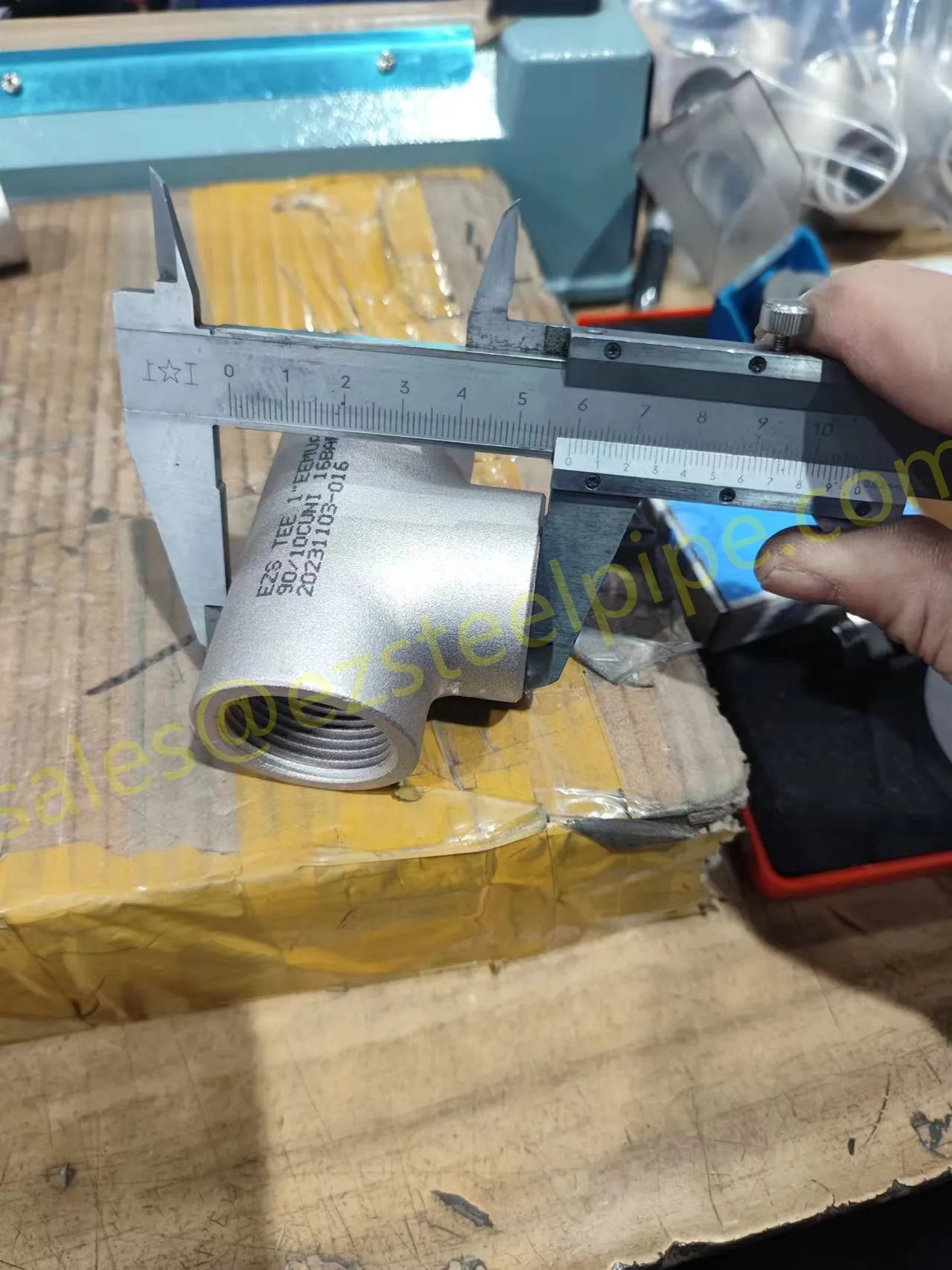
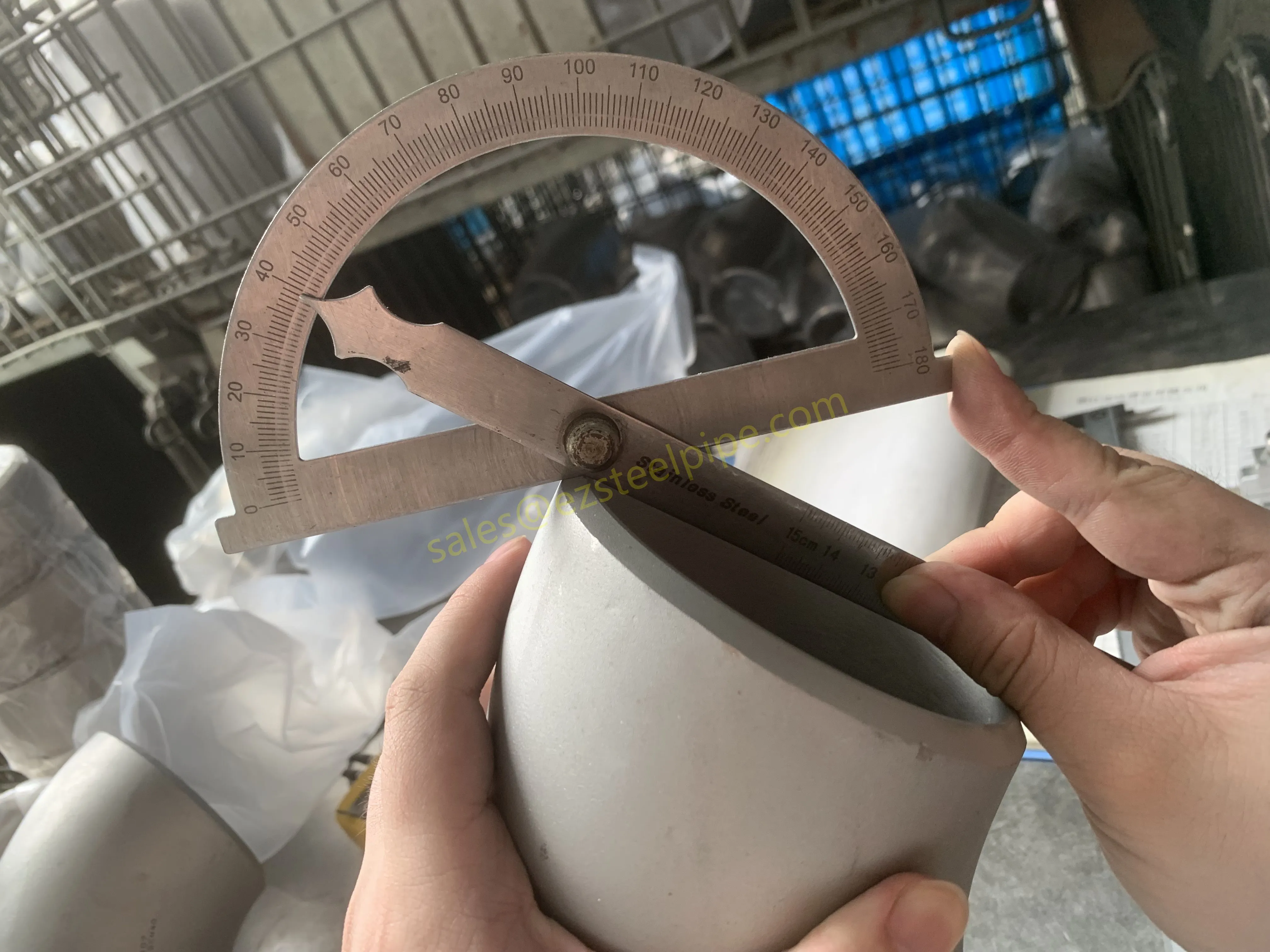
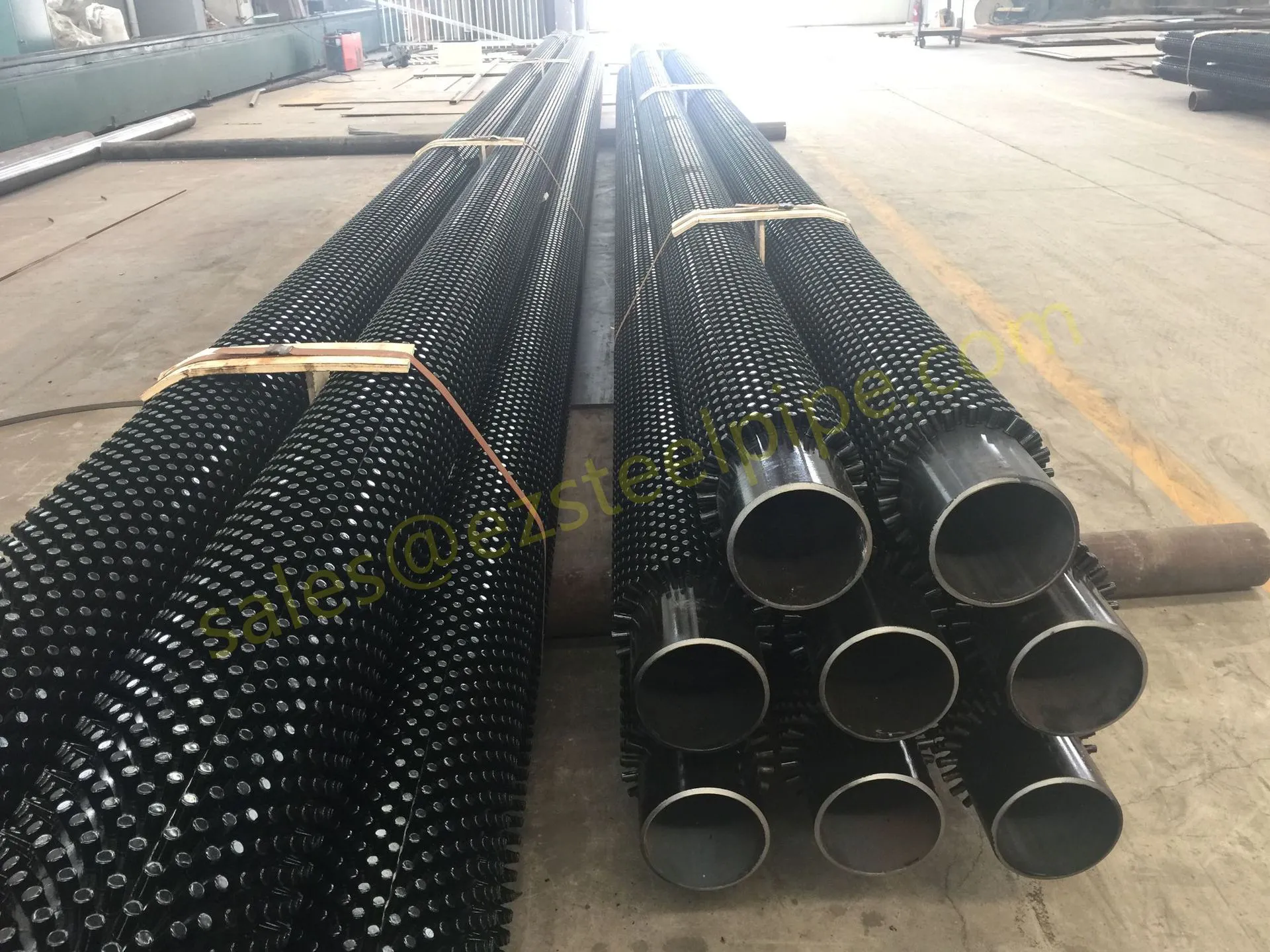
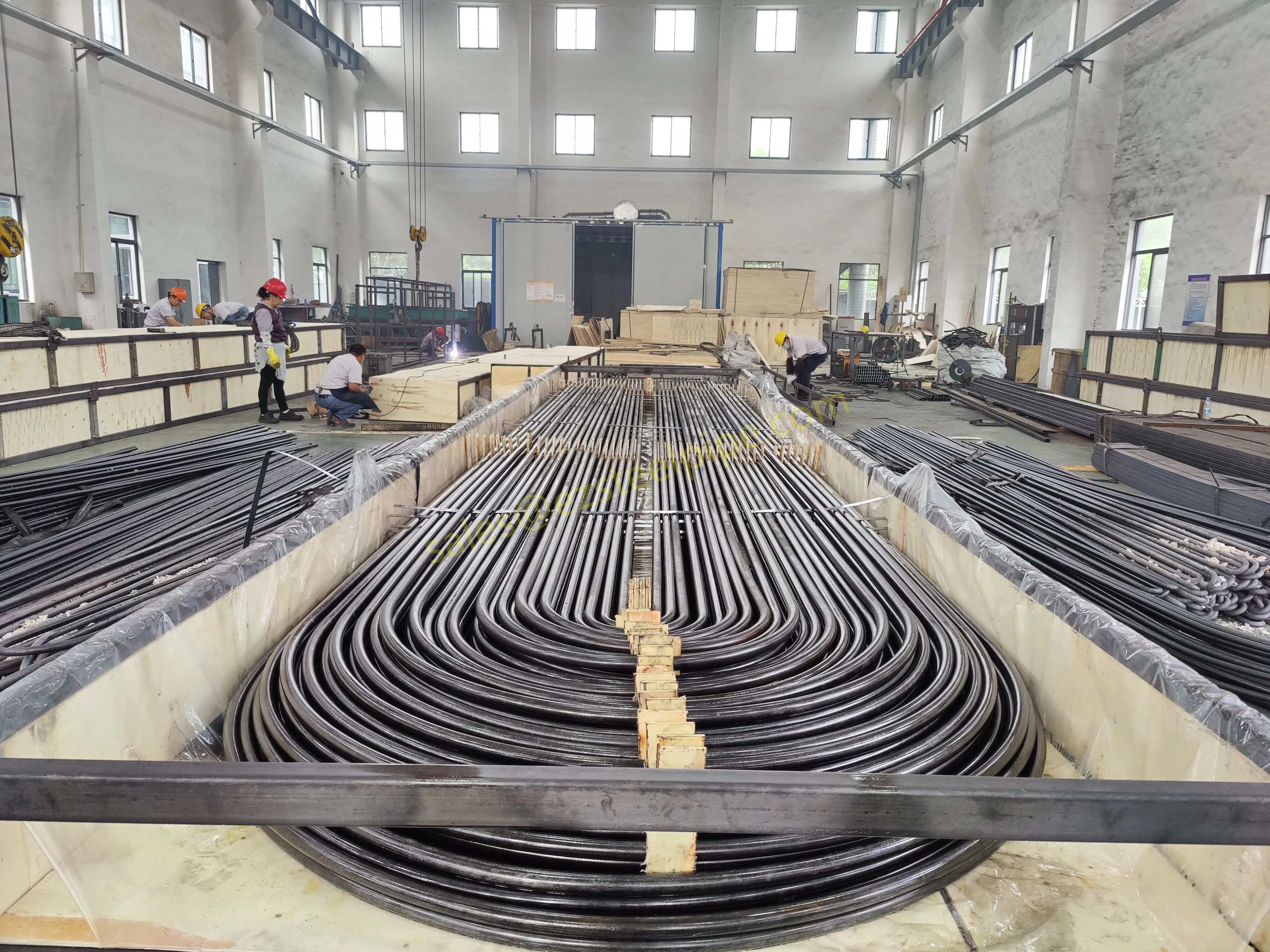
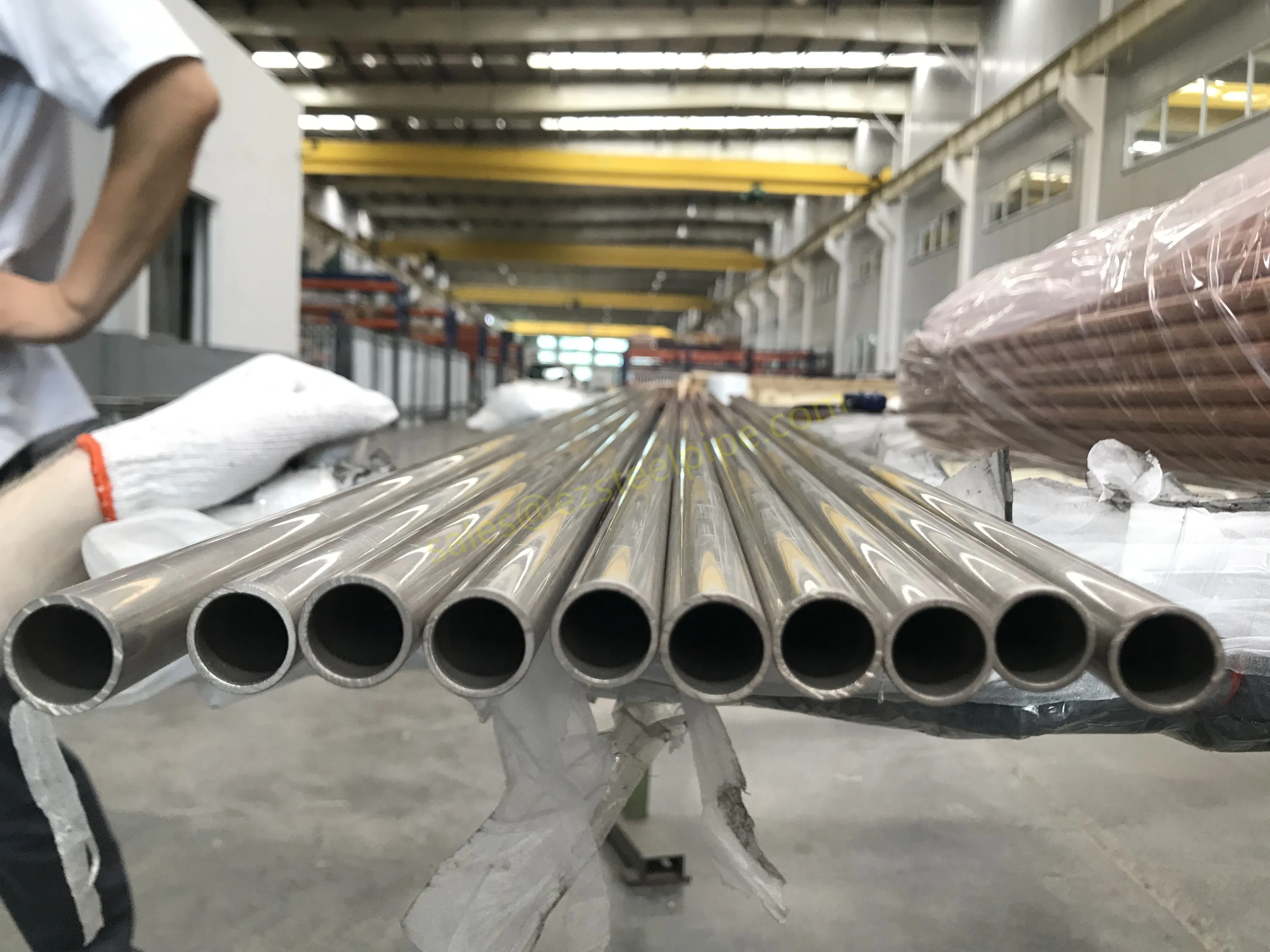
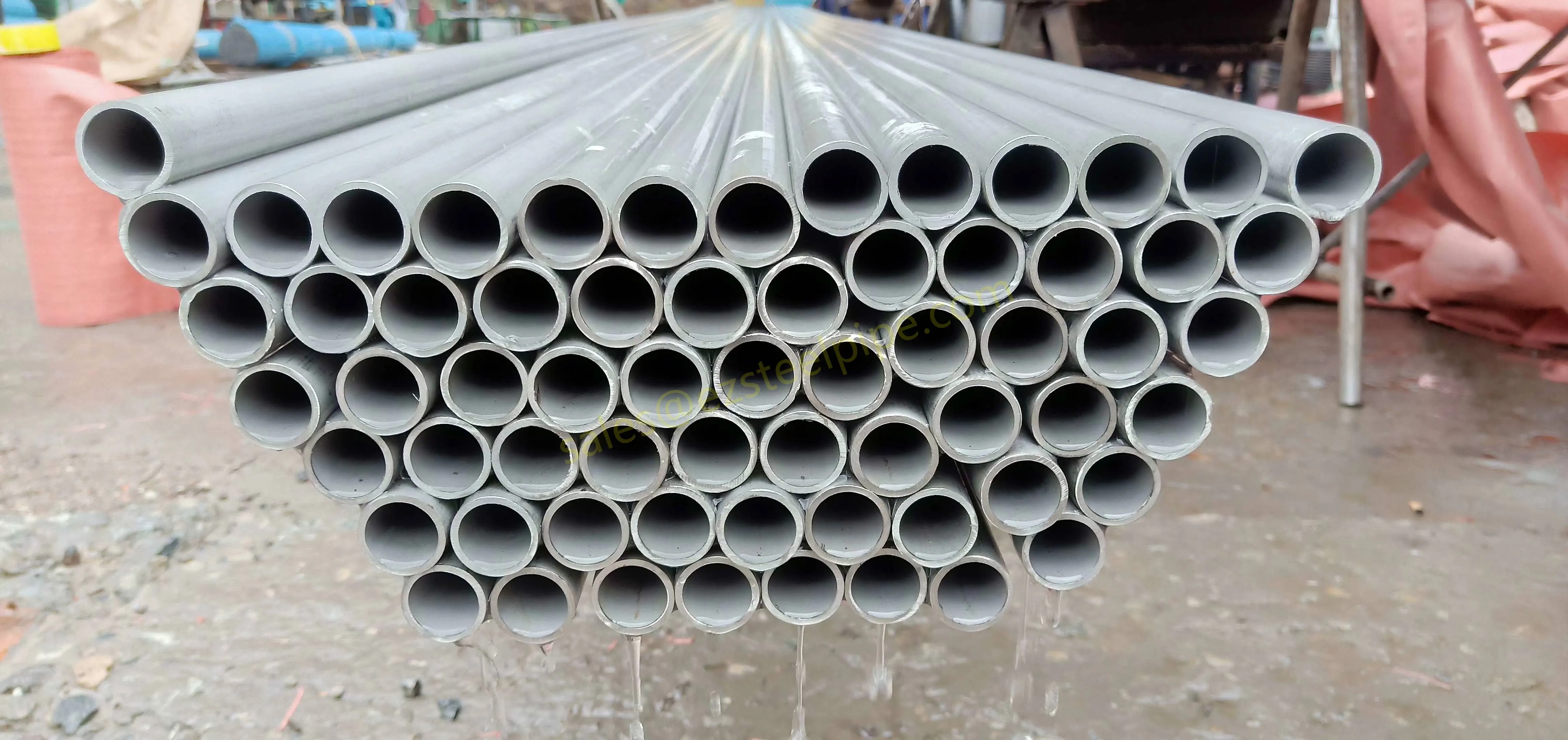
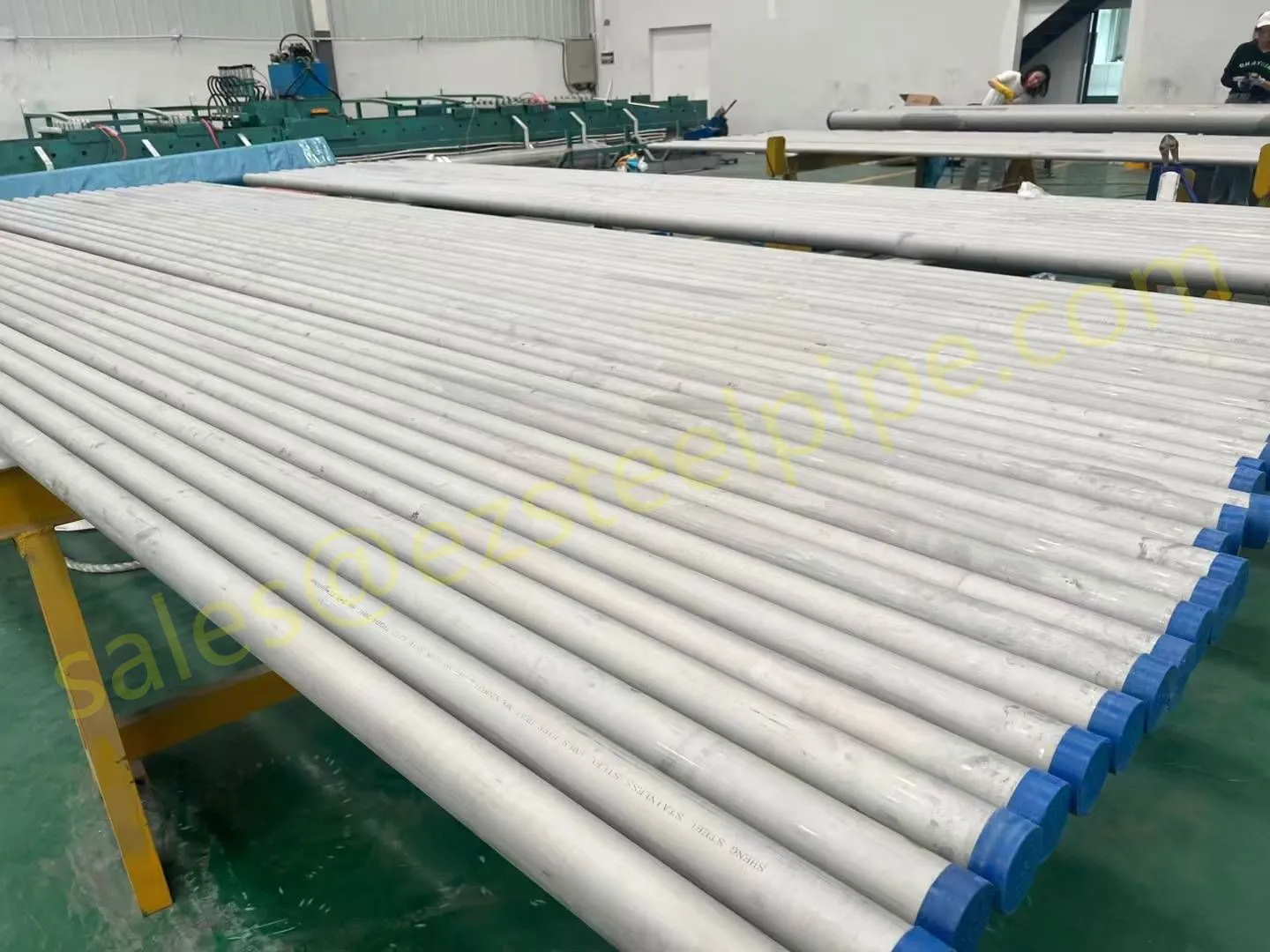
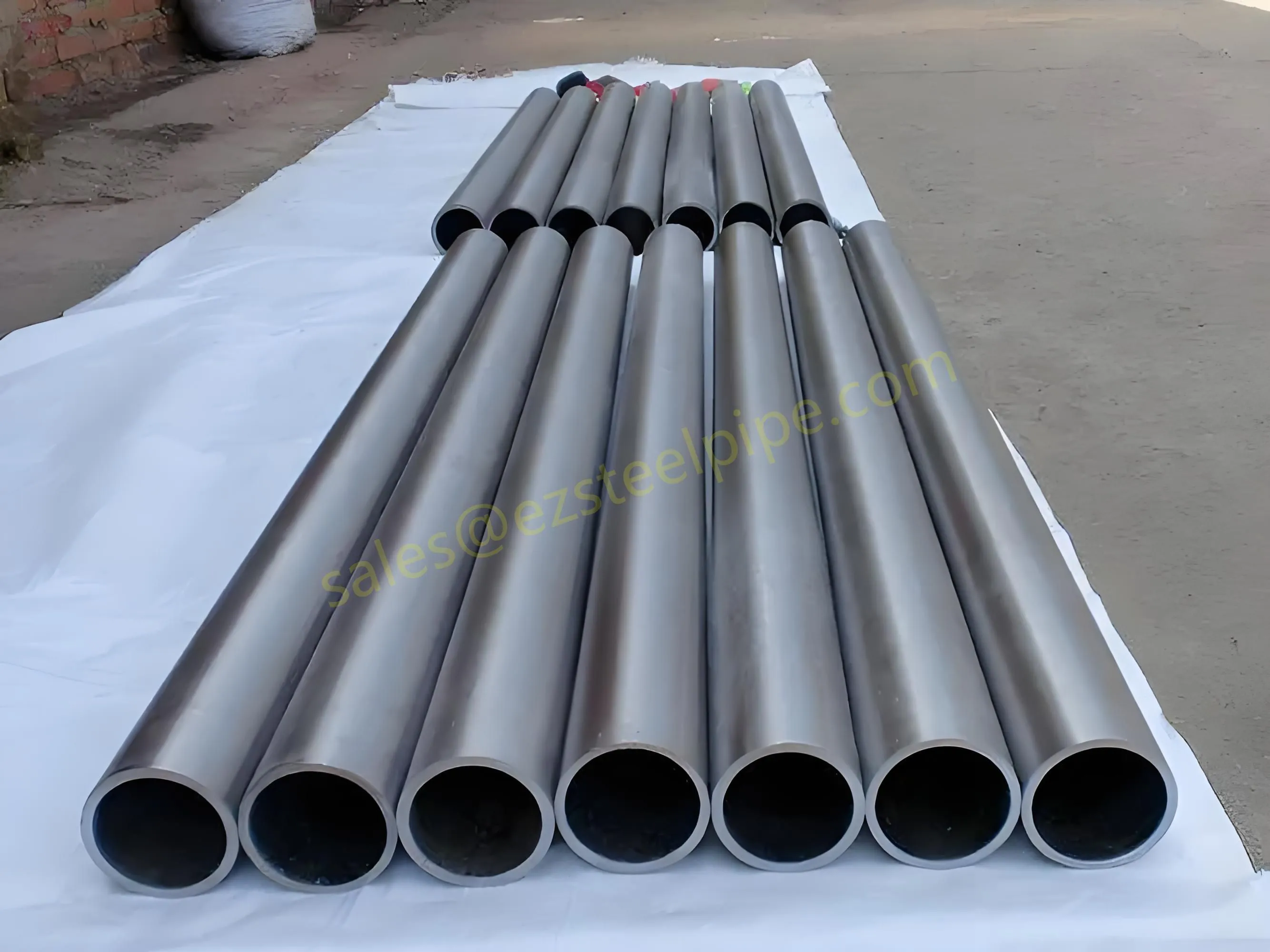
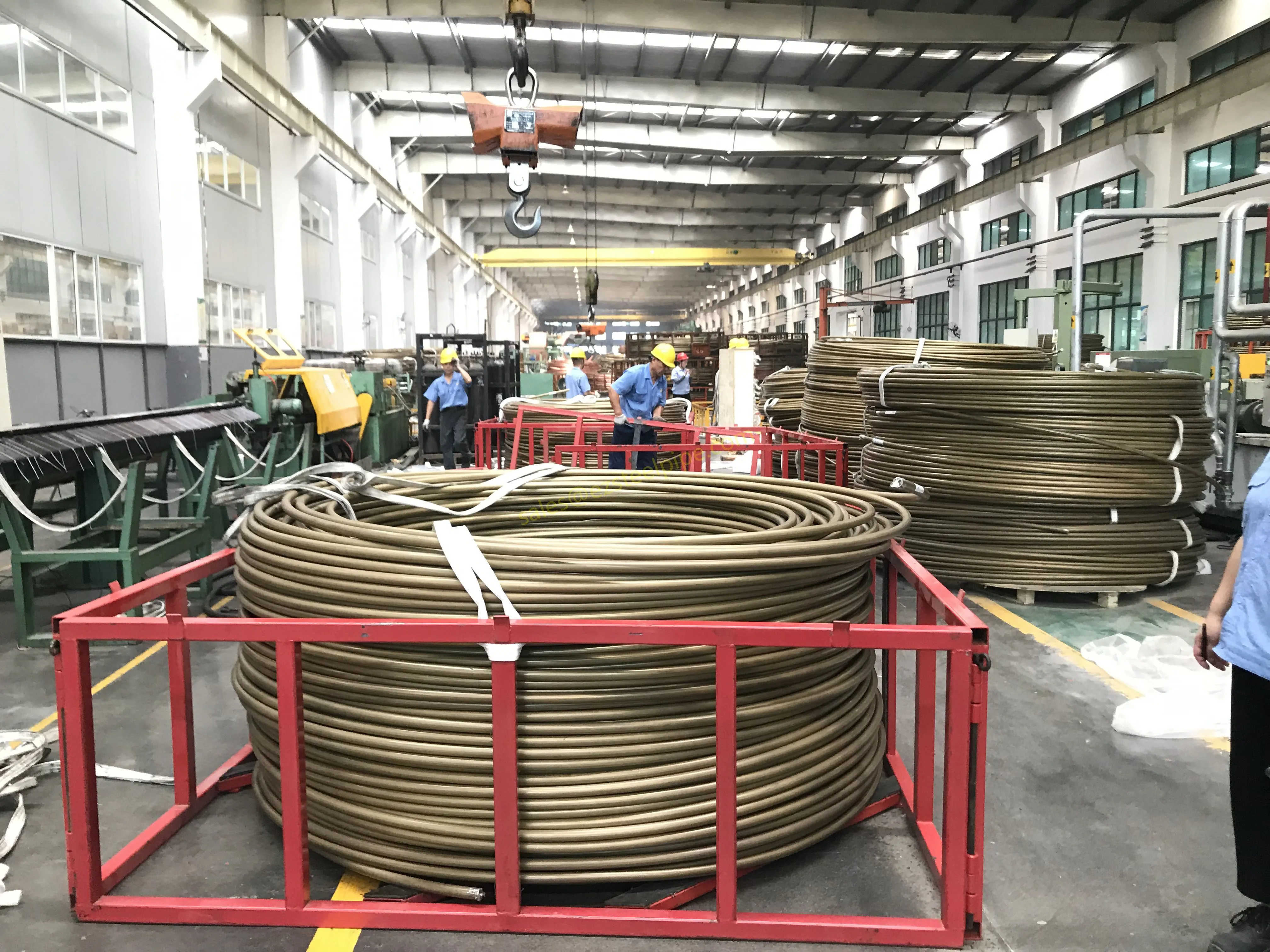
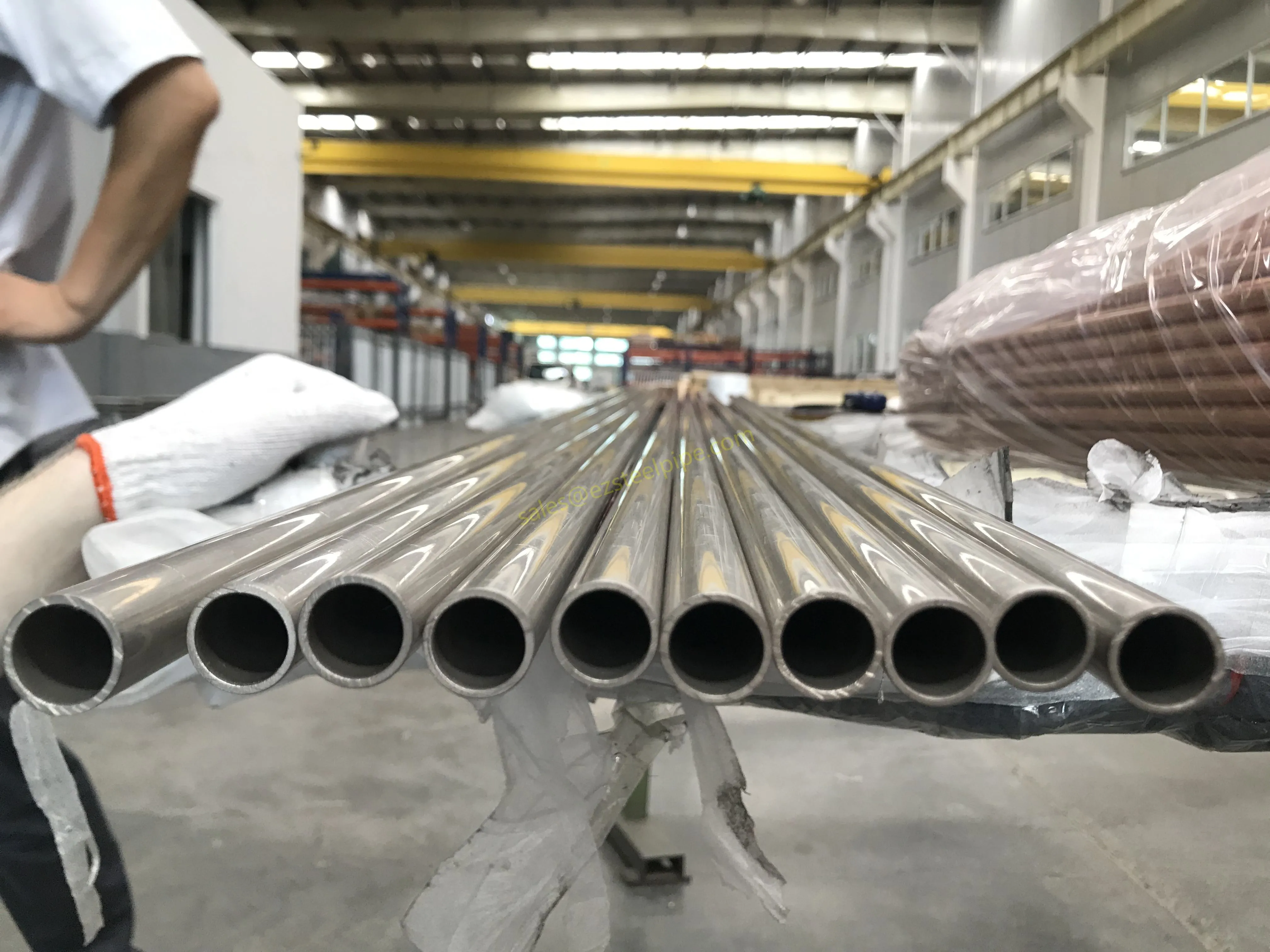
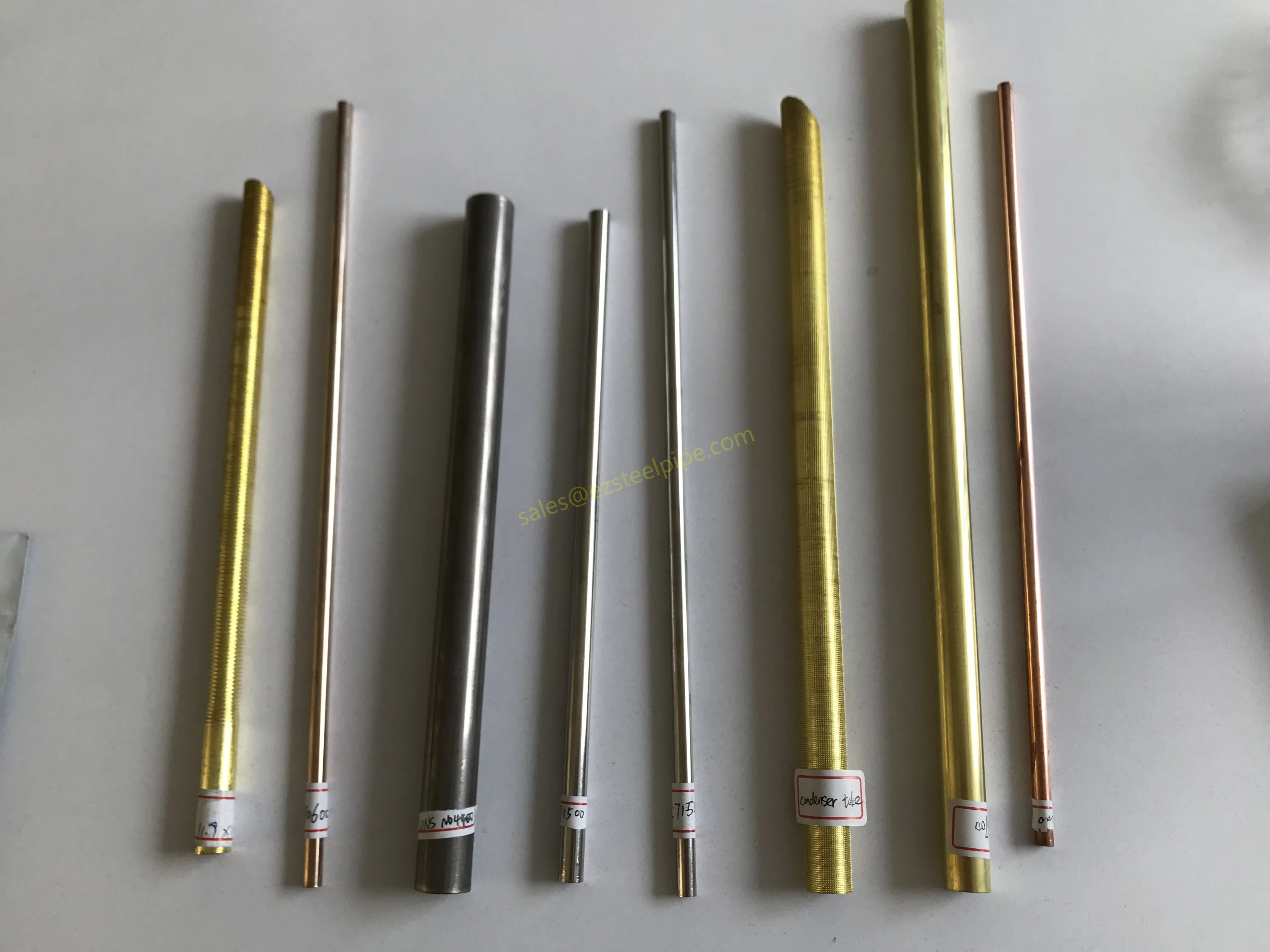
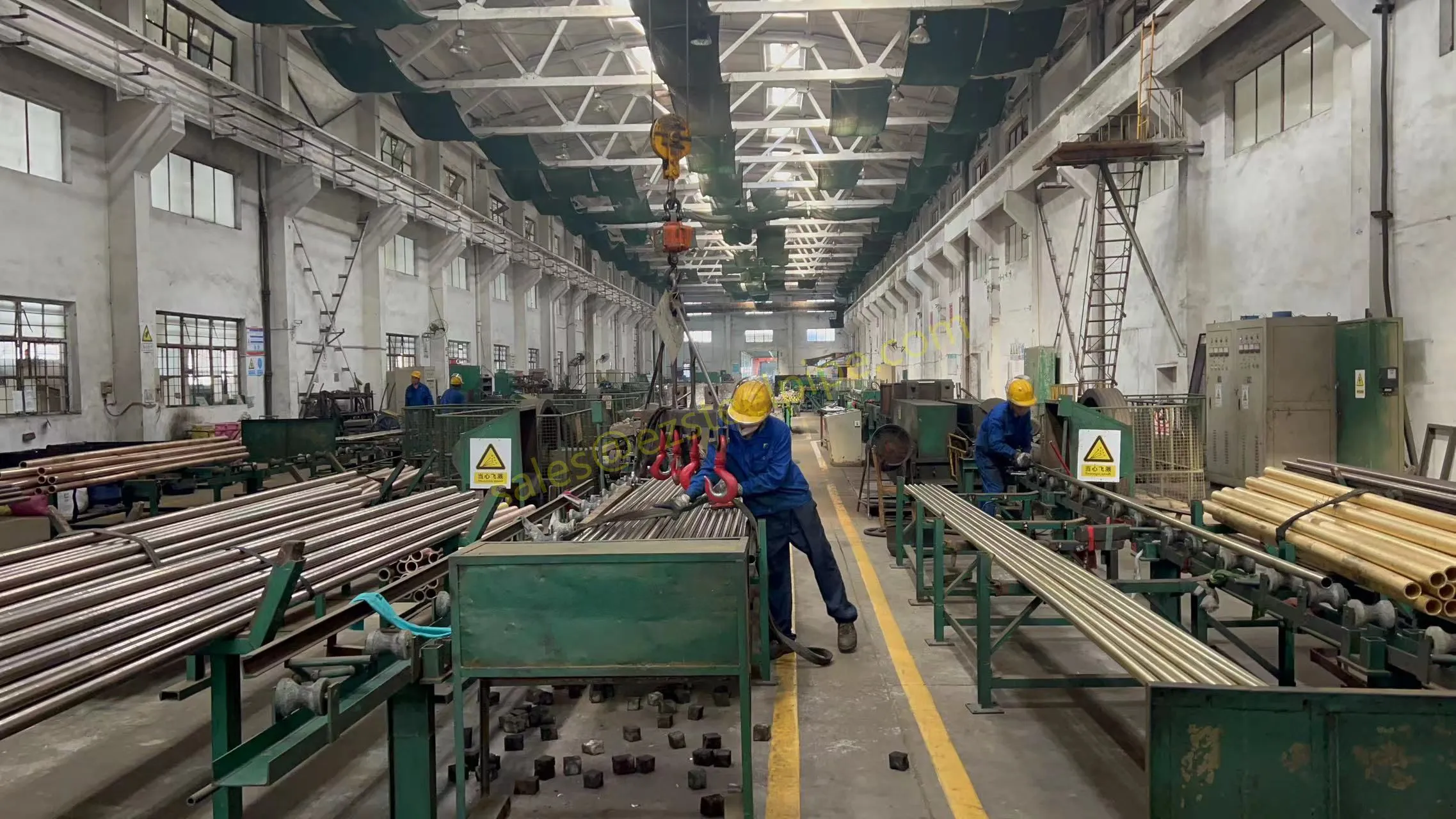
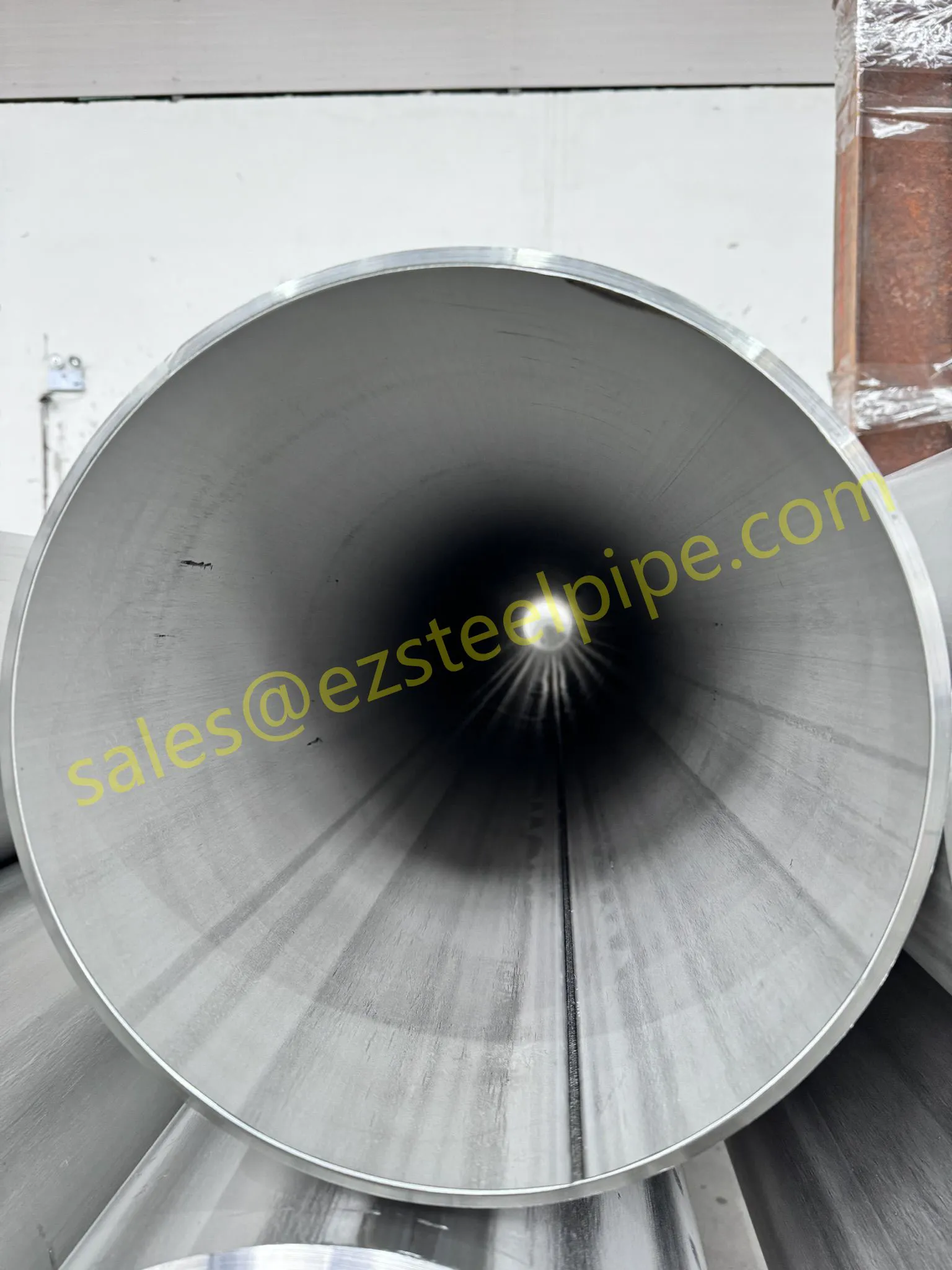
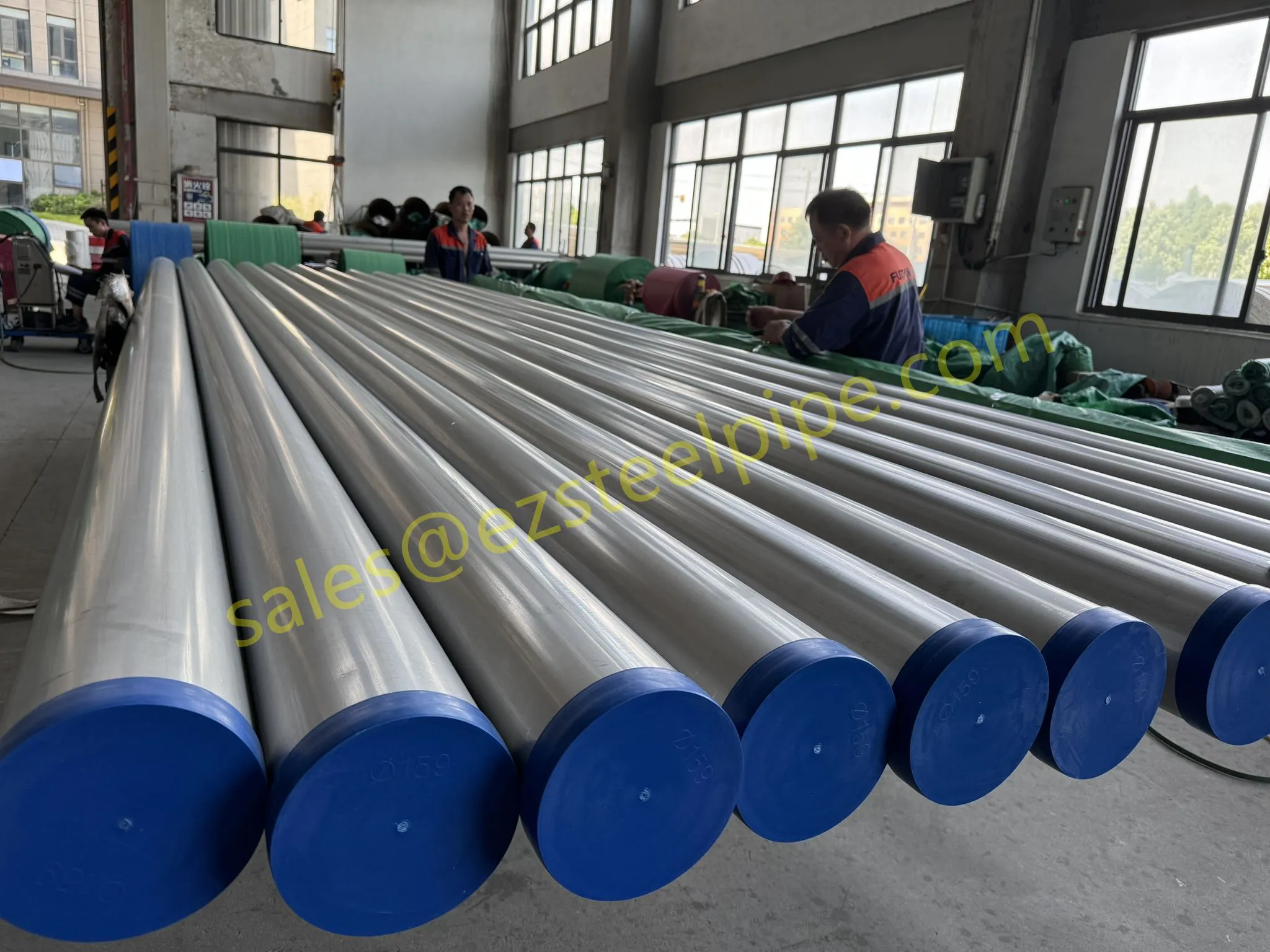
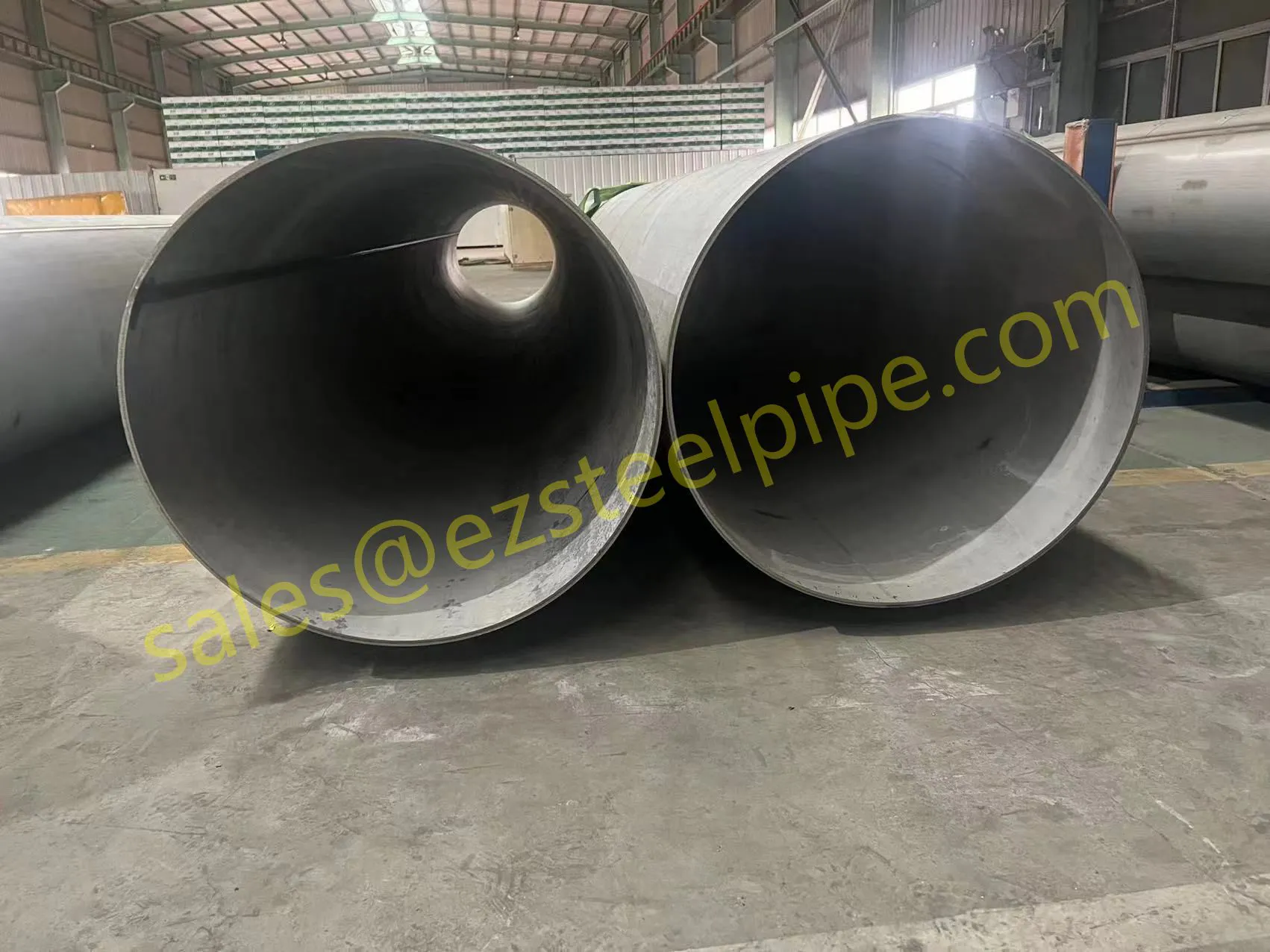
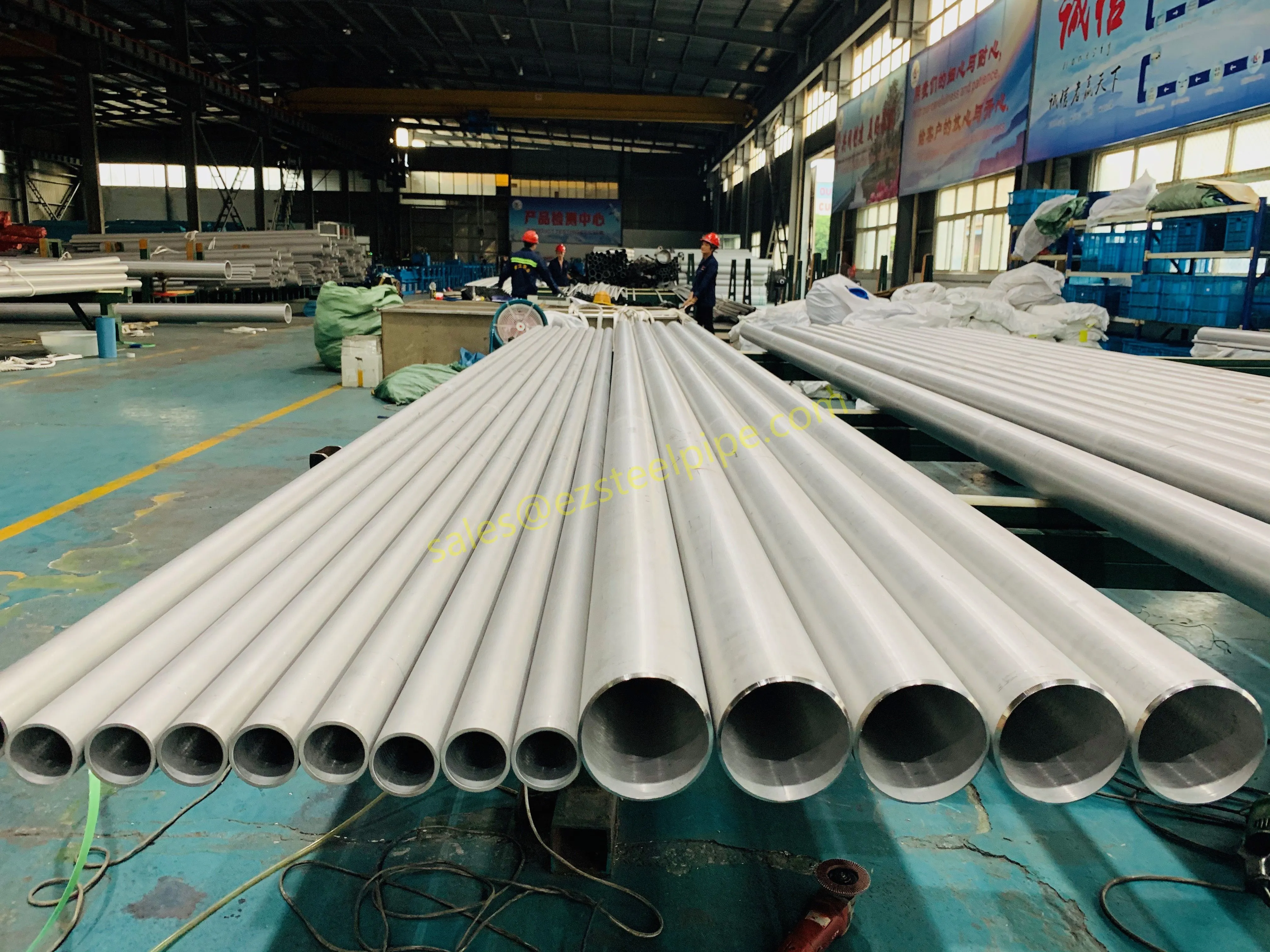
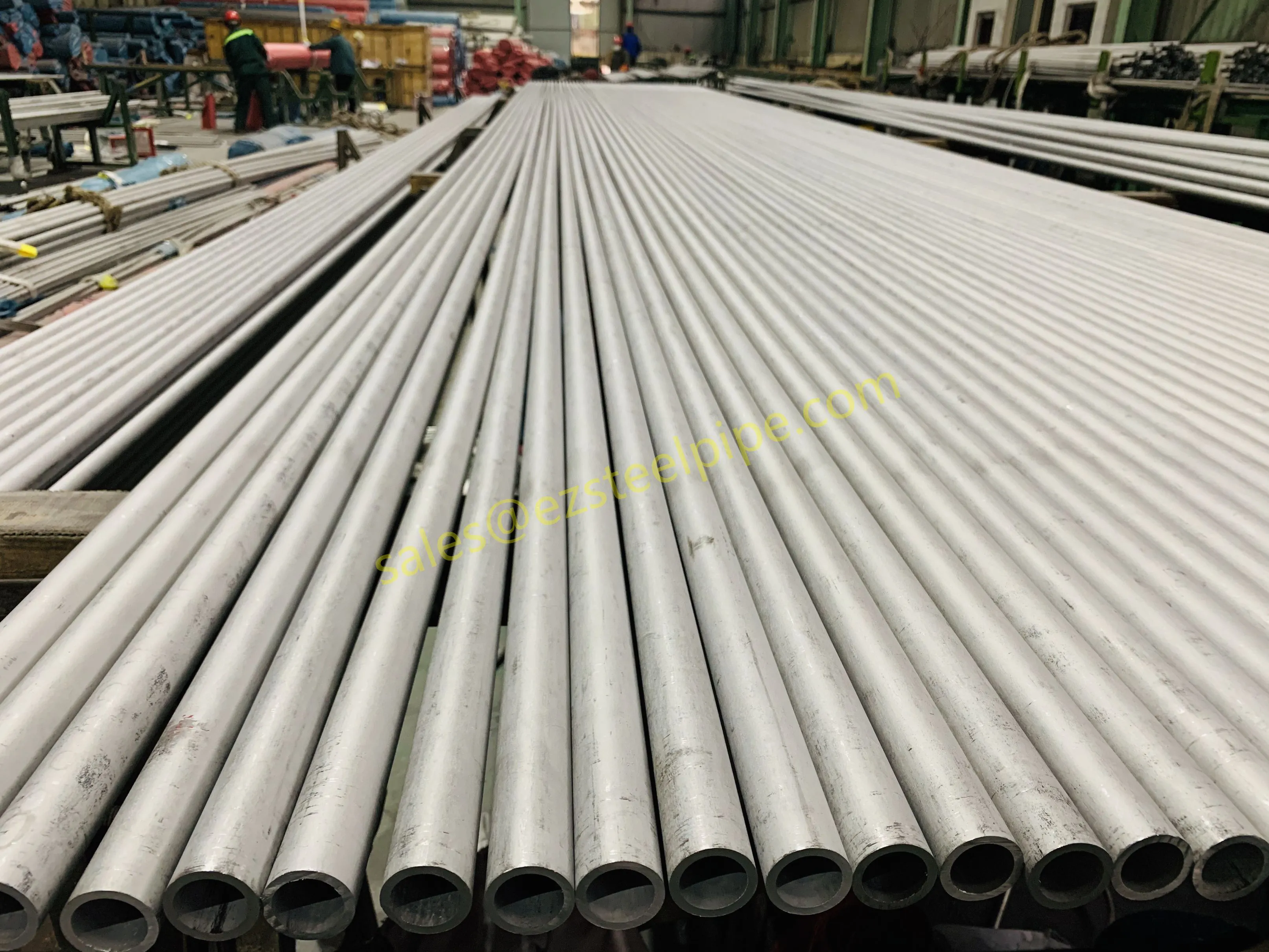
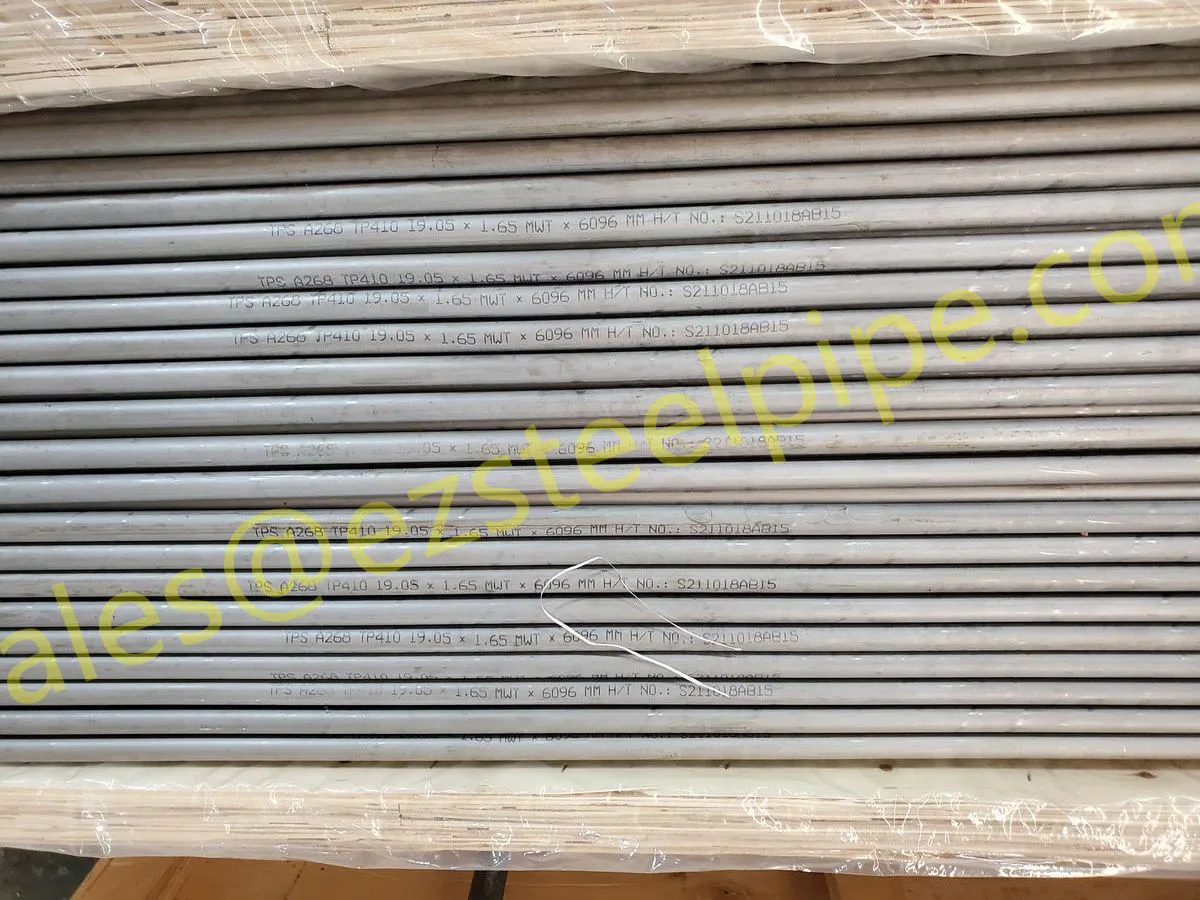
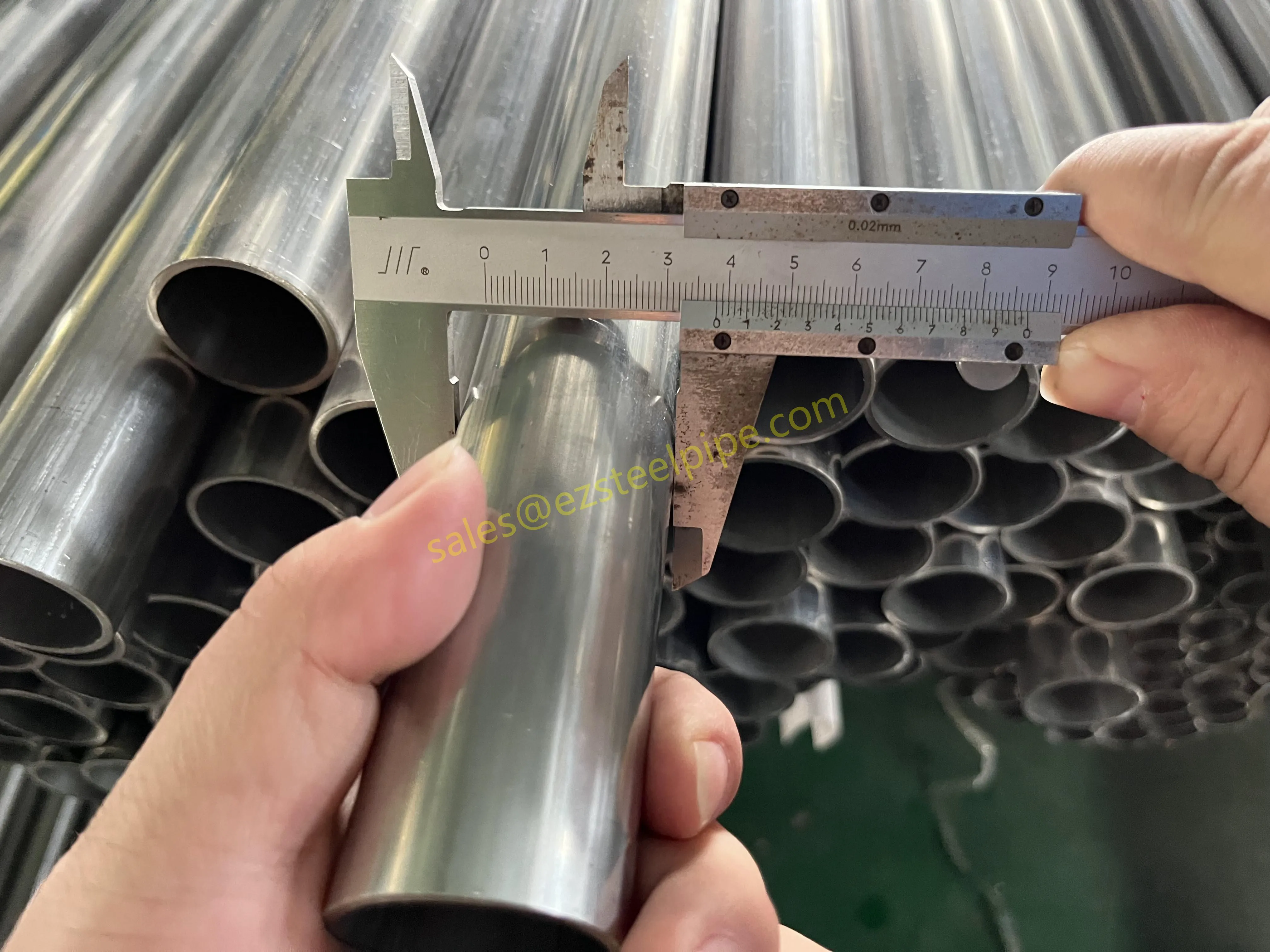
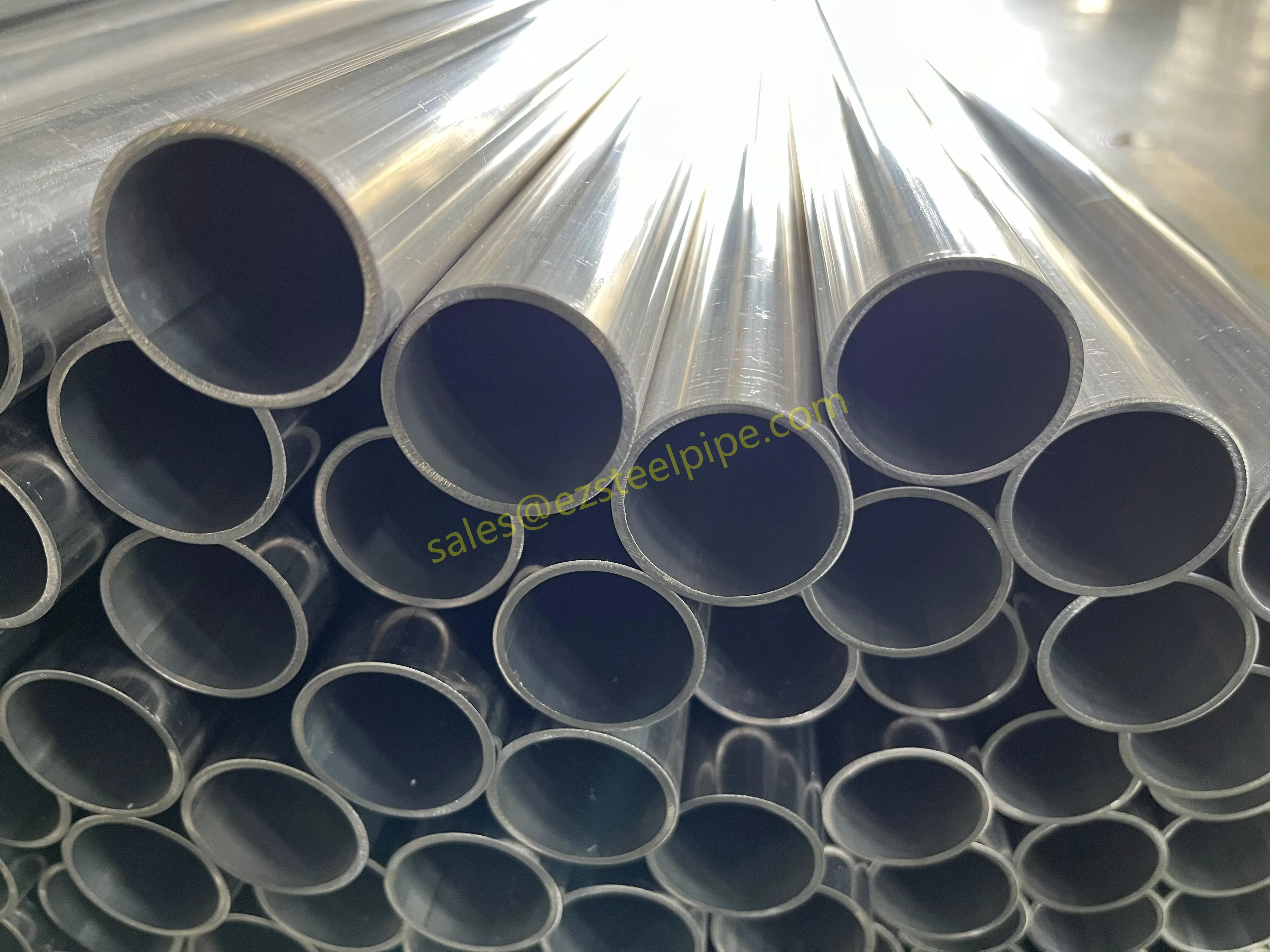
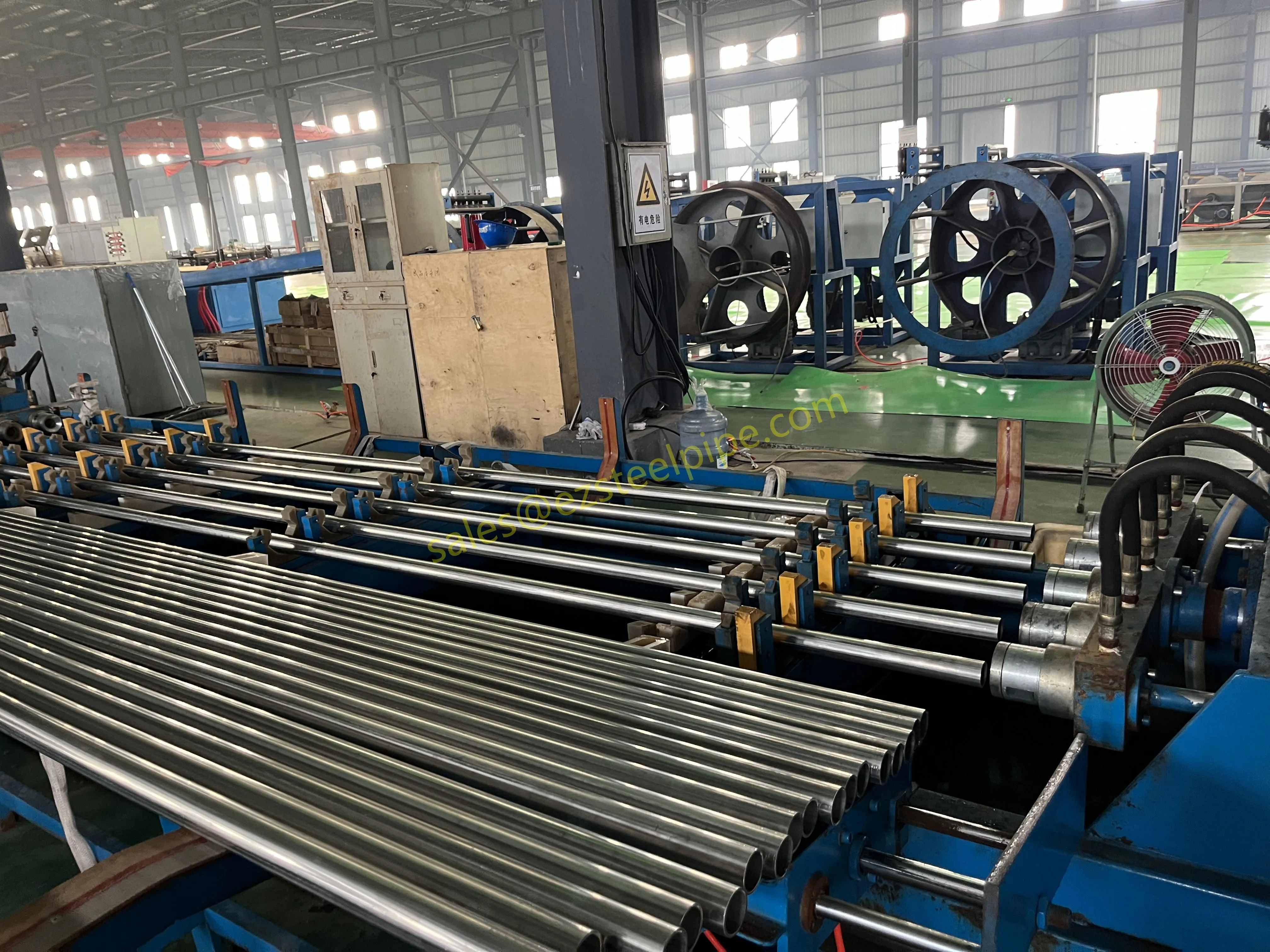
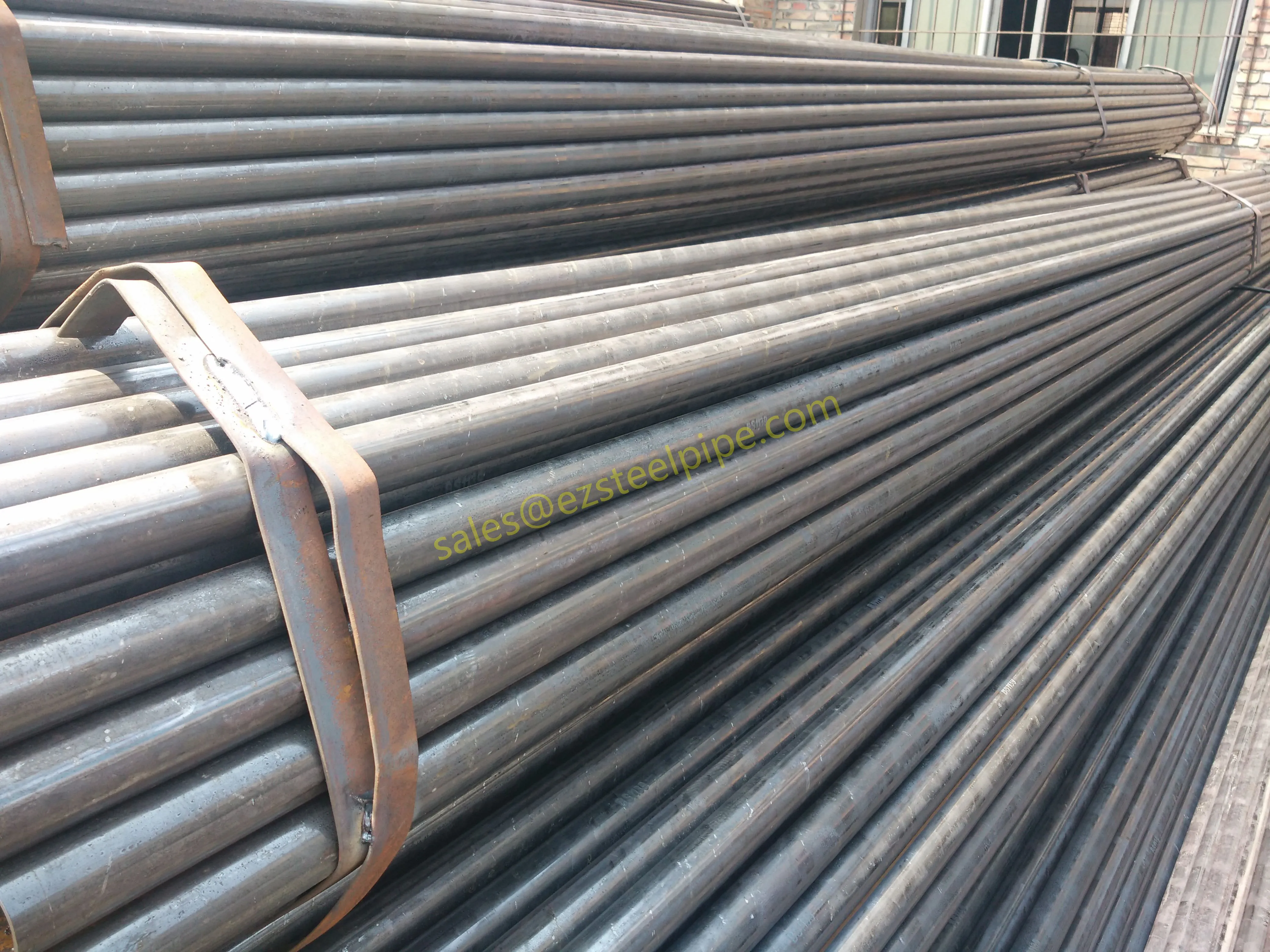
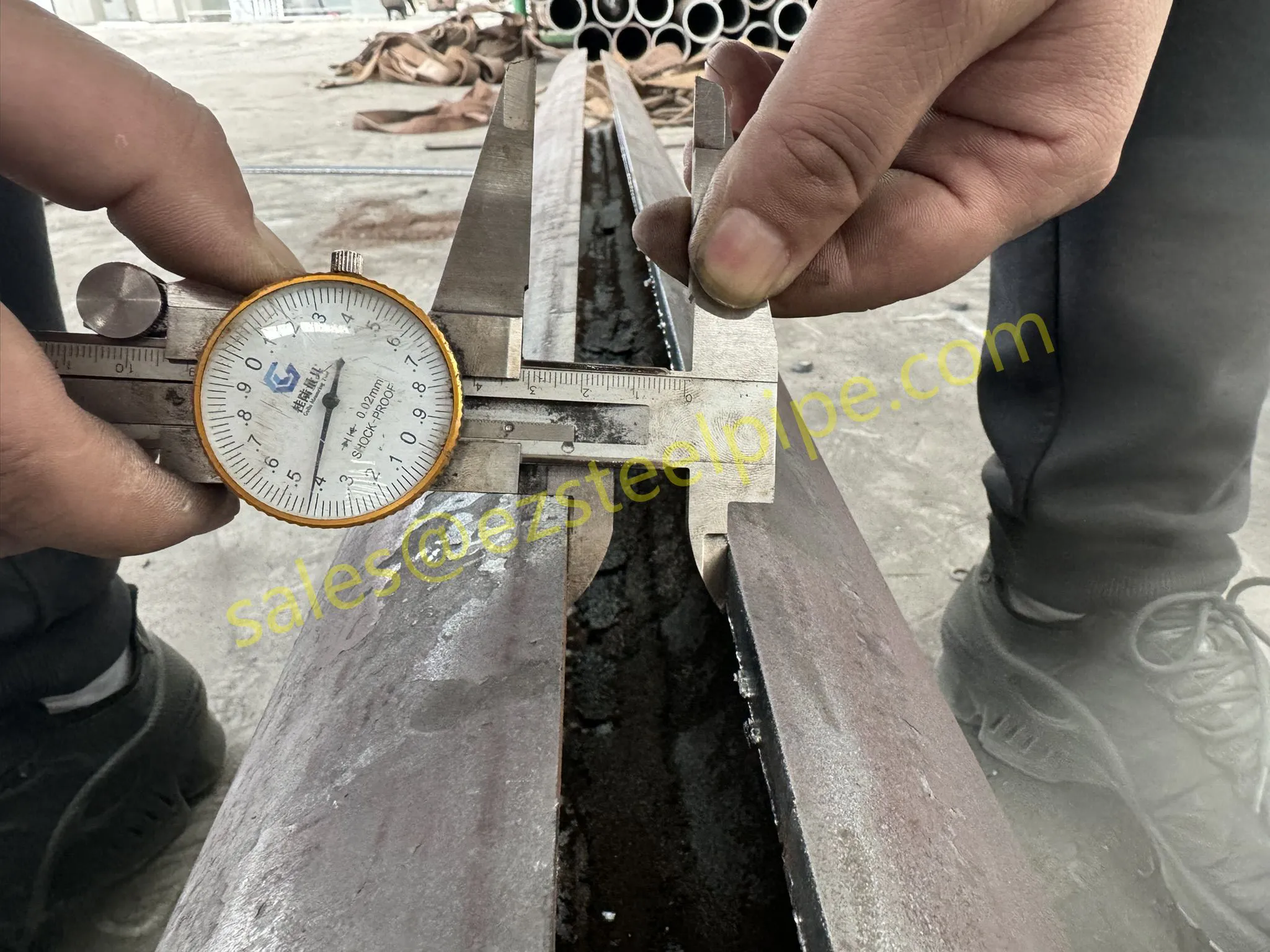
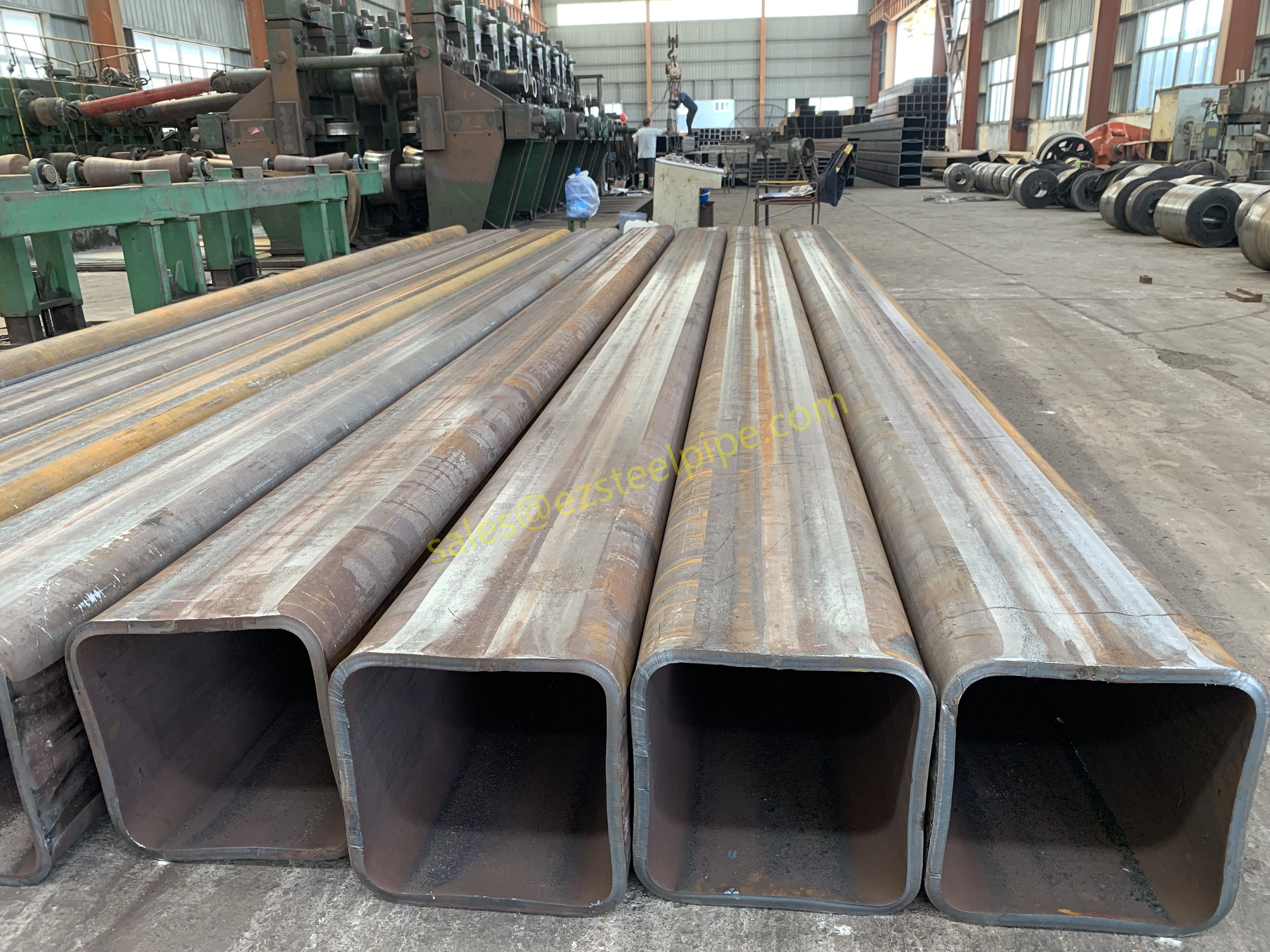
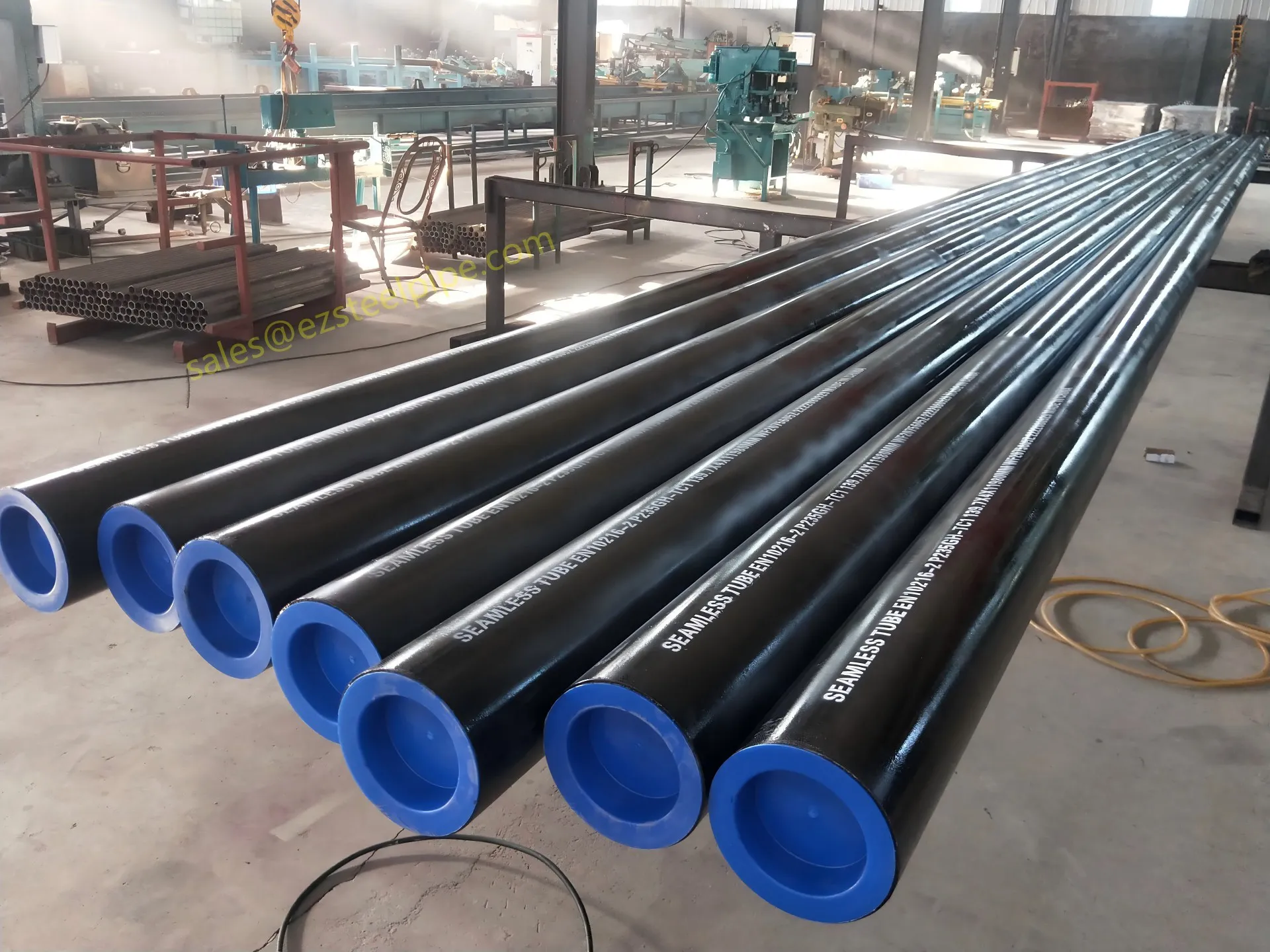
Before diving into materials or specifications, ask: What is this tube actually doing? Pressure tubes wear many hats—they might carry high-pressure fluids in a pipeline, support structural loads in a building, or transfer heat in a condenser. Each role demands a different set of priorities. For example, a tube used in pipeline works needs to handle consistent pressure over long distances, while one in structure works prioritizes tensile strength to support weight.
Let's break down common applications:
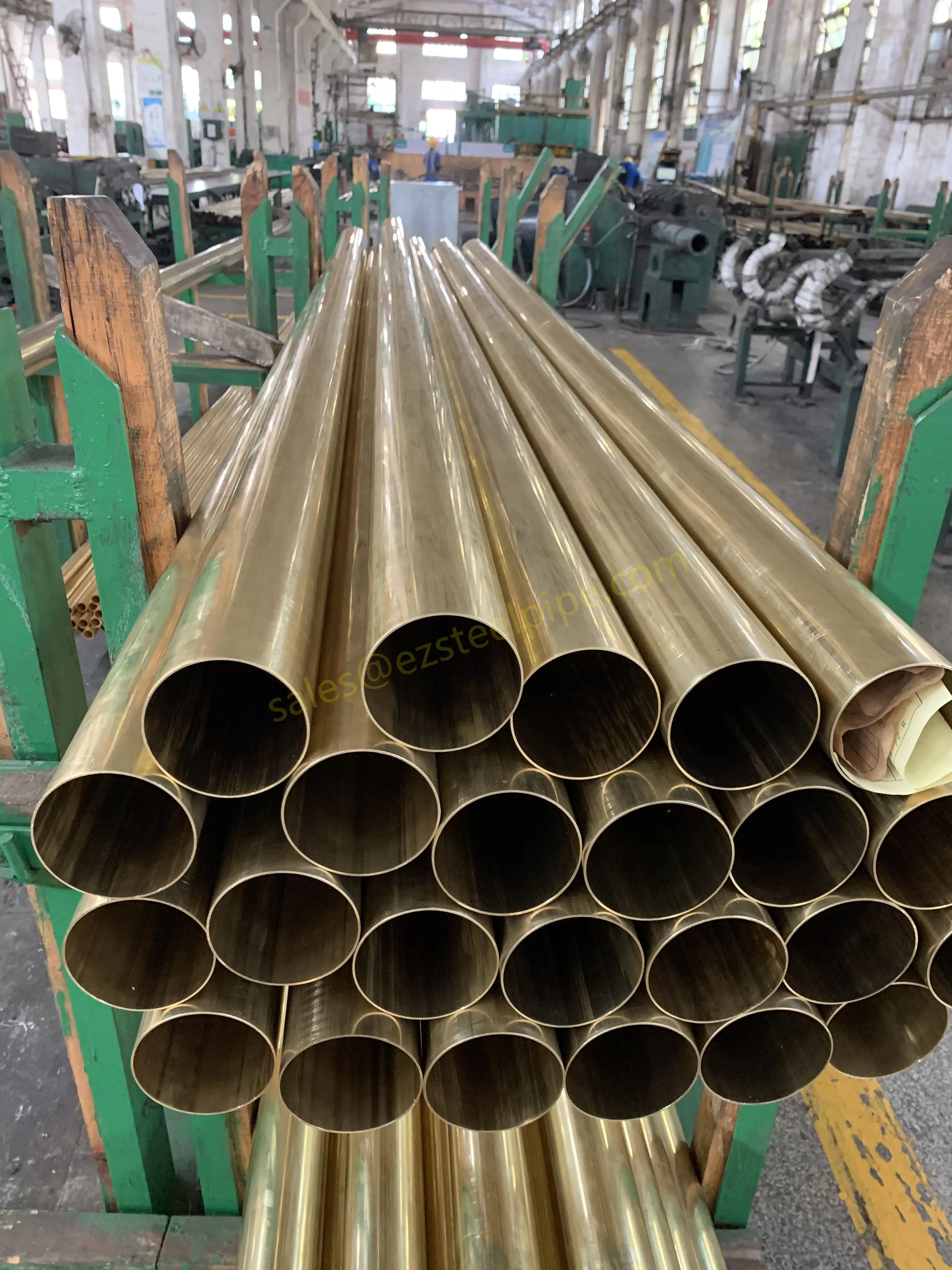
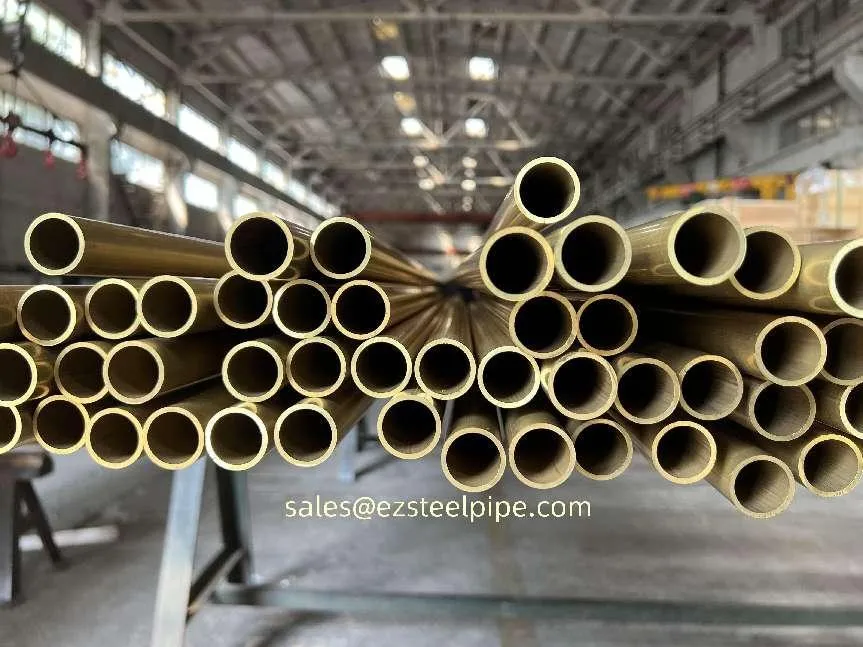
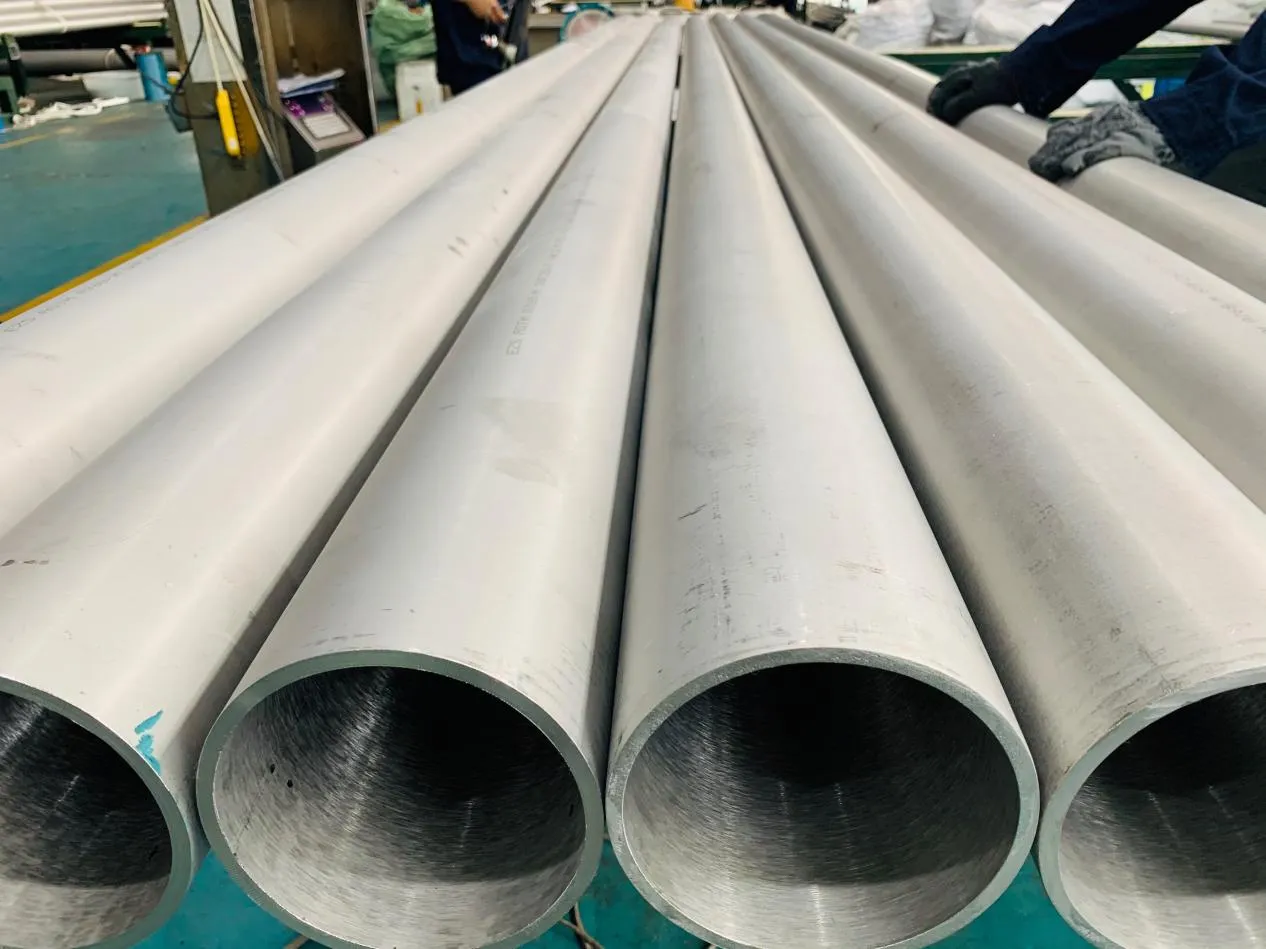
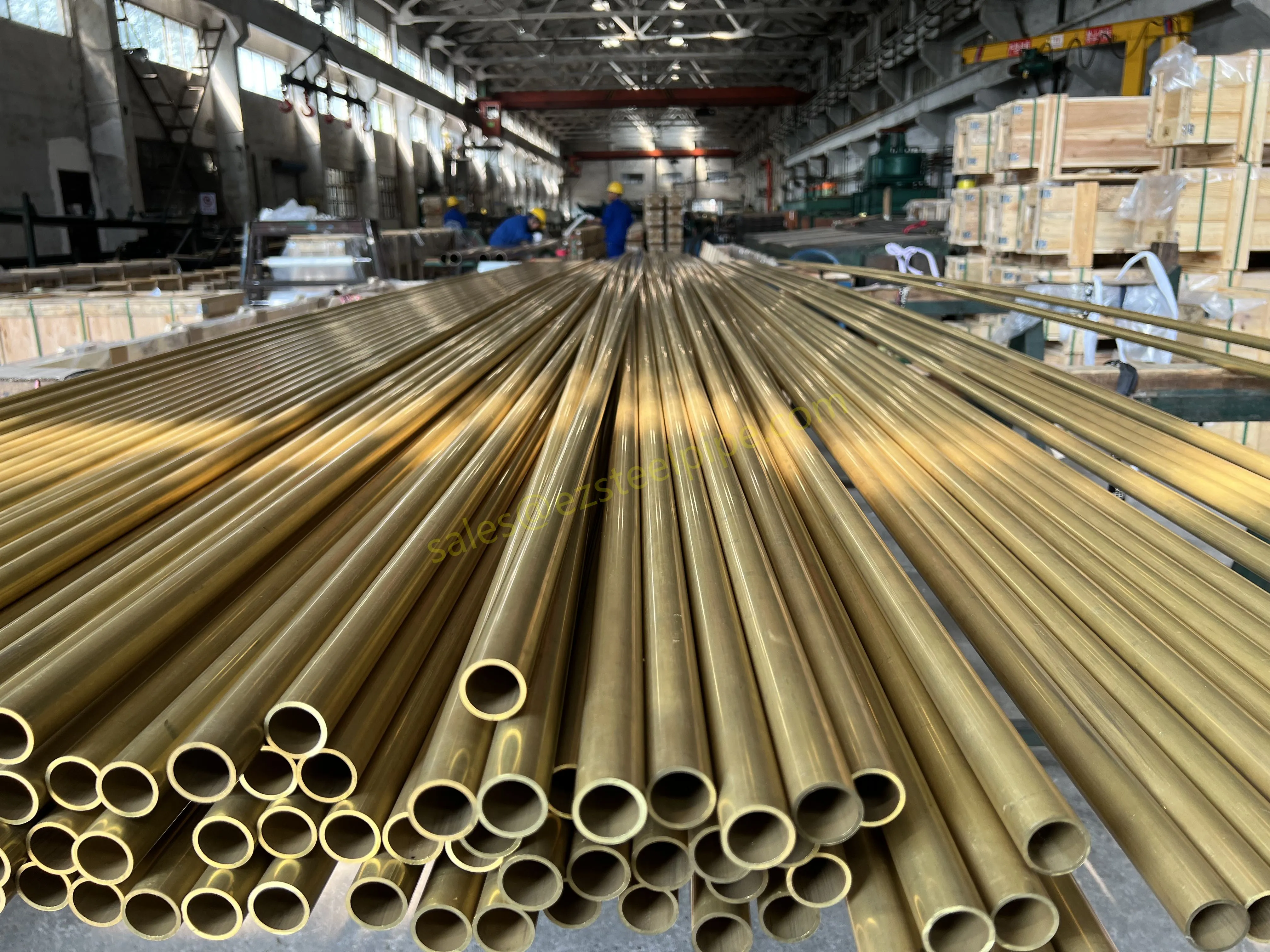
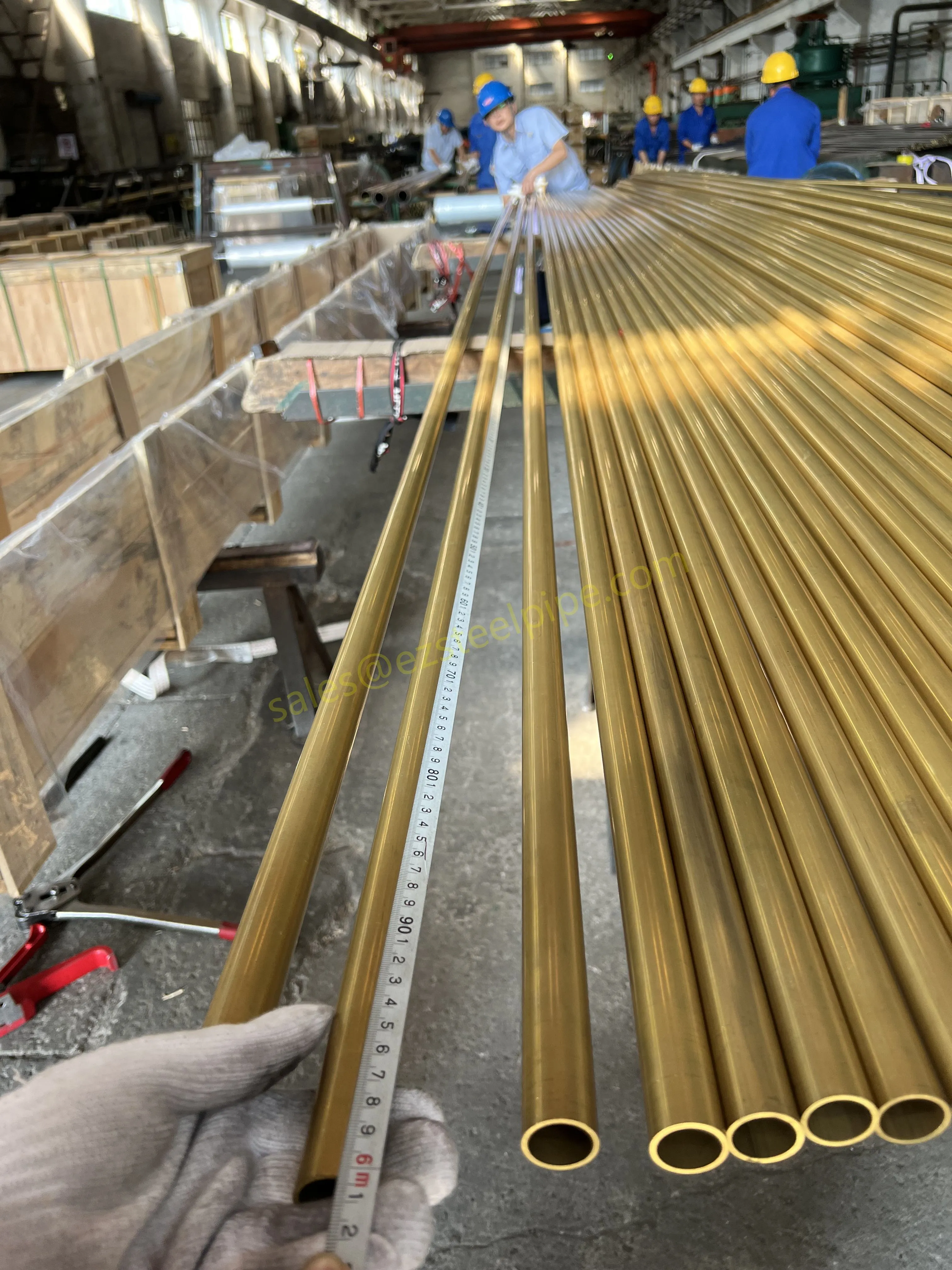
- Heat Exchange Systems: Think boiler tubing, heat exchanger tube, or condenser tube. These tubes thrive on thermal efficiency—they need to transfer heat quickly without warping or corroding. A u bend tube or finned tube might be ideal here, as their design maximizes surface area for better heat transfer.
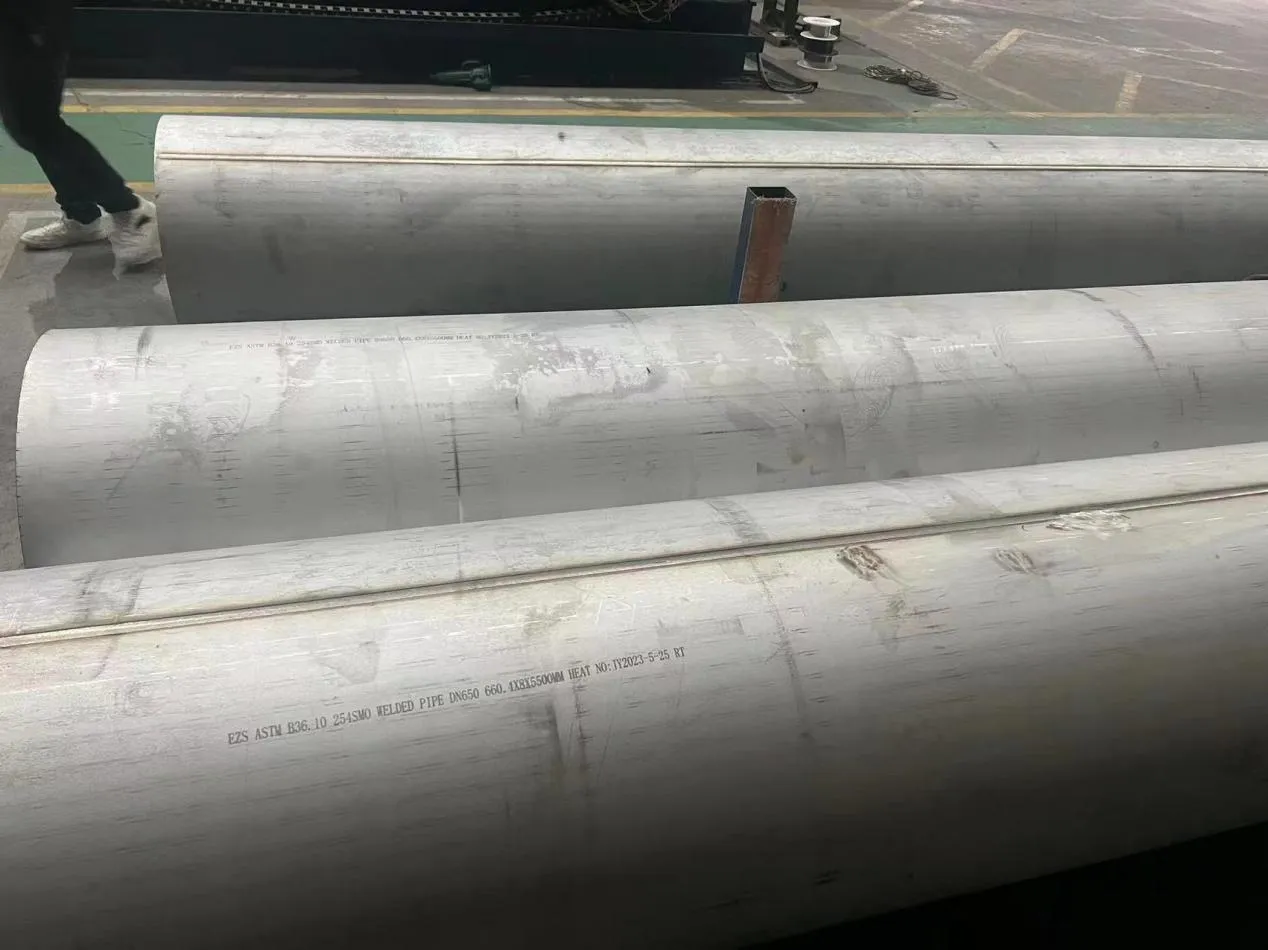
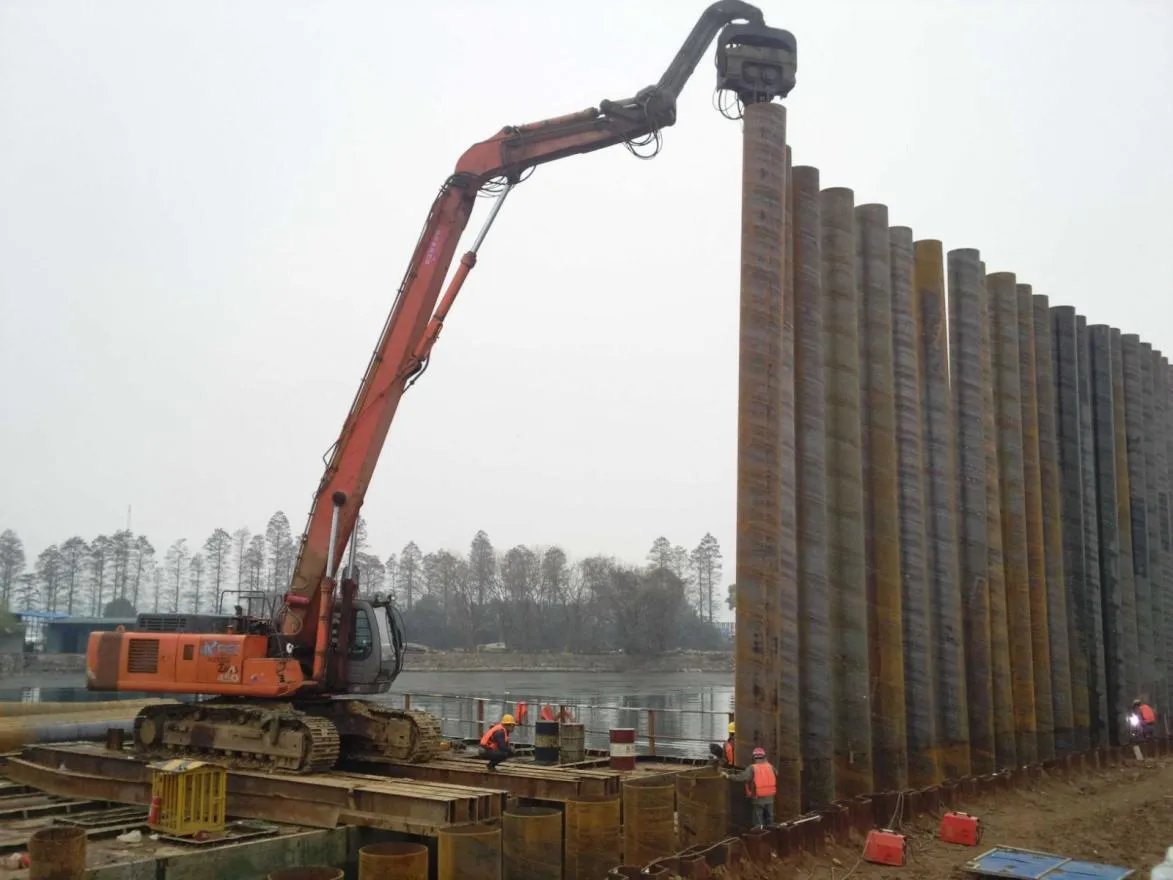
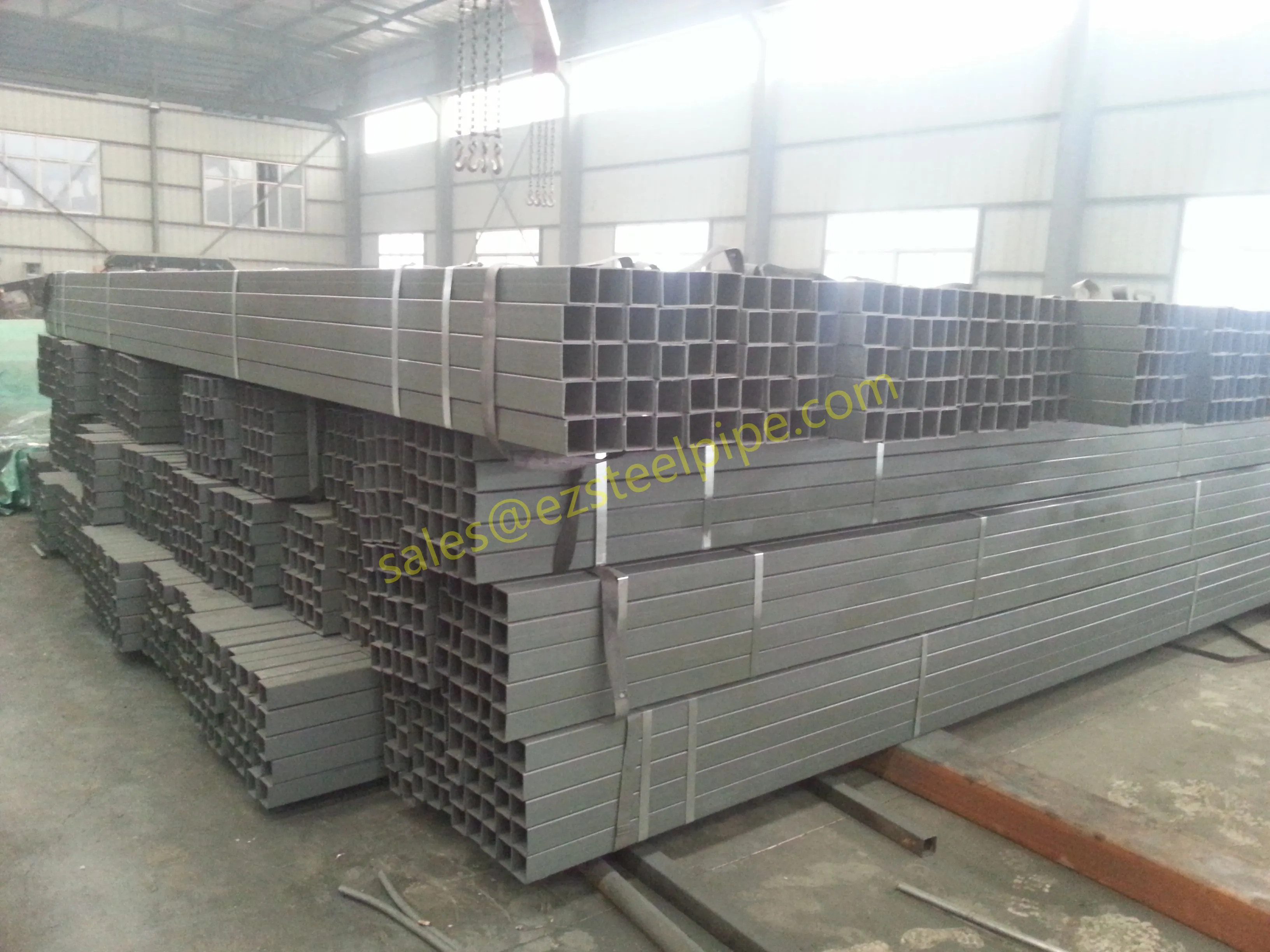
- Structural Support: Steel tubular piles or hollow sections in construction rely on rigidity and load-bearing capacity. Carbon steel is often a go-to here for its strength and cost-effectiveness, but in corrosive environments, you might opt for a coated or alloy alternative.
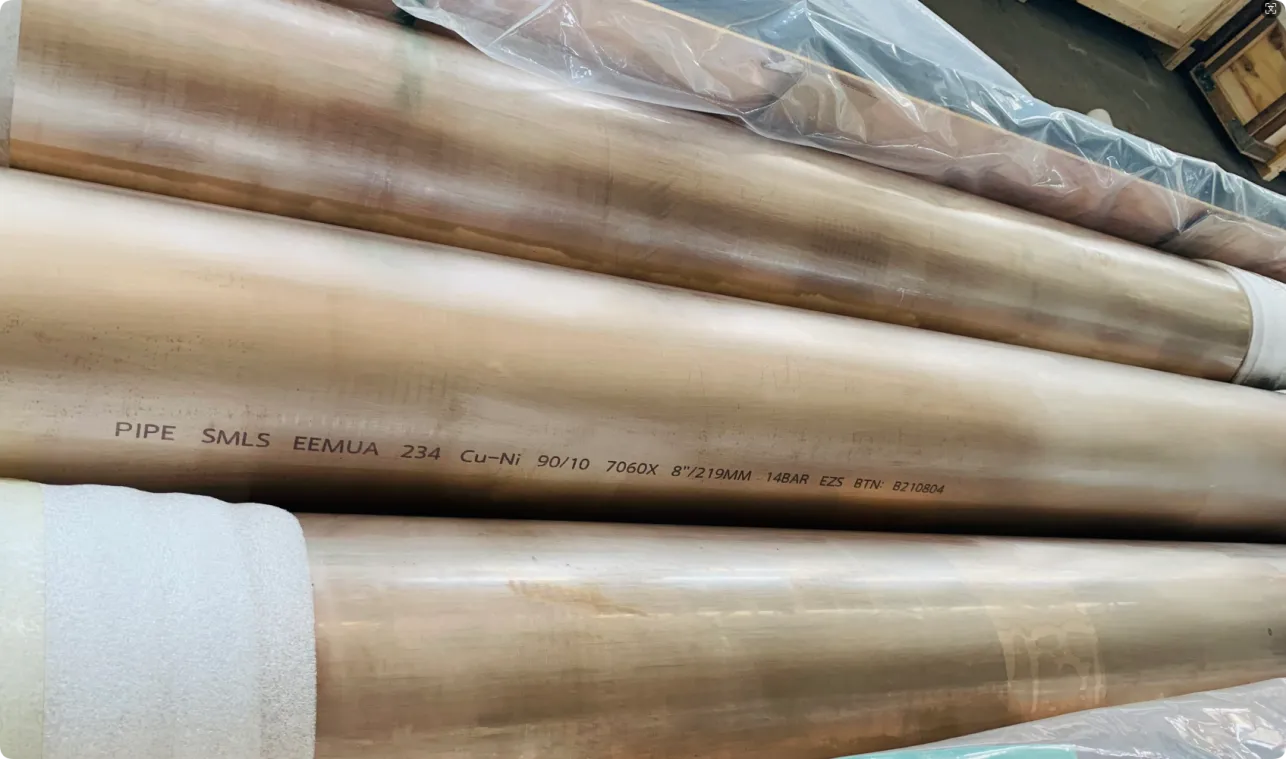
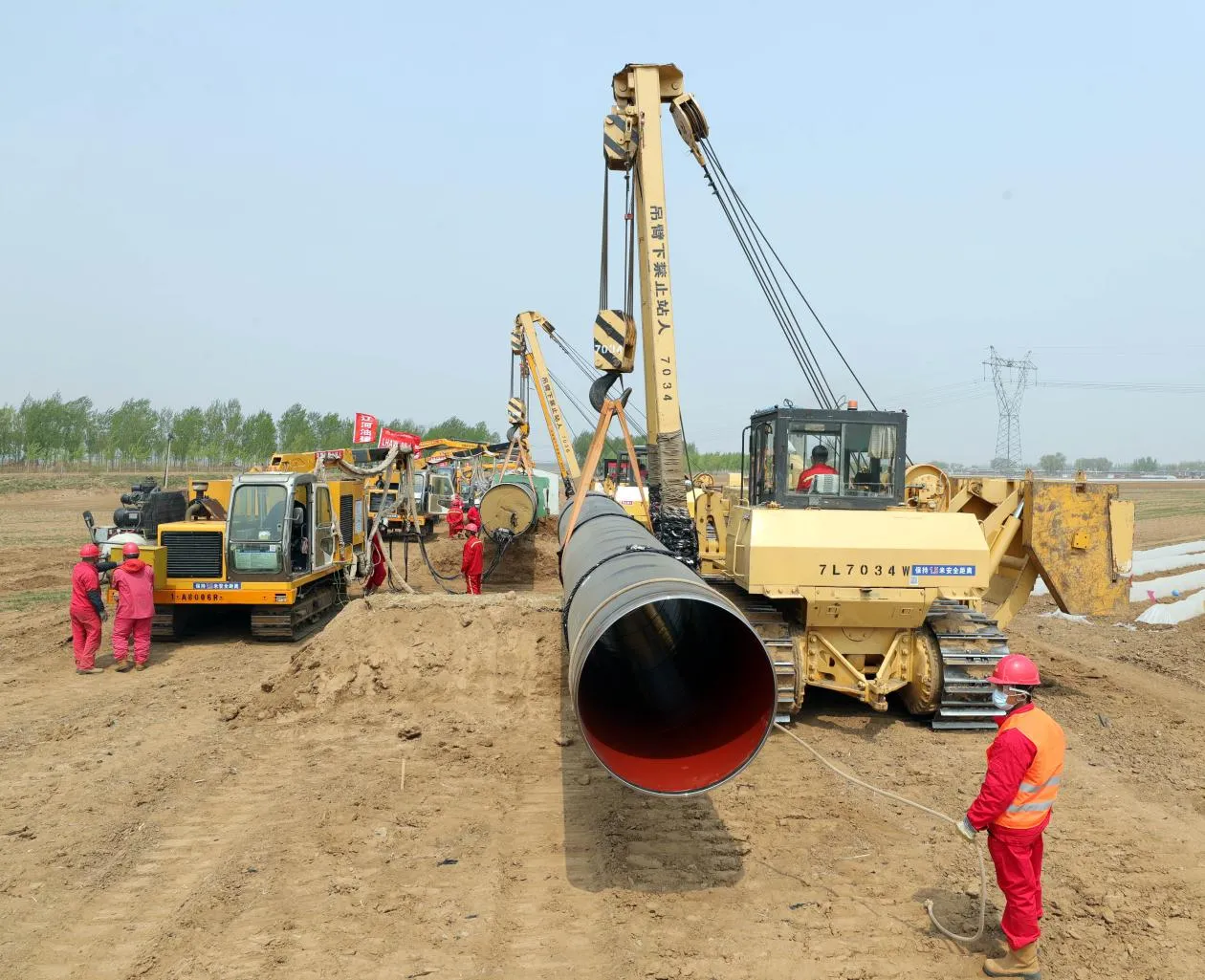
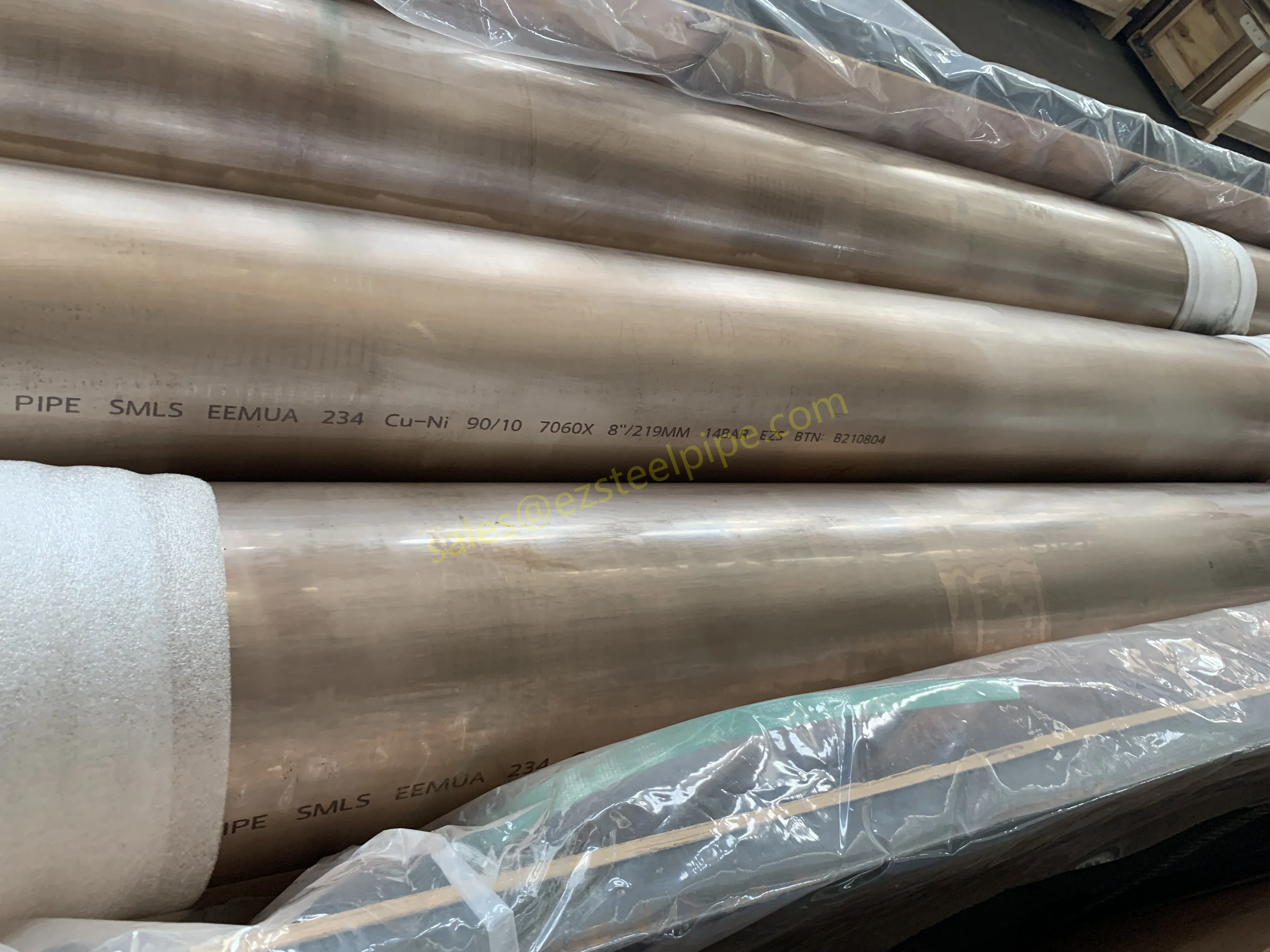
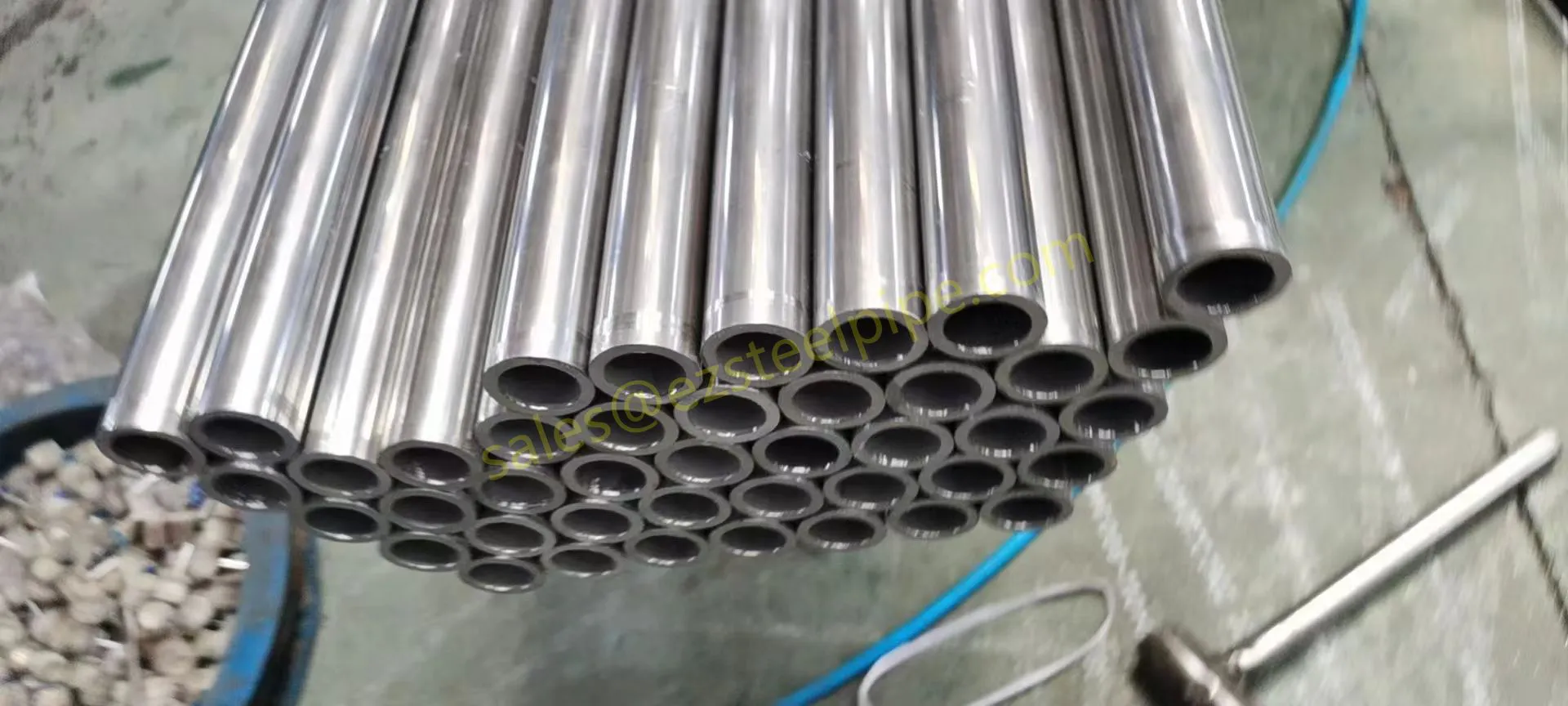
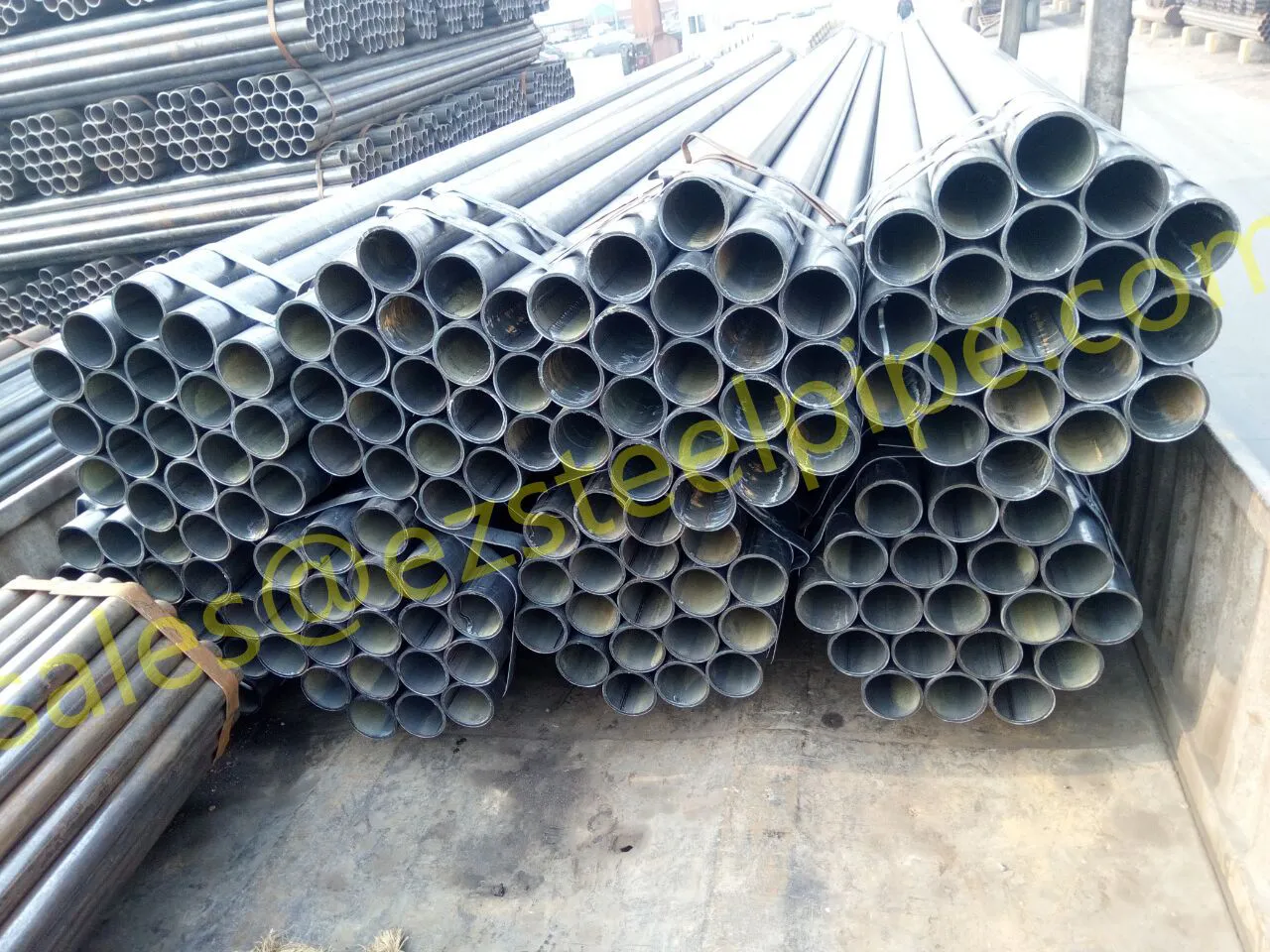
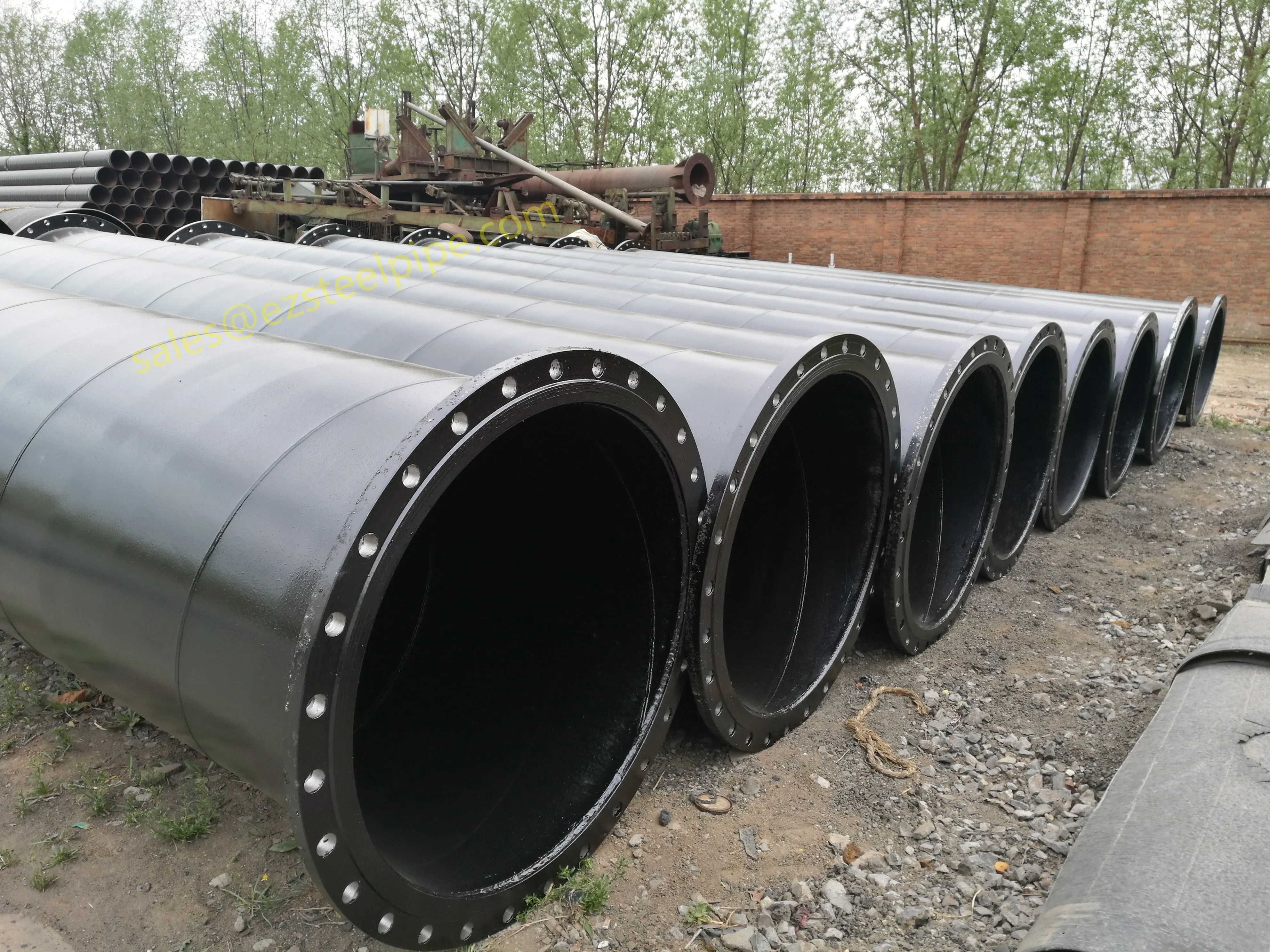
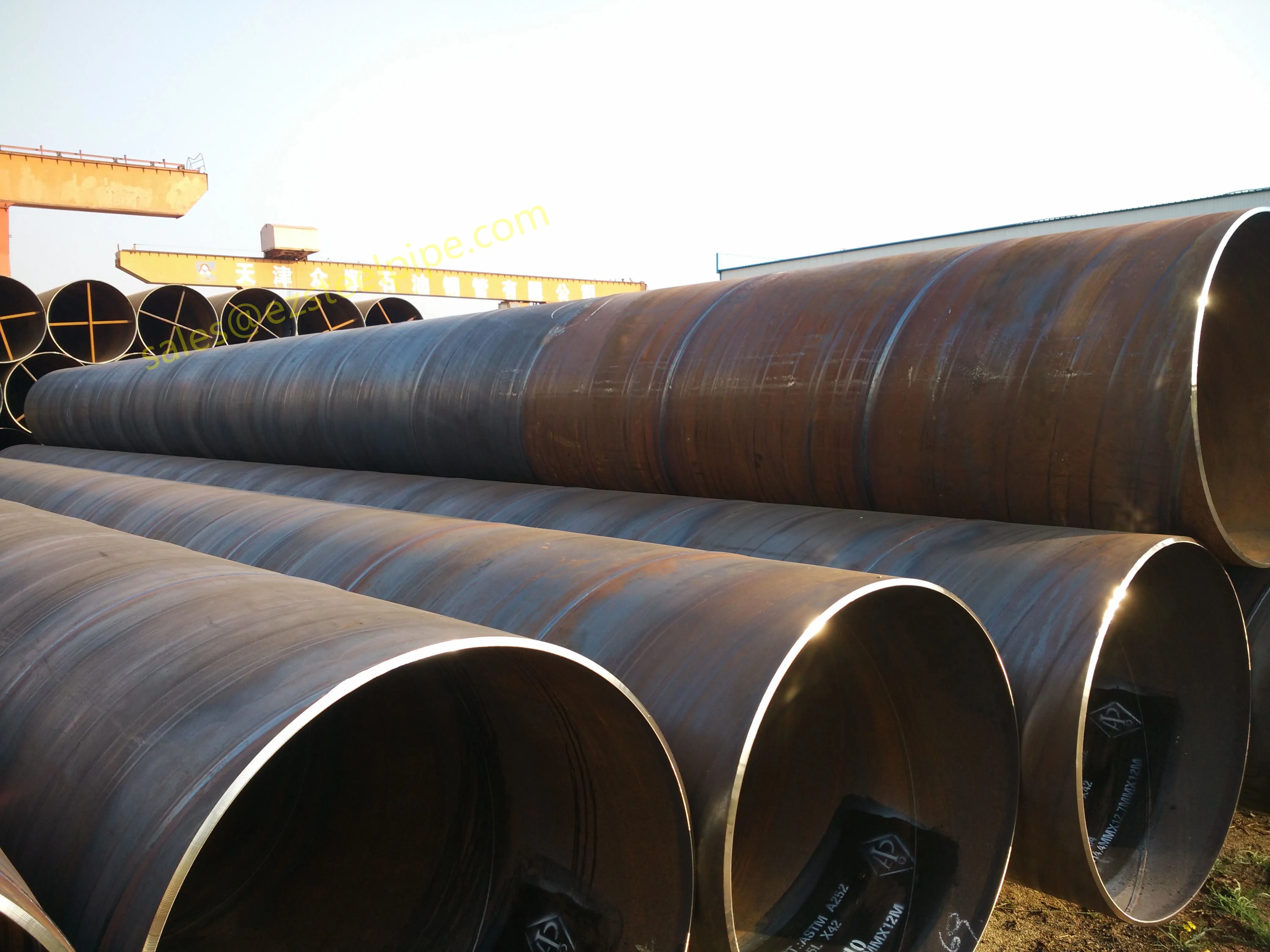
- Transporting Fluids/Gases: Pipelines in petrochemical facilities or water treatment plants need to resist corrosion from the substances they carry. If the fluid is acidic or salty, materials like copper-nickel alloy or stainless steel tube become critical to avoid leaks.
By pinpointing the core application first, you narrow down the field—no more sifting through irrelevant options. It's like shopping for shoes: you wouldn't buy hiking boots for a formal event, right? The same logic applies here.
 export@ezsteelpipe.com
export@ezsteelpipe.com +86 731 8870 6116
+86 731 8870 6116





 Related Products
Related Products





































































