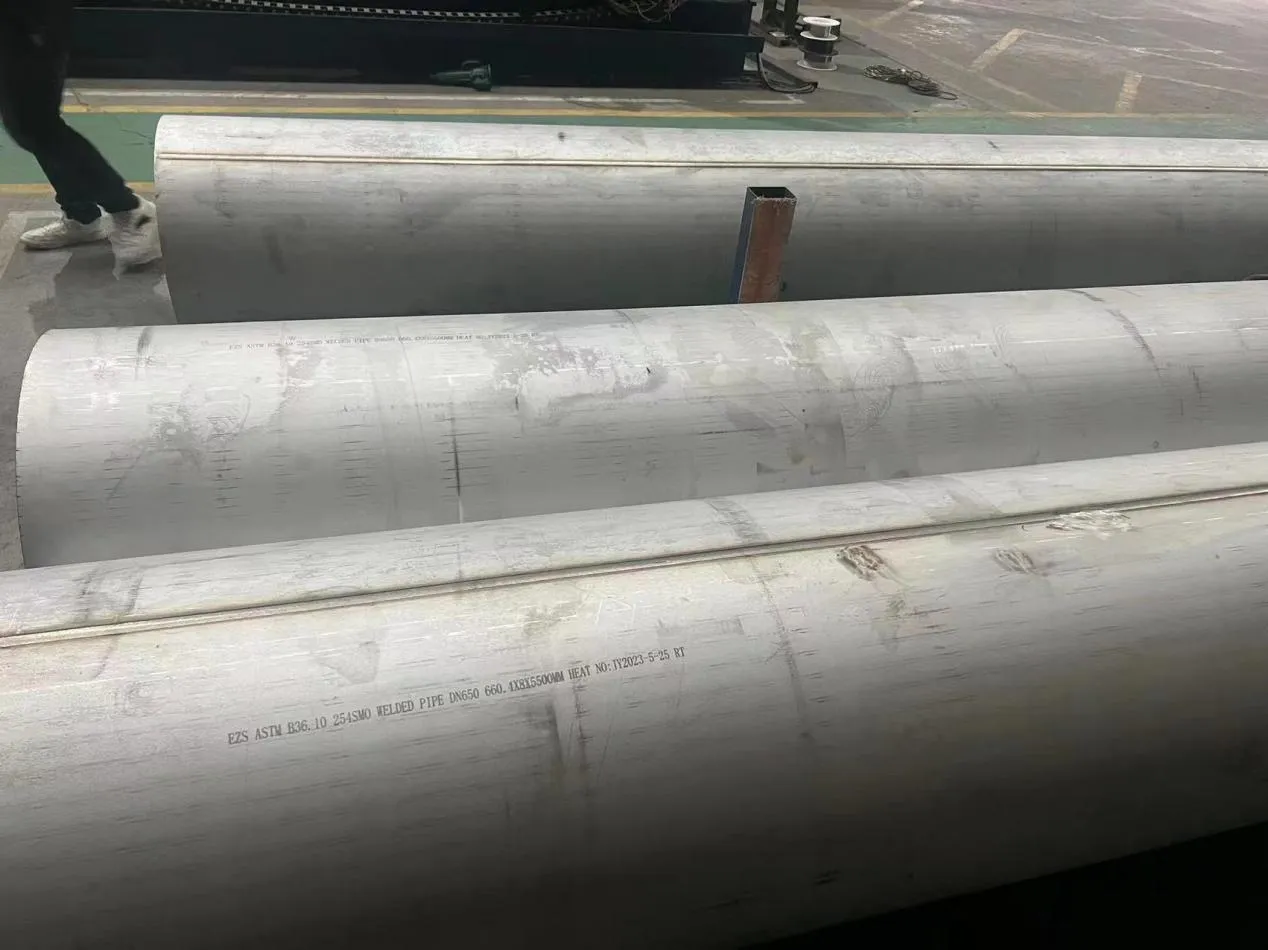
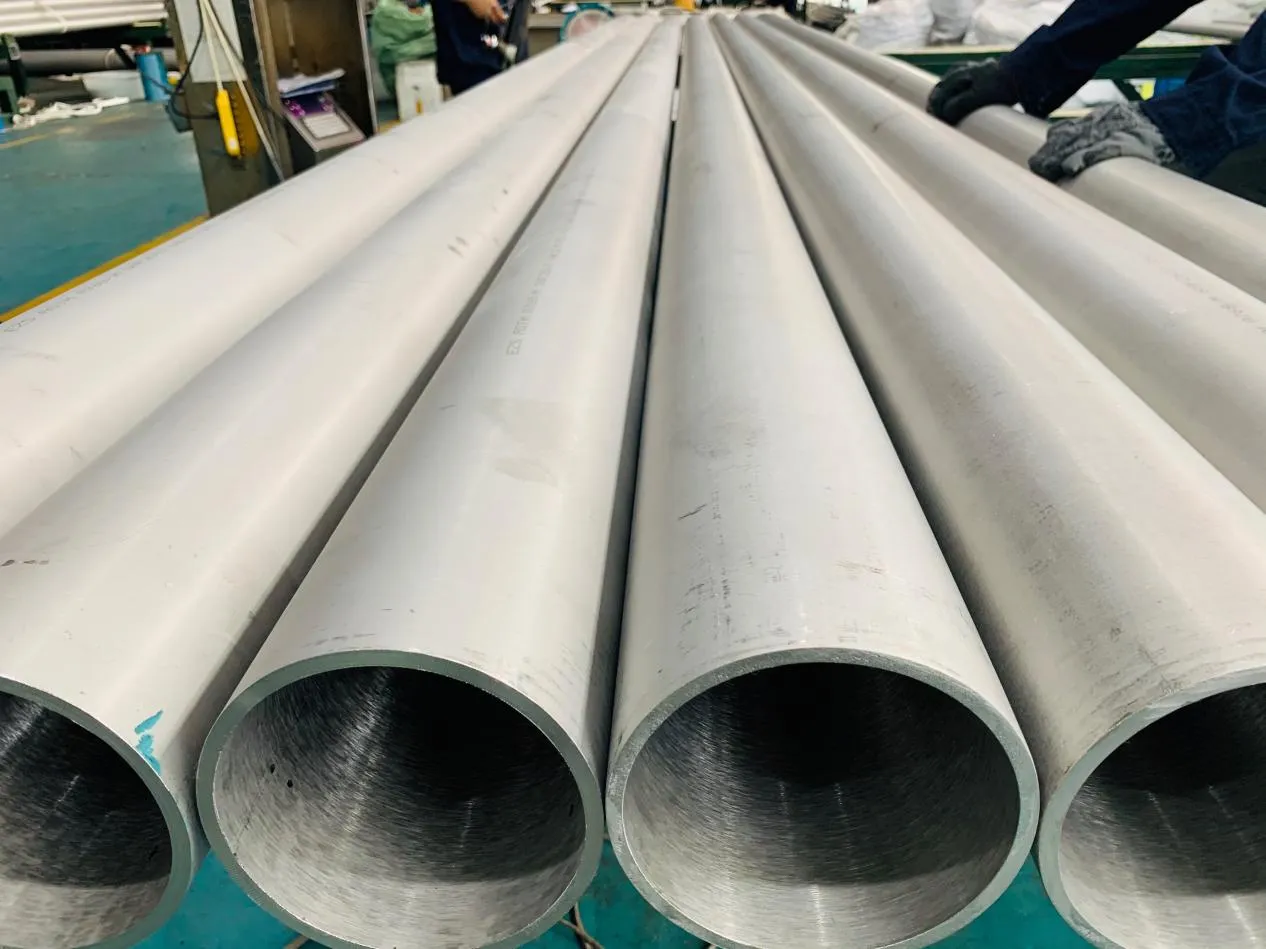
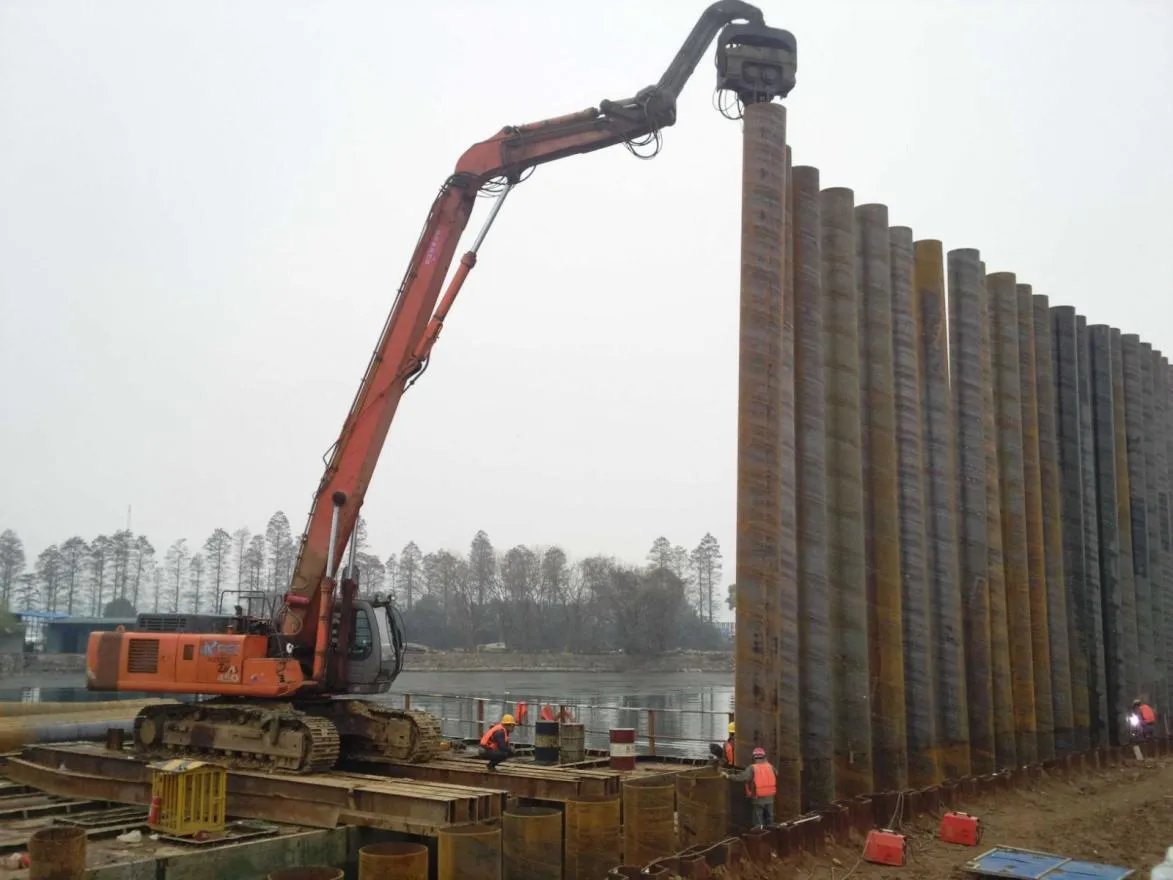
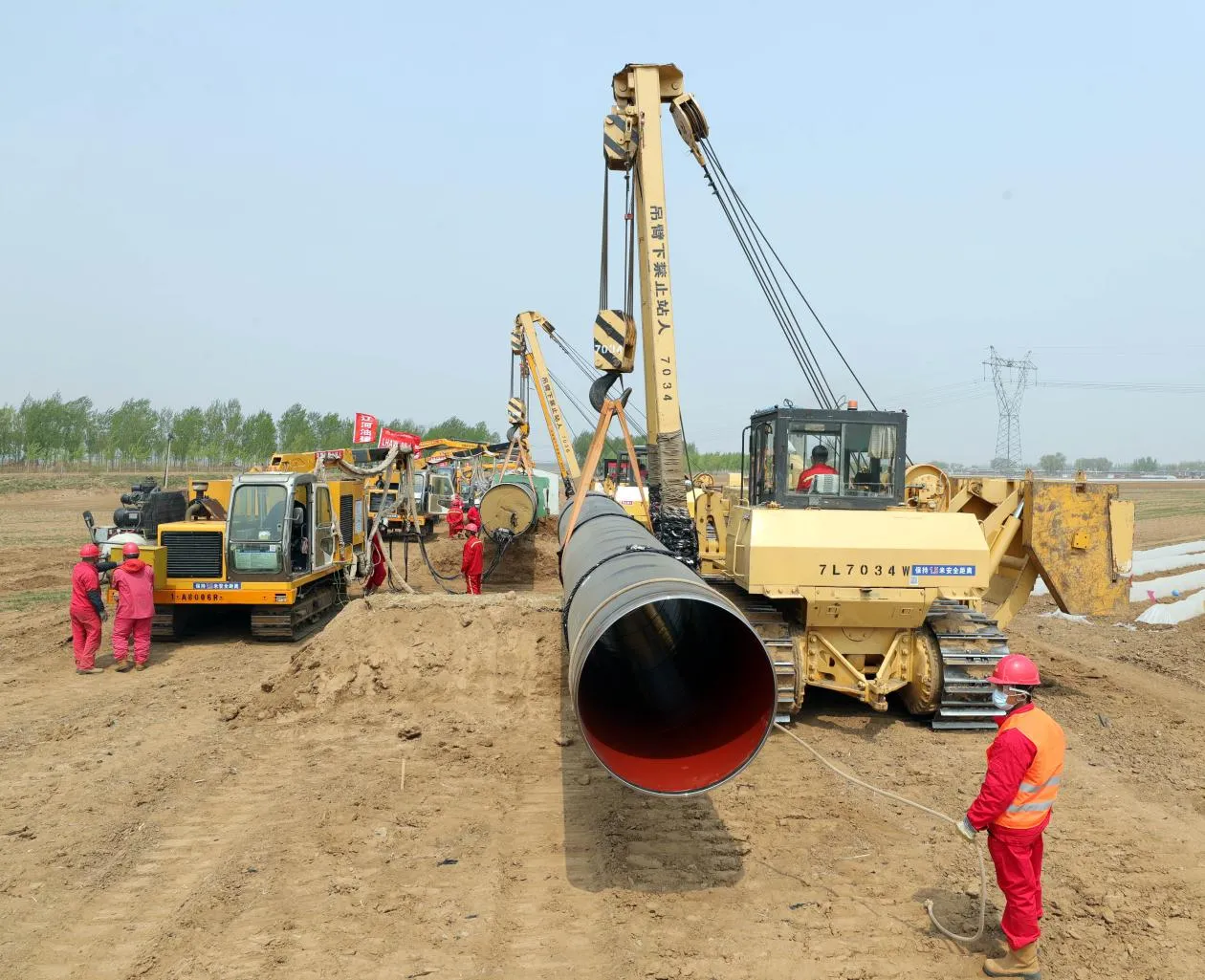
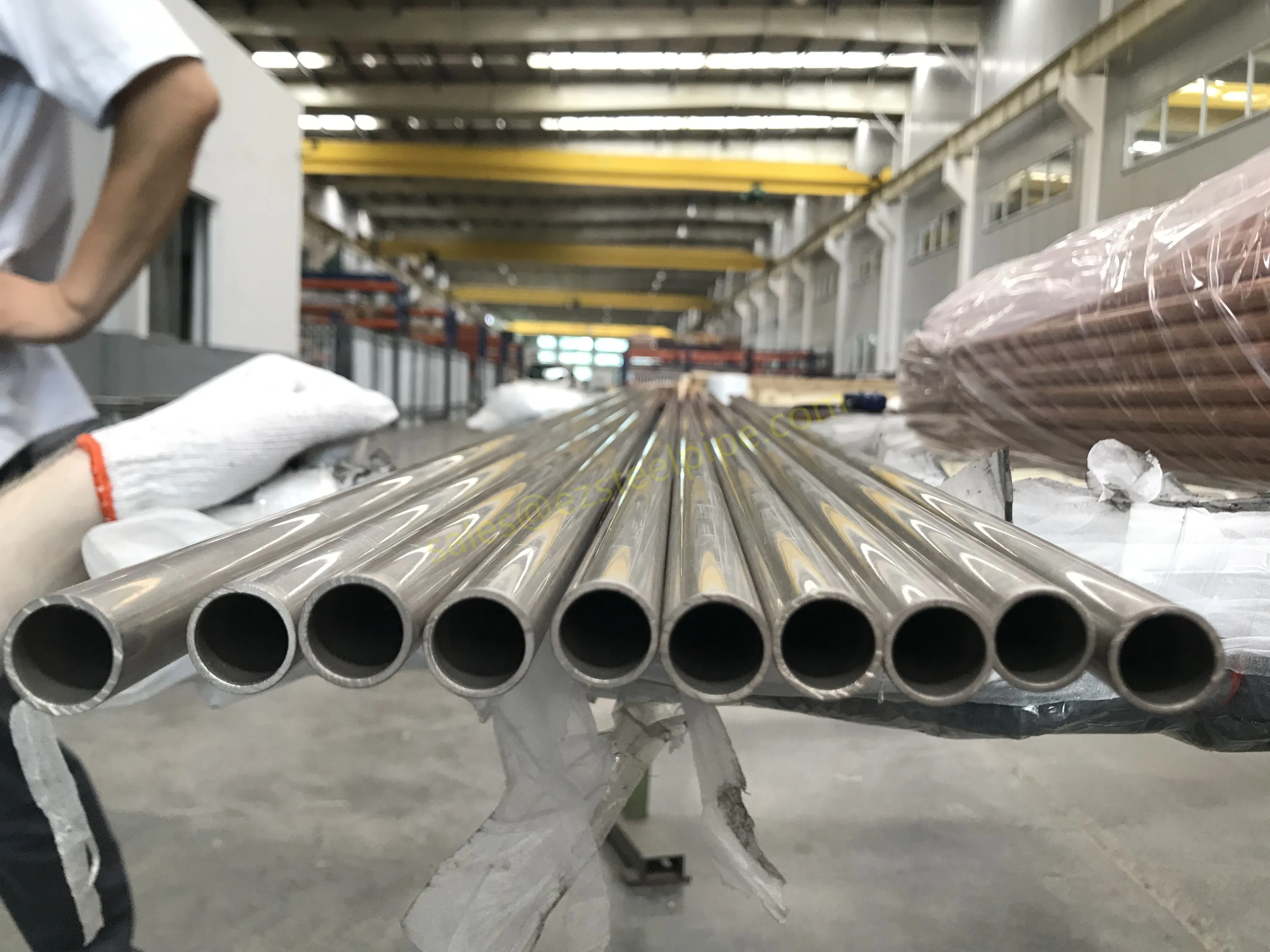
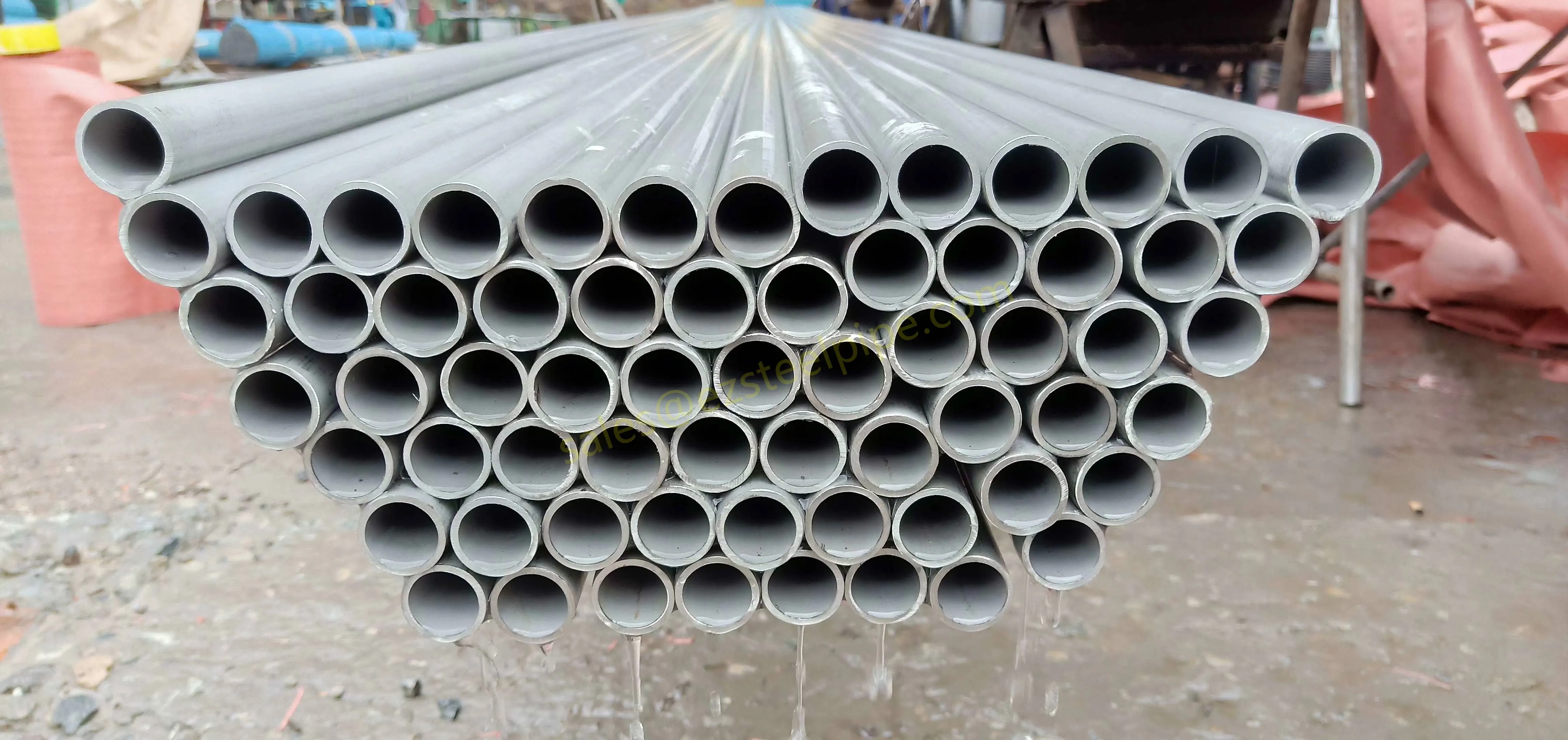
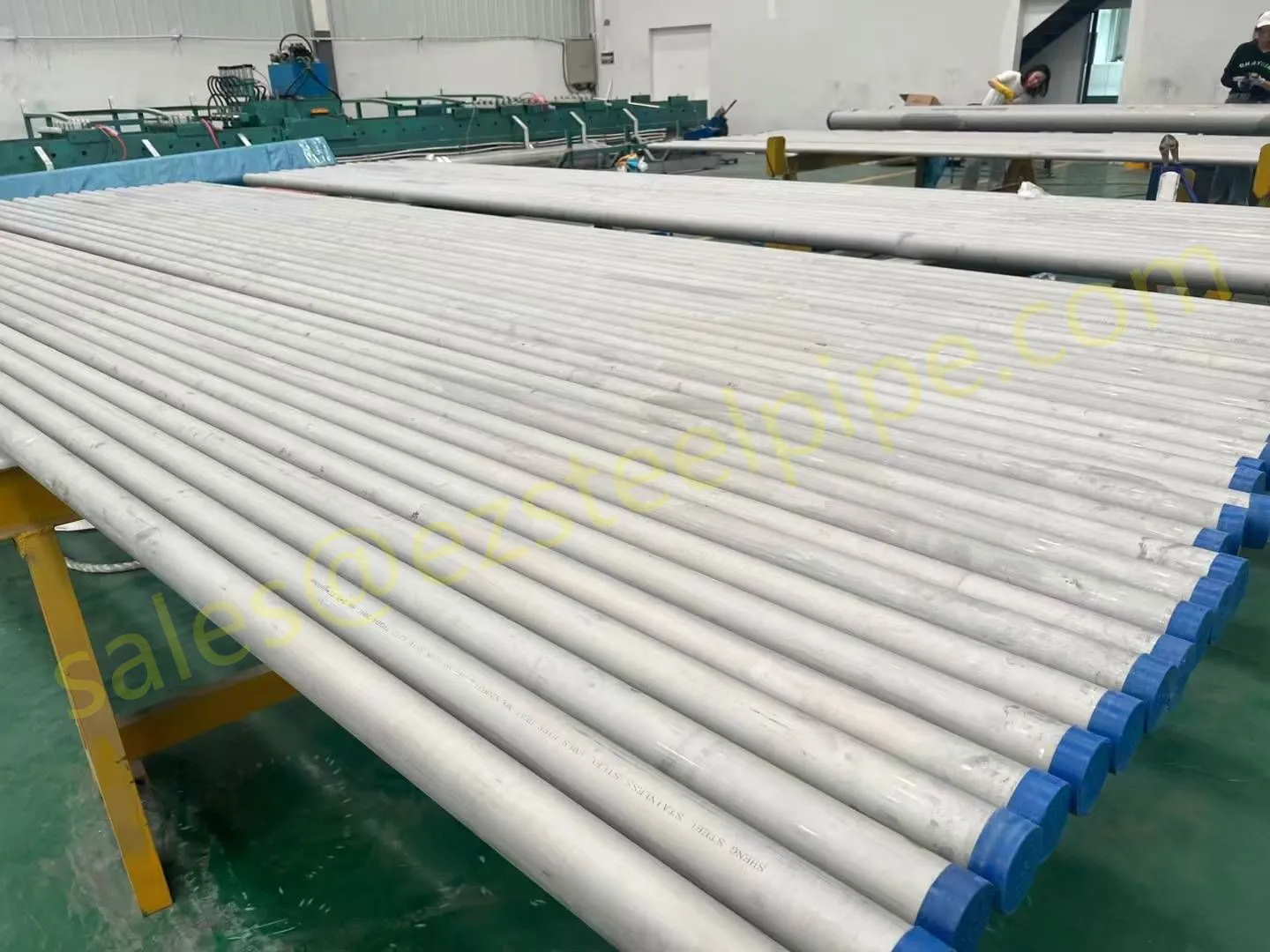
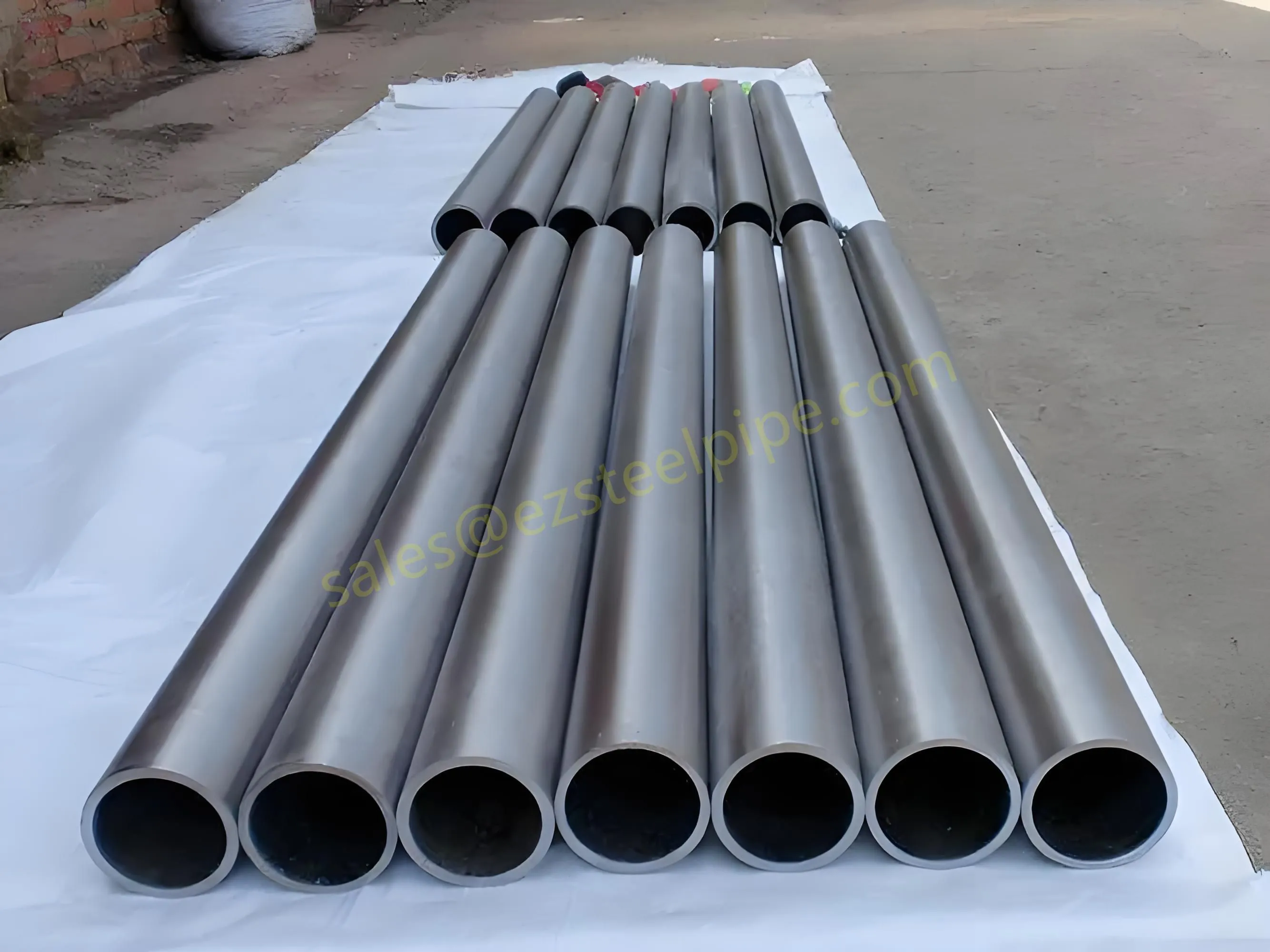
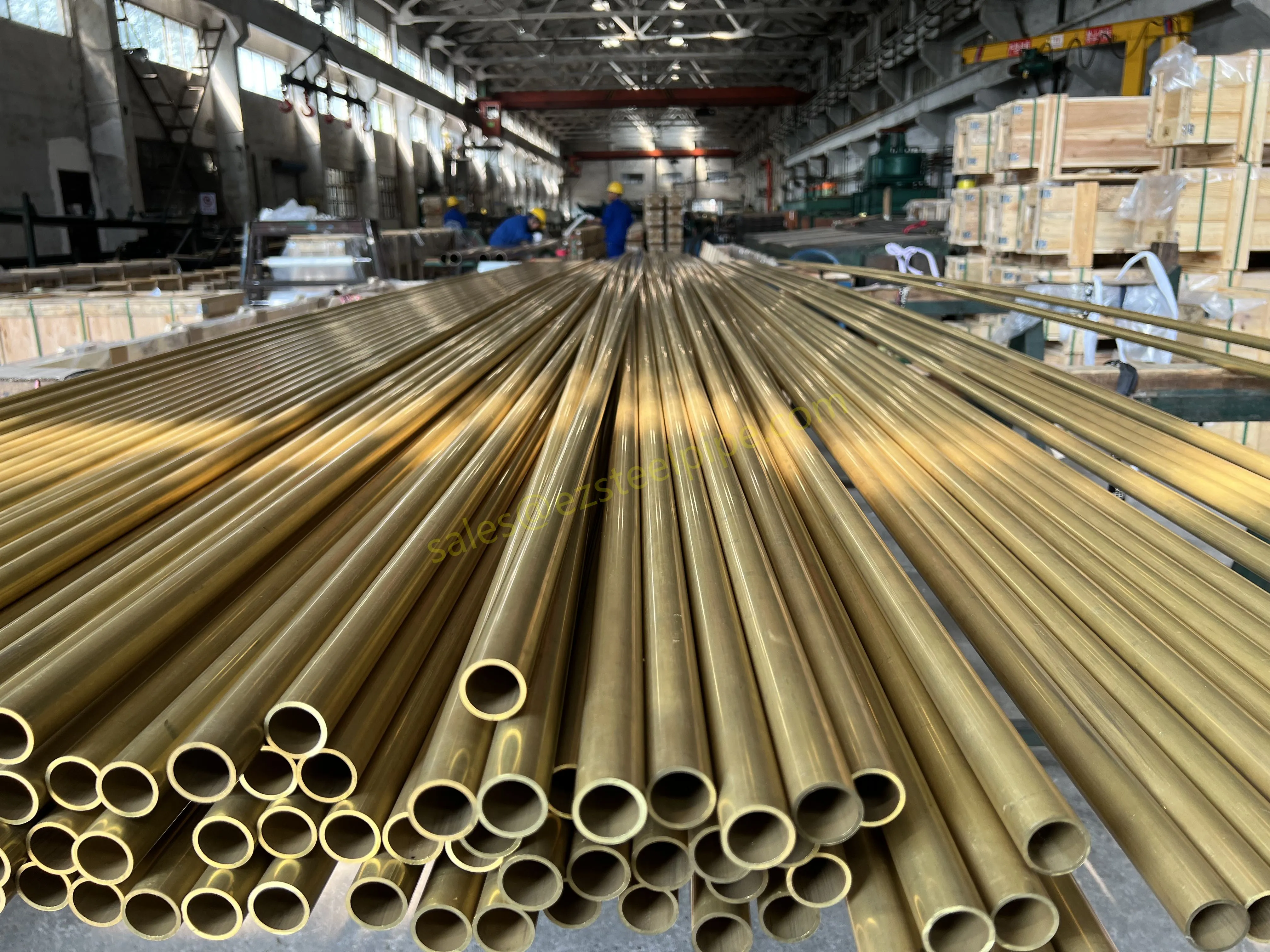
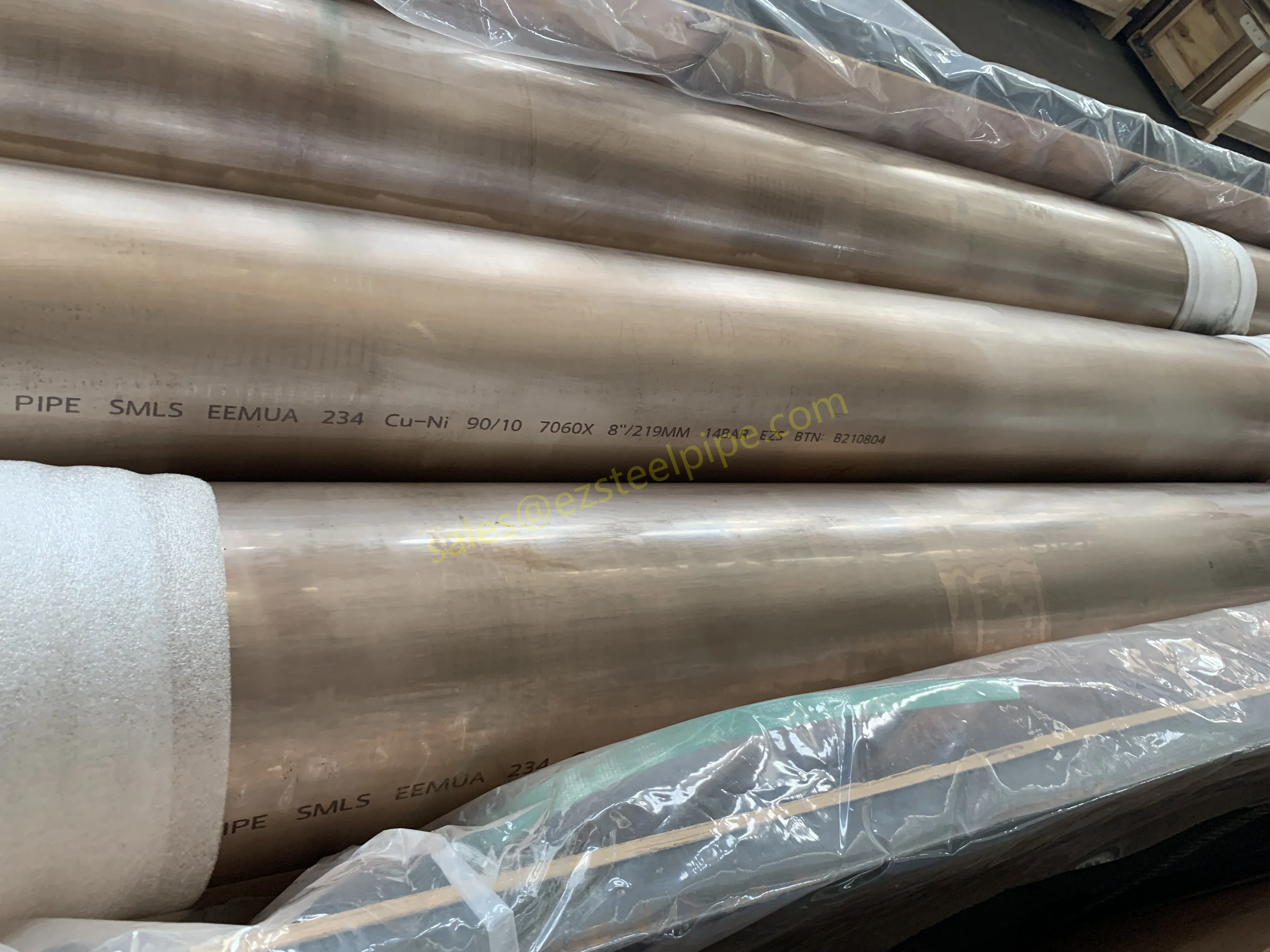
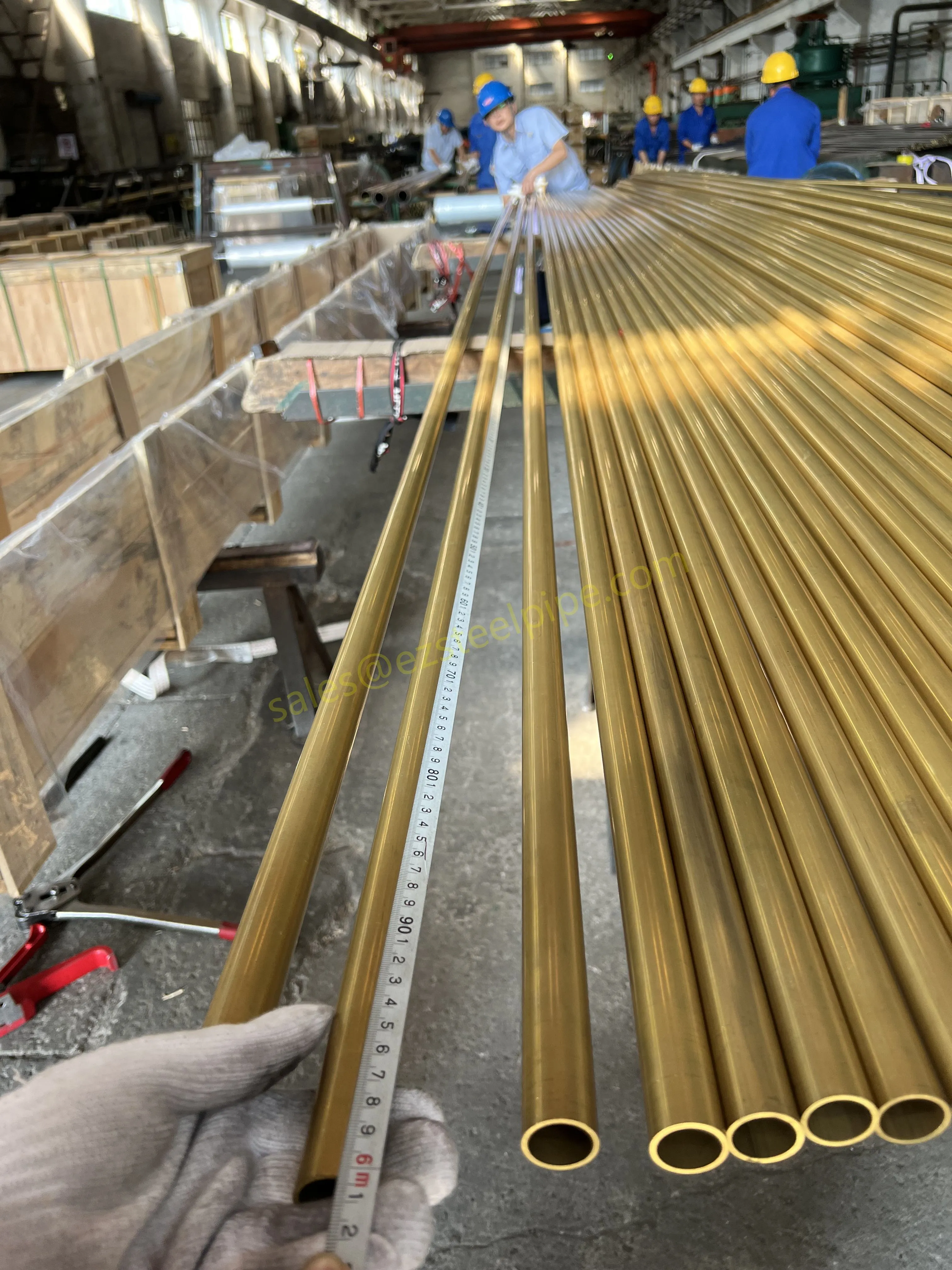
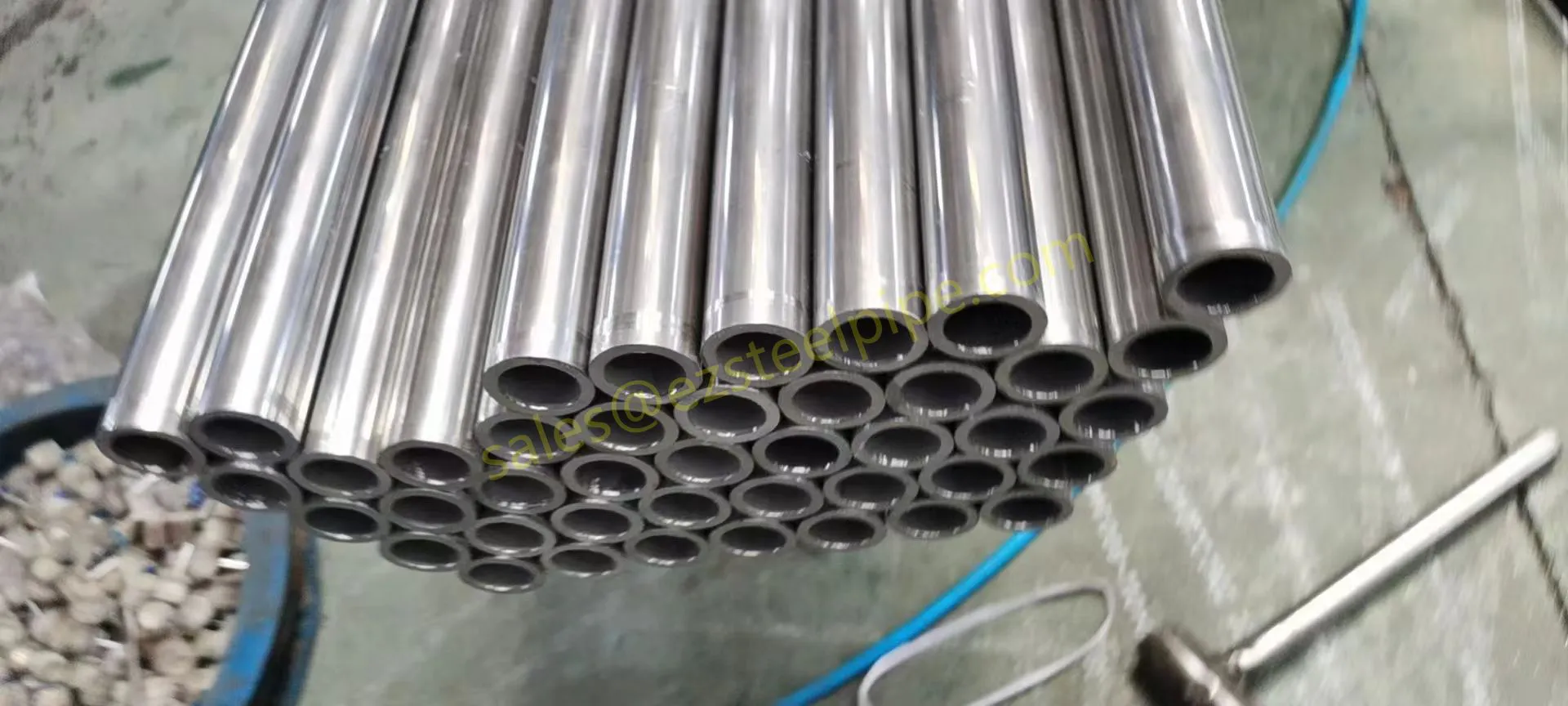
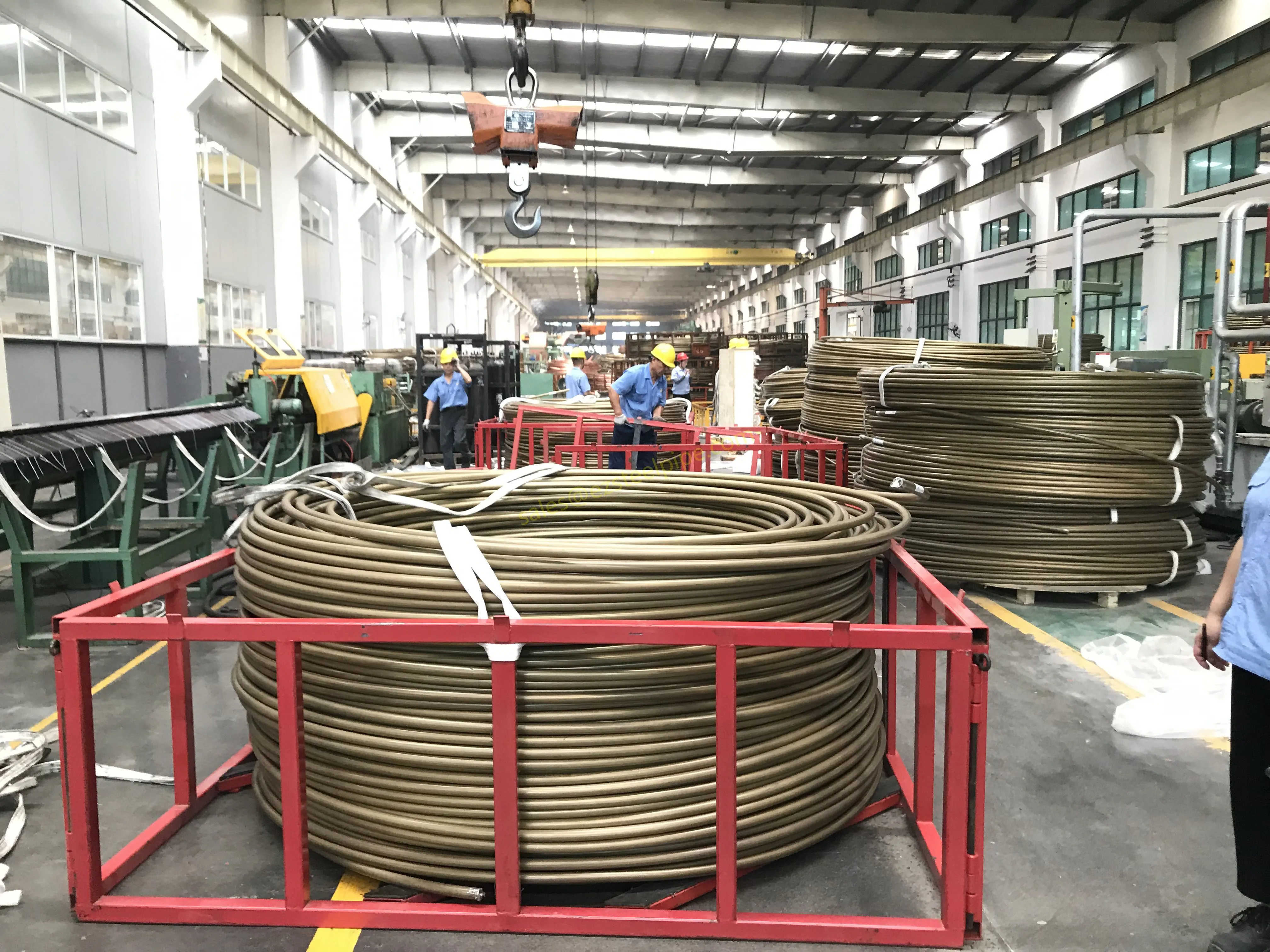
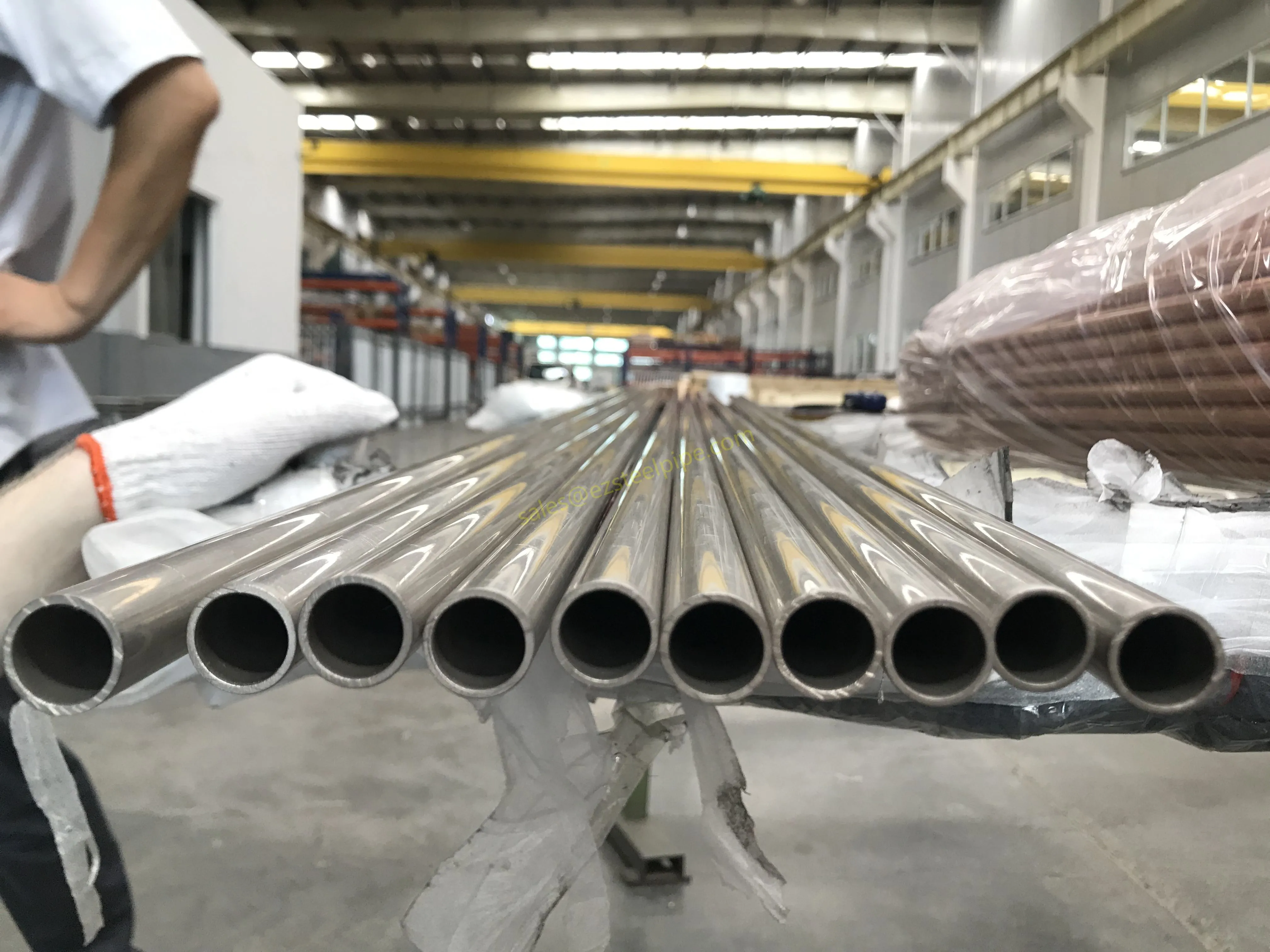
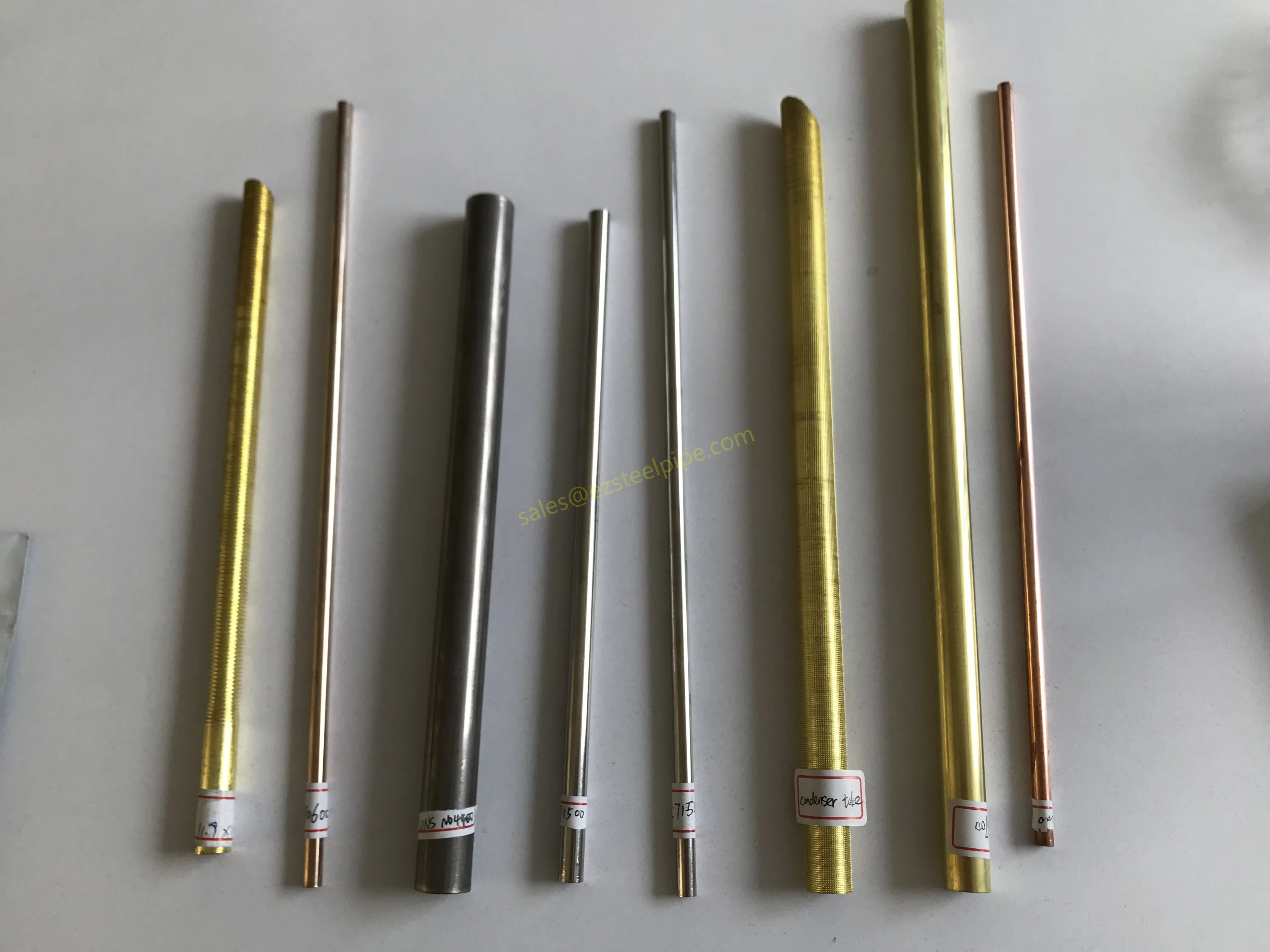
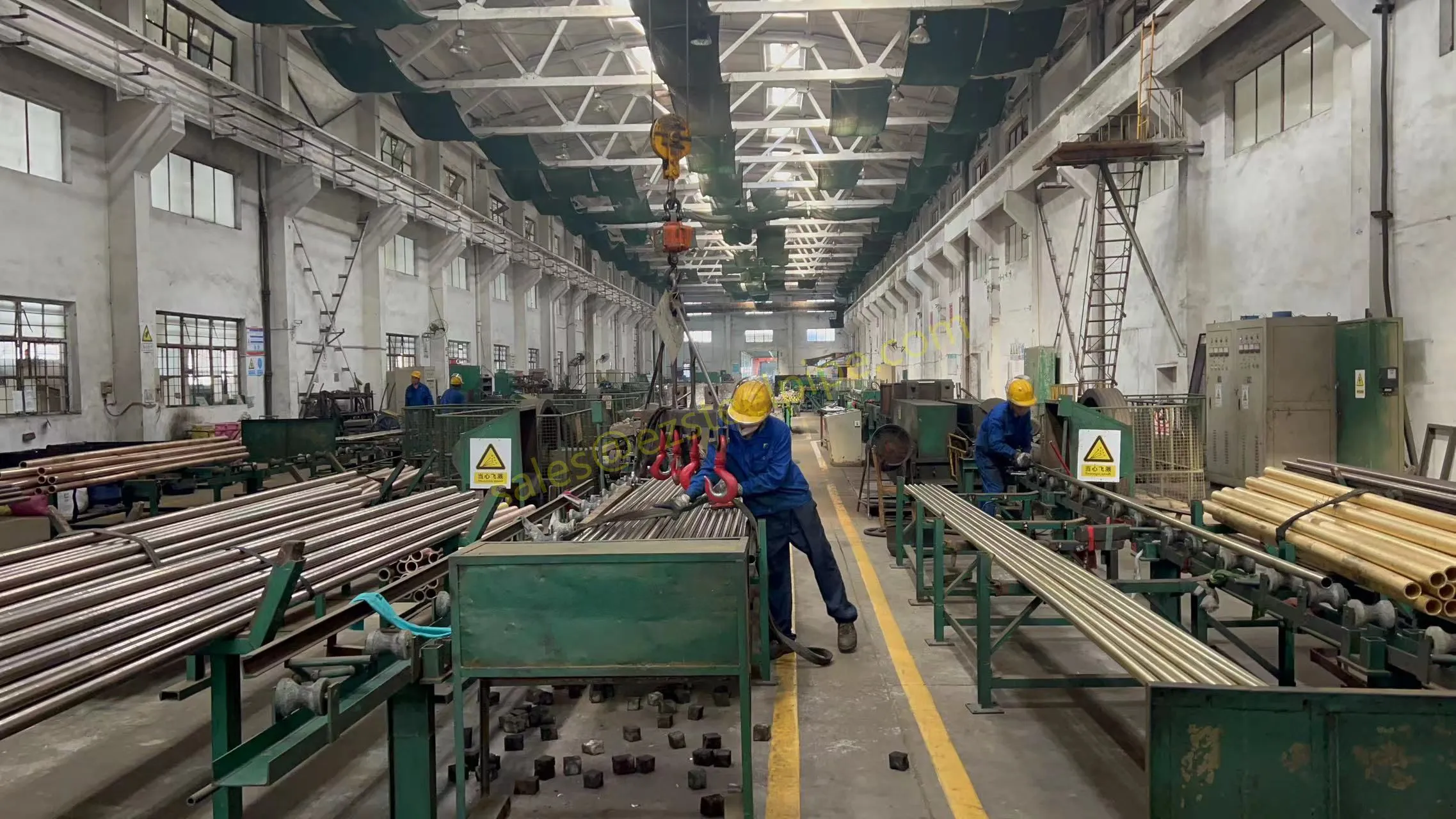
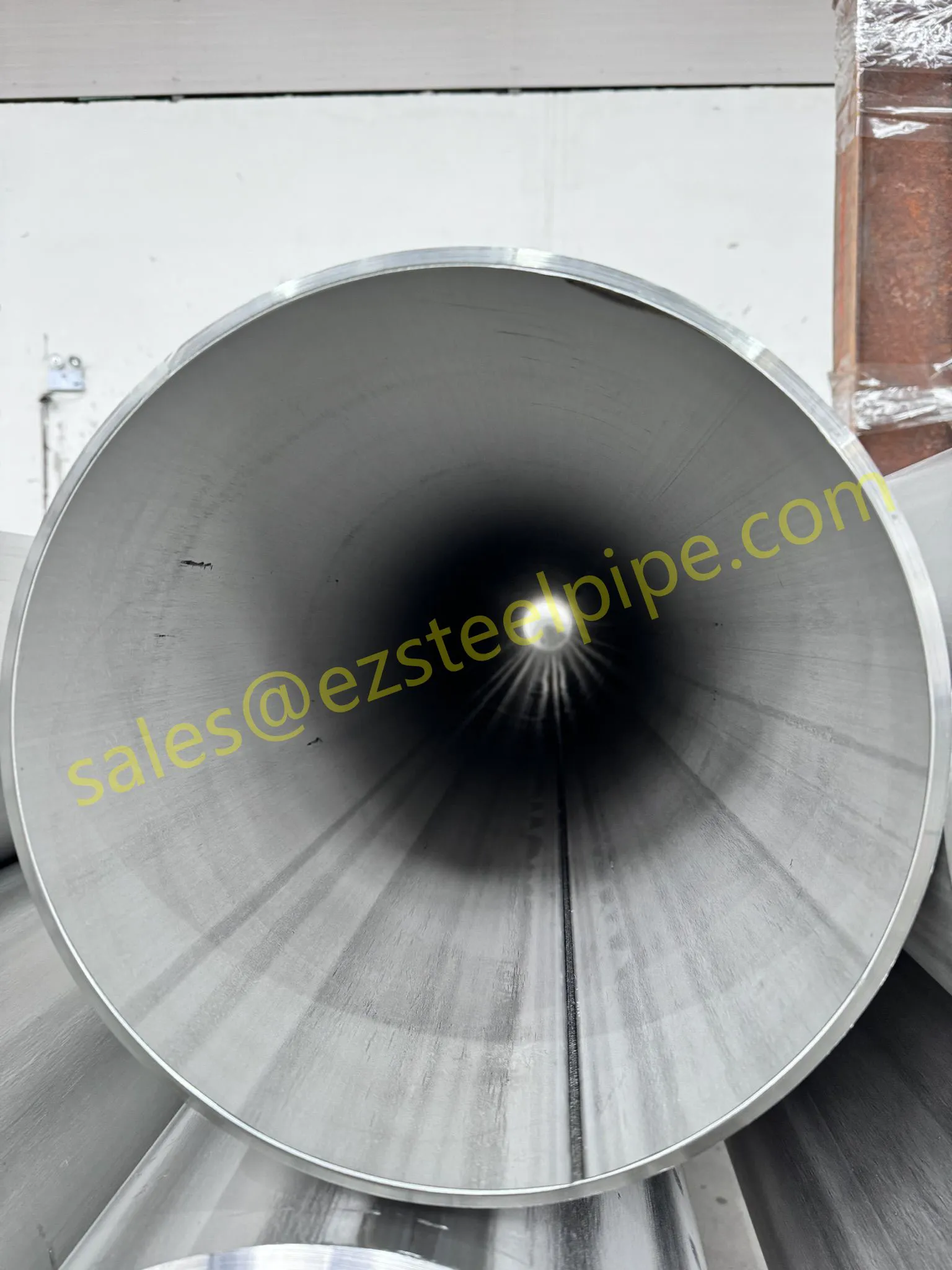
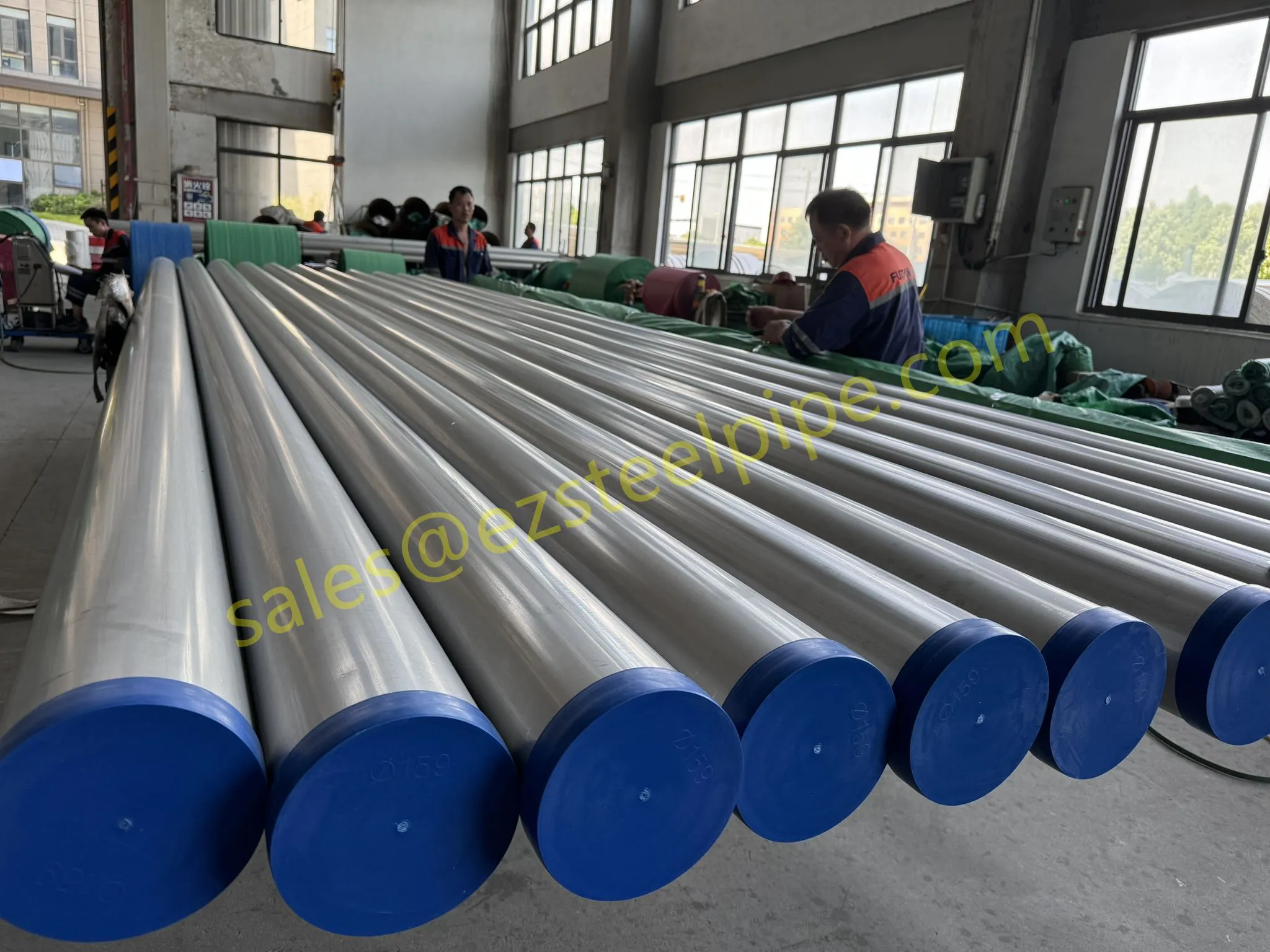
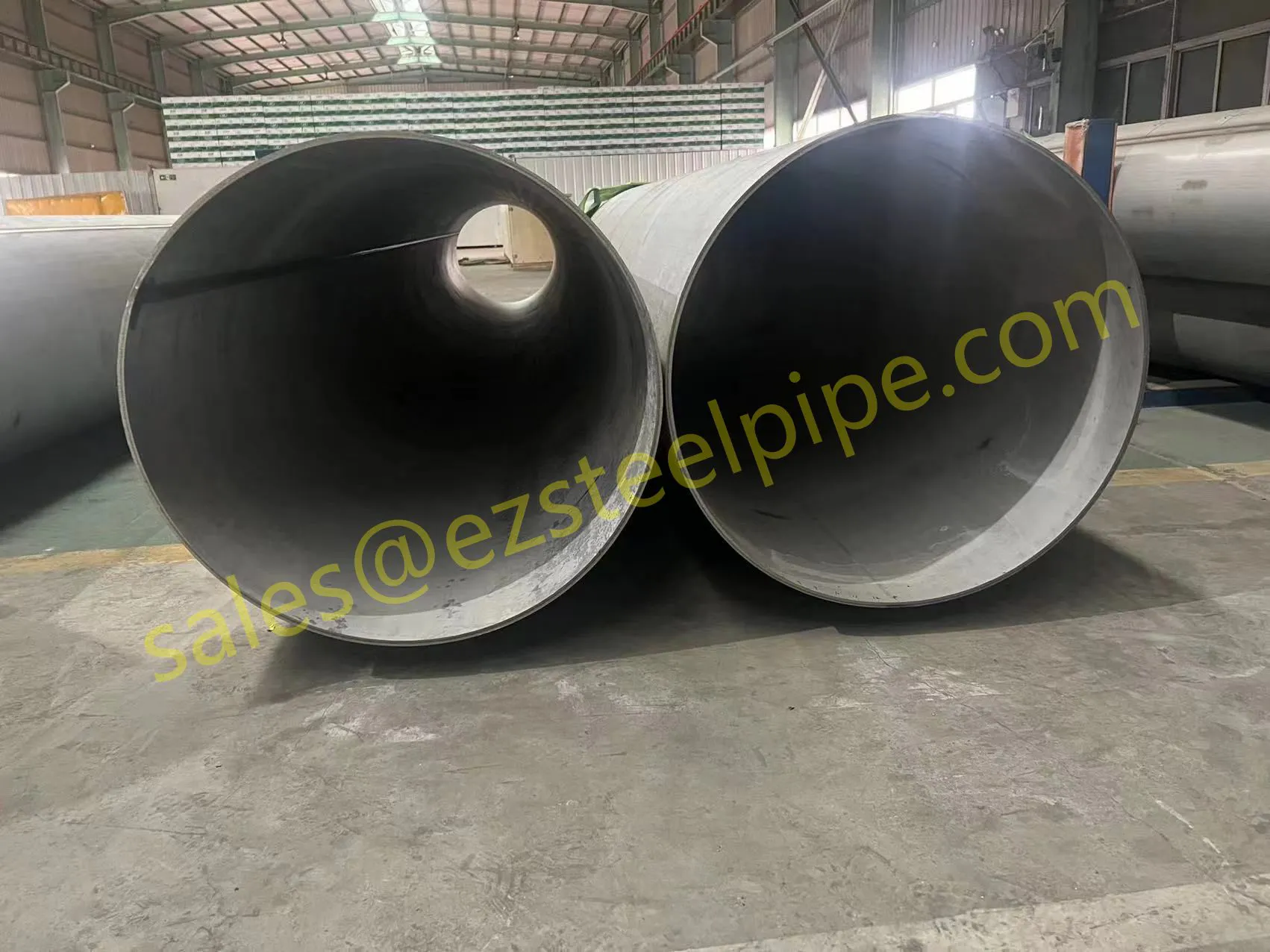
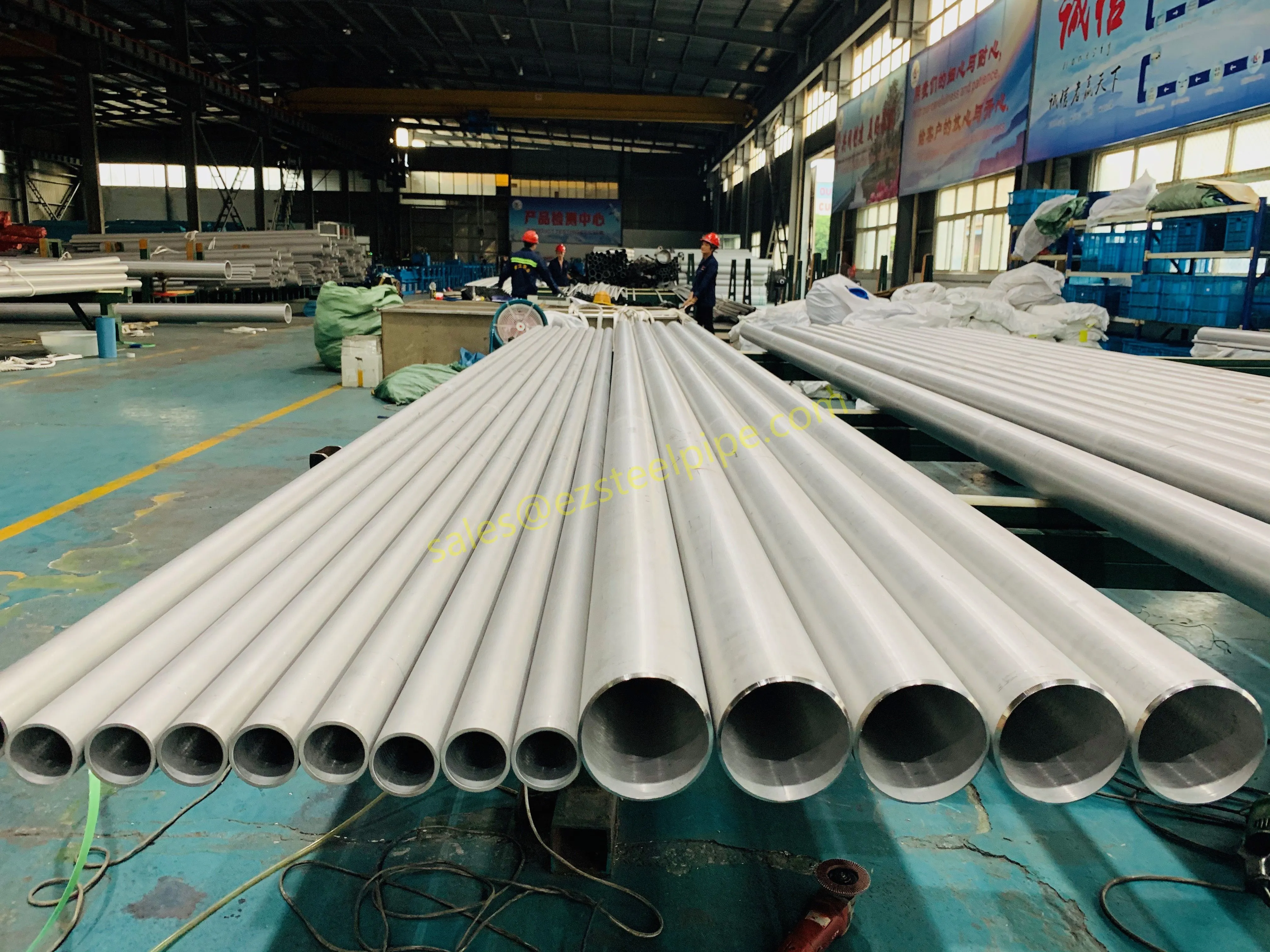
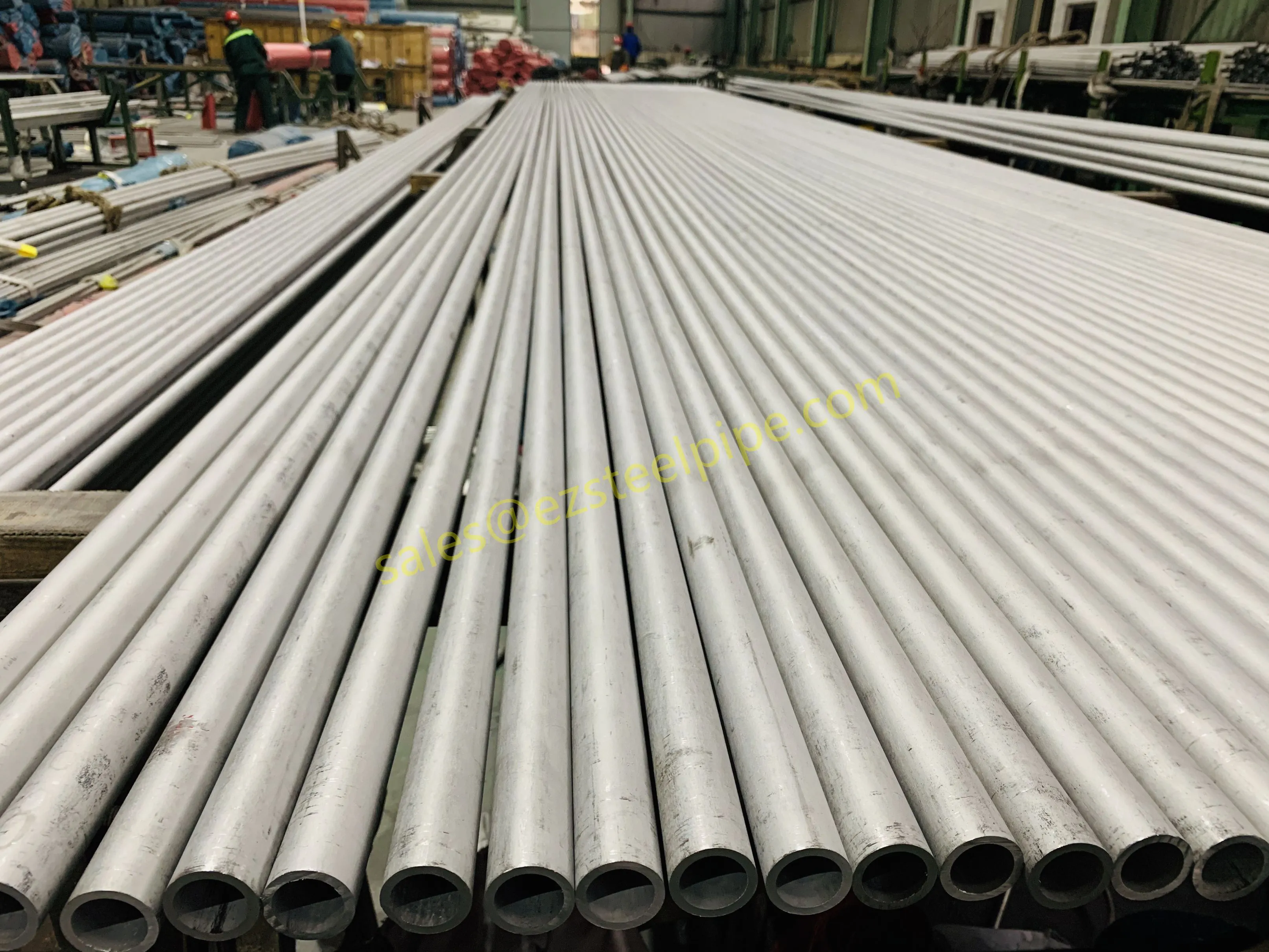
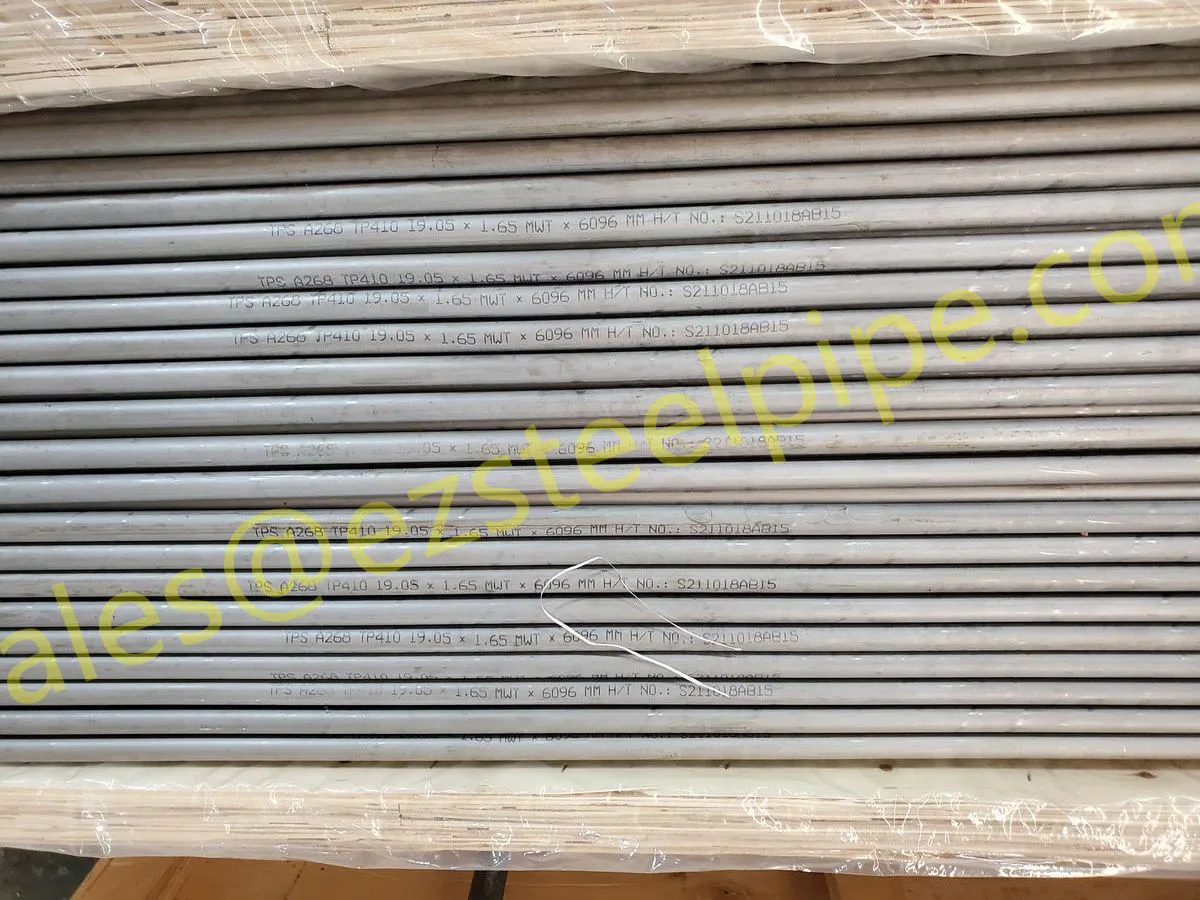
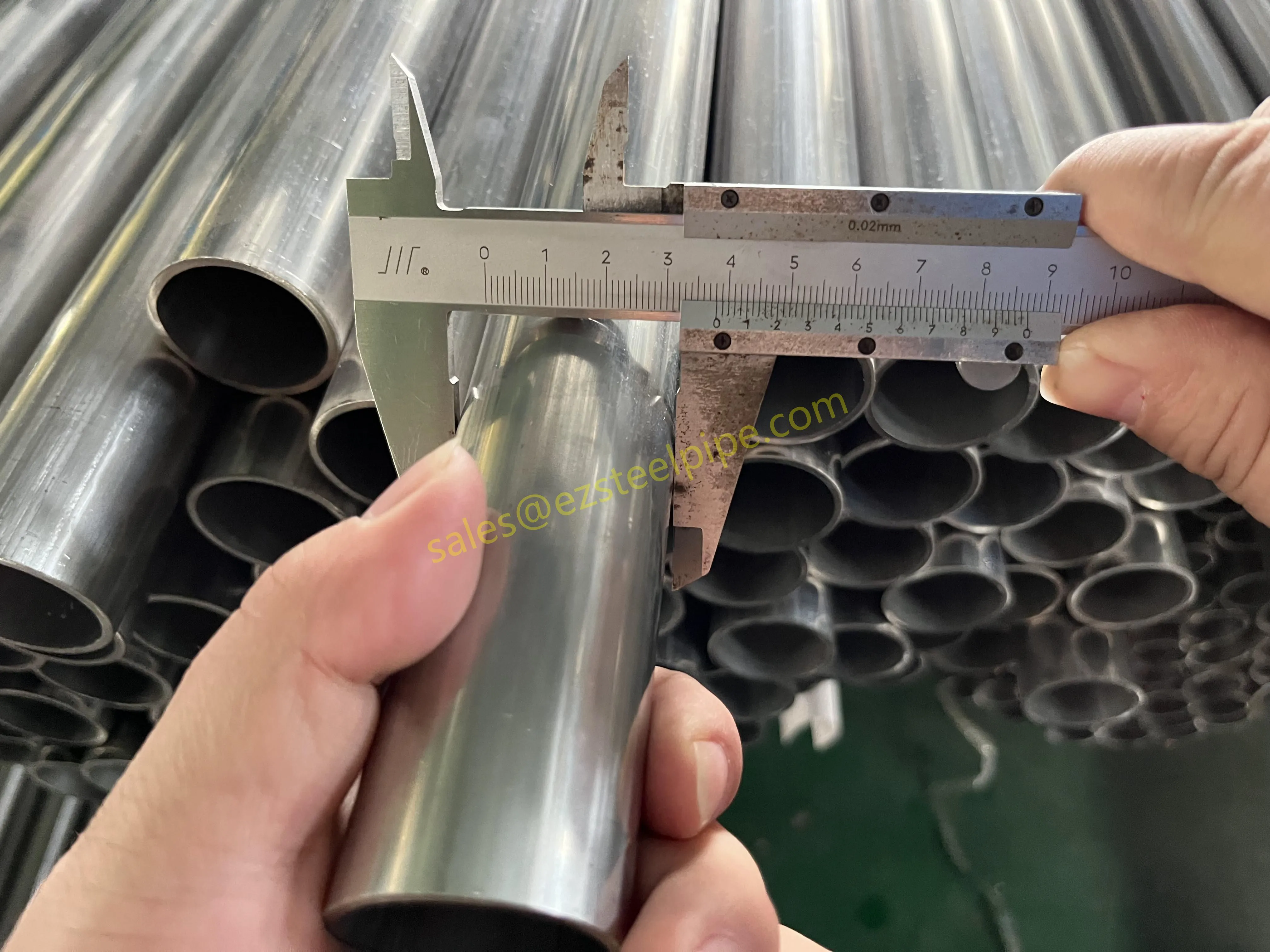
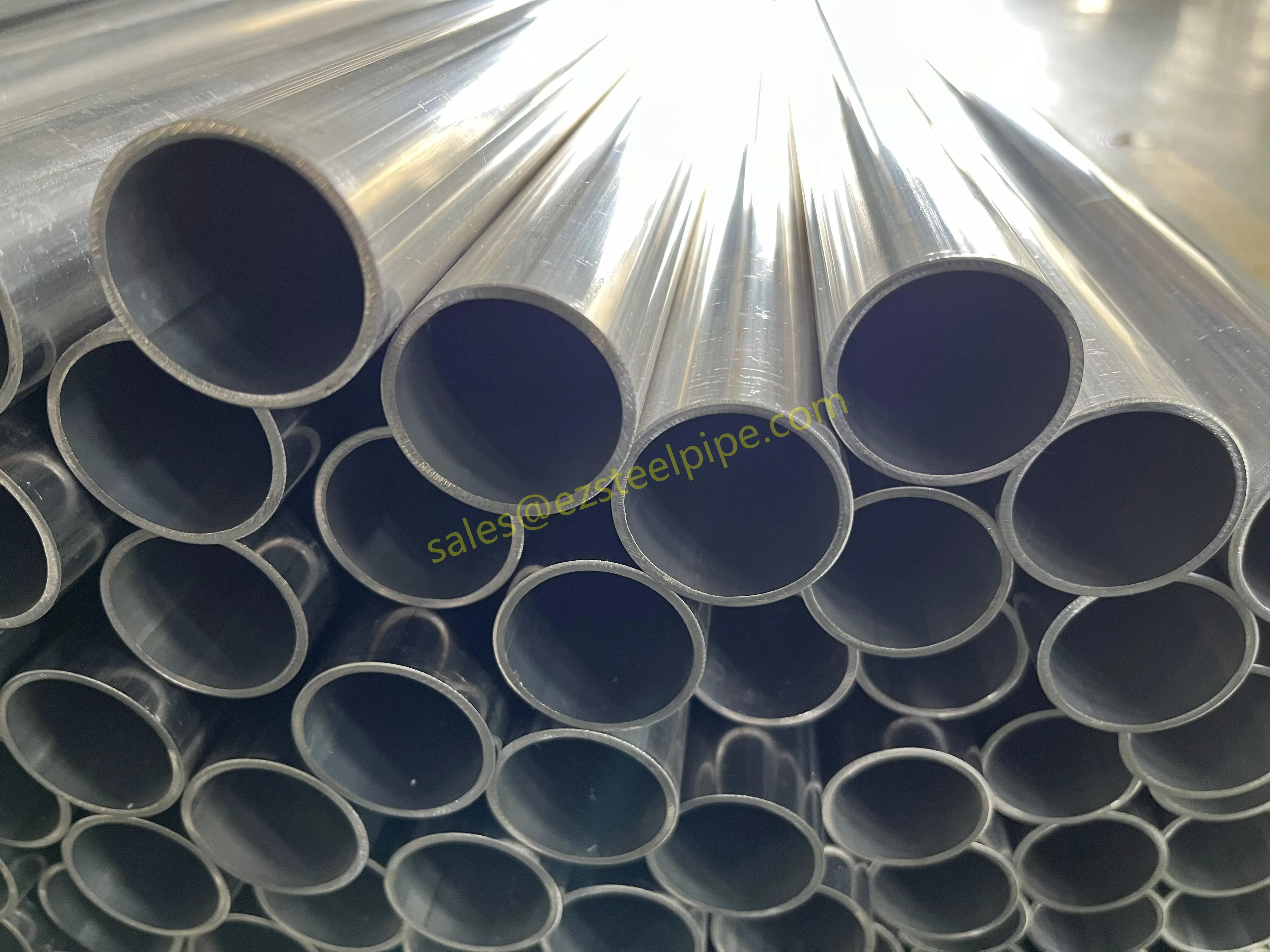
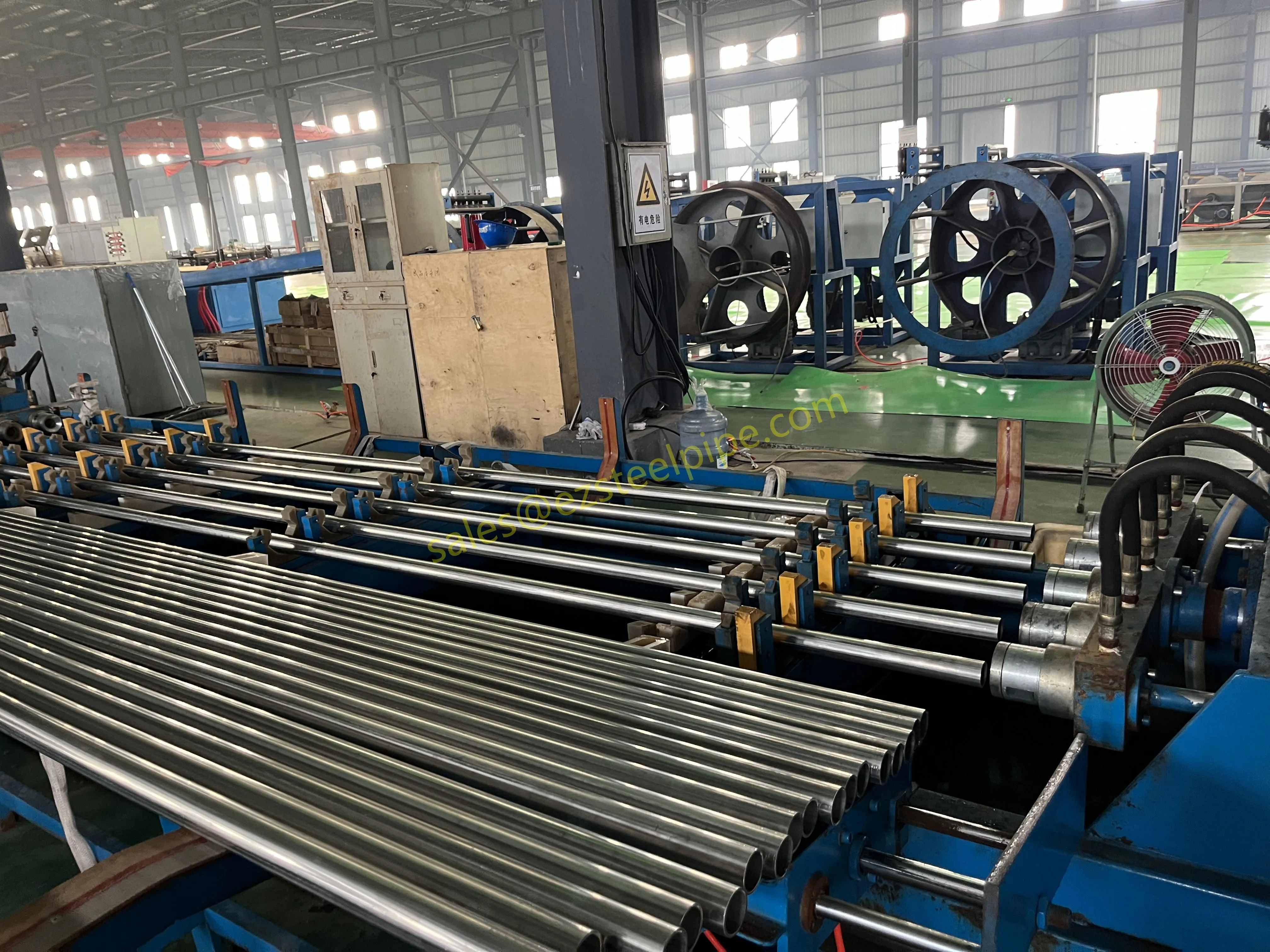
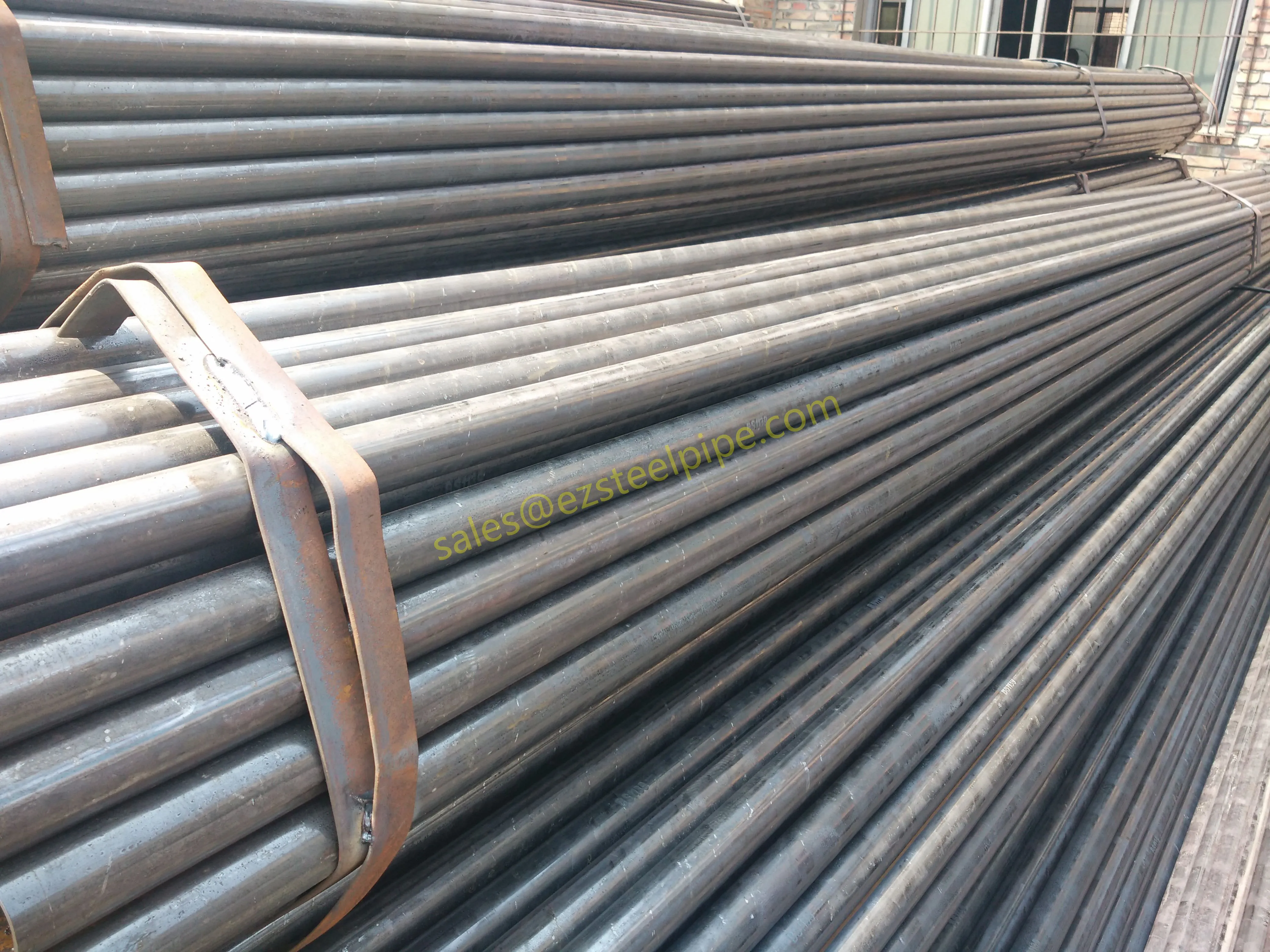
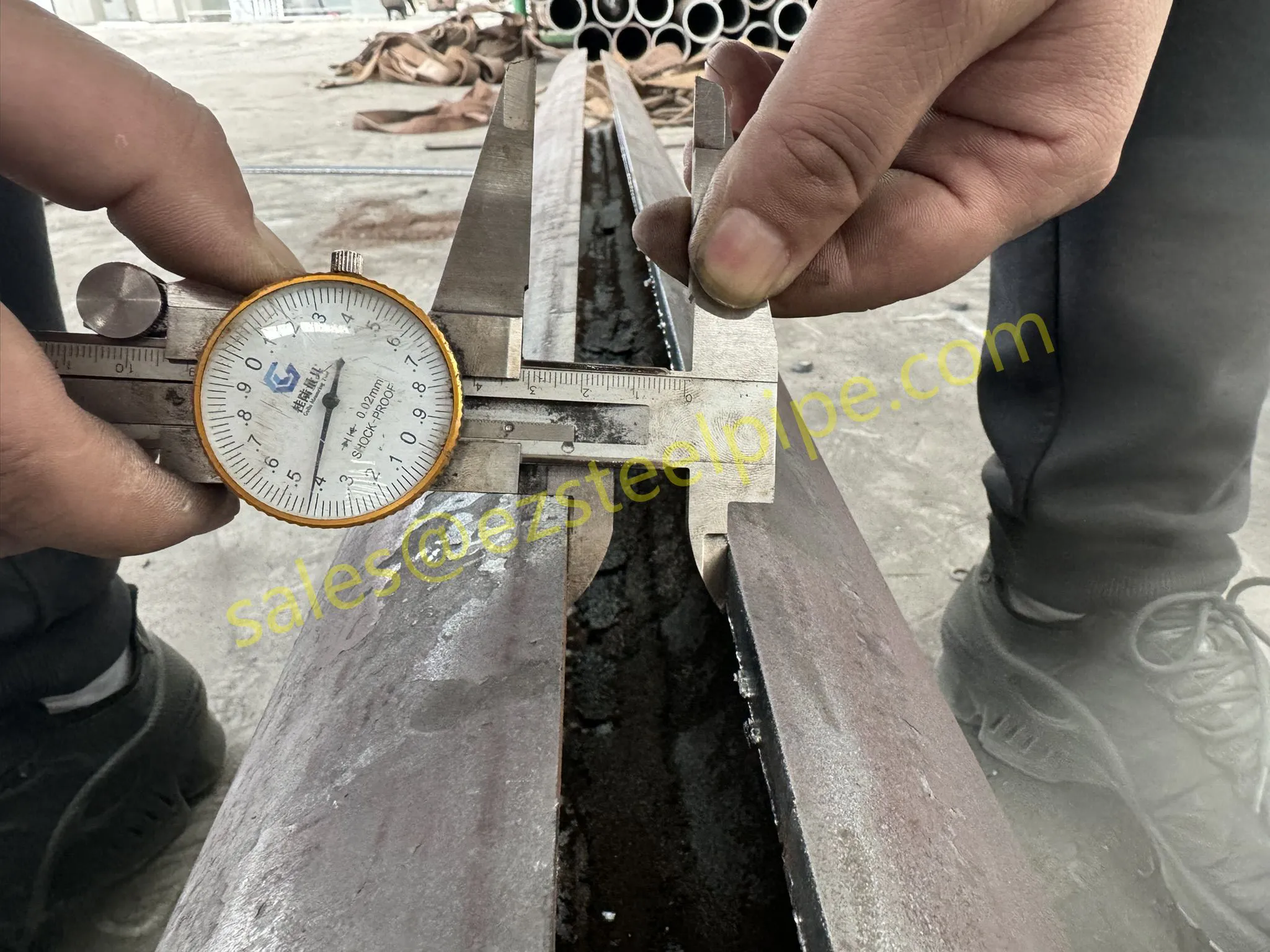
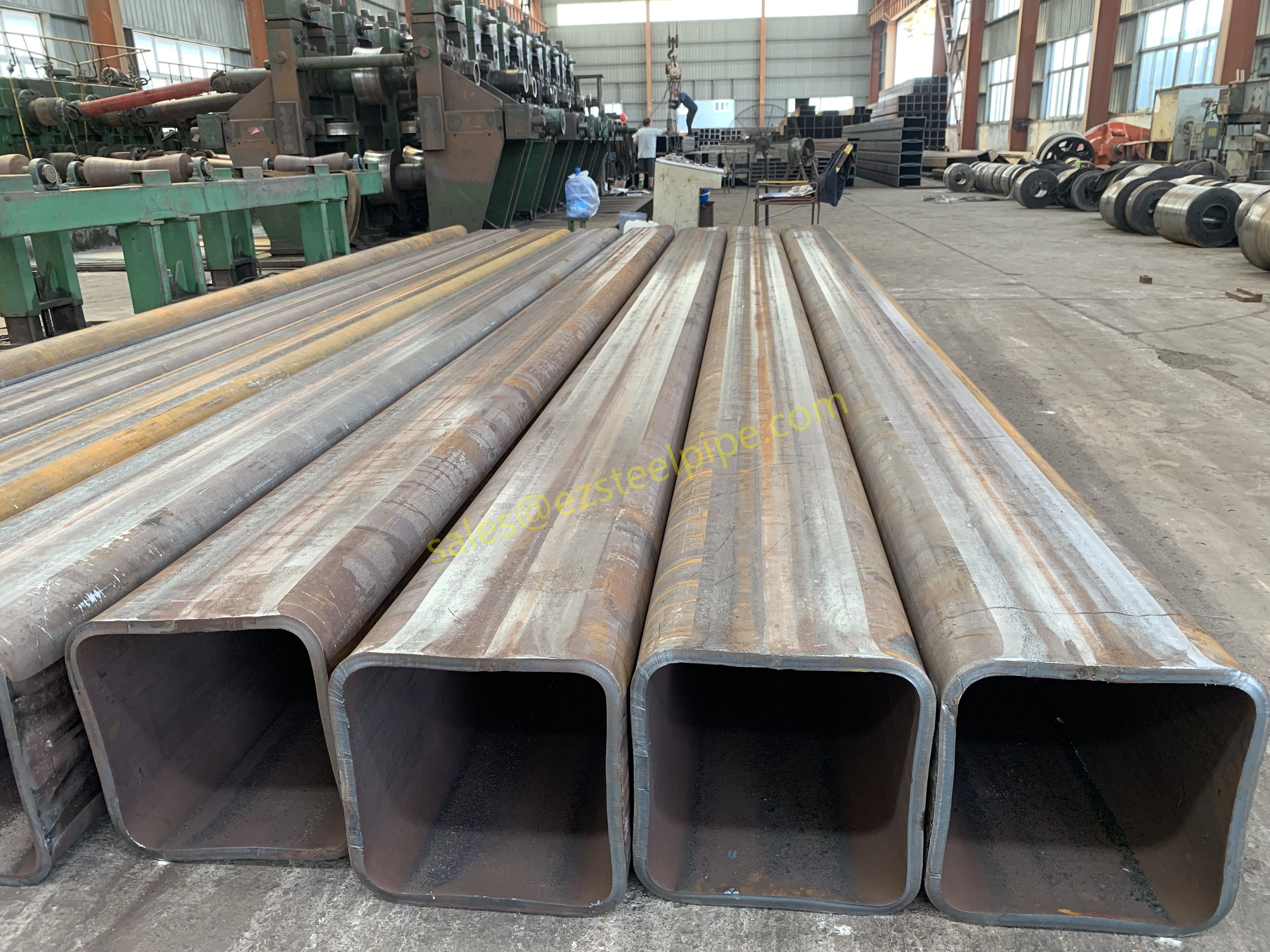
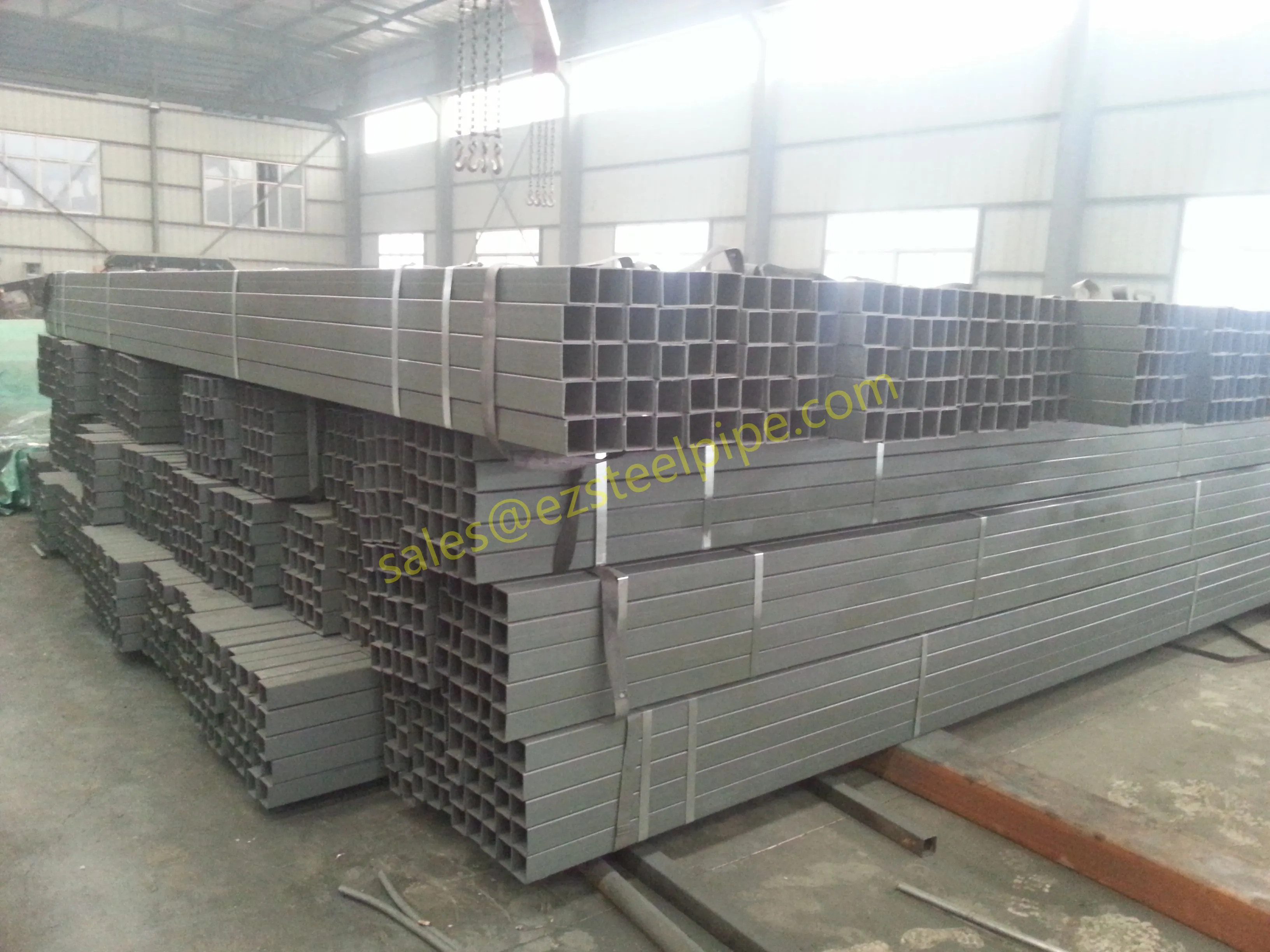
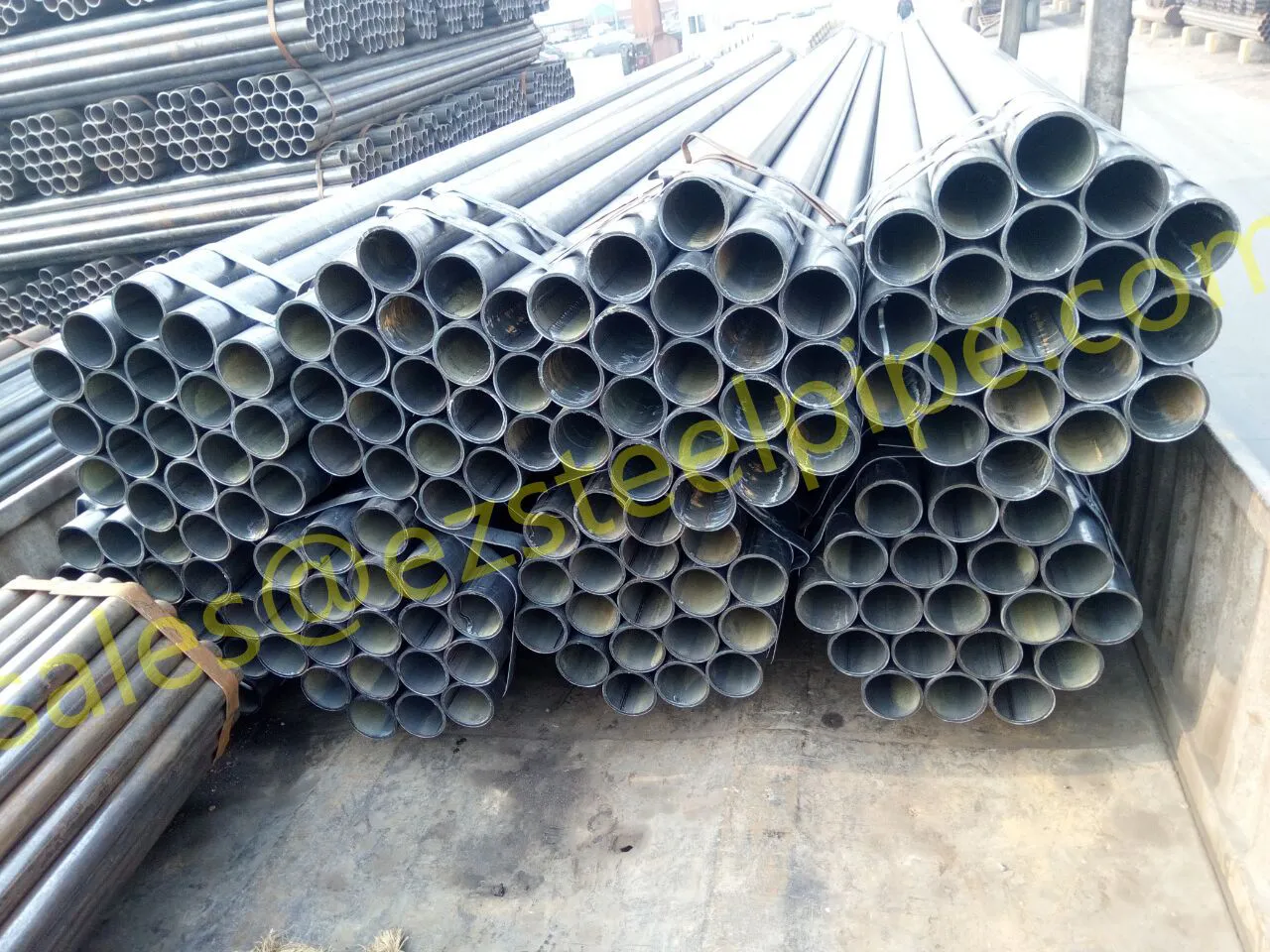
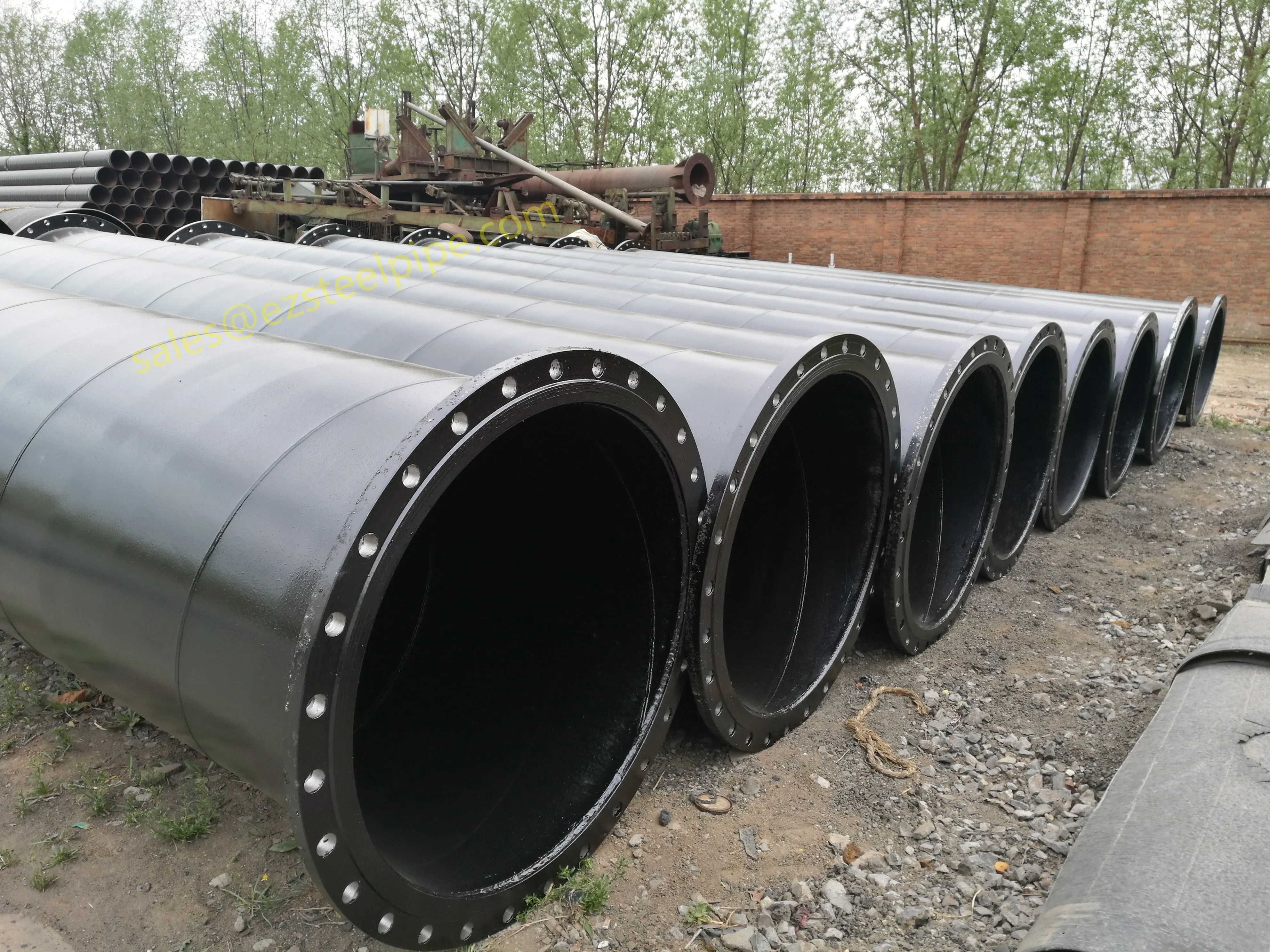
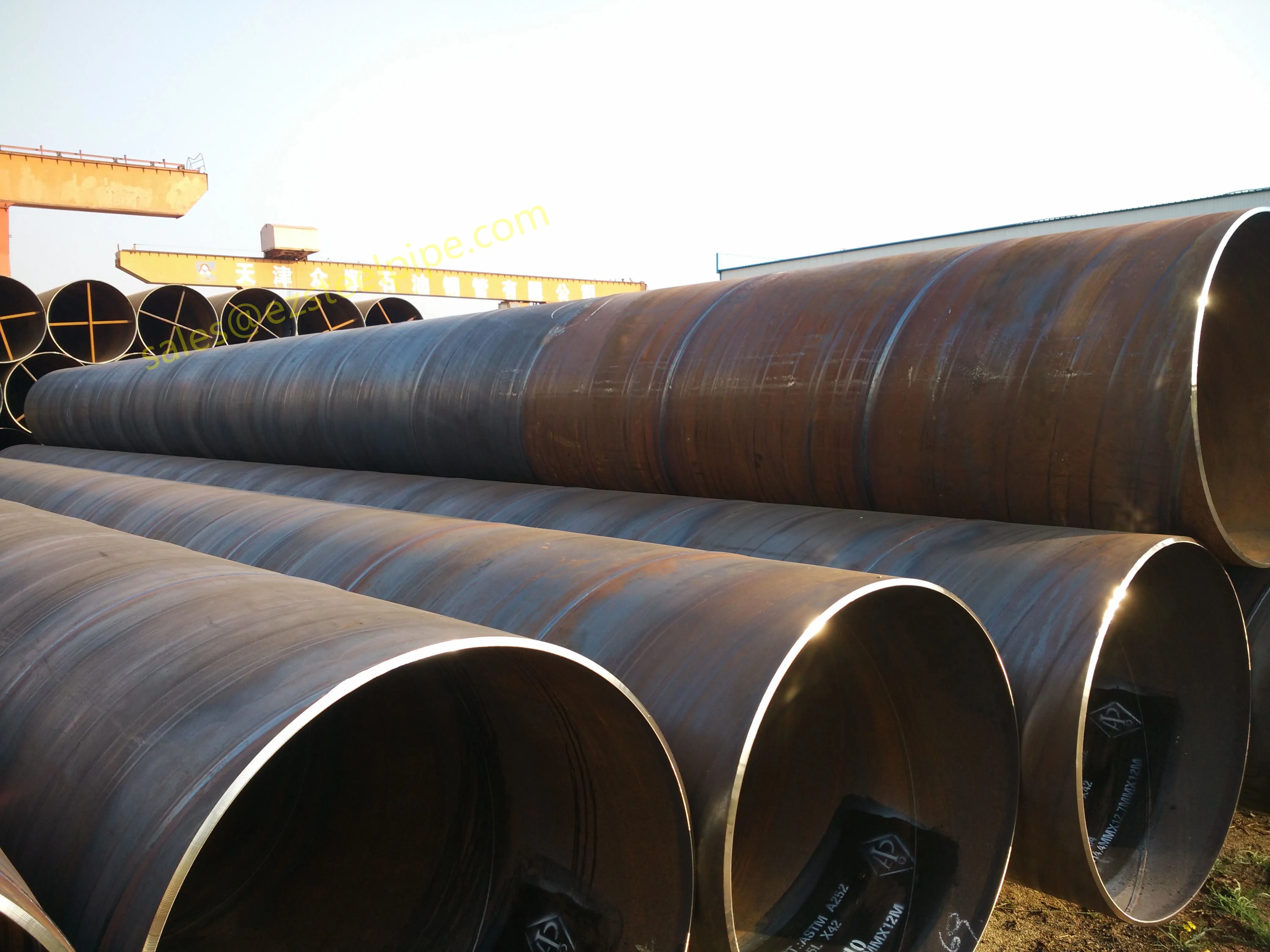
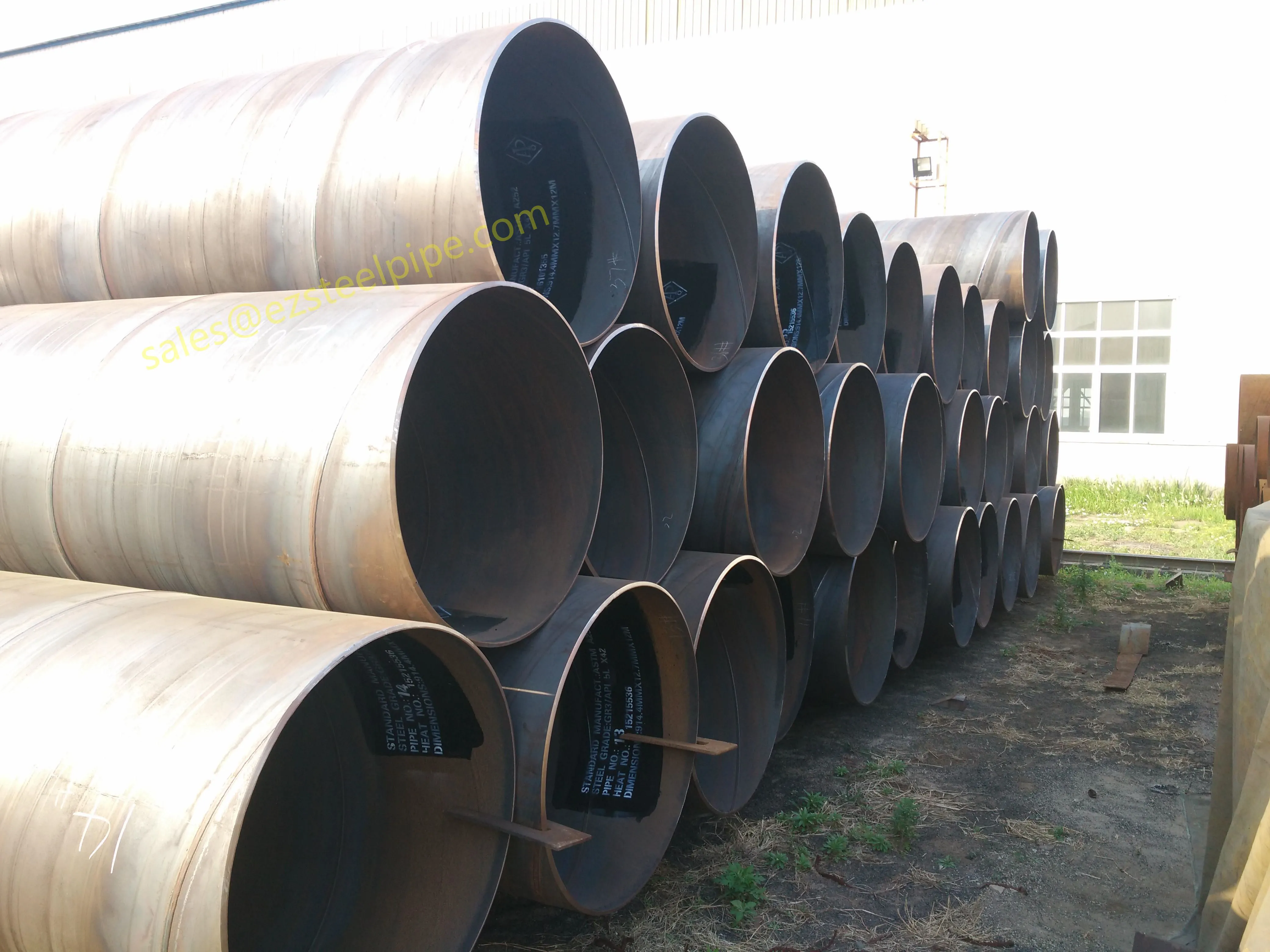
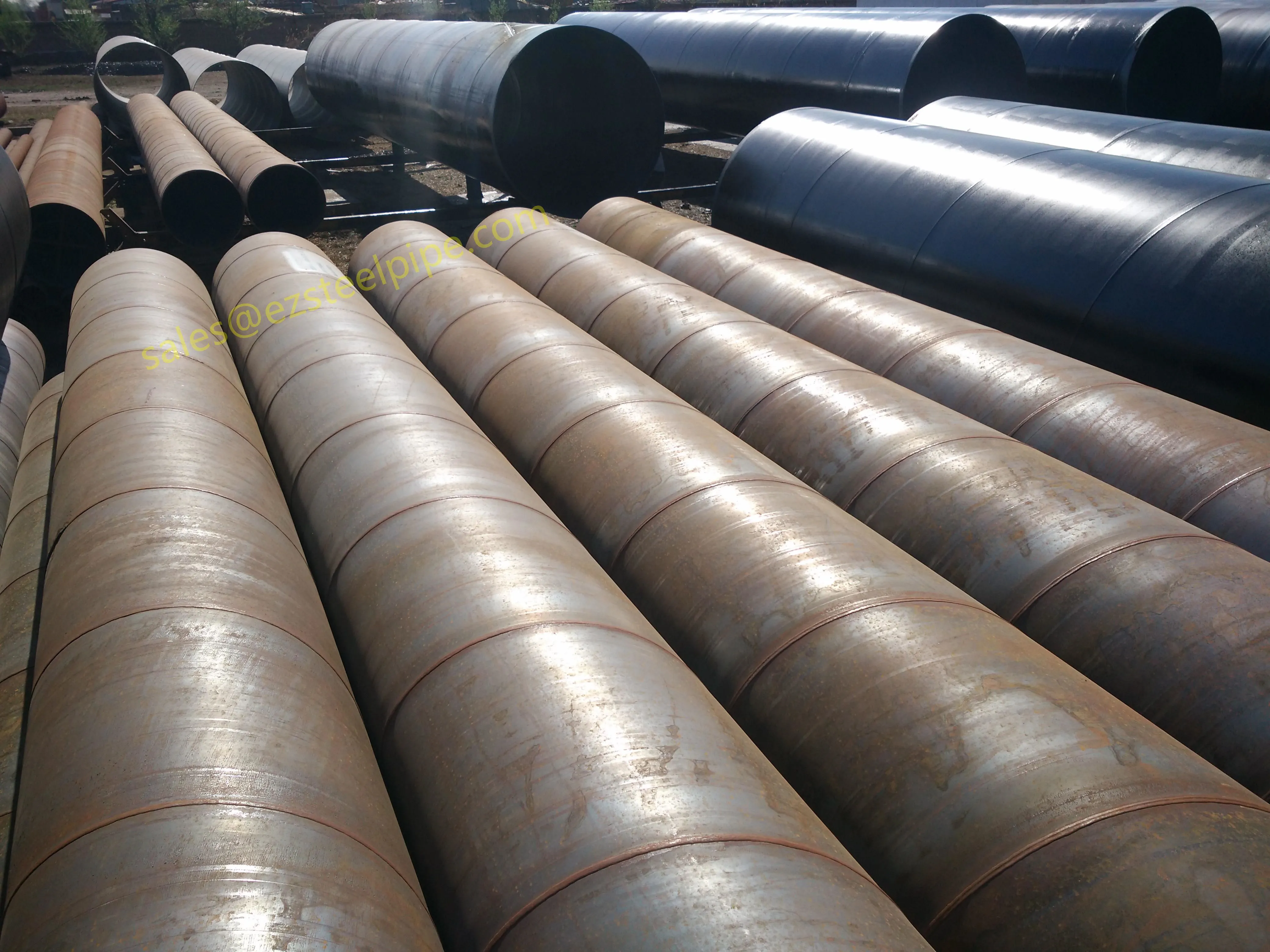
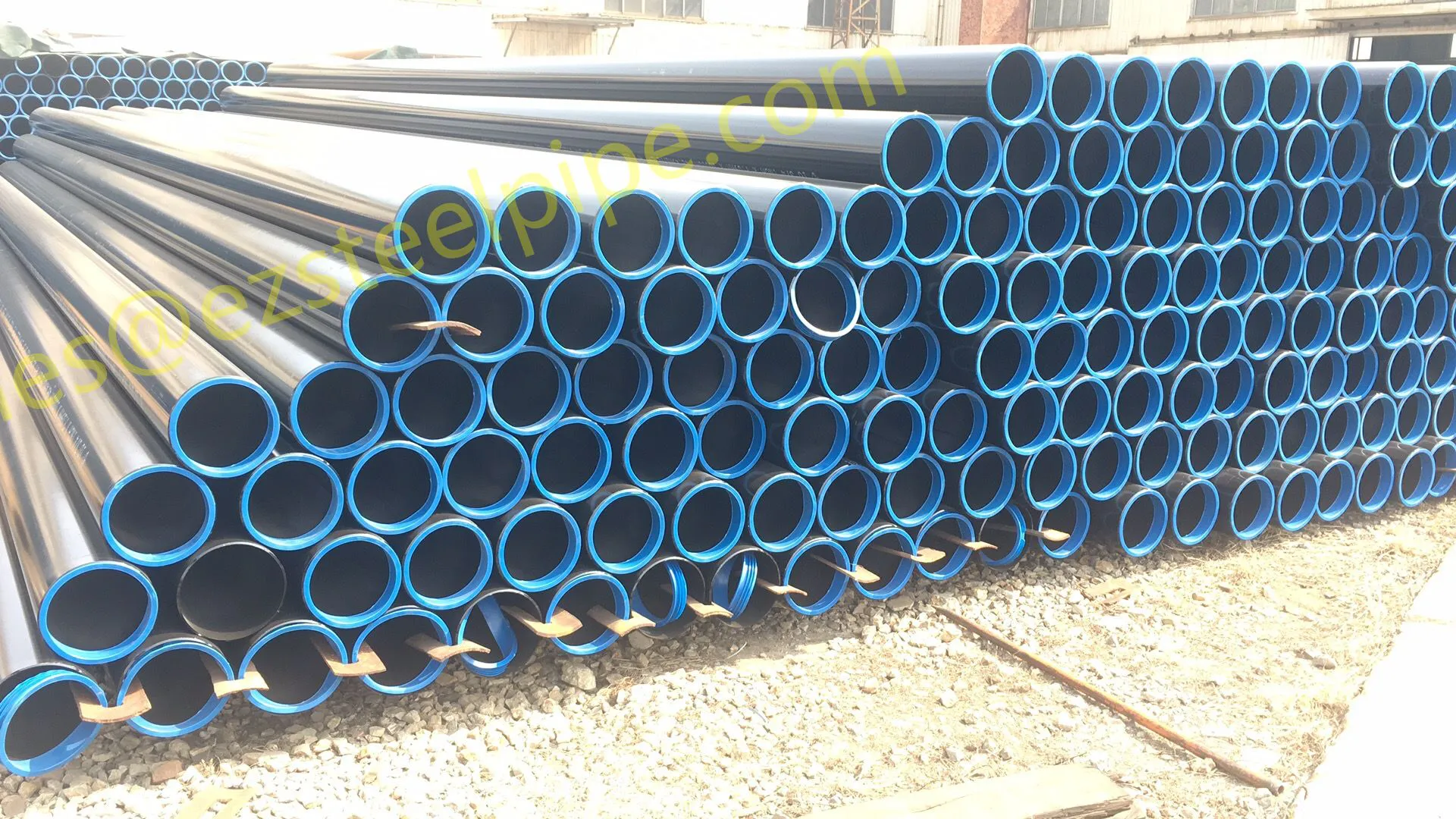
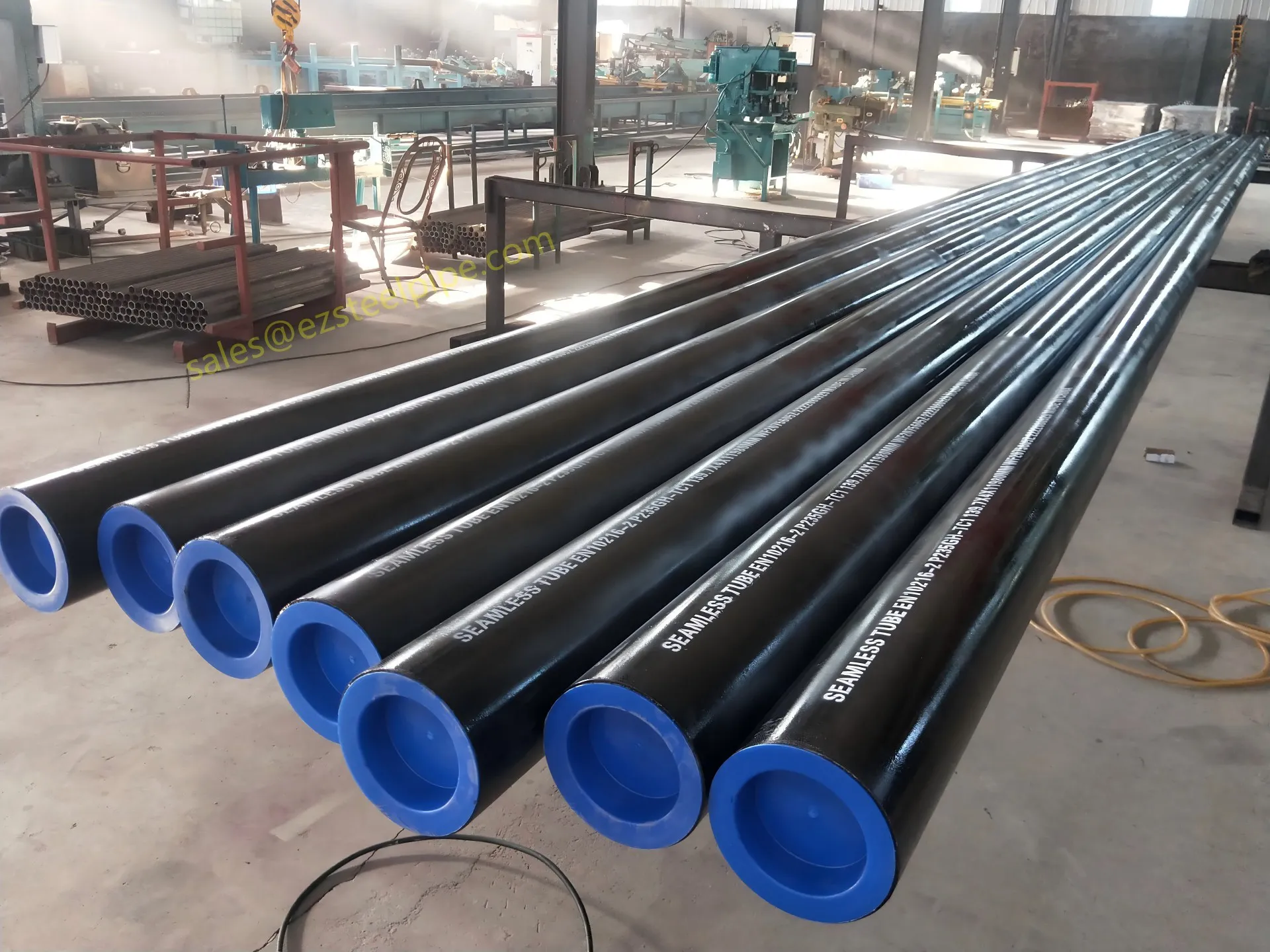
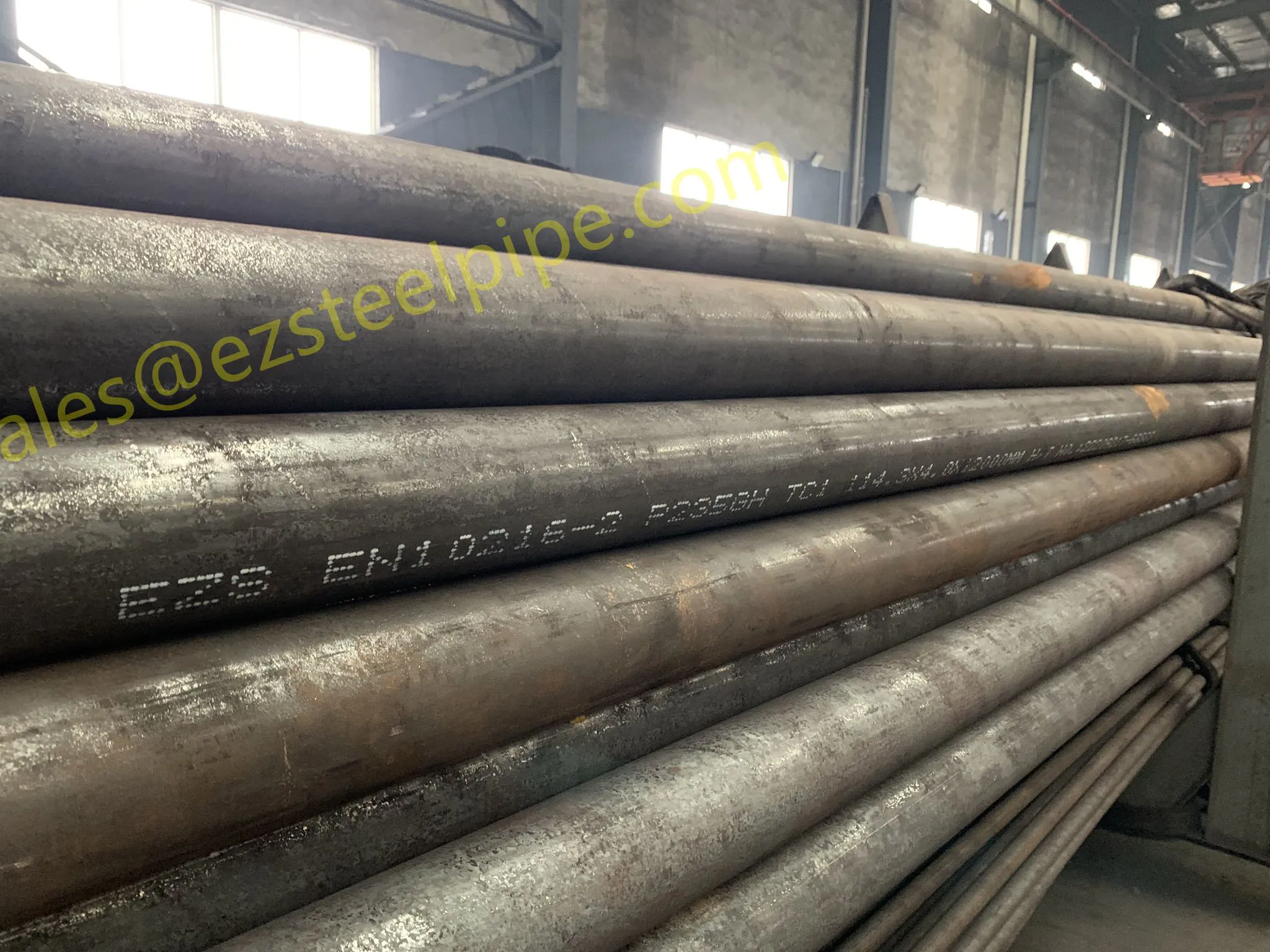
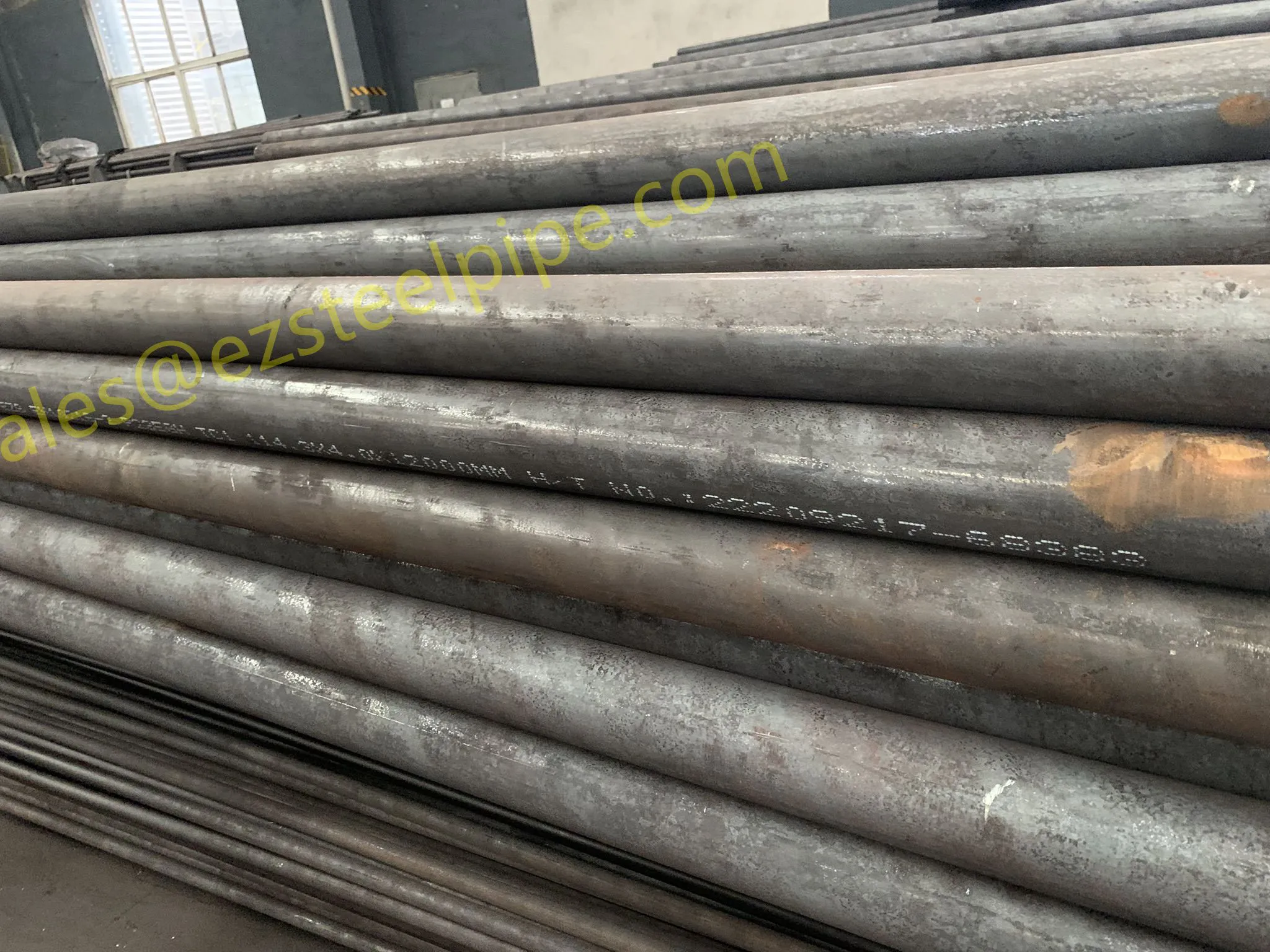
Behind the hum of a power plant, the steady voyage of a cargo ship, or the precise operations of a petrochemical refinery, there's a network of tubes working tirelessly. These aren't just any tubes—they're heat efficiency tubes, the silent workhorses that keep fluids flowing, temperatures regulated, and industries thriving. From transferring steam in a power plant to cooling systems in a ship's engine room, the right tube material can make or break efficiency, safety, and longevity.
But with so many options—carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and more—how do engineers and project managers decide? It all comes down to balance: cost, durability, resistance to corrosion, and the ability to handle extreme temperatures or pressures. In this article, we'll dive into the three heavyweights of heat efficiency tubes: carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. We'll explore their strengths, weaknesses, and the real-world applications where they shine, from pipeline works in rural areas to high-stakes aerospace projects.
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































